unit 3.1.3: communicable diseases (cont.)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/104
Earn XP
Last updated 3:27 PM on 4/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
1
New cards
Influenza
an enveloped virus and an RNA virus
2
New cards
spherical
## Influenza:
### Etiology
Shape of the Capsid
### Etiology
Shape of the Capsid
3
New cards
antigenic glycoprotein, neuraminidase, and hemagglutinin
## Influenza:
### Etiology
Genetic makeup of the Capsid
### Etiology
Genetic makeup of the Capsid
4
New cards
A
## Influenza:
### Etiology
**Least stable** with antigenic drift and antigenic shift of the **H and N antigens producing new strains** responsible for epidemics
### Etiology
**Least stable** with antigenic drift and antigenic shift of the **H and N antigens producing new strains** responsible for epidemics
5
New cards
Hemagglutinin (HA) and Neuraminidase (NA)
# Influenza:
## Etiology
### Subtype A
Classified into **subtypes** based on combinations of ___
## Etiology
### Subtype A
Classified into **subtypes** based on combinations of ___
6
New cards
A(H1N1) and A(H3N2)
# Influenza:
## Etiology
### Subtype A
Currently circulating in humans
## Etiology
### Subtype A
Currently circulating in humans
7
New cards
Type
# Influenza:
## Etiology
### Subtype A
__**A**__/Beijing/262/95
## Etiology
### Subtype A
__**A**__/Beijing/262/95
8
New cards
Site of isolation
# Influenza:
## Etiology
### Subtype A
A/__**Beijing**__/262/95
## Etiology
### Subtype A
A/__**Beijing**__/262/95
9
New cards
Culture number
# Influenza:
## Etiology
### Subtype A
A/Beijing/__**262**__/95
## Etiology
### Subtype A
A/Beijing/__**262**__/95
10
New cards
Year
# Influenza:
## Etiology
### Subtype A
A/Beijing/262/__**95**__
## Etiology
### Subtype A
A/Beijing/262/__**95**__
11
New cards
**B:** B/Yamagata and B/Victoria
## Influenza:
### Etiology
broken down into **lineages**
### Etiology
broken down into **lineages**
12
New cards
C
## Influenza:
### Etiology
Most stable, Low pathogenicity (subclinical infection)
### Etiology
Most stable, Low pathogenicity (subclinical infection)
13
New cards
Antigenic **Drift**
## Influenza:
### Etiology
mutation in the genes of the Influenza virus and would lead to __**changes**__ **in the surface antigens**
### Etiology
mutation in the genes of the Influenza virus and would lead to __**changes**__ **in the surface antigens**
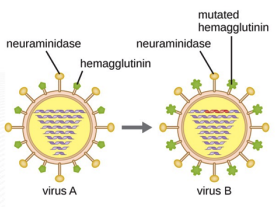
14
New cards
Antigenic **Shift**
## Influenza:
### Etiology
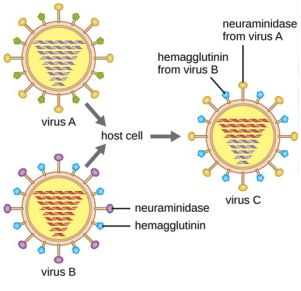
* from the **strains of** **two or more different viruses and they combine** to form another subtype
* newly formed subtype will have a __**mixture**__ **of different surface antigens or the antigenic glycoproteins**
### Etiology
* from the **strains of** **two or more different viruses and they combine** to form another subtype
* newly formed subtype will have a __**mixture**__ **of different surface antigens or the antigenic glycoproteins**
15
New cards
lasts about 5 days
## Influenza:
### Symptoms
Uncomplicated illness
### Symptoms
Uncomplicated illness
16
New cards
*Pneumonia sequelae*
## Influenza:
### Symptoms
main cause of mortality especially in high risk individuals
### Symptoms
main cause of mortality especially in high risk individuals
17
New cards
* Respiratory droplets
* Direct contact
* Highly infectious
* Direct contact
* Highly infectious
## Influenza:
### Epidemiology
Transmission
### Epidemiology
Transmission
18
New cards
1 to 5 days
## Influenza:
### Epidemiology
Incubation Period
### Epidemiology
Incubation Period
19
New cards
2 days before onset of symptoms to 5 days after
## Influenza:
### Epidemiology
Period of Communicability
### Epidemiology
Period of Communicability
20
New cards
**A(H1N1) Swine Flu** (2010)
## Influenza:
### Epidemiology
Occurrence & Distribution
* originated in **Mexico** in 2009
