Biology: 3A - Sexual reproduction (Human)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What are the parts to the male reproductive system?
Bladder, glands, sperm duct, Uretha, penis, testis, foreskin, scrotum.
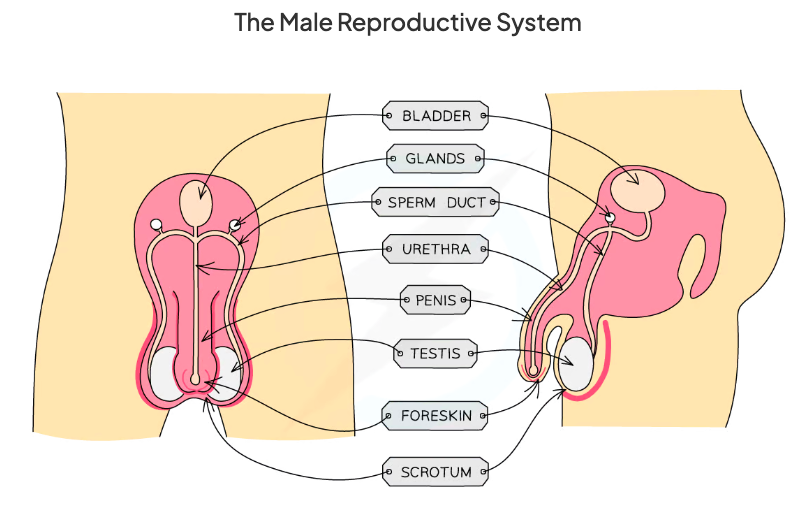
What is the function of the prostate gland in the male?
Produces fluid called semen that provide sperm cell with nutrients.
What is the function of the sperm duct in the male?
Sperm passes through sperm duct to be mixed with fluids produced by glands before being passed int uretha for ejaculation.
What is the function of the urethra in the male?
Tube running down centre of penis that can carry out urine or semen, a ring of muscle in urethra prevents urine and semen from mixing.
What is the function of the testis in the male?
Contained in scrotum and produces sperm and testosterone.
What is the function of the scrotum in the male?
Sac supporting the testes outside the body to ensure sperm kept at slightly lower than body temperature.
What is the function of the penis in the male?
