Sensorimotor systems of the spinal cord
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
communication between incoming sensory signals and outgoing motor signals
afferent information entering the cord and how it is integrated by neurons in the gray matter of the spinal cord to activate muscles
Just a few spinal cord neurons can mediate and sustain intricate, complex movements without input from the brain
Sensorimotor Systems
__ entering the cord and how it is integrated by neurons in the gray matter of the spinal cord to activate muscles
afferent information
Just a few spinal cord neurons can mediate and sustain intricate, complex movements without input from the __
brain
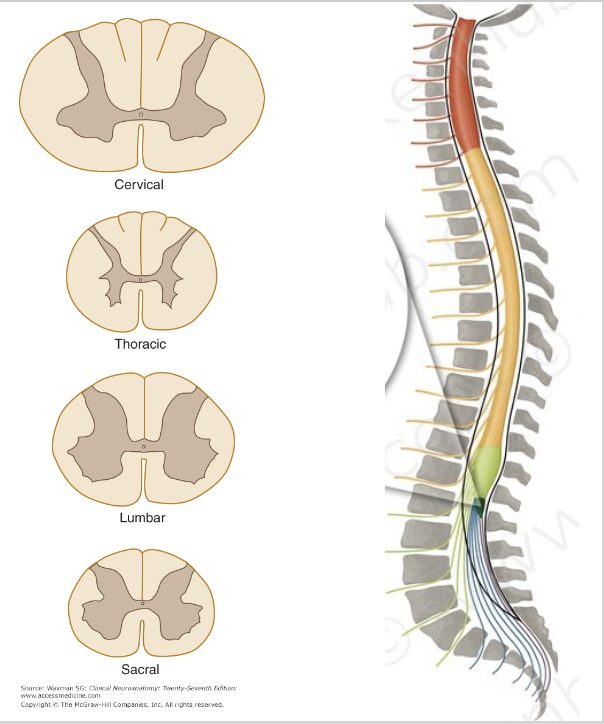
cervical
thoracic
lumbar
sacral
spinal cord
Has largest diameter – easy to injure
Signals between the brain and all 4 limbs pass through the White Matter of Cervical spinal cord
The amount of white matter increases the more rostral you go
Spinal Nerves to:
Neck, Arm & Hand
cervical
which part of the spinal cord has the largest diameter and easiest to injure?
cervical
Lateral horns - contain sympathetic neuron cell bodies
Spinal Nerves to:
Trunk
thoracic
contain sympathetic neuron cell bodies
lateral horns
No Cuneate Fasciculus!
Only Gracile Fasciculus at this level
Spinal Nerves to:
Legs and Feet
lumbar
T/F: the lumbar spinal cord has a cuneate fasciculus
false
Defecation, urination, sexual function
Spinal Nerves to:
Posterior legs
Sensation from perineum and anus
Motor control of External Anal Sphincter
sacral
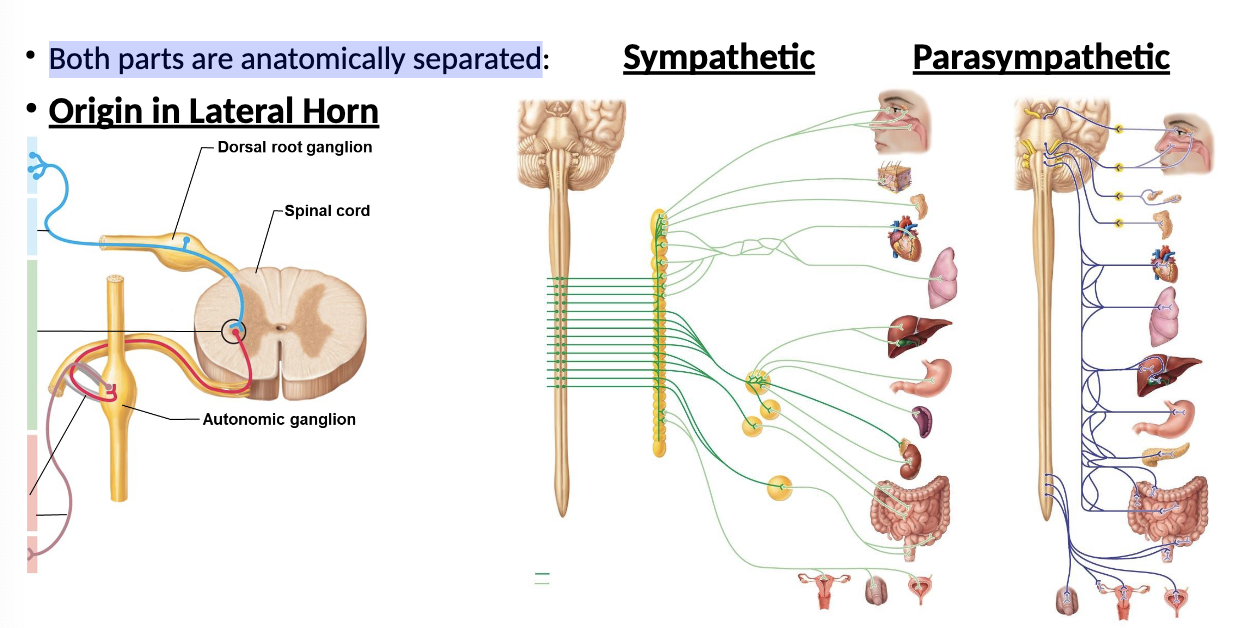
Both parts are anatomically separated from autonomic nervous system:
sympathetic
parasympathetic
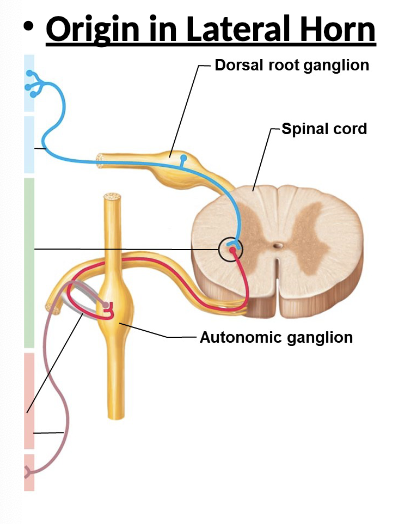
where does sympathetic originate?
lateral horn
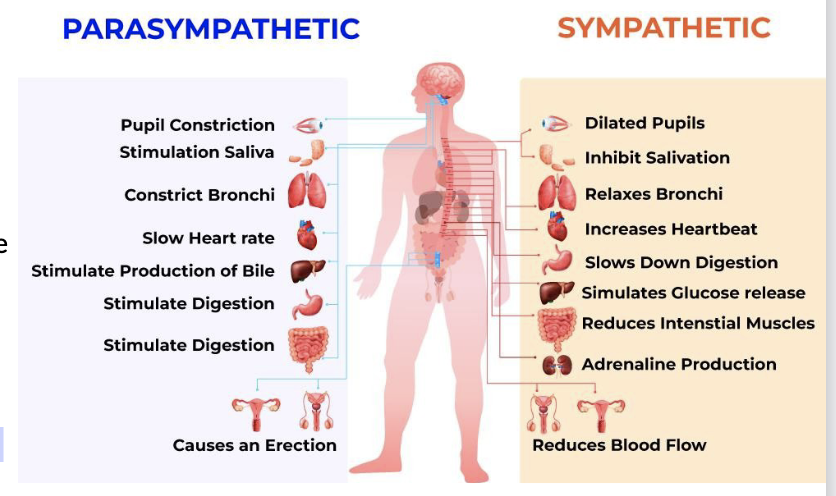
The unconscious nervous system
Receives information from visceral receptors
Has motor control over viscera
Autonomic Nervous System
the Autonomic Nervous System has __ over viscera
motor control
