HUBS Module 3 - Nerve and muscle
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
1
New cards
Explain integration and coordination in nervous system
Integration is sensing environment and coordination is responding to it. E.g. integration is feeling the pain of stepping on something sharp and coordination is responding to it by moving your foot
2
New cards
What are the two parts of the nervous system
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
3
New cards
What does the CNS consist of
Brain and spinal cord (made of neurons and glia)
4
New cards
What does PNS consist of
Peripheral nerves and ganglia (made of neurons and glia)
5
New cards
What are two features of neurons
1. Cells specialised for transmission of information
2. Four morphological types
6
New cards
What is the basic function of glial cells
Support for neurons
7
New cards
Two features of dendrites
Recieve input
Send info to cell body
Send info to cell body
8
New cards
Two features of neuron cell body
Contains nucleus and organelles
Sums input
Sums input
9
New cards
Two features of axon
Carries electrical impulses
May or may not be myelinated
May or may not be myelinated
10
New cards
Two features of axon terminals
End of the axon
Neurotransmitter release
Neurotransmitter release
11
New cards
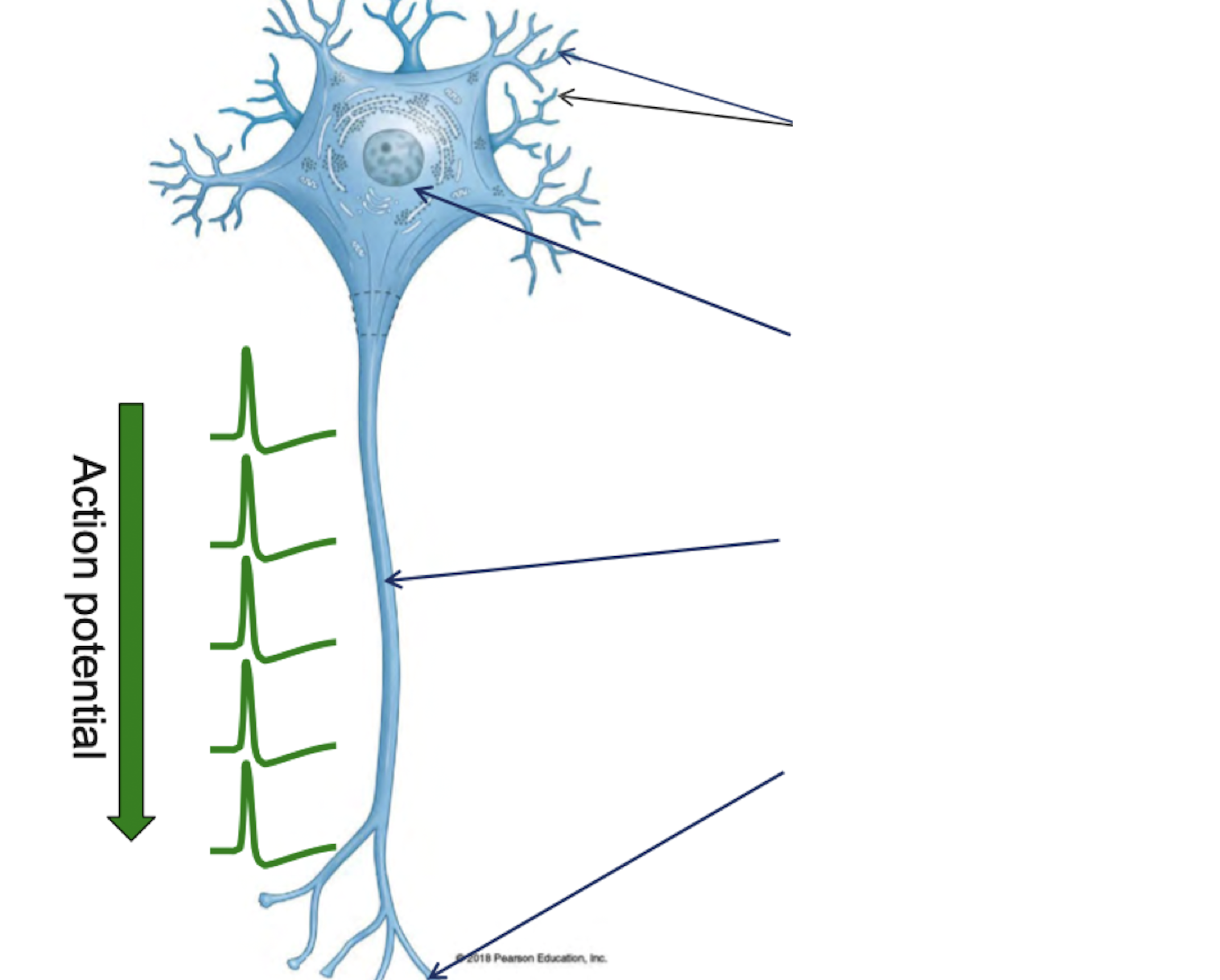
Label
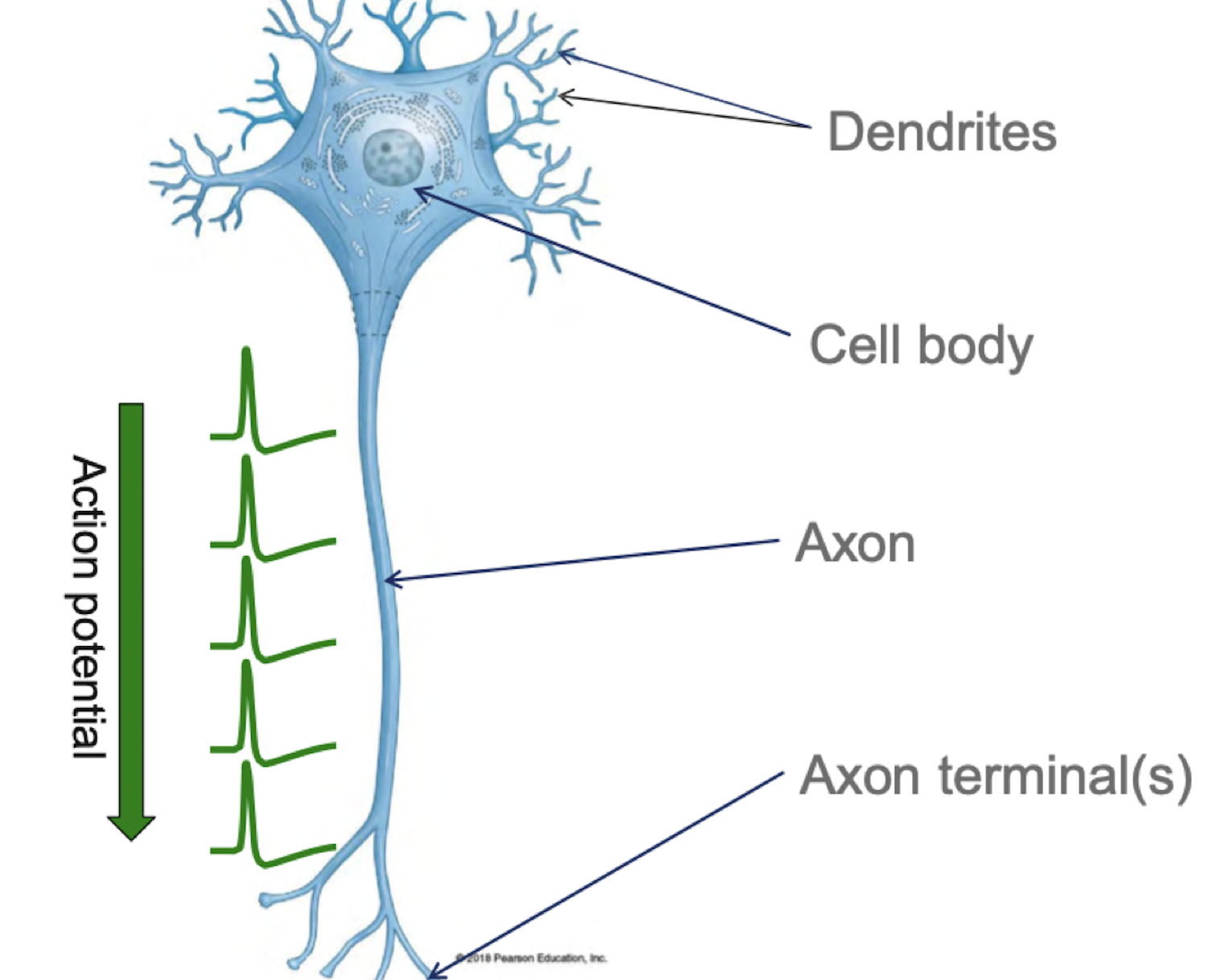
12
New cards
What is nucleus (nervous system)
Group of cell bodies in the CNS
13
New cards
What is a tract (nervous system)
Bundle of axons in the CNS
14
New cards
What is grey matter (nervous system)
Group of cell bodies in cerebral cortex or spinal cord in the CNS
15
New cards
What is white matter (nervous system)
Bundle of axons in cerebral cortex or spinal cord in the CNS
16
New cards
What is a ganglion (nervous system)
Group of cell bodies in the PNS
17
New cards
What is a nerve (nervous system)
Bundle of axons in the PNS
18
New cards
Input zone in neuron (structure and function)
Dendrites and cell body
It recieves CHEMICAL signals from other neurons
It recieves CHEMICAL signals from other neurons
19
New cards
Summation zone in neuron (structure and function)
Axon hillock
It summates inputs
It summates inputs
20
New cards
Conduction zone in neuron (structure and function)
Axon
Carries ELECTRICAL signals between brain areas, to and from spinal cord, or from peripheral sensory receptors to effector cells
Carries ELECTRICAL signals between brain areas, to and from spinal cord, or from peripheral sensory receptors to effector cells
