L6 B12, B9 metabolism and anaemias
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
key role of vitamin b12
maintaining normal function of brain and nervous system
formation of RBC
dna synthesis and regulation
how much vitamin b12 is needed
1-3 micrograms
0.5 to maintain health
absorption of B12
intrinsic factor and gastric acid produced by gastric parietal cells
B12/IF complex moves from stomach to ileum
binds to receptor on enterocyte then absorbed
B12 released into circulation
intrinsic factor is degraded and not recycled
post enterocyte circulation of B12
transcobalamin binds to B12 in circulation, binds to receptor on surface of target cell
Once inside the transcobalamin is degraded by lyososomes to release B12
storage and loss of B12
storage - liver, 3-5mg
Loss - urine and faces, desquamation of epithelial and excretion in bile, 0.05-0,1% of body content daily
Takes years for B12 deficiency to occur - takes long time for stores to be depleted
vitamin b6 common where, absorption and daily requirement
pyridoxine, common in fruit cereal meat, passive absorption in jejunum and ileum, daily requirement 1.5-2.0mg
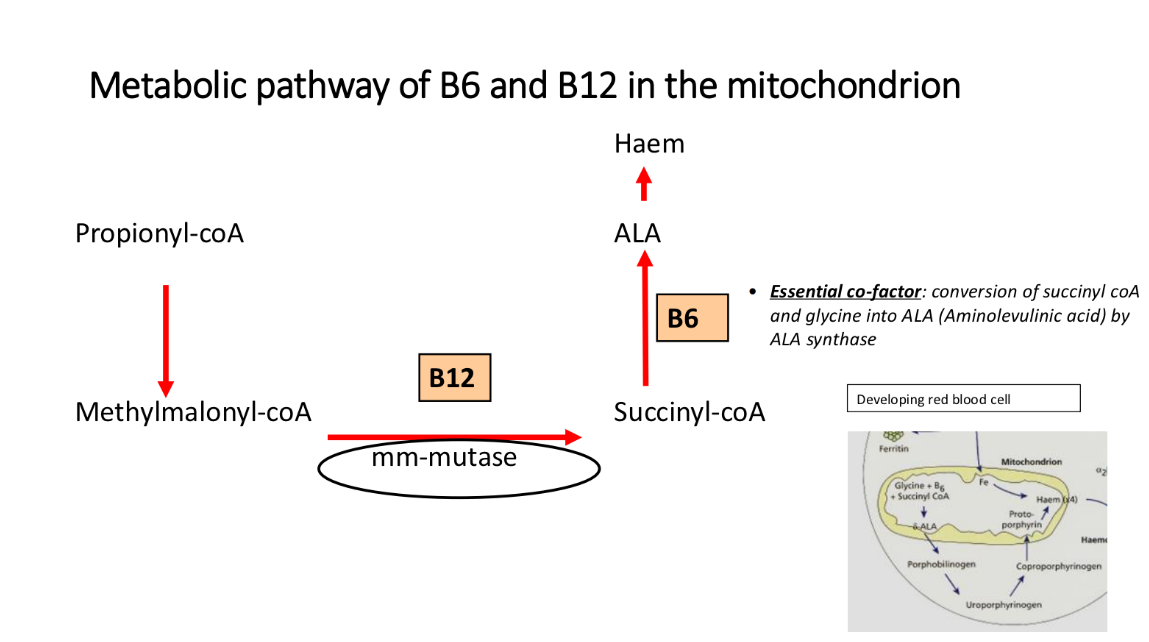
metabolic pathway of B6 and B12 in the mitochondrion
propionyl-coA → methylmalonyl-coA
methylmanoyl-coA → succinyl coA
catalysed by mm-mutase and cofactor B12
succinyl-coA → ALA
cofactor B6
ALA→ Haem
can the body synthesise b9
no
found in lentils, kidney beans, broccoli, spinach..
activation absorption and transport of folic acid
folic acid is reduced to tetrahydrofolate methylTHF by MTHFR
absorbed in the duodenum and jejunum
coverted into 5- methyltetrahydrofolate monoglutamate (5-MTHF monoglutamate) before entering portal system
plasma folate circulates bound or unbound
importance of B9 folate
synthesis of purine and pyrimidine precursors of DNA
important during periods of infancy and pregnancy for cell division
healthy production of RBC
causes of vitamin B12 deficiency
pernicious anaemia -impairs absorption of Italian b12 as a consequence of a reduction in intrinsic factor
Vegans have no b12 in diet
causes of folate deficiency
adequate presence of folate in food (rare)
Poor dietary habits - chronic alcoholic
Impaired absorption or metabolism or inc demand for vitamin
Pregnancy inc need for intake of folate - more proliferating cells, 3rd trimester need for folate will x2
drugs such as anticonvulsants can impair absorption - inc folate metabolism
consequences of folate and B12 deficiency
spina bfida and anencephaly
Progressive demyelination of nerve cells thought to result from inc in methylmalonyl-CoA that results from vitamin B12 deficiency
neuropathy - spinal cord and peripheral nerves affected
tingling in feet, difficulty w gait
glossitis
haemotological disorders from B12 and folate deficiency
megaloblastic anaemia due to folate deficiency
Pernicious anaemia is megaloblastic anaemia due to vitamin B12 deficiency
how does b12 and folate deficiency cause megaloblastic anaemia
deficiency of folate reduces conversion of dUMP to dTMP - rate limiting step in DNA synthesis
DNA synthesis delayed
RNA not delayed, protein synthesis at much faster rate
delayed / incomplete cell division
huge cells but less haemoglobin
haemotological features of megaloblastic anaemia
macrocytosis
inc MCV > 90 fL
dec in number of cell divisions prior to loss of nucleus
inc lobe number in nucleus of neutrophils
chromatin structural abnormalities
oval macrocytes
pernicious anaemia
Autoimmune attack on the gastric mucosa
Stomach wall becomes thin, reduces gastric secretion of acid and intrinsic factor
Antibodies against the gastric parietal cells
test for pernicious anaemia - what increases within the haem pathway?
methylmalonyl-coA increases
treatment for pernicious anaemia
oral dose of folic acid for folate deficiency
B12 intramuscular injection of hydroxycobalmin
diagnosis for megaloblastic anaemia
vitamin B12 deficiency must be ruled out
if vitamin B12 deficient, folate supplementation can alleviate the anaemia but does not reverse neruological deficits
folate deficiency in serum folate
If serum folate is < 3 μg/L (< 7 nmol/L), deficiency is likely
vitamin B12 deficiency readings
A vitamin B12 level < 200 pg/mL (< 145 pmol/L) indicates vitamin B12 deficiency.