exit the Brainstem via Cranial nerves (esp. Vagus (CNX)) and exit the Spinal Cord through spinal nerves from segments S2 – S4
Parasympathetic signals
exit the Spinal Cord through spinal nerves from segments T1 – L2
All Sympathetic signals
On their way into and out of the CNS, __ pass through Ganglia
Such as the Sympathetic Trunk Ganglia (AKA Sym. Chain)
autonomic signals
Autonomic signals entering and exiting the spinal cord travel through __ between the spinal cord and ganglia
Communicating Rami (instead of the Ventral Ramus)
Most motor signals to viscera pass through __
Splanchnic Nerves
Contain cells bodies of Alpha Motor Neurons for each of the muscles of the body
Medial Group
Supply axial muscles
Lateral Group
Supply distal muscles
Intermediate Zone – between dorsal and ventral horns
Spinal Interneurons
For reflexes and organization of muscle synergies
Connect L&R sides of the spinal cord for alternating gait movements
Lower (α)Motor Neurons of the Ventral Horn
Lower (α)Motor Neurons of the Ventral Horn contain cell bodies of __ for each of the muscles of the body
Alpha Motor Neurons
Supply axial muscles
Medial group of ventral horn
Supply distal muscles
Lateral Group of ventral horn
between dorsal and ventral horns
Spinal Interneurons
For reflexes and organization of muscle synergies
Connect L&R sides of the spinal cord for alternating gait movements
intermediate zone
what is the intermediate zone between?
dorsal and ventral horns
what is the intermediate zone for?
For reflexes and organization of muscle synergies
what does the intermediate zone connect?
Connect L&R sides of the spinal cord for alternating gait movements
For movement, motor units, not individual muscle cells, are activated
Motor Units – αMN + muscle cells
an alpha motor neuron and the muscle cells it innervates
An Action Potential in an alpha motor neuron generates a
twitch in each muscle cell it connects with
motor unit
motor units differ by
Number of muscle fibers
Less muscle fibers per motor unit = more precise control
Type of muscle fibers
Less muscle fibers per motor unit = more precise control
