Chem 101 Lab Final
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
beryllium
Be
silicon
Si
potassium
K
chromium
K
manganese
Mn
cobalt
Co
arsenic
As
tin
Sn
Cs
cesium
barium
Ba
uranium
U
nitrate
NO3
carbonate
CO3
acetate
C2H2O2
sulfate
SO4
chlorate
ClO3
hydroxide
OH
strong acids (Ice Cold Beer Never Sits Chilled Properly)
hydroiodic acid (HI)
hydrochloric acid (HCl)
hydrobromic acid (HBr)
nitric acid (HNO3)
sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
chloric acid (HClO3)
perchloric acid (HClO4)
carbonic acid
H2CO3
ammonia
NH3 (base)
potassium hydroxide
KOH (base)
sodium hydroxide
NaOH (base); OH is always hydroxide and all of the bases we need to know have an element + OH
SI unit metric prefixes
tera (T) = 10^12
giga (G) = 10^9
mega (M) = 10^6
kilo (K) = 10³
deci (d) = 10^-1
centi ( c) = 10^-2
milli (m) = 10^-3
micro (u) = 10^-6
nano (n) = 10^-9
pico (p) = 10^-12
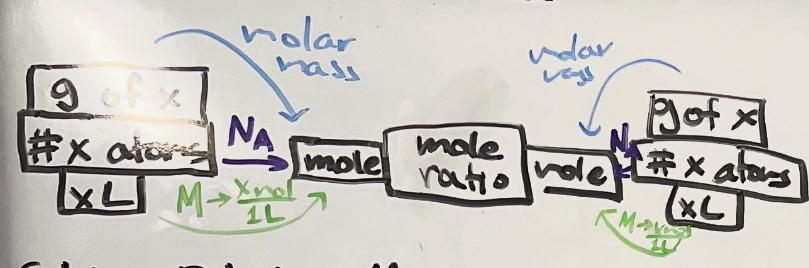
stoichiometry diagram
coffee cup calorimeter
an insulated cup used to measure the heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction
heat
the flow of energy caused by a difference in temperature
enthalpy
the quantity of heat emitted or absorbed by a chemical reaction when the reaction occurs under conditions of constant pressure
specific heat capacity
the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree celcius
Arrhenius acid and base
substances that directly produce H+ or OH- ions respectively in aqueous solutions
neutralization reaction
when an acid and a base react to form water and a salt
equivalence point (in a titration)
when the amount of moles of OH- added is equal to the amount of moles of H+ in the solution
how do you find the limiting reactant, theoretical yield, actual yield, and excess reactant
covert the grams of reactants to mols and then divide by the mole ratio, whichever one is the lowest is the limiting reactant
multiply the moles of LR by mole ratio of (LR/product) and then multiply by molar mass of product
actual yield/theoretical yield time 100
multiply the moles of LR by mole ratio of (mol ex/mol LR) to find how much ex reacted, convert moles reacted to grams, intial g - g reacted
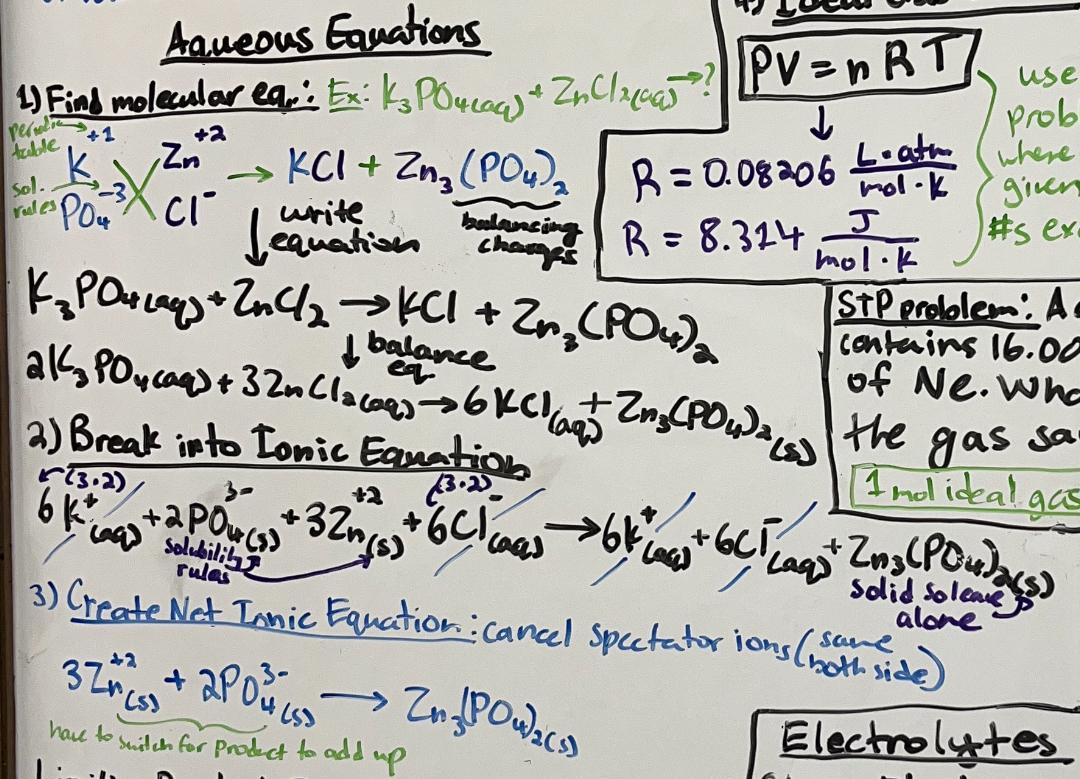
how to write the molecular, ionic, and net ionic formulas for a reaction
how to find the heat of a solution