21
New cards
Output zone in neuron (structure and function)
Axon terminals
Contact with input zone of other neurons or effectors
Release of neurotransmitter (chemical signal)
Contact with input zone of other neurons or effectors
Release of neurotransmitter (chemical signal)
22
New cards
Four morphological types of neurons
Multipolar
Bipolar
Unipolar
Anaxonic
Bipolar
Unipolar
Anaxonic
23
New cards
Multipolar neurons
Multiple processes emanate from the cell body
24
New cards
Bipolar neurons
Two processes emanate from the cell body
25
New cards
Unipolar neurons
One process emanates from the cell body, then branches into dendrite and axon
26
New cards
Anaxonic neurons
No distinct axon, all processes look alike
27
New cards
Five basic types of glia
Astrocytes (CNS)
Microglia (CNS)
Ependymal cells (CNS)
Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
Schwann cells (PNS)
Microglia (CNS)
Ependymal cells (CNS)
Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
Schwann cells (PNS)
28
New cards
Astrocytes functions
Supply nutrients to neurons
Ensheath blood capillaries
Injury response
Ensheath blood capillaries
Injury response
29
New cards
Microglia functions
Immune cells of the CNS
Engulf microorganisms and debris
Engulf microorganisms and debris
30
New cards
Ependymal cells functions
Line fluid filled spaces of brain and spinal cord
Have cilia to circulate CSF
Have cilia to circulate CSF
31
New cards
Oligodendrocytes functions
Support CNS nerve fibres
Ensheath them with myelin
Ensheath them with myelin
32
New cards
Schwann cells functions
Support PNS nerve fibres
Ensheath them with myelin
Ensheath them with myelin
33
New cards
Myelin and its function
Layer of lipid (fat) wrapped around an axon to increase conduction velocity
34
New cards
What are nodes of ranvier
Gaps between the myelin on axons to further increase conduction velocity
35
New cards
What is a synapse
A junction between neurons that communication occurs through
36
New cards
Pre-synaptic neuron
Neuron before synapse
37
New cards
Post-synaptic neuron
Neuron after synapse
38
New cards
\
\
39
New cards
Afferent definition
Information that goes into the brain
40
New cards
Efferent definition
Response that comes out of the brain
41
New cards
What is somatic in the nervous system
The stuff we are aware of and have control over
42
New cards
What is autonomic
The stuff we are not aware of and have no control over
43