Passes urine out of body from bladder and allows semen to pass into vagina of woman.
What are the parts to the female reproductive system?
ovary, uterus, cervix, bladder, urethra, vagina, endometrium, fallopian tube
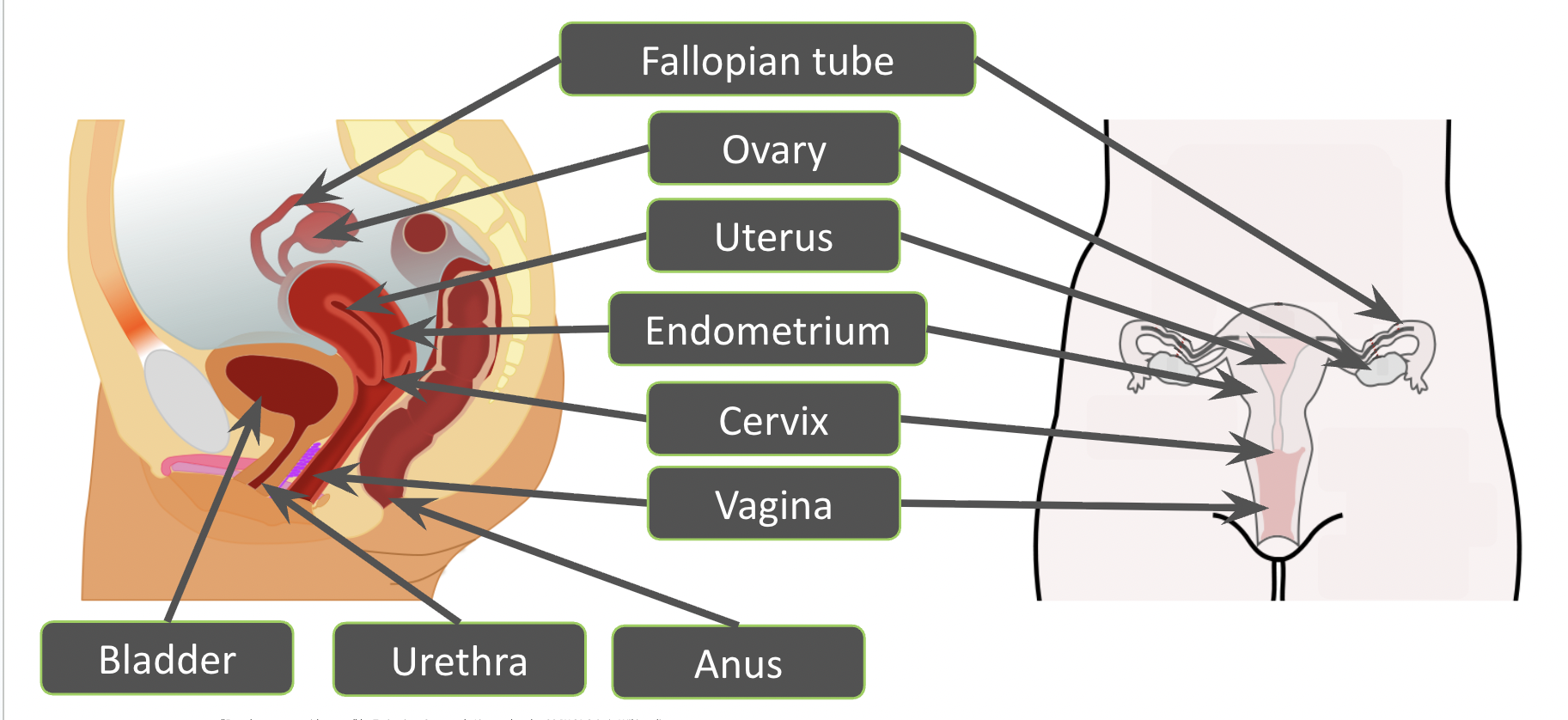
What is the function of the fallopian tube in the female?
The egg will travel down the fallopian tube (oviduct) where it will meet the sperm and fertilisation will occur
What is the function of the endometrium in the female?
The endometrium has a good blood supply so the embryo can implant and grow
What is the function of the ovary in the female?
Produces ova and sex hormones
What is the function of the uterus in the female?
The uterus (womb) is where the embryo grows
What is the function of the cervix in the female?
The cervix is a ring of muscle that holds the developing embryo in the uterus
What is the function of the vagina in the female?
The vagina is used for sexual intercourse, the sperm are deposited here
How many chromosomes are in each gamete?
23, however once fused into a zygote, the zygote has 46.