Number of muscle fibers
muscle cell types
slow twitch
fast twitch
intermediate fibers
small, low force, endurance, aerobic
slow twitch
large, high force, fatigue, anaerobic
fast twitch
possesses properties of both
intermediate fibers
Motor units with low numbers of muscle cells will do light lifting – generate small forces
Also allow for precision movements
motor units in eye muscles contain ~10 muscle fibers
Motor units with high numbers of muscle cells will do heavy lifting – generate large forces
Allows for less precise movements
Motor units in the gastrocnemius contain ~2000 muscle fibers
Motor Units of increasing size are recruited to increase tension
number of muscle fibers
Also allow for precision movements
motor units in eye muscles contain ~10 muscle fibers
Motor units with low numbers of muscle cells will do light lifting – generate small forces
Allows for less precise movements
Motor units in the gastrocnemius contain ~2000 muscle fibers
Motor units with high numbers of muscle cells will do heavy lifting – generate large forces
Motor Units of increasing size are recruited to __
increase tension
Motor units with slow-twitch fibers will do light, repetitive
lifting – generate small forces with enduranceMotor units with intermediate fibers will do medium lifting –
generate medium forces with medium speedMotor units with fast-twitch fibers will do quick heavy lifting –
generate large forces with fatigueMotor Units of increasing strength are recruited to increase tension
type of muscle fibers
what will motor units with slow twitch fibers do?
Motor units with slow-twitch fibers will do light, repetitive
lifting – generate small forces with endurance
what will motor units with intermediate fibers do?
Motor units with intermediate fibers will do medium lifting –
generate medium forces with medium speed
what will motor units with fast twitch fibers do?
Motor units with fast-twitch fibers will do quick heavy lifting –
generate large forces with fatigue
How do αMNs Code for Contraction Strength? Its all about the Frequency!