### Epidemiology
Occurrence & Distribution
* originated in **Mexico** in 2009
21
New cards
**1918 Spanish Flu:** Influenza A
## Influenza:
### Epidemiology
Occurrence & Distribution
* responsible for pandemics and regular seasonal outbreaks
### Epidemiology
Occurrence & Distribution
* responsible for pandemics and regular seasonal outbreaks
22
New cards
rainy seasons
## Influenza:
### Epidemiology
Occurrence & Distribution
* In Tropics
### Epidemiology
Occurrence & Distribution
* In Tropics
23
New cards
winter months
## Influenza:
### Epidemiology
Occurrence & Distribution
* In Temperate Climates
### Epidemiology
Occurrence & Distribution
* In Temperate Climates
24
New cards
PCR (RT-PCR)
## Influenza:
### Diagnosis
method of choice
### Diagnosis
method of choice
25
New cards
Antiviral Agents
## Influenza:
### Treatment
formulated through the **use of the causative agent of the virus**; the genetic makeup of the virus will be **fragmented** and part of the virus will be tested to create an agent to combat the virus
### Treatment
formulated through the **use of the causative agent of the virus**; the genetic makeup of the virus will be **fragmented** and part of the virus will be tested to create an agent to combat the virus
26
New cards
Vaccination
## Influenza:
### Prevention & Control
most effective way to prevent disease
### Prevention & Control
most effective way to prevent disease
27
New cards
WHO **Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System** (GISRS)
## Influenza:
### Prevention & Control
continuously monitors influenza viruses in humans and updates composition of influenza vaccines **twice a year**
### Prevention & Control
continuously monitors influenza viruses in humans and updates composition of influenza vaccines **twice a year**
28
New cards
Personal Protective Measures
## Influenza:
### Prevention & Control
* Regular hand washing
* Good respiratory hygiene
* Early self-isolation
* Avoiding close contact
* Avoiding touching one’s eyes, nose, or mouth
### Prevention & Control
* Regular hand washing
* Good respiratory hygiene
* Early self-isolation
* Avoiding close contact
* Avoiding touching one’s eyes, nose, or mouth
29
New cards
Coronavirus (COVID-19)
causes **respiratory infections** and it spreads from one person to the other through droplets
30
New cards
SARS-CoV
### COVID-19
2003
2003
31
New cards
MERS-CoV
### COVID-19
2012
2012
32
New cards
SARS-CoV-2
### COVID-19
2019
2019
33
New cards
solar corona
## COVID-19:
### Etiology
widely-spaced projections or spikes on the outer surface of the envelope
### Etiology
widely-spaced projections or spikes on the outer surface of the envelope
34
New cards
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome
## COVID-19:
### Etiology
SARS-CoV (2003)
### Etiology
SARS-CoV (2003)
35
New cards
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome
## COVID-19:
### Etiology
MERS-CoV (2012)
### Etiology
MERS-CoV (2012)
36
New cards
**Coronavirus Disease 2019**: Severe Acute Respiratory
Syndrome Coronavirus 2
Syndrome Coronavirus 2
## COVID-19:
### Etiology
COVID-19 Virus
### Etiology
COVID-19 Virus
37
New cards
**bats**: amplified in palm civets
## COVID-19:
### Etiology: Origin
SARS-CoV (2003)
### Etiology: Origin
SARS-CoV (2003)
38
New cards
bats: widespread in **camels**
## COVID-19:
### Etiology: Origin
MERS-CoV (2012)
### Etiology: Origin
MERS-CoV (2012)
39
New cards
bat to a **pangolin**
## COVID-19:
### Etiology: Origin
COVID-19 Virus
### Etiology: Origin
COVID-19 Virus
40
New cards
* Respiratory symptoms
* Fever
* Malaise
* Chills
* Headache
* Dry cough
* Fever
* Malaise
* Chills
* Headache
* Dry cough
## COVID-19:
### Symptoms
Early Symptoms
### Symptoms
Early Symptoms
41
New cards
acute respiratory distress, requiring ventilatory support
## COVID-19:
### Symptoms
abnormal chest radiographs
