IB Economics SL/HL Unit 2 (Microeconomics)
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All microeconomics terms and formulas for IB Economics. Includes both SL and HL. 2022~2029 syllabus. Imported from EcoNinja.net. (Unit 3 Now Available)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
Law of Demand
States that the quantity demanded for a good or service decreases as price increases and vice versa.
The Income Effect
States that as the price of a product falls, consumers' real income increases and more will be bought.
The Substitution Effect
States that as the price of a product increases, more consumers will choose it over rivals and more will be bought.
Substitute Goods
Goods or services that compete against each other and are hence in competitive demand.
Shift
A change in a non-price determinant changes the quantity.
Quantity Supplied
The amount of goods and services producers are willing and able to provide.
Law of Supply
States that the quantity supplied is directly proportional to price.
Diminishing Marginal Returns
As more factors of production are utilized, each additional unit brings declining returns.
Competitive Supply
The output of one good or service prevents the output of another.
Joint Supply
The output of one good or service increases the output of another.
Price Mechanism
The interactions between consumers and producers that allocate resources and determines prices of goods and services.
Signalling Function
Provides information to consumers and producers on where resources should be allocated.
Incentive Function
Provides motivation for consumers and producers to change their behavior to maximize profits.
Rationing Function
Ensures scarce goods and services deter consumers by raising prices.
Consumer Surplus
The gain of all consumers who can consume a product at a lower price than what they were willing and able to pay.
Social Surplus
The sum of consumer and producer surplus.
Allocative Efficiency
The social optimum when resources are distributed in the most effective and beneficial way.
Rational Consumer Choice
The assumption that all consumers make the most rational decisions.
Imperfect Information
A situation where an economic agent has incomplete information on the product they're buying/selling.
Bounded Rationality
The idea that consumers do not always have the capability to make perfectly rational decisions.
Bounded Selfishness
The idea that consumers are not always completely selfish, in contrast to traditional economic theory.
Bounded Self-Control
The idea that consumers may give in to their temptations and consume products they know are not maximizing their utility.
Rule-of-Thumb
General rules consumers stick to when faced with a lack of information regarding a product.
Anchoring Bias
A cognitive bias where consumers over-rely on information they've received in the past, rather than current information.
Framing Bias
A cognitive bias where consumers decide on products based on how positively (or negatively) they are portrayed.
Availability Bias
A cognitive bias where consumers decide on products based on what information they can first remember is associated with the product.
Choice Architecture
The study of how choices can be presented in a way that influences which choice is taken.
Nudge Theory
Ways to influence consumers into choosing something, without actively restricting their choices; They are simply "nudged" into the "right" direction.
Corporate Social Responsibility
The consideration firms make on how they impact society and the environment.
Income Elasticity of Demand
A measure of how quantity demanded for a product varies based on income.
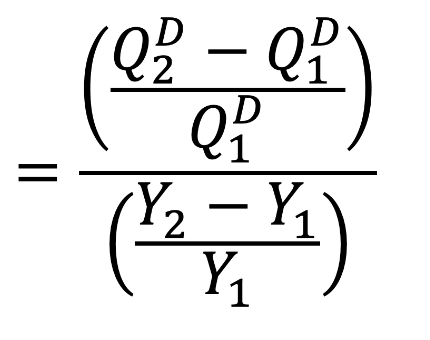
Inferior Goods
Goods with a negative income elasticity (as incomes increase, less will be demanded)
Necessities/Normal Goods
Goods with an income elasticity between 0 and 1 (as incomes increase, more will be demanded, but less than the proportionate change).
Luxury Goods
Goods with an income elasticity of more than 1 (as incomes increase, more will be demanded, and more than the proportionate change).
Indirect Tax
A payment taken indirectly from consumers by charging for their expenditure on goods and services.
Specific Tax
A fixed amount of tax on a good or service.
Ad Valorem Tax
A percentage tax on a good or service.
Government Failure
Arises when government intervention causes more social costs than benefits.
Market Failure
The inability of the free market to achieve allocative efficiency.
Marginal Private Benefits
The additional value gained by households or firms when consuming/producing an extra unit of a good or service.
Marginal Private Costs
The additional expense incurred by households or firms when consuming/producing an extra unit of a good or service.
Marginal Social Benefits
The additional value gained by society when consuming/producing an extra unit of a good or service.
Marginal Social Costs
The additional expense incurred by society when consuming/producing an extra unit of a good or service.
Common Pool Resources
Non-excludable but rivalrous resources.
Tradable Permits
Government-regulated tradable contracts that allow for pollution. They can be traded amongst firms to result in a more socially optimum level.
