Escherichia coli: Origins, Pathogenesis, and Epidemiology
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Theodore von Escherich
German pediatrician; described E. coli in 1884.
Bacterium coli commune
Original name for E. coli by Escherich.
Typhoid fever
Pathological disease caused by E. coli.
Taxonomy of Escherichia
Includes at least 8 species related to Shigella.
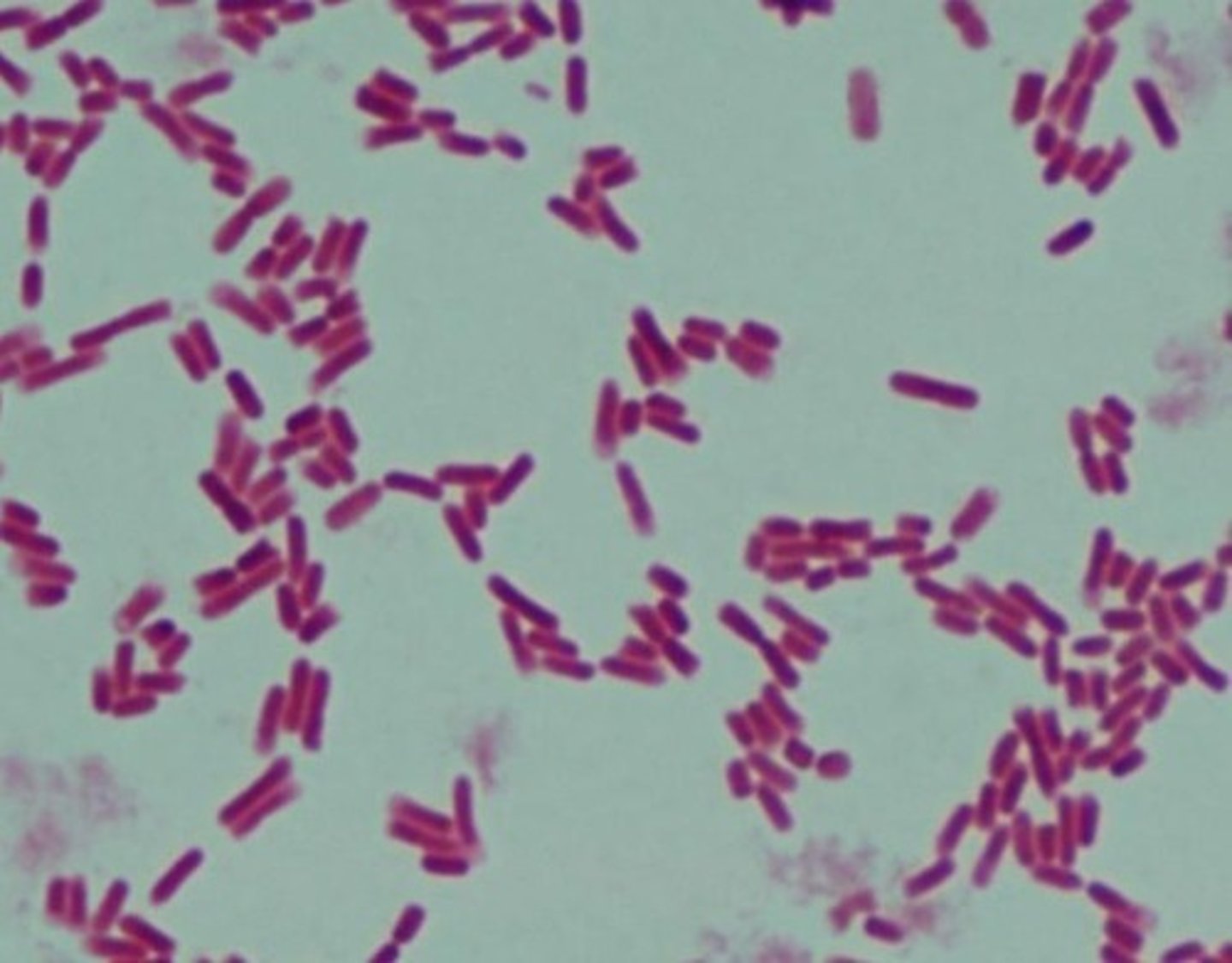
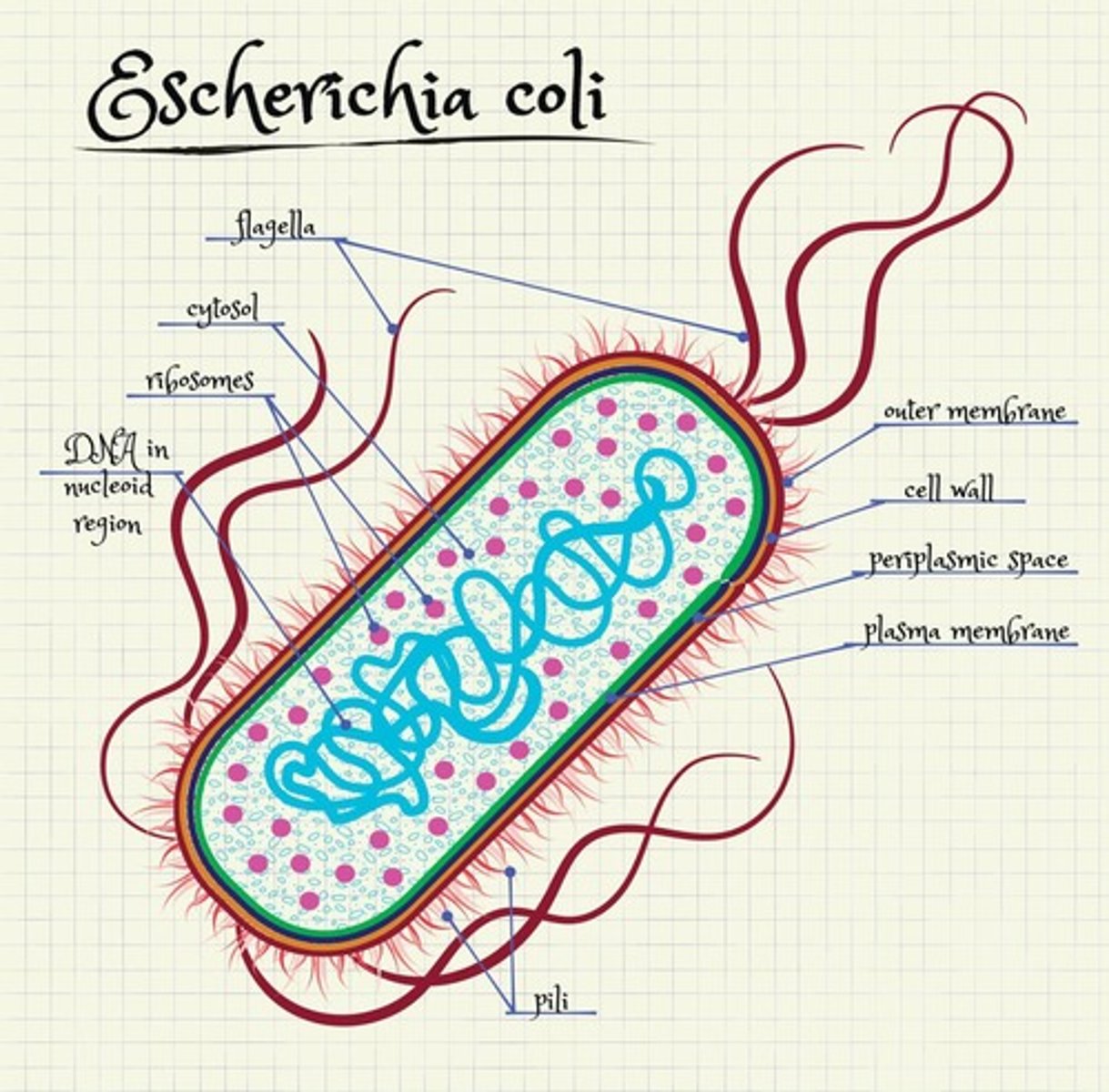
Morphology of E. coli
Bacilli shape; gram-negative; mostly motile.