q = (mass)(specific heat capacity)(temperature change)
steps to draw lewis structure for molecular compound
count total valance electrons (from periodic table charges)
figure out central atom (least electronegative atom; electronegativity increases left to right on periodic table and the electronegativity increases as you go down the columns); carbon has a tendency to be the central atom and hydrogen can never be the central atom bc its too small
ensure all atoms have 8 valance electrons, other than hydrogen which only needs 2 electrons
how do you determine how many hybrid orbitals
it is equivalent to the number of electron groups around the central atom
how do you know if the molecular geometry is different than the electron geometry
the central atom has a lone pair of electrons attached to it taking up space and altering the bond angles to be less than their electron geometry
how do you know the number of sigma and phi bonds
there can only be one sigma bond between the central atom and surrounding atoms
any addition bonds to central atoms, such as a double or triple bond, is the 1 phi or 2 phi bonds
how do you know if a molecule can hydrogen bond with itself or not
OH groups and NH ground can hydrogen bond with themselves, no others can
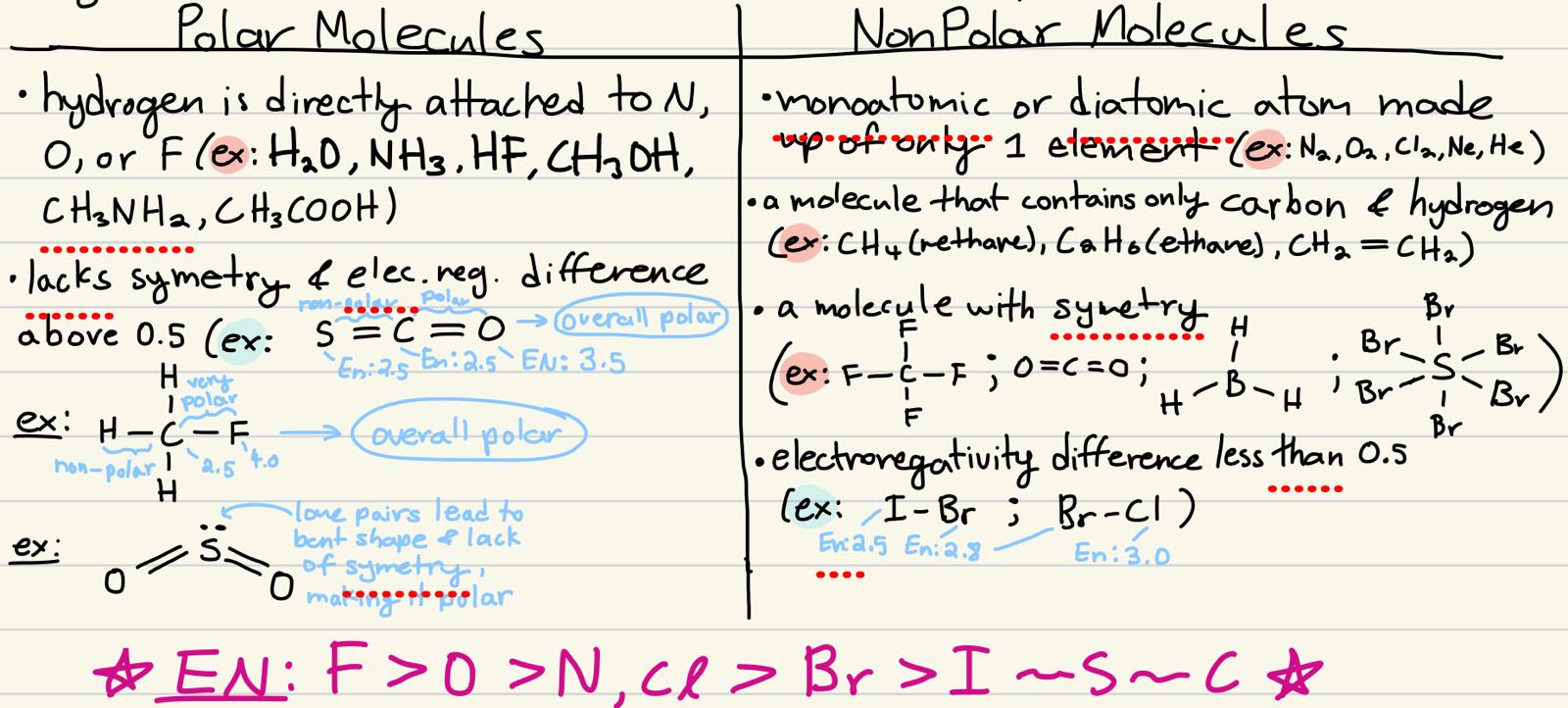
how do you know if a molecule is polar or nonpolar
solution dilution formula
M1 x V1 = M2 x V2
what’s a caliper
an electric device used to measure height and diameter by placing device in between the caliper clamps
how do you determine volume by water displacement
put some amount of water in a graduated cylider and measure initial volume
drop the device whose volume you are measuring into the cylinder and measure final volume
final volume - initial volume
precision
reproducibility; will the procedure produce the same results over and over again
accuracy
closeness to actual
strong electrolytes
any soluble salt or strong acid releasing many H+ ions
weak electrolytes
a compound that releases a few H+ ions; weak acids and sparingly soluble salts
non electrolytes
no H in molecular formula so releases no H+ ions
general lab procedure for ionic precipitation reaction
measure and dilute the two reactants to the appropriate molarity and volume
mix the two reactants into another beaker and place the magnetic stirrer into the breaker and stir and stirring plate for 15 minutes