New cards
What is somatic efferent
Voluntary muscle control
44
New cards
What is somatic afferent
Sensory information we are aware of
45
New cards
What is autonomic efferent
Involuntary muscle control
46
New cards
What is autonomic afferent
Sensory information we don’t know about
47
New cards
What is an effector
The part of the body that responds to a signal from the nervous system
48
New cards
How many neurons are between the brain and effector in somatic efferent division
Two
49
New cards
Which neurons in the somatic efferent division are myelinated
Both upper and lower motor neurons are myelinated in sometic efferent division
50
New cards
What neurotransmitter is used in somatic efferent division
Acetylcholine (Ach)
51
New cards
\
\
52
New cards
What are the effectors in the somatic efferent division
Skeletal muscle
53
New cards
Is the somatic efferent division under voluntary or involuntary control
Voluntary control
54
New cards
Is the autonomic efferent division under voluntary or involuntary control
Involuntary control
55
New cards
Two divisions of autonomic efferent division
Sympathetic and parasympathetic
56
New cards
Autonomic efferent effectors
Smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands, fat tissue
57
New cards
What are preganglionic neurons
* Neurons located in the CNS (brainstem or spinal cord)
* Part of autonomic efferent division
* Extend their axons to the autonomic ganglia
* Neuron #2 in autonomic efferent division
* Part of autonomic efferent division
* Extend their axons to the autonomic ganglia
* Neuron #2 in autonomic efferent division
58
New cards
What are postganglionic neurons
* Located in autonomic ganglia (PNS)
* Part of autonomic efferent division
* Extend their axons to the effectors
* Neuron #3 in autonomic efferent division
* Part of autonomic efferent division
* Extend their axons to the effectors
* Neuron #3 in autonomic efferent division
59
New cards
What are autonomic ganglia
* An area of a cluster of nerve cell bodies located outside the CNS and their activiation leads to either the sympathetic or parasympathetic response in target tissues
60
New cards
Which neurons in the autonomic efferent division are myelinated
Neuron #2 is myelinated and neuron #3 is unmyelinated
61
New cards
Which neurotransmitter does neuron #2 of the autonomic efferent division use
Acetylcholine
62
New cards
Which neurotransmitter does neuron #3 of the autonomic efferent division use
* Acetylcholine for parasympathetic