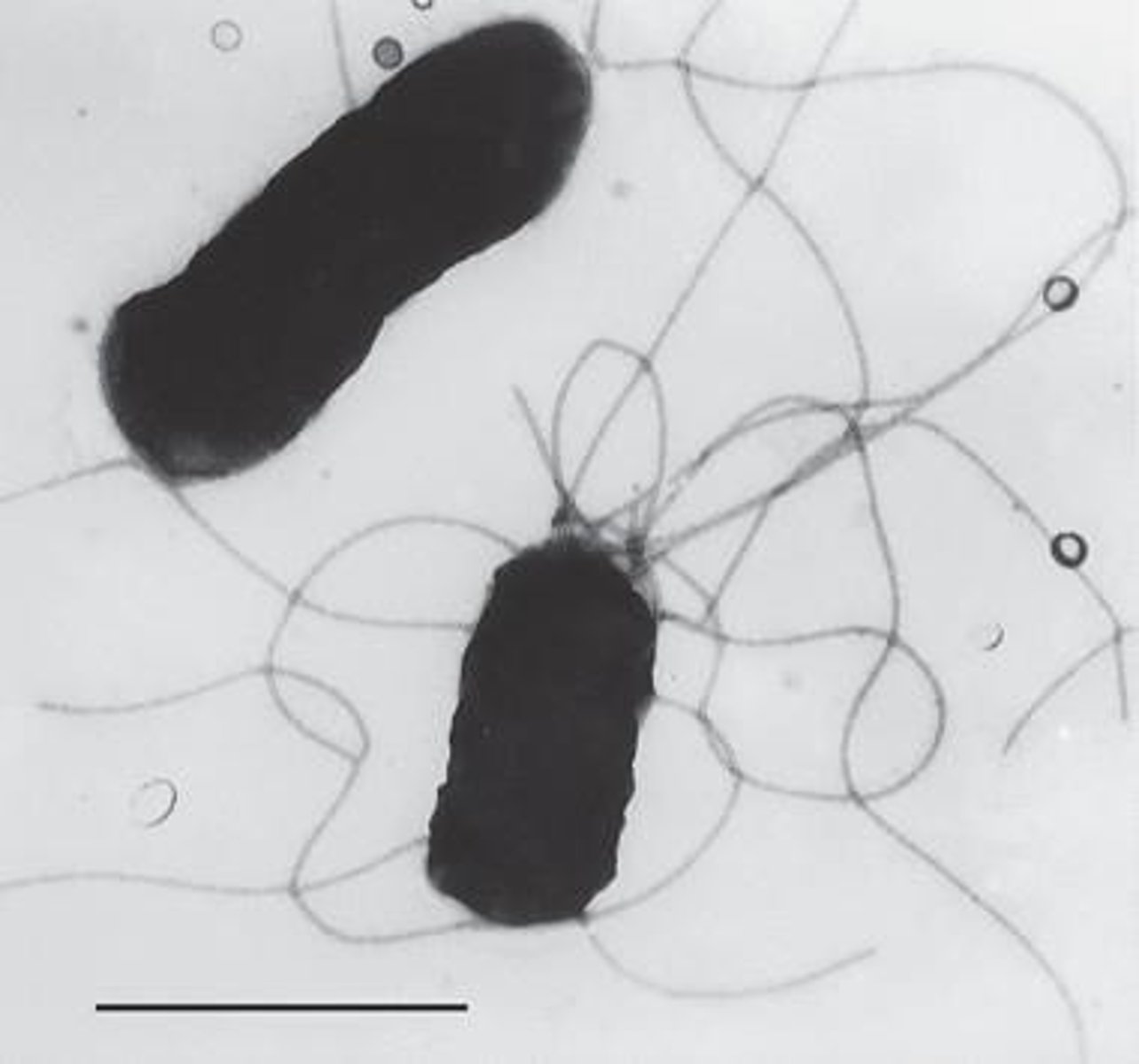
Peritrichous flagella
Flagella arrangement in E. coli for motility.