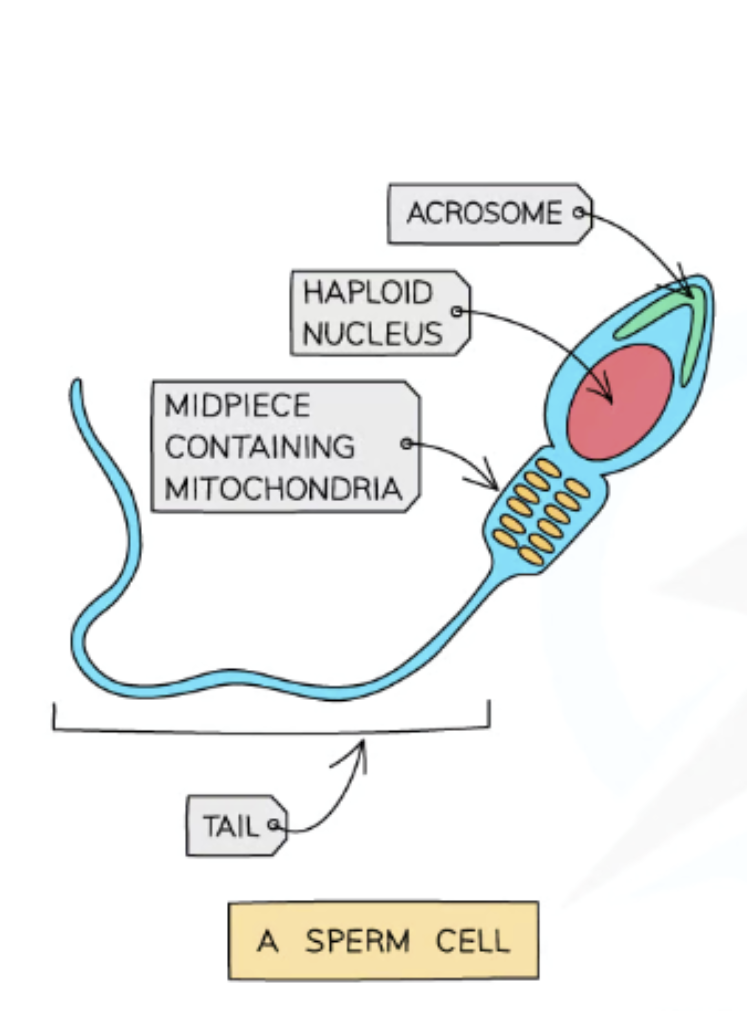
What are the features and reasoning for sperm cell?
Has a flagellum (tail): Enables it to swim to egg.
Contains enzymes in head region (acrosome): To digest through jelly coat and cell membrane of egg cell when it meets one.
Contains many mitochondria: Provide energy from respiration so flagellum can move back and forth for locomotion.
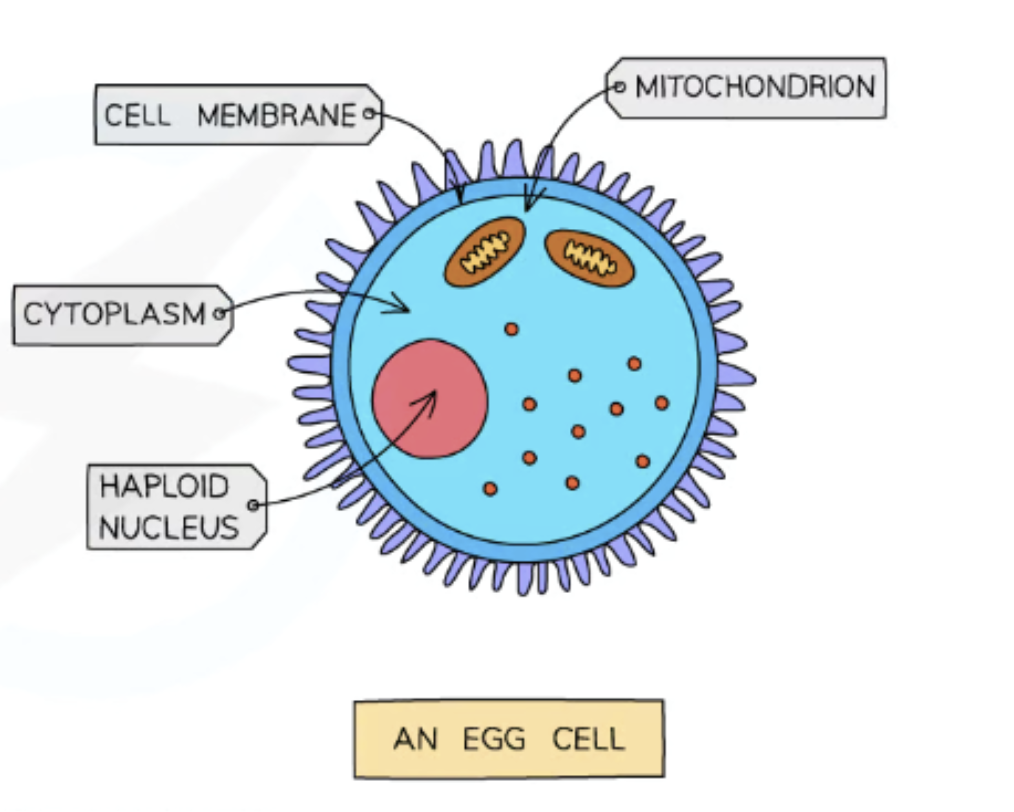
What are the features and reasoning for egg cell?
