Atacama desert - Case study
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Atacama desert description
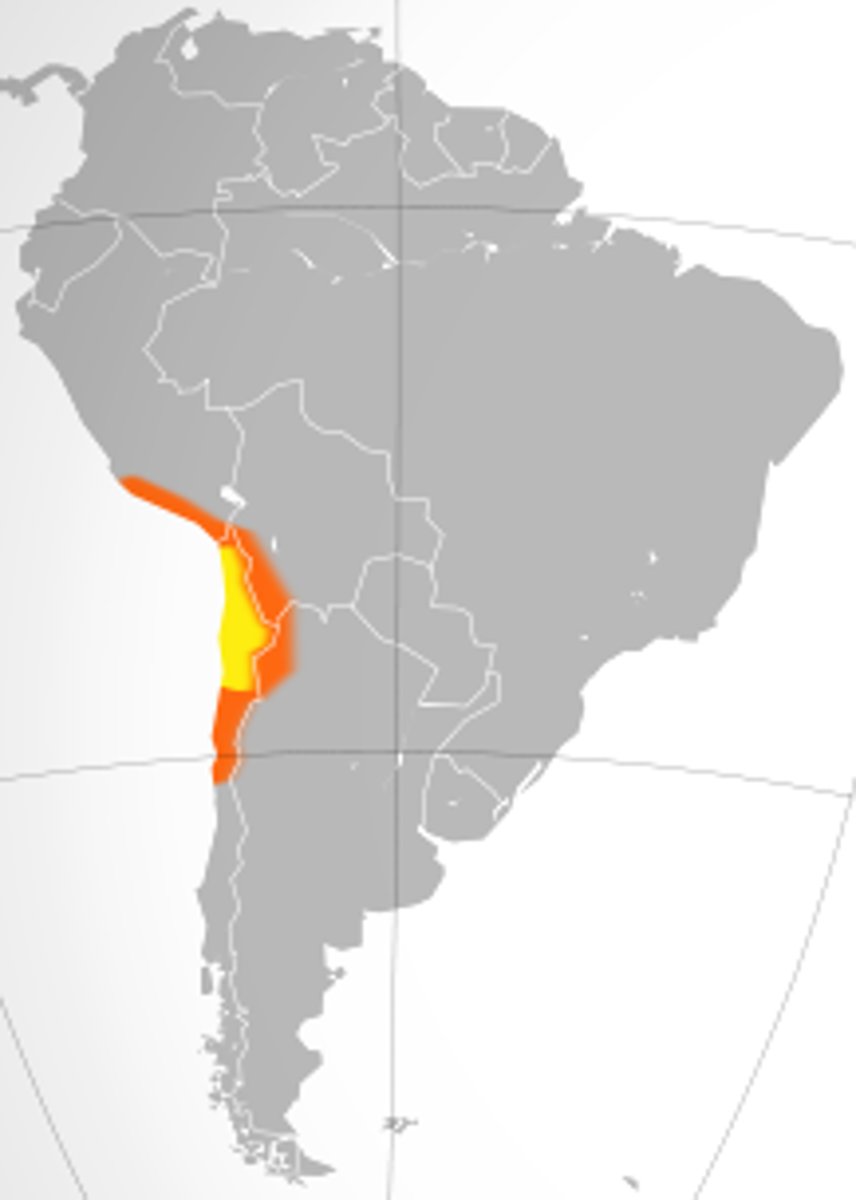
- desert plateau which stretches from southern peru to chile, covering a 1,600km strip of land on the pacific coast, west of the Andes Mountains
- lattitues of 23.8 degrees S and 69 degrees W (important for why it is arid)
- one the oldest deserts on earth
Climate in the Atacama
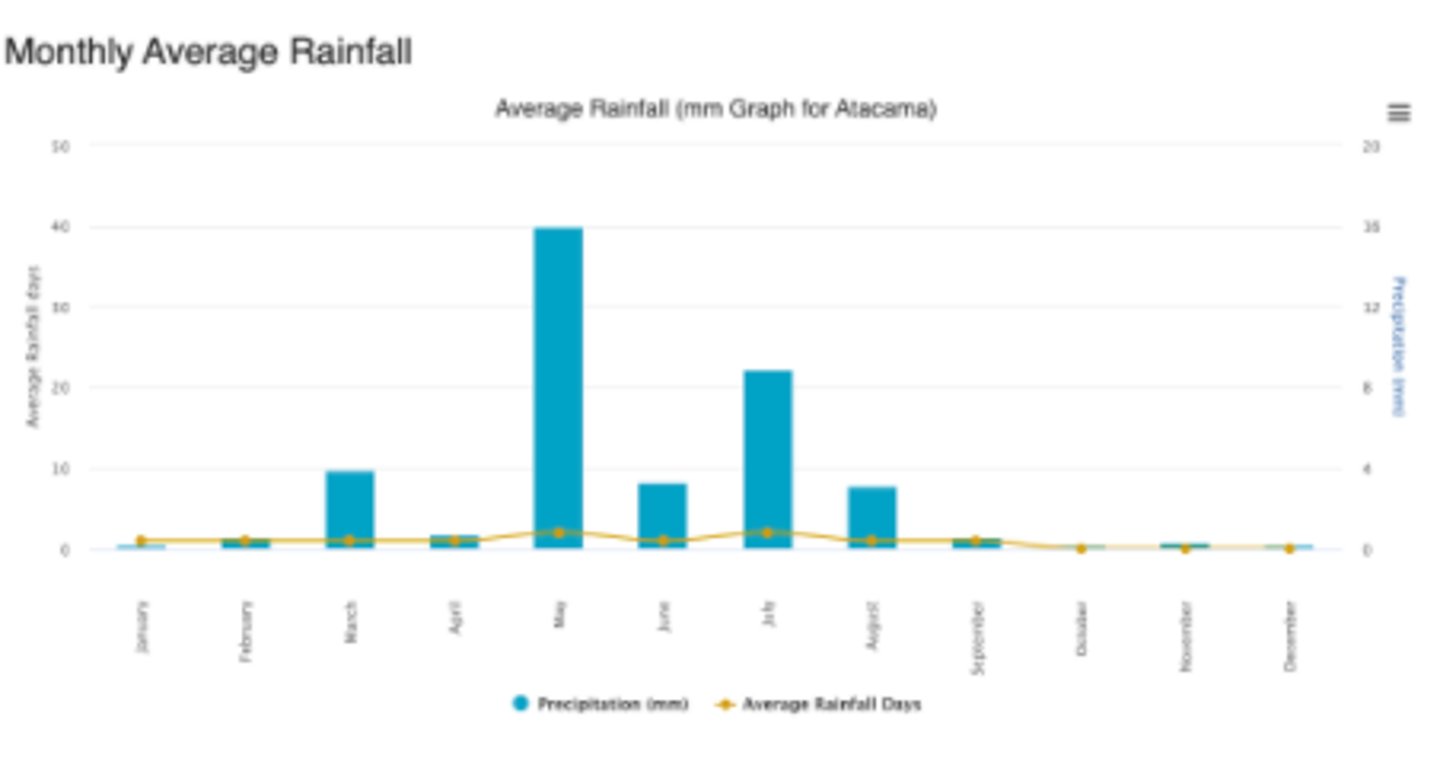
- driest nonpolar desert on Earth
- owes its extreme aridity due to the atmospheric pressure, relief and rain-shadow effect, offshore winds and cold ocean currents
- Rainfall from the East is blocked by the Andes Mountains
- On average, the driest part of the Atacama receives less than 1 millimetre of rain each year and is 50x drier than Death Valley
Soils in the Atacama desert
- Gypsum-cemented soil (gypsum is a very soluble salt) buried in some places by landslide + fluvial deposits therefore in some places is a paleosol
- GS soils restricted to areas that receive <3cm of precipitation per year
→ In the Future, this soil could change lives, as it contains a type of bacteria which is called actinobacteria and helps fight off antibiotic resistance
Vegetation in the Atacama
- cacti are not common but Mesquite trees are: numerous twisted, low-lying branches that give the trees a lot of area for buds to emerge and blossom into flowers, ephemerals which bloom in small periods of rain and survive drought by lying dormant