Summation
Unfused Tetanus
Maximal tension with a “shake”
Partial relaxation occurs, allowing slight recovery
Fused Tetanus
Fatigue occurs quickly
The force, speed, and duration of muscle contraction are determined in the spinal cord
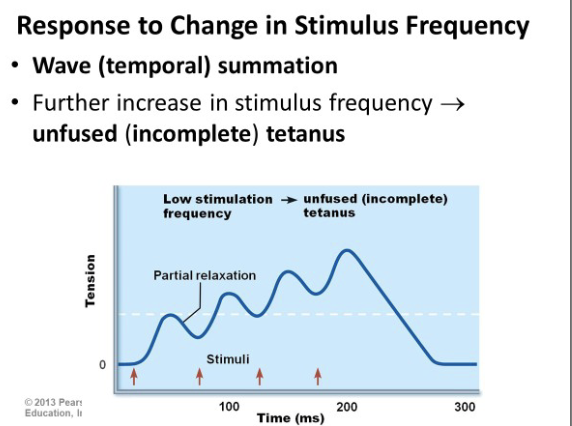
Maximal tension with a “shake”
Partial relaxation occurs, allowing slight recovery
unfused tetanus
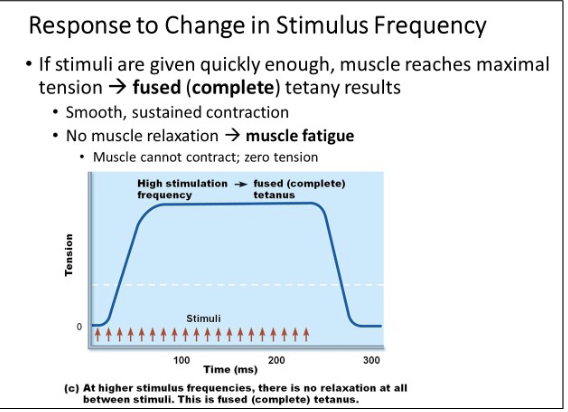
smooth, sustained contraction
Fatigue occurs quickly
fused tetanus
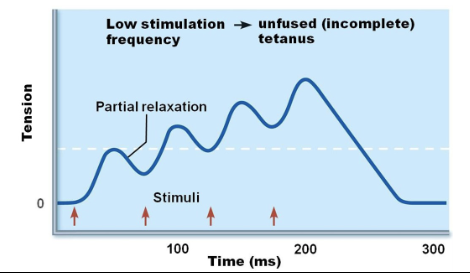
response to change in stimulus frequency
increased stimulus frequency (muscle does not completely relax between stimuli) → second contraction of greater force
summation: wave (temporal)
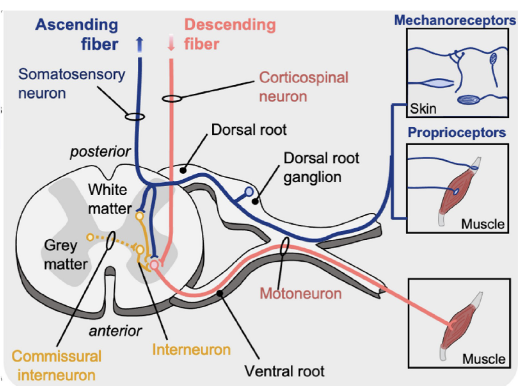
If Alpha (α) Motor Neurons Control Muscle Contraction, what controls the α Motor Neurons ?
Descending signals (including UMNs) from the brain
Somatosensory (afferent) signals from receptors (Cut. + Proprio.)