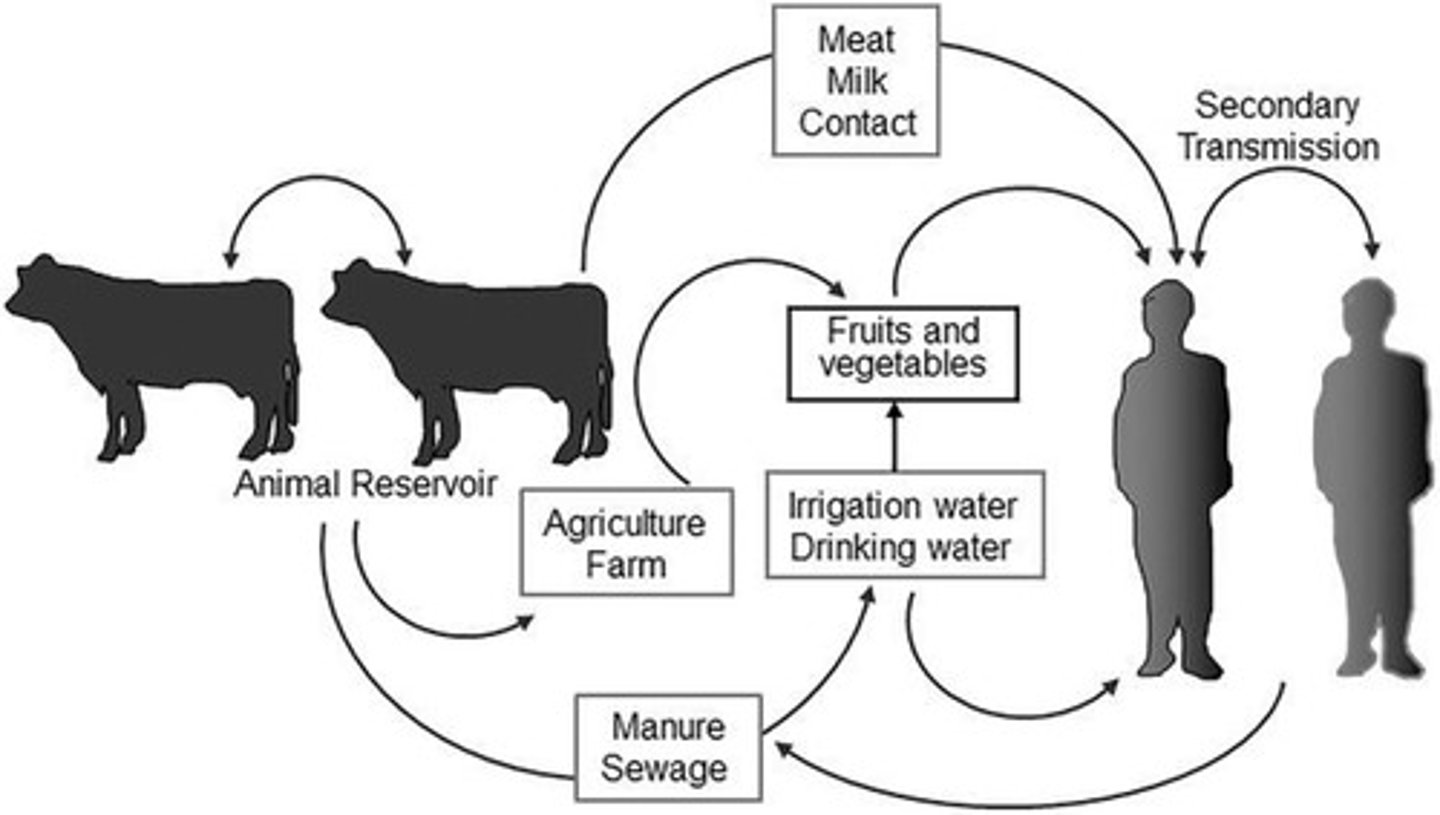
Epidemiology of E. coli
Responsible for 111 million gastroenteritis cases yearly.
Global UTI cases
E. coli causes 140 million UTIs annually.
Shigellosis
Accounts for 180-190 million cases yearly.
Reservoirs for E. coli
Found in ungulates, humans, and environment.
Human carriage rates
E. coli colonizes human intestines at 100%.
Zoonotic E. coli
Pathogenic strains acquired from animal reservoirs.
