Chemistry Chapter 10 & 11
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:59 PM on 12/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
1
New cards
Writing Lewis Structures
* Draw skeletal structures of compound showing what atoms are bonded to each other. Put least electronegative element in the center
* Count total number of valence e- . Add 1 for each negative charge. Subtract 1 for each positive charge
* Complete an octet for all atoms except hydrogen
* If short electrons, add bonds
* If there are extra electrons, add them to the central atom
* Count total number of valence e- . Add 1 for each negative charge. Subtract 1 for each positive charge
* Complete an octet for all atoms except hydrogen
* If short electrons, add bonds
* If there are extra electrons, add them to the central atom
2
New cards
Electronegativity
* The ability of an atom to attract toward itself the electrons in a chemical bond
* F is highest
* F is highest
3
New cards
Electrons are shared unequally in what type of bond?
Polar covalent
4
New cards
Type of bond is determined by what?
Difference in electronegativity
5
New cards
Electronegativity < 0.4
Pure (nonpolar) covalent
6
New cards
Electronegativity 0.4-2.0
Polar covalent
7
New cards
Electronegativity > 2.0
Ionic
8
New cards
Polar molecules must
* Have polar bonds
* Have a shape (geometry) that allows it to be polar
* Dipoles that are equal and opposite cancel each other out
* Have a shape (geometry) that allows it to be polar
* Dipoles that are equal and opposite cancel each other out
9
New cards
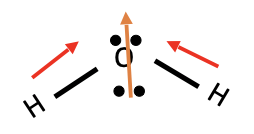
H2O
* Dipole moment
* Polar molecule
* Polar molecule
10
New cards
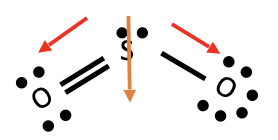
SO2
* Dipole moment
* Polar molecule
* Polar molecule
11
New cards
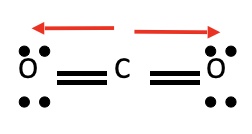
CO2
* No dipole moment
* Nonpolar molecule
* Nonpolar molecule
12
New cards
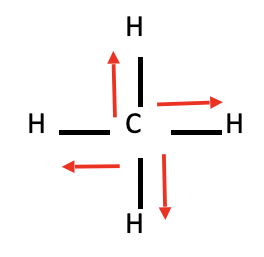
CH4
* No dipole moment
* Nonpolar molecule
* Nonpolar molecule
13
New cards
Non-polar
As long as dipoles are equal (same atoms) and opposite
14
New cards
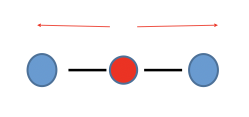
Linear
Non-polar
15
New cards
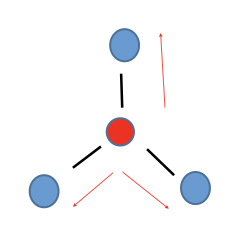
Trigonal Planar
Non-polar
16
New cards
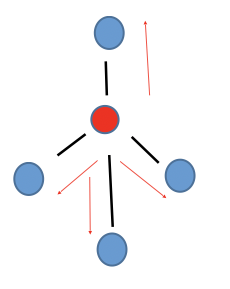
Tetrahedral
Non-polar
17
New cards
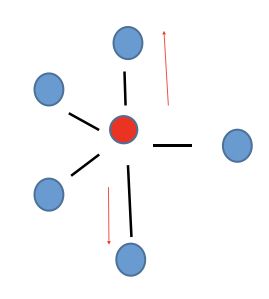
Trigonal Bipyramidal
Non-polar
18
New cards
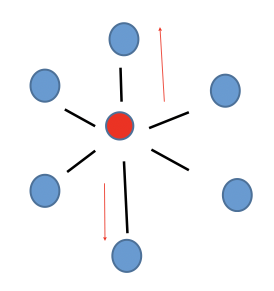
Octahedral
Non-polar
19
New cards
Polar
Shapes that are not symmetrical are polar
20
New cards
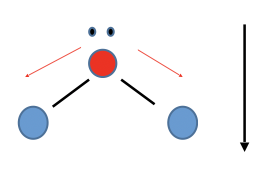
Bent
Polar
21
New cards
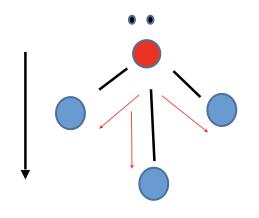
Trigonal Pyramidal
Polar
22
New cards
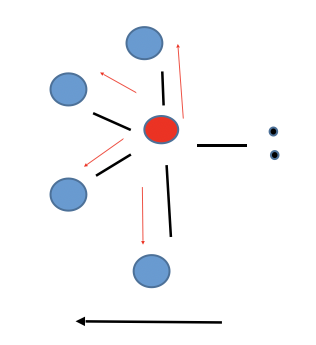
Distorted Tetrahedral (see-saw)
Polar
23
New cards
Intermolecular Forces
Attractive forces between molecules
24
New cards
Intramolecular Forces
Hold atoms together in a molecule
25
New cards
Intermolecular vs Intramolecular
* 41 kJ to vaporize 1 mole of water (inter)
* 930 kJ to break all O-H bonds in 1 mole of water (intra)
* 930 kJ to break all O-H bonds in 1 mole of water (intra)
26
New cards
“Measure” of intermolecular force
* Boiling point
* Melting point
* ΔHvap
* ΔHfus
* ΔHsub
* Melting point
* ΔHvap
* ΔHfus
* ΔHsub
27
New cards
Kinetic Energy vs Interactive Forces
* KE lowest, IF highest
* KE intermediate, IF intermediate
* KE highest, IF lowest
* KE intermediate, IF intermediate
* KE highest, IF lowest
28
New cards
The boiling point increases as the __ increases
Atomic number
29
New cards
The stronger the particles’s attractions for each other, the _
Greater the amount of energy needed to separate them
30
New cards
The greater the energy required to separate these particles, the
Higher the boiling points
31
New cards
Dispersion (London) Forces (LDF)
Intermolecular force between nonpolar molecules or atoms caused by the presence of temporary dipoles in the molecules
32
New cards
Temporary (induced) Dipole
Separation of charge produced in an atom or molecule by a molecule by a momentary uneven distribution of electrons
33
New cards
Polarizability
Relative ease with which the electron cloud in a molecule, ion, or atom can be distorted, inducing a temporary dipole
34
New cards
All molecules and atoms have…
Dispersion forces
35
New cards
Dispersion
Momentary shift in e- density
36
New cards
Factors affecting strength of dispersion