* Norephinephrine for sympathetic
* Norephinephrine for sympathetic
63
New cards
Characteristics and effects of sympathetic nervous system
* Prepares the body for stress responses
* Fight or flight system
* Effects:
* increased heart rate
* increased blood flow to muscles, decreased blood flow to skin
* decreased gastric motility
* decreased salivation
* increased pupil size
* increased sweating
* Fight or flight system
* Effects:
* increased heart rate
* increased blood flow to muscles, decreased blood flow to skin
* decreased gastric motility
* decreased salivation
* increased pupil size
* increased sweating
64
New cards
Characteristics and effects of parasympathetic nervous system
* Prepares the body for restful situations
* Rest and digest sytem
* Effects:
* decreased heart rate
* increased gastric motility
* increased salivation
* decreased pupil size
* Rest and digest sytem
* Effects:
* decreased heart rate
* increased gastric motility
* increased salivation
* decreased pupil size
65
New cards
Structural differences between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system:
* Neruon 2 has a short axon
* Neuron 3 has a long axon
* Sympathetic ganglion close to CNS
Parasympathetic nervous system:
* Neruon 2 has a long axon
* Neuron 3 has a short axon
* Parasympathetic ganglion far from CNS
* Neruon 2 has a short axon
* Neuron 3 has a long axon
* Sympathetic ganglion close to CNS
Parasympathetic nervous system:
* Neruon 2 has a long axon
* Neuron 3 has a short axon
* Parasympathetic ganglion far from CNS
66
New cards
What is sympathetic chain ganglia
A type of autonomic ganglia that are related to the sympathetic nervous system that are located on either side of the spinal column
\
For the sympathetic nervous system, neuron #2 (preganglionic) synapses onto neuron #3 (postganglionic) in the sympathetic chain ganglia
\
For the sympathetic nervous system, neuron #2 (preganglionic) synapses onto neuron #3 (postganglionic) in the sympathetic chain ganglia
67
New cards
Basic process of chemically ion gated channels
The chemical (in this case the neurotransmitter eg ACh) binds to a site on the channel, opening the channel and allowing ions to to cross the membrane, driven by the gradient.
68
New cards
Basic process of voltage gated ion channels
They are opened by a change in voltage, then go into an inactivated state so cannot open again until the membrane has been repolarised
69
New cards