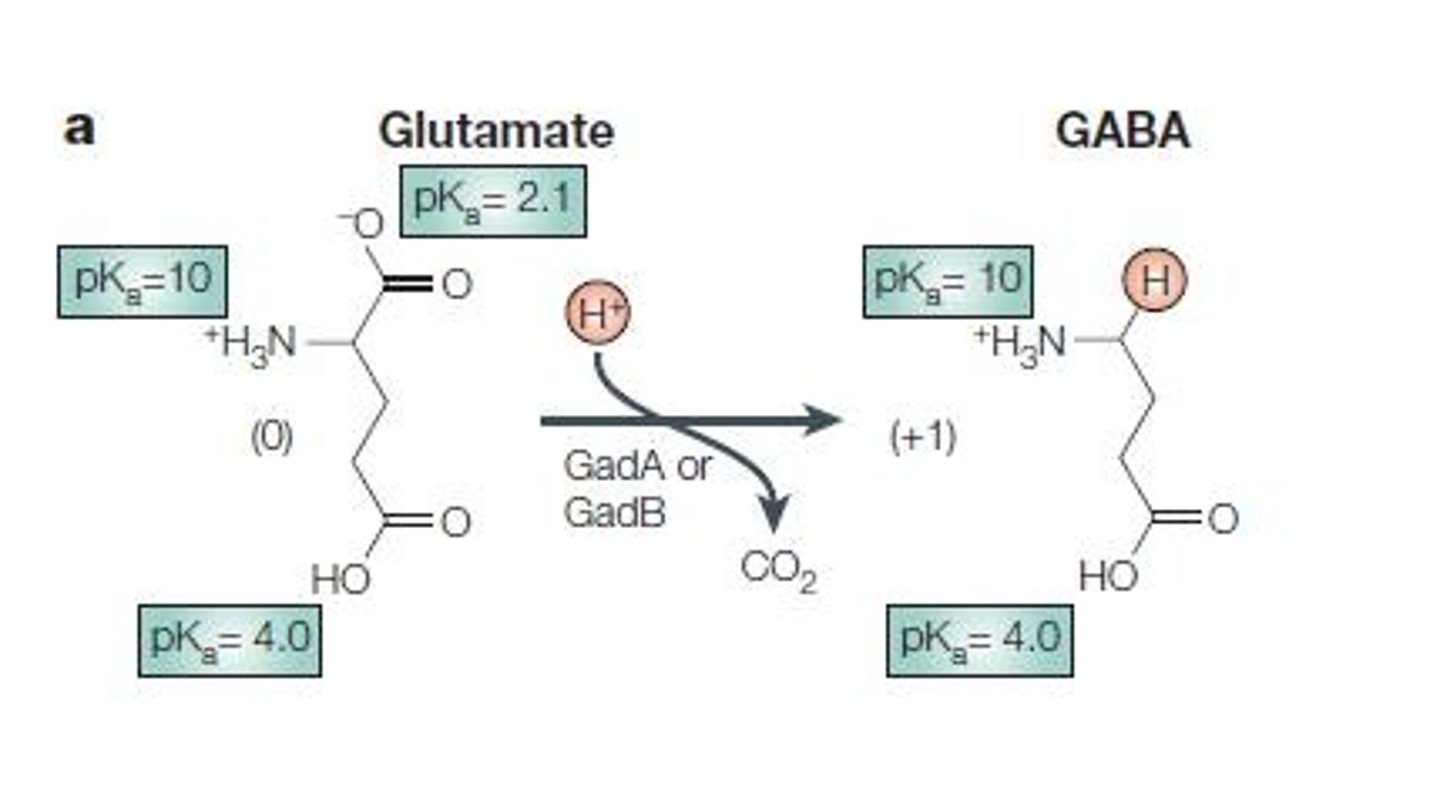
Acid tolerance
E. coli survives stomach acidity, pH 1-4.
Acid fitness island (AFI)
12 kb gene cassette for acid tolerance.