• Afferent DriveSpinal Interneurons in the intermediate zone of the spinal cord grey matter
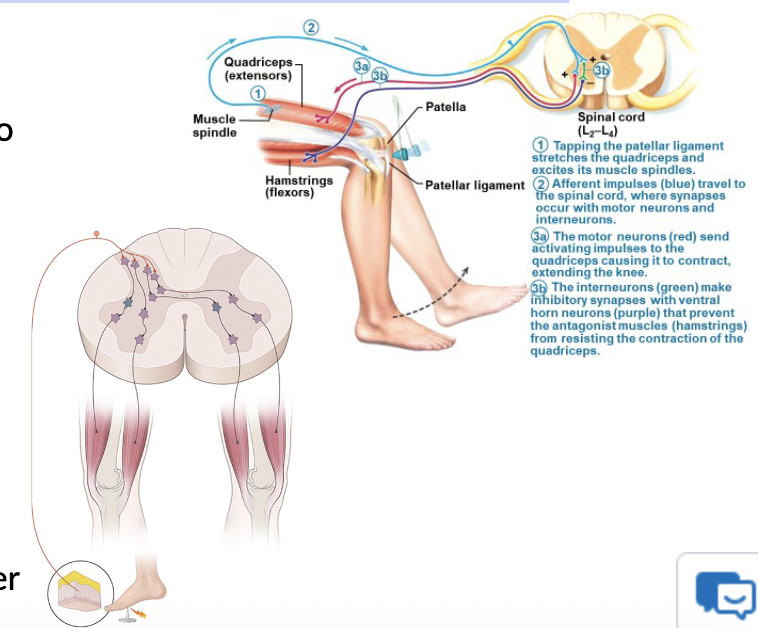
Stretch reflex features a monosynaptic circuit
allows for a rapid reaction to proprioceptive stimulus
Afferent Drive (incoming somatosensory information)
Helps coordinate synergies and gait patterns
1 sensory neuron synapses with Many cells in the CNS
αMN and Interneurons
Axon collaterals split from each other in the grey matter
divergence of the signal
__ synapses with Many cells in the CNS
αMN and Interneurons
1 sensory neuron
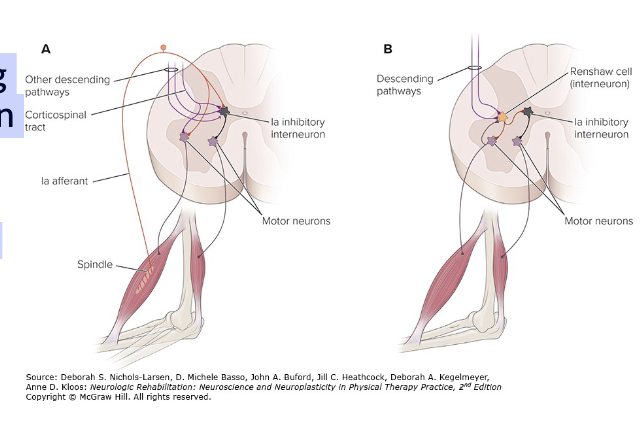
Receive signals from the brain and sensory receptors
“Decide” if an activation signal is strong enough to be “worthy” of generating an Alpha NM action potential signal to its motor unit of muscle cells
Last-order Interneuron: interneurons that synapse with α motor neurons
Types of ‘Last-order’ Interneurons:
1a Inhibitory
1b Inhibitory
Renshaw Cells
Spinal Interneurons
where does spinal interneurons receive signals from?
the brain and sensory receptors
what do spinal interneuron “decide”?
if an activation signal is strong enough to be “worthy” of generating an Alpha NM action potential signal to its motor unit of muscle cells
• Last-order Interneuron: interneurons that synapse with α motor neurons
interneurons that synapse with α motor neurons
last order interneuron
Involved in the stretch reflex
Sums together all Excitatory and Inhibitory Signals
Inhibits α motor neurons to antagonists muscles
The stretched muscle can contract unopposed
1a inhibitory
which reflex is 1a inhibtory involved in?
Involved in the stretch reflex
what does 1a inhibitory sum up together?