### Symptoms
abnormal chest radiographs
42
New cards
* Pneumonia
* Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome
* Kidney Failure
* Death
* Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome
* Kidney Failure
* Death
## COVID-19:
### Symptoms
Severe Cases
### Symptoms
Severe Cases
43
New cards
Coronavirus-associated Enteritis
## COVID-19:
### Symptoms
have not been clearly described
### Symptoms
have not been clearly described
44
New cards
Basic Reproduction Number of Diseases
## COVID-19:
### Epidemiology
basic measure to **track the infectiousness** of the disease
### Epidemiology
basic measure to **track the infectiousness** of the disease
45
New cards
PCR (RT-PCR): preferred
## COVID-19:
### Diagnosis
Nucleic Acid Detection
### Diagnosis
Nucleic Acid Detection
46
New cards
Serodiagnosis
## COVID-19:
### Diagnosis
Serology
* acute and convalescent sera is one means of confirming
### Diagnosis
Serology
* acute and convalescent sera is one means of confirming
47
New cards
serum
## COVID-19:
### Diagnosis
Serology
* ELISA specimen
### Diagnosis
Serology
* ELISA specimen
48
New cards
Shepherd’s crook morphology
## Ebola:
### Etiology
”U” or “6” shape
### Etiology
”U” or “6” shape
49
New cards
Reston virus
## Ebola:
### Etiology
cause disease in **primates**
### Etiology
cause disease in **primates**
50
New cards
Filovirus
## Ebola:
### Etiology
highly virulent and require maximum containment facilities for laboratory work
### Etiology
highly virulent and require maximum containment facilities for laboratory work
51
New cards
bats (fruit bats)
## Ebola:
### Etiology
Natural/Reservoir Hosts
### Etiology
Natural/Reservoir Hosts
52
New cards
Filovirus
## Ebola:
### Symptoms
appear to be **immunosuppressive**
### Symptoms
appear to be **immunosuppressive**
53
New cards
* Direct contact
* Contaminated needle and syringes
* **saliva** and through large **droplets**
* Contaminated needle and syringes
* **saliva** and through large **droplets**
## Ebola:
### Epidemiology
Transmission
### Epidemiology
Transmission
54
New cards
viral hemorrhagic fevers is 25-90%
## Ebola:
### Epidemiology
Mortality Rate
### Epidemiology
Mortality Rate
55
New cards
50%
## Ebola:
### Epidemiology
Fatality Rate
### Epidemiology
Fatality Rate
56
New cards
2013-2016 West African Outbreak
## Ebola:
### Epidemiology
Outbreaks
* Major ebola outbreak in Guinea
### Epidemiology
Outbreaks
* Major ebola outbreak in Guinea
57
New cards
WHO **declared the epidemic** an international public health emergency
## Ebola:
### Epidemiology
Outbreaks
* 8 Aug 2014
### Epidemiology
Outbreaks
* 8 Aug 2014
58
New cards
Sudan Outbreak
## Ebola:
### Epidemiology
Outbreaks
* first known outbreak of EVD
### Epidemiology
Outbreaks
* first known outbreak of EVD
59
New cards
Zaire Outbreak
## Ebola:
### Epidemiology
Outbreaks
* second outbreak (Democratic Republic of the Congo)
### Epidemiology
Outbreaks
* second outbreak (Democratic Republic of the Congo)
60
New cards
village’s headmaster
## Ebola:
### Epidemiology
Outbreaks
* First person with the disease
### Epidemiology
Outbreaks
* First person with the disease
61
New cards
White blood & Oral fluid
## Ebola:
### Diagnosis
Specimen
### Diagnosis
Specimen
62
New cards
* Low white cell count
* Platelet count
* Elevated liver enzymes
* Platelet count
* Elevated liver enzymes
## Ebola:
### Diagnosis
Laboratory Findings
### Diagnosis
Laboratory Findings
63
New cards
Experimental Ebola Vaccine: rVSV-ZEBOV
## Ebola:
### Treatment
Not yet out in the market because it is still in the experimental process
### Treatment
Not yet out in the market because it is still in the experimental process
64
New cards
Mosquitos of ***Aedes*** **group**
### Dengue:
Vector
Vector
65
New cards
* *Aedes aegypti*
* *Aedes albopictus*
* *Aedes albopictus*
## Dengue:
### Vector
Species responsible for transmission and spread of Zika, Chikungunya