Cytoplasm containing a store of energy: Provides energy for the dividing zygote after fertilisation.
Jelly-like coating that changes after fertilisation: Forms impenetrable barrier after fertilisation to prevent other sperm nuclei entering sperm cell.
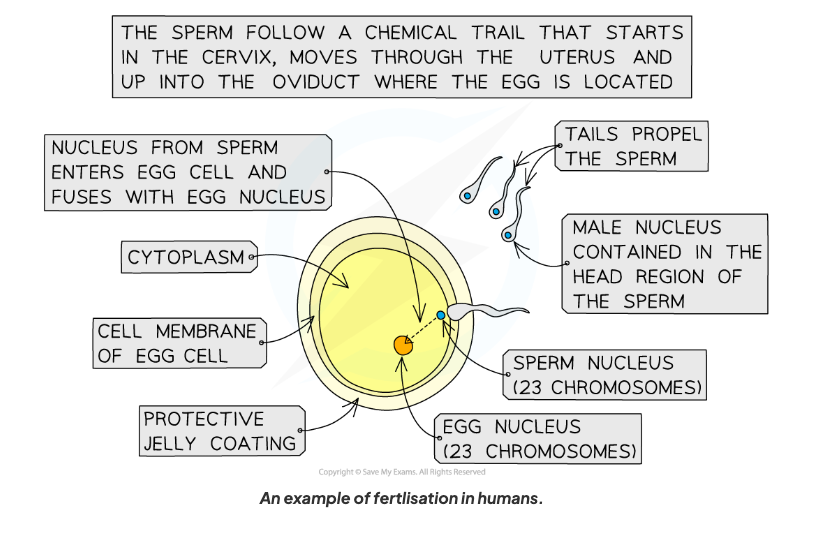
Describe the journey of the sperm.
During ejaculation in the male, millions of sperm cells move along the sperm duct
The sperm are suspended in semen
The semen passes into the urethra
During sexual intercourse, semen is ejaculated into the vagina of the female, near the cervix
The sperm cells then follow a chemical trail and travel through the plug of mucus in the cervix to reach the uterus (the womb)
The sperm cells then travel into the oviducts
If a sperm cell meets an egg cell in the oviduct, fertilisation can occur.
What is fertilisation for humans?
The fusion of a male (sperm) and female (ovum) gamete to produce a zygote (fertilised egg cell).
What happens after fertilisation?
The zygote divides by mitosis until an embryo is formed after a few days, which then travels down the uterus and implants into the endometrium.
What is the placenta and it’s function?
Once an embryo has implanted, the placenta develops.
It provides oxygen and nutrients to the growing embryo.
It removes waste such as urea and carbon dioxide.
It secretes female hormones that maintain the pregnancy.
What are the adaptations to the placenta and reasons?
A large surface area provided by the villi
A thin wall for efficient diffusion
(blood / capillaries) maintains gradient / makes steep gradient
thin / short distance / maternal and fetal blood are close
What is the amnion and it’s function?
During pregnancy the amnion (amniotic sac) encloses the developing embryo.
This secretes a fluid called amniotic fluid which protects the developing embryo.
