(1-2) Extractive Metallurgy | Hydrometallurgy
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
HYDROMETALLURGY
selective reaction of valuable metals using aqueous reagents.
PYROMETALLURGY
involves heat
ELECTROMETALLURGY
electrolysis is used
LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ELEMENTS
The quantity of element is neither decreased nor increased
BLACK BOX REACTION
Steady-state assumption
Time is not a factor
What comes in also comes out
PRINCIPLES OF COMBINING VOLUMES
Atoms combine to form molecule
Expressed by the product of atomic weight and small whole
LAW OF COMBINING VOLUMES
When gases react, the volume consumed and produced
GAY-LUSSAC’S LAW
Fixed amount of gas
Pressure is proportional to temperature (k)
GAY-LUSSAC’S LAW (formula)
P1/T1 = P2/T2
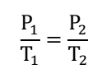
CHARLES’ LAW
• Volume is proportional to temperature
CHARLES’ LAW (formula)
V1/T1 = V2/T2
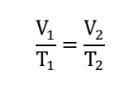
BOYLE’S LAW
Pressure and volume are inversely proportional
High pressure, Low Volume
Low Pressure, High Volume
BOYLE’S LAW (formula)
P1V1 = P2V2
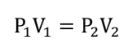
IDEAL GAS LAW
The state of an ideal gas is determined by the macroscopic and microscopic parameters like pressure, volume, temperature.
IDEAL GAS LAW (formula)
PV = nRT
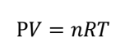
COMBINED GAS LAW
Pressure is inversely proportional to volume, or higher volume equals lower pressure
Pressure is directly proportional to temperature, or higher temperature equals higher pressure.
COMBINED GAS LAW (formula)
P1V1/n1T1 = P2V2/n2T2
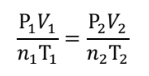
HYDROMETALLURGY
involves chemical reactions carried out in aqueous solutions
To recover metals from low-grade ores
Form high-grade concentrates that are roasted
Preliminary operation to mineral processing
ADVANTAGES OF HYDROMETALLURGY (3)
Mineral Beneficiations (optional)
Roasting (optional)
Leaching
Solid-liquid separation
Metal recovery
Solid/waste treatment
GENERAL STEPS IN HYDROMETALLURGY (6)
MINERAL BENEFICIATION
Control the fineness of the feed material
ROASTING
Conversion of valuable minerals into soluble forms
LEACHING
To dissolve the valuable mineral/metal into the liquor
SOLID-LIQUID SEPARATION
Separation of leach liquor from undissolved residue
METAL RECOVERY
Final extraction of metal from the solution
SOLID/WASTER TREATMENT
Neutralization for recycling or prior to disposal
LEACHING
Selective dissolution of the valuable metal in the suitable reagent or leachant (usually sulfuric acid)
Process of dissolving in a suitable reagent or leachant
LIXIVIANTS
Liquid or reagent used to selectively extract metals
water
acids
bases
aqueous salts
Common Lixiviants (4)
Readily available in quantity
Relatively cheap
Does not react unduly with gangue minerals
Non-corrosive
Amenability of regeneration/recycling
Requirements of Lixiviants (5)
DUMP LEACHING
HEAD LEACHING
IN-SITU LEACHING
VAT/PERCOLATION LEACHING
PRESSURE LEACHING
5 DIFFERENT LEACHING METHODS
DUMP LEACHING
Actual ore in the specific part of the site
Feed of lixiviant is downward
PREGNANT LEACH SOLUTION
term given for the product of dump leaching
HEAP LEACHING
We construct reaps
Lixiviant are sprinkled from the top-most part
Inclined position
IN-SITU LEACHING
“In-place” leaching
On site or in site leaching
VAT/PERCOLATION LEACHING
Composed of series of tanks
Ore is fed on every tanks
Lixiviant is fed on the side
PRESSURE LEACHING
Uses autoclase
Big tanks
High pressure at 10 atm
ION EXCHANGE
SOLVENT EXTRACTION
ADSORPTION
3 Methods of Solution Purification/Concentration
ION EXCHANGE
Exchange of ions in a polymeric resin with significant ions present in solution
Functionalized resin
SORPTION
ELUTION
2 Methods of Ion Exchange
SORPTION
Resin is contained in a column
ELLUTION
Retained ions are displaced from resin
We feed eluant (organic) for metals to leave the resin
SOLVENT EXTRACTION
Involved a distributive reaction wherein metals is allowed to partition
Uses solvents to extract metals
Organic solution
ADSORPTION
Activated carbon – most important
Adherence to the surface of another particle
CARBON-IN-PULP
Leaching → Adsorption
cyanidation leaching first and then adding the activated carbon in the slurry
CARBON-IN-LEACH
simultaneously leaching and adsorbing
activated carbon is added to the leaching tank, the leaching and adsorption are carried out at the same time
METAL SEPARATION AND RECOVERY
Also known as metal winning
Final step of hydrometallurgy
Precipitation
Electrometallurgy
Methods of Metal Winning (2)
PRECIPITATION
Formation of a solid product from solution as a result of addition of a reagent
Single-replacement method
Metal is recovered as salt or oxide
ELECTROMETALLURGY
Also known as Also known as ELECTROWINNING
Recovery and purification of metals using electrode position of metals at a cathode
Employs redox reaction
ELECTROREFINING
Improves the purity of metal
Copper Leaching
Bacterial Leaching
Solvent Extraction
Gold Leaching
Cyanidation
Adsorption
Cobalt
HPAL
Moa-Bay Process
Aluminum
Bayer Process
Hydrometallurgical Processes
Bacterial Leaching
Solvent Extraction
Hydrometallurgical Process in Copper Leaching
Cyanidation
Adsorption
Hydrometallurgical Process in Gold Leaching
High Pressure Acid Leaching (HPAL)
Moa-Bay Process
Hydrometallurgical Process in Cobalt Extraction
Bayer Process
Hydrometallurgical Process in Aluminum Extraction