### Vector
Species responsible for transmission and spread of Zika, Chikungunya
66
New cards
*Aedes albopictus*
## Dengue:
### Vector
* it can withstand **cold temperatures**
* black color and with distinctive white markings
### Vector
* it can withstand **cold temperatures**
* black color and with distinctive white markings
67
New cards
stagnant water, old tires, empty tins or others that can collect water
## Dengue:
### Vector
breeding grounds for mosquitoes
### Vector
breeding grounds for mosquitoes
68
New cards
* Sudden-onset fever
* Headache
* Mouth and nose bleeding
* Muscle and joint pains
* Vomiting
* Rash
* Diarrhea
* Headache
* Mouth and nose bleeding
* Muscle and joint pains
* Vomiting
* Rash
* Diarrhea
## Dengue:
### Symptoms
Febrile Phase
### Symptoms
Febrile Phase
69
New cards
* Hypotension
* Pleural effusion
* Ascites
* Gastrointestinal bleeding
* Pleural effusion
* Ascites
* Gastrointestinal bleeding
## Dengue:
### Symptoms
Critical Phase
### Symptoms
Critical Phase
70
New cards
* Altered level of consciousness
* Seizures
* Itching
* Slow heart rate
* Seizures
* Itching
* Slow heart rate
## Dengue:
### Symptoms
Recovery Phase
### Symptoms
Recovery Phase
71
New cards
Herman’s Rash
## Dengue:
### Symptoms
* acute stage of the infection
* **blanches** when the back is pressed with the finger
* *“Classic island of white in a sea of red”*
* small red spots on the skin
* starts on the arms and legs and spreads to the rest of the body
### Symptoms
* acute stage of the infection
* **blanches** when the back is pressed with the finger
* *“Classic island of white in a sea of red”*
* small red spots on the skin
* starts on the arms and legs and spreads to the rest of the body
72
New cards
Zika
## Dengue:
### Symptoms
Mostly **mild** and people can recover without severe hospitalization
* Guillain-Barre syndrome
* Microcephaly
### Symptoms
Mostly **mild** and people can recover without severe hospitalization
* Guillain-Barre syndrome
* Microcephaly
73
New cards
Chikunguya
## Dengue:
### Symptoms
Severe joint pains
### Symptoms
Severe joint pains
74
New cards
increased **30-fold** over the last 50 years
## Dengue:
### Epidemiology
Incidence
### Epidemiology
Incidence
75
New cards
**~50 to 100 million** infections
## Dengue:
### Epidemiology
annually in >100 endemic countries
### Epidemiology
annually in >100 endemic countries
76
New cards
3\.9 billion
## Dengue:
### Epidemiology
at risk of infection with Dengue viruses
### Epidemiology
at risk of infection with Dengue viruses
77
New cards
ubiquitous
## Dengue:
### Epidemiology
appearing or found everywhere
### Epidemiology
appearing or found everywhere
78
New cards
**“Asian” Genotypes** of DENV-2 and DENV-3
## Dengue:
### Epidemiology
associated with severe disease accompanying secondary Dengue infections
### Epidemiology
associated with severe disease accompanying secondary Dengue infections
79
New cards
Severe Dengue
## Dengue:
### Epidemiology
first recognized in the Philippines and Thailand in the 1950s during Dengue epidemics
### Epidemiology
first recognized in the Philippines and Thailand in the 1950s during Dengue epidemics
80
New cards
**rainy season** (May-Nov)
\
# Dengue:
## Epidemiology
### Philippines
Peak Transmission
# Dengue:
## Epidemiology
### Philippines
Peak Transmission
81
New cards
0.55%
# Dengue:
## Epidemiology
### Philippines
Case Fatality Rate
## Epidemiology
### Philippines
Case Fatality Rate
82
New cards
Climate
## Dengue:
### Epidemiology
one **important driver** of the current distribution and incidence of Dengue
### Epidemiology
one **important driver** of the current distribution and incidence of Dengue
83
New cards
Temperature
## Dengue:
### Epidemiology
most important **predictor** of distribution
### Epidemiology
most important **predictor** of distribution