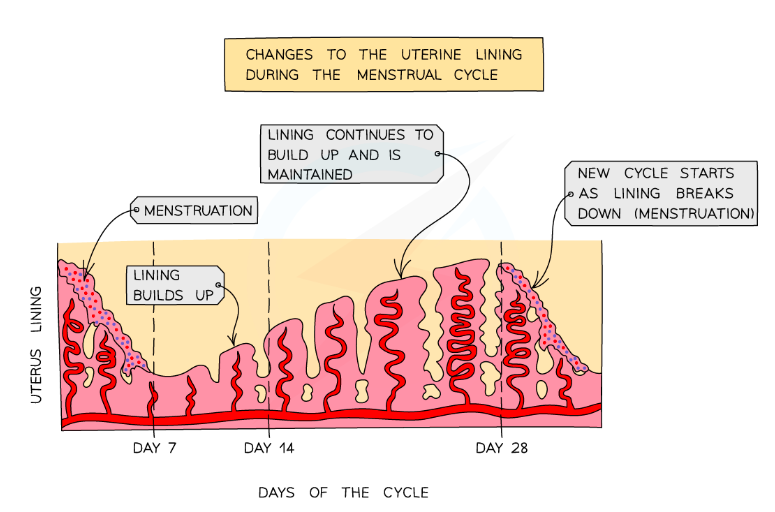
Give an overview of the menstrual cycle and the timings.
The average menstrual cycle is 28 days long
Ovulation (the release of an egg) occurs about halfway through the cycle (day 14) and the egg then travels down the oviduct to the uterus
Failure to fertilise the egg causes menstruation to occur - this is caused by the breakdown of the thickened lining of the uterus
Menstruation lasts around 5 - 7 days and signals the beginning of the next cycle
After menstruation finishes, the lining of the uterus starts to thicken again.
What controls the menstrual cycle?
Hormones released from the ovary and pituitary gland.
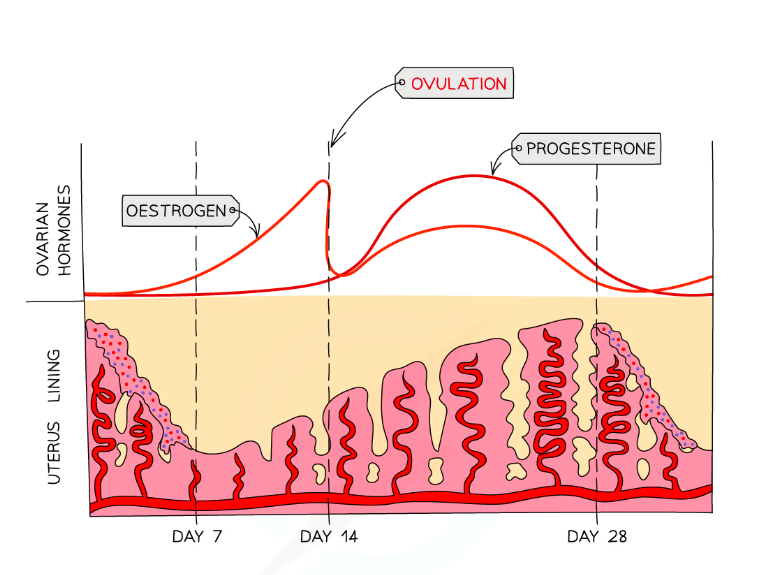
What is the role of the hormone oestrogen in the menstrual cycle?
Oestrogen levels rise from day 1 to peak just before day 14
This causes the uterine wall to start thickening and the egg to mature
The peak in oestrogen occurs just before the egg is released
What is the role of the hormone progesterone in the menstrual cycle?
Progesterone stays low from day 1 – 14 and starts to rise once ovulation has occurred
The increasing levels cause the uterine lining to thicken further; a fall in progesterone levels causes the uterine lining to break down (menstruation / ‘period’)
What are primary sexual characteristics?
Primary sexual characteristics are present during development in the uterus and are the differences in reproductive organs etc between males and females.
What are secondary sexual characteristics?
The changes that occur during puberty as children become adolescents.
What are these characteristics controlled by?
The release of hormones. Oestrogen in girls and testosterone in boys.