* Size of atoms/molecules
* Shape of molecules
* Shape of molecules
37
New cards
Dispersion - Size of atoms/molecules
* Larger atoms/molecules are more polarizable than smaller atoms/molecules
* Dispersion increases with polarizability
* Dispersion increases with polarizability
38
New cards
Dispersion - Shape of molecules
* Increased surface area = increased interactions between molecules
* Linear molecules have higher dispersion than branched molecules of similar molecular weight
* Linear molecules have higher dispersion than branched molecules of similar molecular weight
39
New cards
Effect of Shape on Dispersion
The more spread out a molecule, the stronger the opportunity for dispersion forces and the higher the boiling point
40
New cards
Dipole-Dipole Interactions
Attractive force between polar molecules
41
New cards
Hydrogen Bond
* Strongest dipole-dipole interaction
* Occurs between H atom bonded to a small, highly electronegative element (F, O, N) and an atom of O or N or F in another molecule
* Occurs between H atom bonded to a small, highly electronegative element (F, O, N) and an atom of O or N or F in another molecule
42
New cards
Ion-Dipole Interaction
Attractive force between an ion and a molecule that has a permanent dipole
43
New cards
Sphere of Hydration
* Cluster of water molecules surrounding an ion in aqueous solution
* Sphere of solvation if solvent is other than H2O
* Sphere of solvation if solvent is other than H2O
44
New cards
Dipole-Induced Dipole
* Proximity of polar molecule causes dipole-induced dipole
45
New cards
Relative Strengths of Intermolecular Forces
* Weakest - Dispersion Forces
* Dipole Induced Dipole Forces
* Dipole-Dipole Forces
* Hydrogen Bonding
* Strongest - Ion Dipole Forces
* Dipole Induced Dipole Forces
* Dipole-Dipole Forces
* Hydrogen Bonding
* Strongest - Ion Dipole Forces
46
New cards
Solubility
Depends on relative strength of solute-solvent interactions compared to solute-solute or solvent-solvent
47
New cards
Like dissolves like
* Ionic/polar solutes will be soluble in polar solvents
* Nonpolar solutes will be soluble in nonpolar solvents
* Nonpolar solutes will be soluble in nonpolar solvents
48
New cards
Combination of Forces
More than one intermolecular force may need to be considered when examining larger molecules dissolved in a liquid solvent
49
New cards
Solubility decreases are relative energy of…
Hydrogen bonding decreases and dispersion increases
50
New cards
Hydrophobic (water-fearing)
Interaction that repels water, diminished water solubility
51
New cards
Hydrophilic (water-loving)
Interaction that attracts water, promotes water solubility
52
New cards
Equilibrium Vapor Pressure
* The vapor pressure measured when a dynamic equilibrium exists between condensation and evaporation
* H2O (L) → H2O (g)
* H2O (L) → H2O (g)
53
New cards
Dynamic Equilibrium
Rate of Condensation = Rate of Evaporation
54
New cards
Molar Heat of Vaporization (Δ*H*vap)
The energy required to vaporize 1 mole of liquid at its boiling point
55
New cards
Clausius-Clapeyron Equation
* ln P = \[ (-Δ*H*vap) / (RT) \] + C
* P = equilibrium vapor pressure
* T = temperature (K)
* R = gas constant (8.314 J/K x mol)
* P = equilibrium vapor pressure
* T = temperature (K)
* R = gas constant (8.314 J/K x mol)
56
New cards
Clausius-Clapeyron Equation at two temperatures
ln (p1 / p2) = (Δ*H*vap / R) x \[ (1 /T2) - (1 / T1) \]
57
New cards
Boiling Point
The temperature at which the (equilibrium) vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to the external pressure
58
New cards
Normal Boiling Point
The temperature at which a liquid boils when the external pressure is 1 atm
59
New cards
Factors Affecting Physical States
* Intermolecular Forces: strength of attractive forces compared to kinetic energy of atoms/molecules
* Temperature: affects kinetic energy of atoms/molecules
* Pressure: affects distance between atoms/molecules
* Temperature: affects kinetic energy of atoms/molecules
* Pressure: affects distance between atoms/molecules
60
New cards
Solid-Liquid Equilibrium
* H2O (s) → H2O (L)
* The melting point of a solid or the freezing point of a liquid is the temperature at which the solid and liquid phases coexist in equilibrium
* The melting point of a solid or the freezing point of a liquid is the temperature at which the solid and liquid phases coexist in equilibrium