Subsidies
Financial assistance from the government to firms that lower their costs of production, in order to increase output.
Public Goods
Goods for consumption that are non-excludable and non-rivalrous.
Free-Rider Problem
The issue that arises when people that do not pay for a good or service have access to it.
Asymmetric Information
The issue that arises when the seller has more information about the good or service than the buyer, or vice versa.
Adverse Selection
A market situation where buyers and sellers have more information than the other, leading to the party with the most information making optimal decisions for themselves, at the cost of the other party.
Moral Hazard
A market situation where a buyer or seller protected from risk makes optimal decisions for themselves, at the cost of the other party.
Perfect Competition
A market structure with many firms holding no market power, no barriers to entry, and homogeneous products.
Monopolistic Competition
A market structure with many firms holding little market power, low barriers to entry, and differentiated products.
Oligopoly
A market structure with a few large firms holding significant market power, high barriers to entry, and differentiated products.
Collusive Oligopoly
A market structure where oligopolistic firms engage in practices to restrict competition by price fixing or limiting output.
Monopoly
A market structure with one large firm holding all market power, high barriers to entry, and no close substitute products.
Natural Monopoly
A market structure where only one large firm is able to operate with profit.
Variable Costs
Expenses that change with output of a good or service.
Profit Maximization
When a firm produces at the largest possible difference between total revenue and total costs.
Income Inequality
The issue of income being unequally distributed in a country.
Wealth Inequality
The issue of assets being unequally distributed in a country.
Quantity Demanded
The amount of goods and services consumers are willing and able to purchase.
Diminishing Marginal Utility
As more of a product is consumed, each additional unit brings declining satisfaction, and consumers are only willing to buy more at lower prices.
Market Demand Curve
The sum of all individual demand for a good or service.
Complementary Goods
Goods or services that are jointly demanded.
Movement
A change in price changes the quantity.
Marginal Costs
The cost of producing one additional good or service.
= (Change in TC) / (Change in Q)
Market Supply Curve
The sum of all individual supply for a good or service.
Shortage
When there is excess demand for a good or service.
Surplus
When there is excess supply for a good or service.
Producer Surplus
The gain of all producers who can produce a product at a higher price than what they were willing and able to earn.
Perfect Information
A situation where an economic agent has complete information about everything related to the product they're buying/selling.
Price Elasticity of Demand
A measure of how quantity demanded for a product varies based on price.
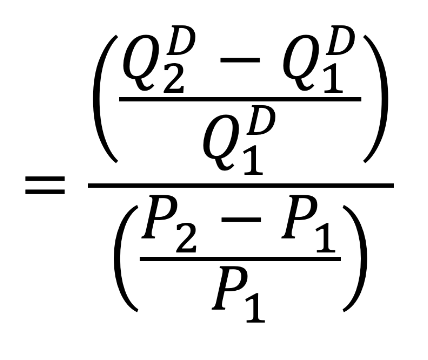
Price Elasticity of Supply
A measure of how quantity supplied for a product varies based on price.
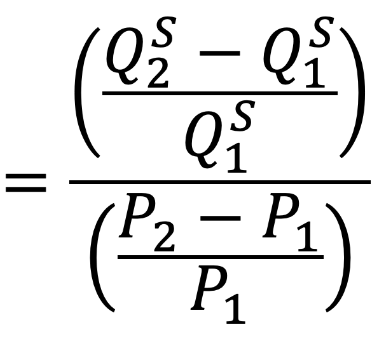
Price Ceiling
Government regulations that set a maximum price for a good or service.
Price Floor
Government regulations that set a minimum price for a good or service.
Positive Externalities
Benefits of a good or service enjoyed by a third party not directly involved in an economic transaction.
Negative Externalities
Costs of a good or service experienced by a third party not directly involved in an economic transaction.
Merit Goods
Goods and services that create positive externalities when produced or consumed
Demerit Goods
Goods and services that create negative externalities when produced or consumed
Carbon Tax
A tax on greenhouse gas emissions that aim to reduce pollution.
Market Power
The ability of a firm to manipulate prices of a good or service.
Revenue
The money gained by a firm for selling their goods and services.
Fixed Costs
Expenses that do not change with output of a good or service.
Profit
The money remaining after expenses have been subtracted from revenue.
= TR - TC
Marginal Revenue
The additional revenue when producing one additional unit of a good or service.
= (Change in TR) / (Change in Q)
Abnormal Profit
Profit left after accounting for costs, incentivizing the entry of new firms into the market.
Normal Profit
When the cost of production equals the revenue of selling.