Sums together all Excitatory and Inhibitory Signals
1a inhibitory inhibits alpha-motor neurons to what muscles?
antagonists muscles
Involved in the Golgi Tendon reflex
Sums together all Excitatory and Inhibitory Signals
Inhibits α motor neurons to tensed muscles
The inhibited muscle can relax so the antagonist muscle can contract unopposed
1b inhibtory
what reflex is 1b inhibitory involved in?
Involved in the Golgi Tendon reflex
what does 1b inhibitory sum up together?
Sums together all Excitatory and Inhibitory Signals
1b inhibitory inhibits alpha-motor neurons to what muscles?
Inhibits α motor neurons to tensed muscles
The inhibited muscle can relax so the antagonist
muscle can contract unopposed
Provides negative feedback to firing αMNs
Receives signals from αMNs and descending signals from the brainstem
Inhibit 1a Inhibitory Interneurons
Rhythmically active during locomotion
Balances contractions of agonist, antagonists and synergists at a joint during locomotion
help stabilize the motor system and prevent
overstimulation of muscles
renshaw cells (inhibitory)
what does Renshaw cells provide?
Provides negative feedback to firing αMNs
Receives signals from αMNs and descending signals from the brainstem
when is Renshaw rhythmically active?
Rhythmically active during locomotion
Balances contractions of agonist, antagonists and synergists at a joint during locomotion
what does the Renshaw cells stabilize?
help stabilize the motor system and prevent overstimulation of muscles
• An alpha motor neuron is excited and sends an action potential
towards its motor unit.
• A collateral (a small branch) of that motor neuron's axon loops
back and forms an excitatory synapse with a Renshaw cell.
• The Renshaw cell releases the inhibitory neurotransmitters
glycine and GABA onto the original motor neuron
• This inhibitory feedback reduces the firing rate of the motor
neurons, creating a self-regulating system that prevents
excessive muscle contraction
how renshaw cells work
An alpha motor neuron is excited and sends an __ towards its motor unit
action potential
A collateral (a small branch) of that motor neuron's axon loops back and forms an __ with a Renshaw cell.
excitatory synapse
The Renshaw cell releases the
inhibitory neurotransmitters glycine and GABA onto the original motor neuron
This inhibitory feedback reduces the firing rate of the motor neurons, creating a __ that prevents excessive muscle contraction
self-regulating system
attacks Renshaw cells, resulting in uncontrolled muscle spasm
tetanus toxin