84
New cards
**high fever** (40°C or 104°F) and two accompanying symptoms
### Dengue:
Symptoms
Symptoms
85
New cards
Positive tourniquet test & Low white cell count
## Dengue:
### Diagnosis
### Diagnosis
86
New cards
PCR (RT-PCR)
## Dengue:
### Diagnosis
Nucleic Acid Detection
### Diagnosis
Nucleic Acid Detection
87
New cards
NS1 (nonstructural protein 1)
## Dengue:
### Diagnosis
Viral Antigen Detection
### Diagnosis
Viral Antigen Detection
88
New cards
ELISA
## Dengue:
### Diagnosis
Antibody Testing (Serological test)
### Diagnosis
Antibody Testing (Serological test)
89
New cards
**Breeding of fish**: Guppies
## Dengue:
### Vector Control
**Biologic Control**
* **eliminate** mosquitoes from larger containers used to store potable water
### Vector Control
**Biologic Control**
* **eliminate** mosquitoes from larger containers used to store potable water
90
New cards
Indoor Residual Spraying
## Dengue:
### Vector Control
**Chemical Control**
* Application of **long-acting chemical insecticides** on the walls and roofs
* short period of time
### Vector Control
**Chemical Control**
* Application of **long-acting chemical insecticides** on the walls and roofs
* short period of time
91
New cards
Space Sprays
## Dengue:
### Vector Control
**Chemical Control**
* Massive, rapid **destruction** of adult vector population
* **emergency situation**s to suppress an ongoing epidemic
* aircraft, vehicle, hand-held equipment
### Vector Control
**Chemical Control**
* Massive, rapid **destruction** of adult vector population
* **emergency situation**s to suppress an ongoing epidemic
* aircraft, vehicle, hand-held equipment
92
New cards
Environmental Modification
## Dengue:
### Vector Control
**Environmental Management**
* Improvement of water supply and water-storage systems
### Vector Control
**Environmental Management**
* Improvement of water supply and water-storage systems
93
New cards
Environmental Manipulation
## Dengue:
### Vector Control
**Environmental Management**
* Mosquito-proofing
### Vector Control
**Environmental Management**
* Mosquito-proofing
94
New cards
Changes to Human Habitation or Behavior
## Dengue:
### Vector Control
**Environmental Management**
* Mosquito screening & repellants
### Vector Control
**Environmental Management**
* Mosquito screening & repellants
95
New cards
> “Kung Walang Lamok, Walang Dengue”
## Dengue:
### Vector Control
Mag 4S Kontra Dengue by the DOH
### Vector Control
Mag 4S Kontra Dengue by the DOH
96
New cards
June 15, 2018
## Dengue:
### Vector Control
Asean Dengue Day
### Vector Control
Asean Dengue Day
97
New cards
**Dengvaxia®** (CYD-TDV)
### Immunization
Developed by Sanofi Pasteur
Developed by Sanofi Pasteur
98
New cards
**seropositive** individuals
### **Dengvaxia®:**
persons who have had a previous dengue virus infection -- **efficacious and safe**
persons who have had a previous dengue virus infection -- **efficacious and safe**
99
New cards
**seronegative** individuals
### **Dengvaxia®:**
first natural dengue infection after vaccination -- **increased risk of severe dengue**
first natural dengue infection after vaccination -- **increased risk of severe dengue**
100
New cards
*Wolbachia*
### Dengue:
* A natural bacteria present in up to **60% of insects**, including some of the mosquitoes, (the primary species responsible for transmitting the virus to humans) but **not usually found in aedes mosquitoes**
* Self-perpetuating intracellular bacteria with **disease blocking action**
* mosquito **resistant** to dengue virus
* A natural bacteria present in up to **60% of insects**, including some of the mosquitoes, (the primary species responsible for transmitting the virus to humans) but **not usually found in aedes mosquitoes**
* Self-perpetuating intracellular bacteria with **disease blocking action**
* mosquito **resistant** to dengue virus