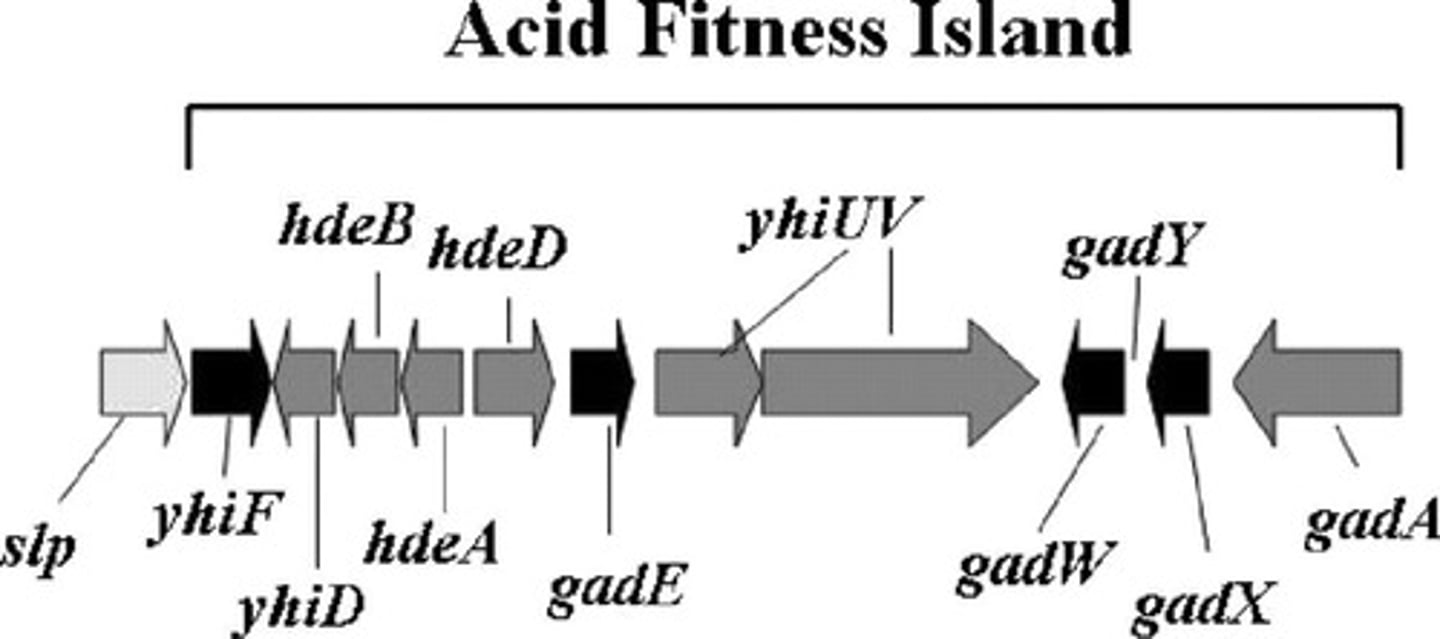
Gad system
Includes GadA, GadC, and GadE for acid tolerance.
ID50 of E. coli
Infectious dose is 10-100 CFU.
Adherence factors
E. coli uses fimbriae to colonize tissues.
Type I fimbriae
Colonizes oropharyngeal and intestinal tissues.
P-fimbriae
Binds receptors in urinary tract for colonization.
Uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC)
Responsible for 80% of community-acquired UTIs.
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
Emerging pathogen causing hemorrhagic colitis.
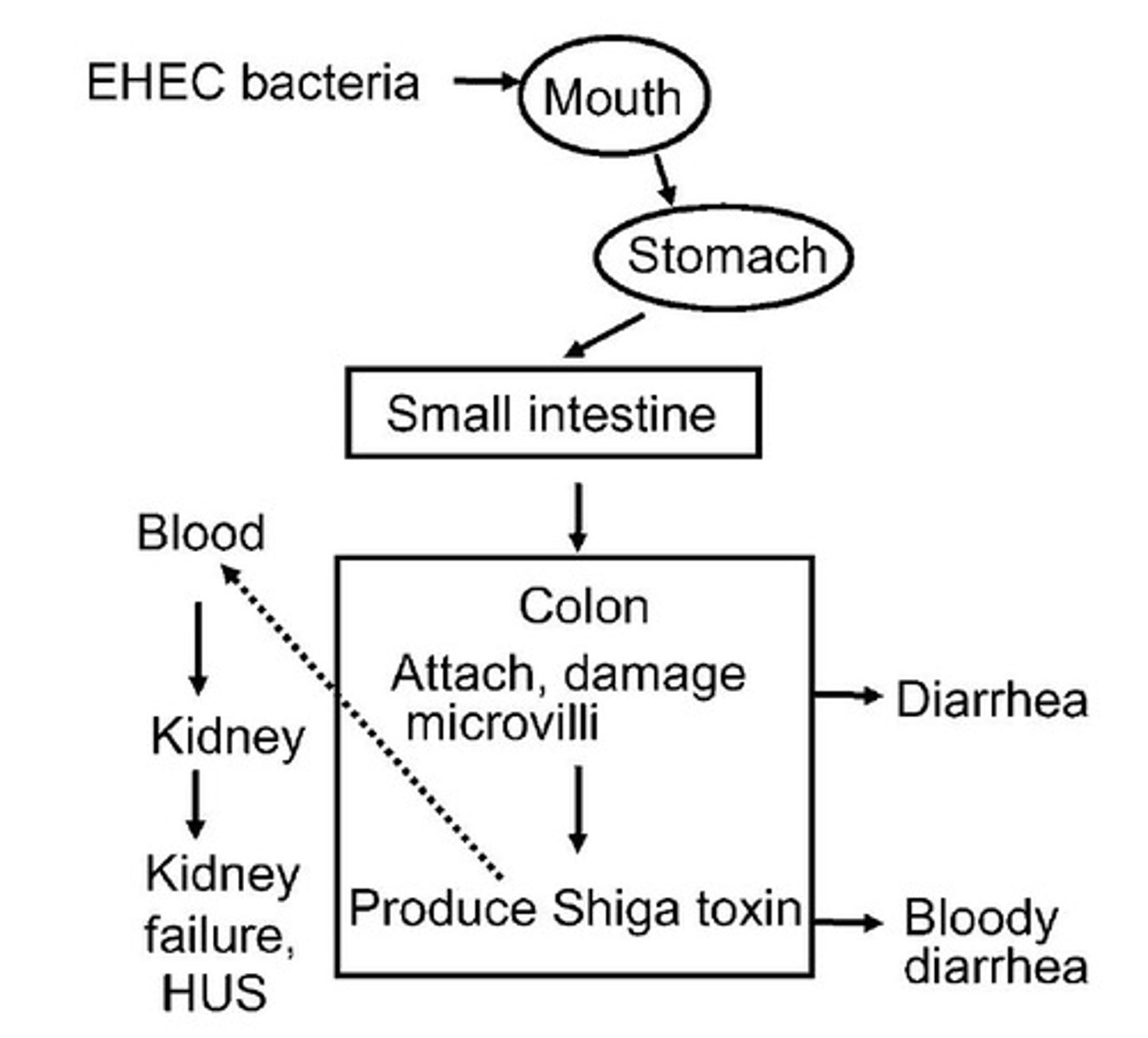
Toxin-mediated hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)
Severe complication from EHEC infection.
Type III secretion system (T3S)
Transports virulence factors into host tissues.
Locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE)
Pathogenicity island encoding EHEC T3S genes.
Pedestal lesions
Formed by EHEC colonization using T3S.
Intimin
Adherence factor interacting with Tir in EHEC.
Tir
Translocated receptor for EHEC adherence.
T3S
Type III secretion system for injecting virulence factors.
Pedestal
Actin-rich structure formed beneath EHEC.
AE lesions
Attaching and effacing lesions damaging intestinal barrier.
EHEC
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli causing severe intestinal disease.
Shiga toxin
Cytotoxin produced by EHEC and Shigella dysenteriae.
AB class toxin
Toxin with A and B subunits affecting cells.
28S rRNA