clean, dry, and label an empty 100mL breaker and a piece of filter paper and record mass
place your stirred solution into a vacuum filtration apparatus to help the precipitate dry for 5 minutes
move the filter paper with the precipitate into the weighed beaker and let air dry
weight mass of precipitate and divide by theoretical yield to find percent yield
general lab procedure for a titration
get a ring stand and place a burette clamp on it, then clamp the burette onto one side
rinse burette with water and then the sodium hydroxide (base) solution
fill the burette with the base and record the starting volume
using a volumetric pipette, fill 20mL of the unknown molarity acid solution into an Erlenmeyer flask
add 2 to 3 drops of phenolphthalein indicator into the flask and mix
place the flask under the burette and begin simultaneously swirling solution with your hand and adding the base
continue until there is a persistent light pink color and record the volume of base required
use all data collected to calculate molarity of acid solution
how do you find the heat of the reaction from the heat of the solution
qrxn = -qsol; add a negative sign
how do you find delta Hrxn
qrxn/moles of the acid solution
general lab procedure for the quantitative determination of food dyes
choose 1 color of dye and make 5 solutions with increasingly larger concentrations of the dye diluted with distilled water
use a spectrometer to measure for 90 second and then stop the recording
find the max wavelength of solution 5 (10.0 mL dye and 0.0 mL DI water) and record both the max wavelength and the corresponding absorbance
repeat for the other 4 solutions and record the absorbance at the max wavelength determined for solution 5
find the equation for the absorbance - concentration graph of that dye
repeat to the find the equation and the max wavelength for the other 2 dyes
fill 3 cuvets with each of the 3 unknown dye drink samples
place a sports drink sample in the spectrometer and record their absorbance at the max wavelengths for each of the 3 dyes
use the formulas for each of the 3 dyes and plug in the absorbance of the dye in the sports drink for y and solve for x to find the concentration of the dye in the sports drink
repeat for all 3 drinks and all three dyes