Basic process of mechanically gated ion channels
Channels are gated in response to physical touch/mechanical pressure
70
New cards
What ion channels are on the dendrites of neurons
Chemically gated
71
New cards
What ion channels are on the axons of neurons
Voltage gated Na+ channels, voltage gated K+ channels, and voltage gated Ca2+ channels
72
New cards
\
\
73
New cards
Types of ion channels
Chemically gated, voltage gated, mechanically gated
74
New cards
What ion channels are in dendrites and cell body
Chemically gated
75
New cards
\
\
76
New cards
What ion channels are in axon terminals
Voltage gated Ca2+
77
New cards
What is presynaptic nerve terminal
The part of the axon terminal that forms a synapse with a target cell
78
New cards
What is a synaptic cleft
The small gap between the presynaptic and post synaptic neurons where a synapse occurs
79
New cards
What are synaptic vesicles
Vesicles made of membrane that are filled with a chemicall signalling substance specific to the type of nerve terminal they are in. They live in the presynaptic nerve terminal
80
New cards
Explain the process of a synapse
* A wave of depolarisation from the action potential along the axon reaches the terminal
* The inside of the terminal becomes positive relative to the outside
* The change in voltage activates the Ca2+ ion channelsm causing Ca2+ ions to enter the axon terminal, further increasing the positivity of the terminal
* This triggers the synaptic vesicles containing the neurotransmitter (e.g. ACh) to leave through exocytosis
* The neurotransmitter binds to the chemically gated Na+ channels, causing sodium ions to enter the postsynaptic neuron, causing a graded depolarisation
* If the depolarisation is big enough it will trigger an action potential if the threshold is reached
* The neurotransmitter is then broken down, (e.g. ACh is broken down into acetate (A) and choline (Ch) by AChE (acetylcholinesterase))
* The axon terminal reabsorbs the broken down neurotransmitter to recycle it and synthesise new molecules of ti (e.g. Ch is reabsorbed to make more ACh)
* The inside of the terminal becomes positive relative to the outside
* The change in voltage activates the Ca2+ ion channelsm causing Ca2+ ions to enter the axon terminal, further increasing the positivity of the terminal
* This triggers the synaptic vesicles containing the neurotransmitter (e.g. ACh) to leave through exocytosis