If you injure your right foot, your left foot has to carry more body weight, therefore contralateral muscles will be activated to stabilize the contralateral limb
Also crucial for communication to the contralateral lower motor neurons
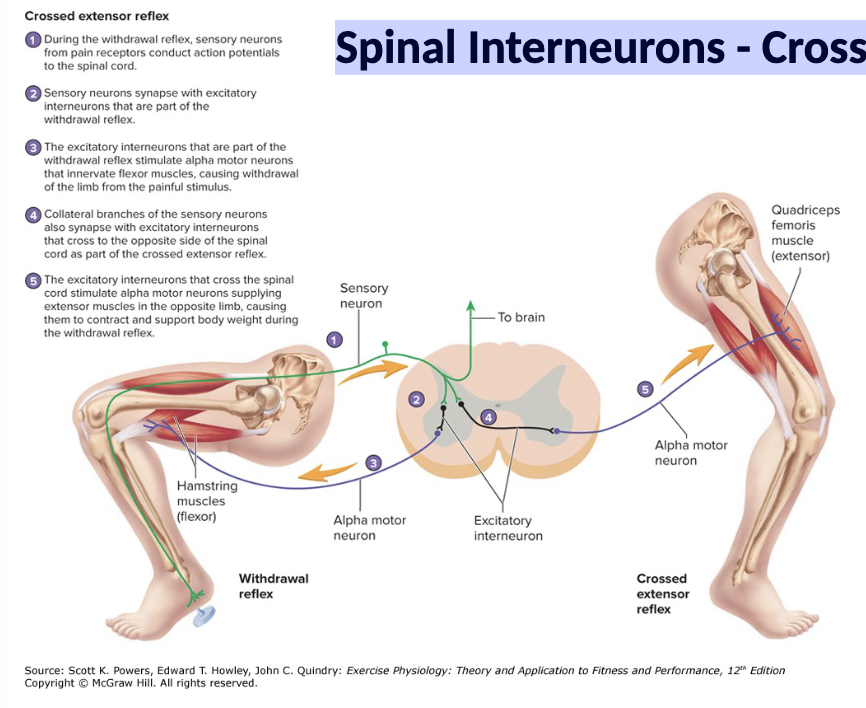
Spinal Interneurons - Crossed Extensor Reflex
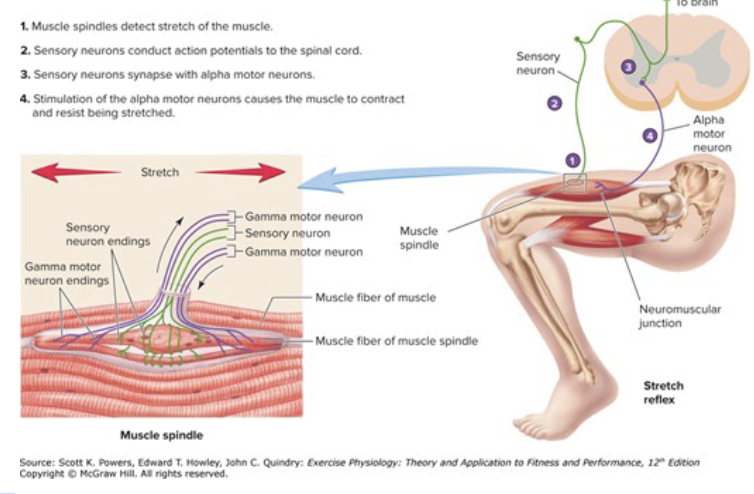
A muscle stretch/length receptor
Takes part in:
regulation of movement
maintenance posture
Produces a reflex contraction in response to a rapid increase in muscle length
Thigh muscles play a huge role in standing posture
If one is standing upright and starts to sway to the left, muscles in the legs and torso are stretched, activating the myotatic reflex to counteract the sway
muscle spindle reflex
what does muscle spindle reflex take part in?
regulation of movement
maintenance posture
muscle spindle reflex produces what?
Produces a reflex contraction in response to a rapid increase in muscle length
Thigh muscles play a huge role in
standing posture
If one is standing upright and starts to sway to the left, muscles in the legs and torso are stretched, activating the __ to counteract the sway.
myotatic reflex
Stretch Reflex Tests are called __ because they are tested by tapping the muscle tendon in order to stretch the muscle suddenly
Deep Tendon Reflex Tests
• Assess health of all reflex arc components, spinal nerves, etc.
• Assess Myotome function
• Help determine if a motor issue is the result of a UMN injury (hyperreflexia) or LMN injury (areflexia/hyporeflexia)
purpose of deep tendon reflex tests
Help determine if a motor issue is the result of a __ or __
UMN injury (hyperreflexia) or LMN injury (areflexia/hyporeflexia)
CPGs produce rhythmic motor patterns without input from the brain
Central Pattern Generators
from the Lower extremity can provide the “go signal” that produces alternating excitation and inhibition of antagonistic muscle groups in a gait pattern
Somatosensory signals
CPGs are also responsible for
stimulating the right and left limbs in an alternating sequence of Swing and Stance
Once CPG’s receive a __ they become self- stimulating and produce repetitive synchronized activity that continues until a __occurs
“go signal” / “stop signal”
CPGs feature lots of __
E.g., in order to flex a joint, simultaneous signals are sent to the flexor MNs and the Extensor MNs
Flexor MNs receive an excitatory signal
Extensors MNs receive an inhibitory signal
reverberating circuits
receive an excitatory signal
Flexor MNs
receive an inhibitory signal
extensor MNs