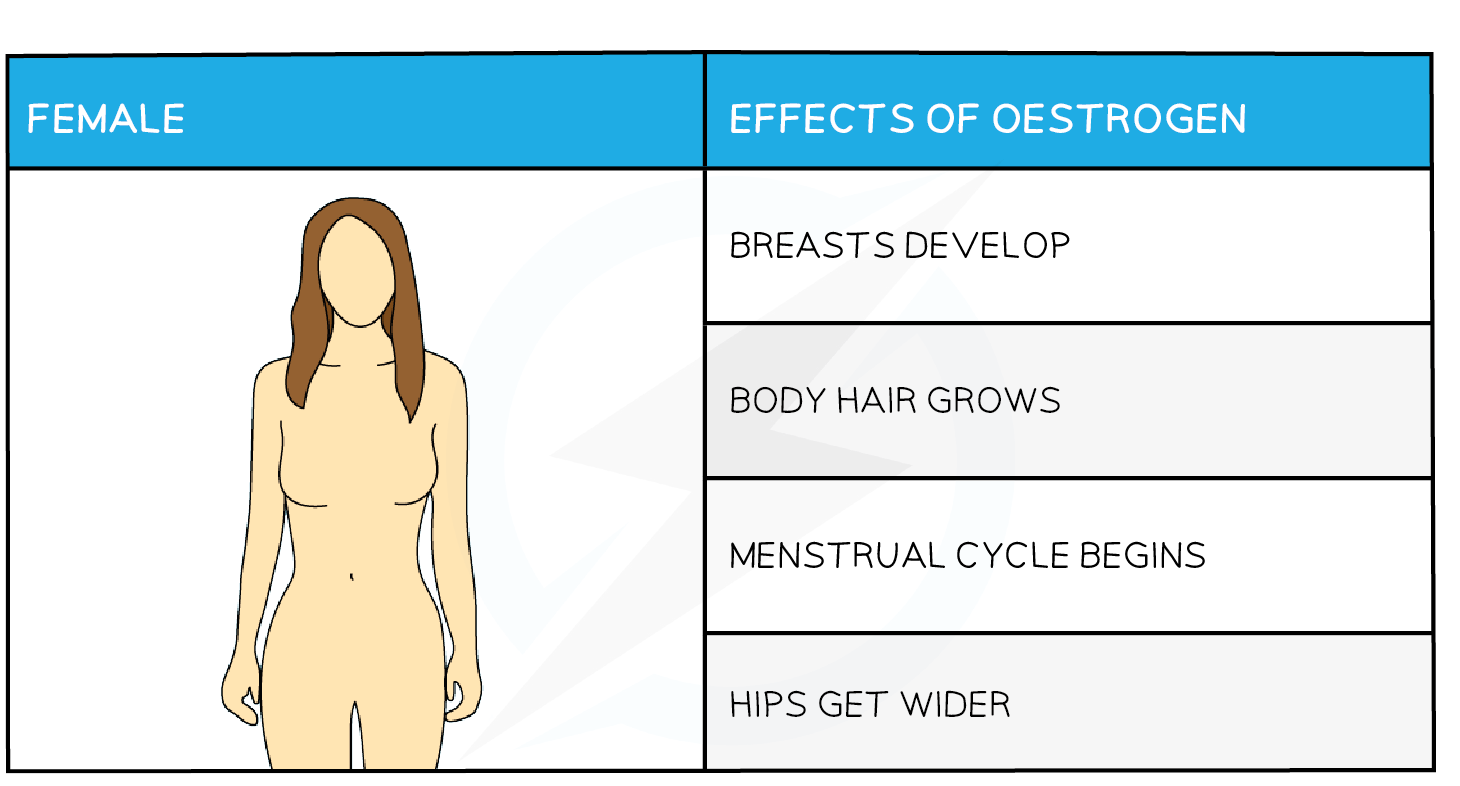
What are the female secondary sexual characteristics?
Breasts develop, body hair grows, menstrual cycle begins, hips get wider.
What are the male secondary sexual characteristics?
Growth of penis and testes, growth of facial and body hair, muscles develop, voice breaks, testes start to produce sperm.