* The neurotransmitter binds to the chemically gated Na+ channels, causing sodium ions to enter the postsynaptic neuron, causing a graded depolarisation
* If the depolarisation is big enough it will trigger an action potential if the threshold is reached
* The neurotransmitter is then broken down, (e.g. ACh is broken down into acetate (A) and choline (Ch) by AChE (acetylcholinesterase))
* The axon terminal reabsorbs the broken down neurotransmitter to recycle it and synthesise new molecules of ti (e.g. Ch is reabsorbed to make more ACh)
81
New cards
What are electrical synapses
A special type of synapse where the pre and post synaptic neuron are joined by a gap junction. Depolarisation can pass straight through this junction, meaning there is no opportunity for signal modulation which is why this type of synapse is rare
82
New cards
Nerve to nerve synapse information
* Synapses are tiny and there are thousands of them at each cell
* An AP in an individual neuron will rarely bring the next one to threshold
* Inputs may be exitatory or inhibitory and many neurotransmitters are used
* An AP in an individual neuron will rarely bring the next one to threshold
* Inputs may be exitatory or inhibitory and many neurotransmitters are used
83
New cards
Nerve to skeletal muscle synapse information
* Synapses are huge, each muscle fibre recieves input from only one neuron at one site
* An AP in a neuron is very likely to bring a muscle cell to threshold
* There are only excitatory inputs and only ACh is used as a neurotransmitter
* An AP in a neuron is very likely to bring a muscle cell to threshold
* There are only excitatory inputs and only ACh is used as a neurotransmitter
84
New cards
What are local potentials
A localised change in voltage across the membrane of a cell which can lead to an action potential
85
New cards
What are inhibitory potentials
Make the membrane potential more negative (K+ ions exit)
86
New cards
What are excitatory potentials
Make the membrane potential more positive (Na+ ions enter)
87
New cards
How do local potentials turn into action potentials
Local potentials are graded (meaning the magnitude of the voltage is related to the strength of the stimulus), local potentials also undergo spacial and temporal summation (meaning the local potentials are summed over time and space). If the net voltage change of the summed local potentials exceeds the threshold an action potential will be generated
88
New cards
What is the usual threshold voltage for an AP
10mV
89
New cards