Target of Shiga toxin for protein synthesis inhibition.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Cellular uptake via receptor binding.
Cellular trafficking
Movement of substances within cells.
IpaB
Effector protein that destroys macrophages.
Invasins
Virulence factors promoting intracellular invasion.
The Zipper mechanism
Invasion via external receptor interaction.
The Trigger mechanism
Invasion triggered by secreted effectors.
Phagosome
Membrane-bound vacuole containing engulfed pathogens.
pINV plasmid
Plasmid essential for Shigella pathogenesis.
SHI
Pathogenicity island in Shigella's pINV plasmid.
VirG
T3S protein recruiting host actin for invasion.
MacConkey Agar
Selective medium differentiating lactose fermenters.
SMAC plates
Differential medium for EHEC serotype O157:H7.
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS)
Serious complication from EHEC infection.
Doxycycline
Antibiotic sometimes used for diarrheagenic infections.
Trimethoprim (TMP)
First-line antibiotic for UTIs.
Ciprofloxacin
Fluoroquinolone antibiotic for bacterial infections.
Lateral propagation
Invasion of adjacent cells by replicating pathogens.
Endosome
Vesicle formed during endocytosis.
Caspase-dependent cell death
Programmed cell death activated by IpaB.
Food safety measures
Practices to prevent foodborne infections.
Immunoassays
Tests detecting specific antigens or antibodies.
PCR for Shiga toxin
Molecular method for detecting STX presence.
EHEC O157:H7
Serotype of E. coli lacking sorbitol fermentation.