61
New cards
Molar Heat of Fusion (Δ*H*fus)
The energy required to melt 1 mole of a solid substance at its freezing point
62
New cards
Solid-Gas Equilibrium
H2O (s) → H2O (g)
63
New cards
Molar Heat of Sublimation (Δ*H*sub)
The energy required to sublime 1 mole of a solid
64
New cards
Hess’s Law
Δ*H*sub = Δ*H*fus + Δ*H*vap
65
New cards
Cohesion
The attraction of like molecules due to intermolecular forces
66
New cards
Adhesion
The attraction of different molecules due to intermolecular forces
67
New cards
Cohesive Forces are responsible for…
Some properties of liquids such as surface tension and viscosity
68
New cards
Phase Diagram
A graphical representation of how the stabilities of the physical states of a substance depend on temperature and pressure
69
New cards
Equilibrium Lines
Represent phase changes between solid/liquid, liquid/gas, and solid/gas under specific conditions (T,P)
70
New cards
Supercritical Region
4th state of matter with properties intermediate between gas and liquid
71
New cards
Critical Temperature (Tc)
The temperature above which the gas cannot be made to liquify, no matter how great the applied pressure
72
New cards
Critical Pressure (Pc)
The minimum pressure that must be applied to bring about liquifacation at the critical temperature
73
New cards
Phase Diagram - Triple Point
Temperature/pressure where all 3 phases of a substance coexist
74
New cards
Phase Diagram - Critical Point
Specific temperature/pressure at which the liquid and gas phases have the same density
75
New cards
Phase Diagram - Supercritical Fluid
A substance above its critical temperature and pressure
76
New cards
The equation to calculate amount of heat (q) entering/leaving a substance
* q = c x m x ΔT
* q = c x m x (Tf - Ti)
* q = c x m x (Tf - Ti)
77
New cards
T final > T initial
If a substance gains thermal energy, then the value of q is positive
78
New cards
T final < T initial
If a substance loses thermal energy, then the value of q is negative
79
New cards
Molar Heat of Fusion (Δ*H*fus)
The energy required to melt 1 mole of a solid substance at its freezing point
80
New cards
Enthalpy in Change of State equations
* *q* = *n*Δ*H*fus
* *q* = *n*Δ*H*vap
* *q* = *n*Δ*H*vap
81
New cards
Solutions are __ made up of two or more substances
Homogenous mixtures
82
New cards
Solute
Substance being dissolved
83
New cards
Solvent
* Substance that is doing the dissolving
* Typically, present in largest amount
* Typically, present in largest amount
84
New cards
Solid Solution
Metal alloys (two or more metals)
85
New cards
Gas Solution
Example: air - made up of multiple gases
86
New cards
Three types of intermolecular forces influence whether substances will form a solution
* Solute-Solute
* Solvent-Solvent
* Solute-Solvent
* Solvent-Solvent
* Solute-Solvent
87
New cards
Step 1 Solution Formation
* Solute-Solute IMFs must be overcome
* Energy is consumed
* Energy is consumed
88
New cards
Step 2 Solution Formation
* Solvent-Solvent IMFs must be overcome
* Energy is consumed
* Energy is consumed
89
New cards
Step 3 Solution Formation
* Solvation-Solute-Solvent attractive forces are established
* Energy is released
* Energy is released
90
New cards
Nonpolar solvents dissolve
Nonpolar solutes
91
New cards
Polar solvents dissolve
Polar solutes and many ionic solutes
92
New cards
Electrolytes
Substances that dissolve in water and undergo a physical or chemical change to produce ions
93
New cards
Nonelectrolytes
Substances that do not produce ions when dissolved in water
94
New cards
Strong Electrolytes
Essentially 100% of the dissolved substance generates ions
95
New cards
Weak Electrolytes
Only a relatively small fraction of the dissolved substance generates ions
96
New cards
Ion-Dipole Attraction
The electrostatic attraction between an ion and a molecule with a dipole (polar molecule)
97
New cards
Dissociation
Water molecules surround and solvate the separated ions
98
New cards
Competing forces influence the extent of solubility…
Of an ionic compound
99
New cards
If Ion-Dipole attraction is the dominant force, then
The compound it “pulled” into solution and has very high water solubility
100
New cards
The force of attraction between oppositely charged ions
If this is the dominant force then the compound tends to remain un-dissolved and in the solid state, and have very low water solubility