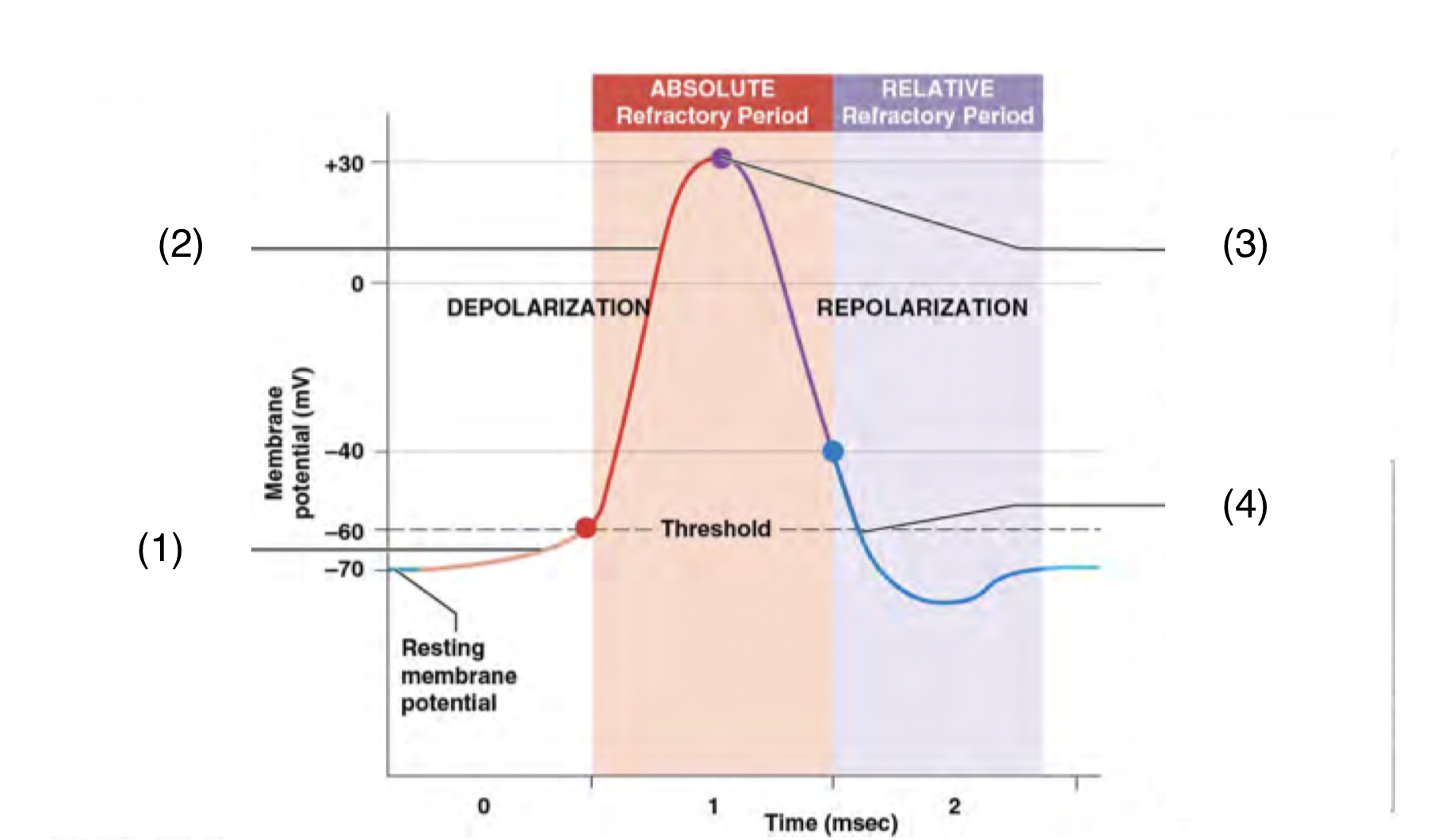
What happens at each number
(1) A graded depolarisation brings an area of excitable membrane to threshold
\
(2) Voltage gated sodium channels open and sodium ions move into the cell. The membrane potential rises to \~+30mV
\
(3) Sodium channels close, voltage gated potassium channels open, and potassium ions move out of the cell. Repolarisation begins
\
(4) The voltage gated potassium channels begin closing. Near threshold, the voltage gated sodium channels begin reactivating, and the membrane returns to its normal resting state
\
(2) Voltage gated sodium channels open and sodium ions move into the cell. The membrane potential rises to \~+30mV
\
(3) Sodium channels close, voltage gated potassium channels open, and potassium ions move out of the cell. Repolarisation begins
\
(4) The voltage gated potassium channels begin closing. Near threshold, the voltage gated sodium channels begin reactivating, and the membrane returns to its normal resting state
90
New cards
What is an absolute refractory period
A period of time during the action potential where no matter how large the stimulus, another AP cannot be generated
91
New cards
What is a relative refractory period
A period of time during the action potential where an AP can be generated but only in response to a very large stimulus
92
New cards
Why are there refractory periods
To prevent the AP propogating backwards
93
New cards
Explain how action potentials propogate along axons
* An action potential develops at the initial segment, the membrane depolarises to +30mV
* Graded depolarisation quickly brings the membrane in segment 2 to threshold
* An AP develops in segment 2, while the initial segment begins repolarisation and is in a refractory period
* Graded depolarisation quickly brings segment 3 to threshold, while segment 2 enters a refractory period
* Graded depolarisation quickly brings the membrane in segment 2 to threshold
* An AP develops in segment 2, while the initial segment begins repolarisation and is in a refractory period
* Graded depolarisation quickly brings segment 3 to threshold, while segment 2 enters a refractory period
94
New cards
Differences in propogation along myelinated vs unmyelinated axons
When APs are propogated along myelinated axons, the myelin acts as an insulator that the ions cant pass through so the AP ‘jumps’ from one node of ranvier to the next while in unmyelinated axons they have to travel the whole way down.