- plant life also includes small, deep rooted, thorny plants with long roots, fleshy leaves
Causes of Aridity in the Atacama
1. Atmospheric pressure
2. Relief and the rainshadow effect
3. Cold ocean currents
4. offshore winds
Causes of Aridity in the Atacama- Atmospheric pressure
- found in 23.6°S of the equator (deserts always found 20-35 degrees N or S of the equator)
- because it is between Ferrel and Hadly cell where air cools and sinks back towards the Earth's surface creating high pressure
- sinking air is warmed by compression, preventing cloud formation and rain
- Meaning that the area is persistently dry, has high insolation and high evaporation
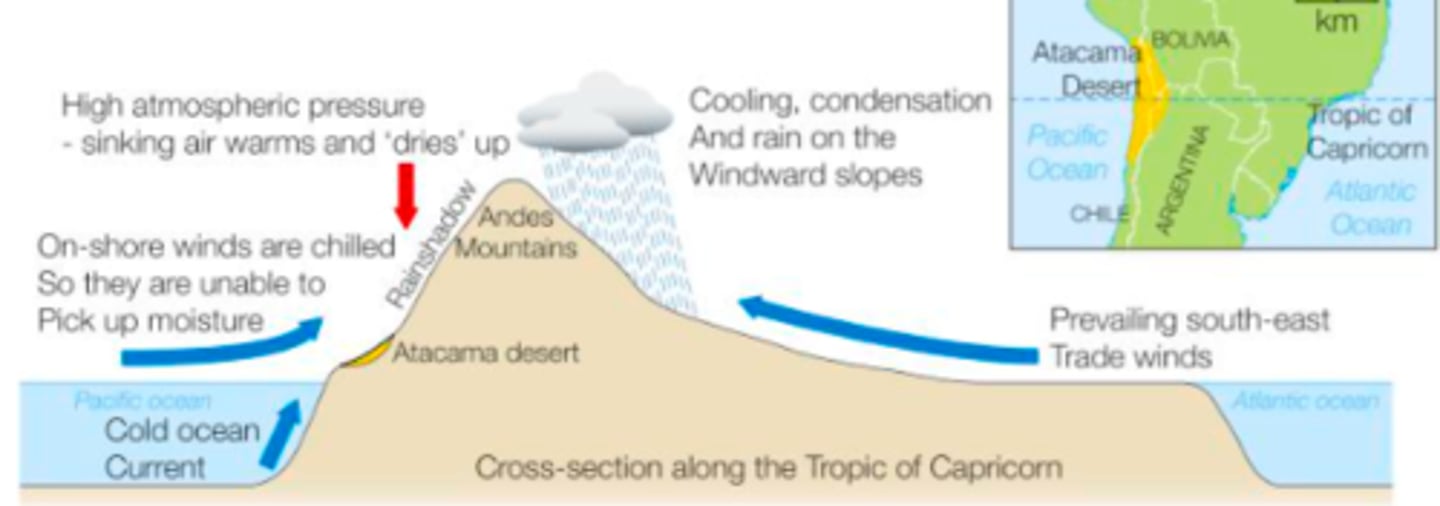
Causes of Aridity in the Atacama - Relief and rainshadow effect
- Due to the Relief created by the Andes Mountains, prevailing south east trade winds cool and condense into rain
- rainshadow effect takes place on the Leeward side (western), where the Atacama desert is located
- An area of high pressure, so descending air warms and dries up
- On shore winds, are chilled so unable to pick up any moisture
- Therefore the Atacama desert has little precipitation and is extremely arid
Causes of Aridity in the Atacama - Cold ocean currents
Atacama is located by the cold Peru currents → deserts often exist near cold ocean currents where there is a cold surface, cold air above, lack of evaporation, all factors of dry conditions
Causes of Aridity in the Atacama - Offshore winds
- The Atacama experiences prevailing south-east trade winds which blow across the large continental expanse of north Africa
- These winds carry little moisture by the time they reach the Atacama region
Landforms in the Atacama
- Playas/salt lakes
- Alluvial fans
- Yardangs
- Dunes
Landforms in the Atacama - Playas/salt lakes
Most of the Atacama Desert's core is caked in thick salt deposits called playas which can stretch for miles and nearly half a metre thick in some places (explain how they are formed)
Landforms in the Atacama - Alluvial fans
- Connects the desert plateau with the mountains that surround it and suggest that water once flowed from the Andes into the desert
→ formed by sediment washing out through a wadi or a canyon to form a delta like alluvial fan
→ river water spreads from mountain front and when energy is lost, sediment deposited rapidly
Landforms in the Atacama - Yardangs
- Yardangs are sufficiently huge to be noticeable on satellite symbolism
→ formed when ridges of soft and hard rock with vertical joints run parallel to the direction of the prevailing wind
→ wind erodes the softer rock and leaves the ridges standing up as yardangs
→ can become slightly rounded due to abrasion eroding the outer edge
Landforms in the Atacama - Dunes
Barchan and seif dunes (talk about prevailing wind direction x and y)