This results in myelinated axons have a much faster condunction speed than unmyelinated axons (120m/s compared to 1m/s)
This results in myelinated axons have a much faster condunction speed than unmyelinated axons (120m/s compared to 1m/s)
95
New cards
Where does the spinal cord start and finish, and where is it located
Starts at the foramen magnum
Ends at 1st lumbar vertebra L1
It is located in the spinal cavity within the vertebrae surrounded by a sac of meninges
Ends at 1st lumbar vertebra L1
It is located in the spinal cavity within the vertebrae surrounded by a sac of meninges
96
New cards
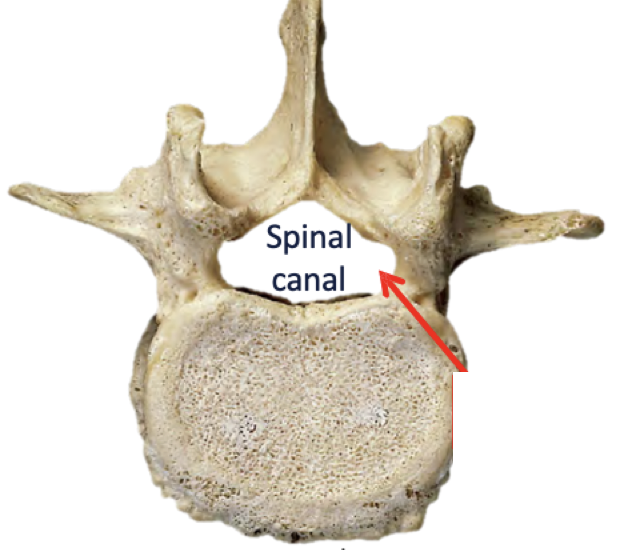
Which is the dorsal and which is the ventral side
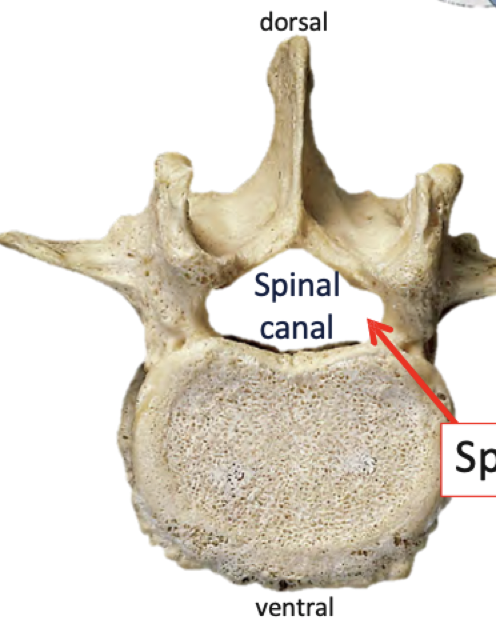
97
New cards
What is spinous process
The dorsal side of vertebrae
98
New cards
What is conus medularis
The end of the spinal cord that is made of non neural tissue and is the attachment point for filum terminale
99
New cards
What is filum terminale
Fibrous, non neural tissue that anchors the spinal cord from the conus medularis to the end of the spinal cavity
100
New cards
Segments of the spinal cord
31 in total
* 8 pairs of cervical spinal nerves
* 12 pairs of thoracic spinal nerves
* 5 pairs of lumbar spinal nerves
* 5 pairs of sacral spinal nerves
* 1 pair of coccygeal spinal nerves
* 8 pairs of cervical spinal nerves
* 12 pairs of thoracic spinal nerves
* 5 pairs of lumbar spinal nerves
* 5 pairs of sacral spinal nerves
* 1 pair of coccygeal spinal nerves