bio 152 ecology uw madison
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
what is a terrestial biome?
the major life zones characterized by vegetation type over a broad vegetative area
what is considered the warmest in the northern hemisphere?
A. lower elevation, lower latitudes, north facing slopes
B. lower elevation, higher latitudes, north facing slopes
C. lower elevation, lower latitudes, south facing slopes
D higher elevation, higher latitudes, north facing slopes
E none of these
C. lower elevation, lower latitudes, south facing slopes
what is a population?
A. individuals of 2 species occupying the same general area, utilizing the same space, resources & influenced by similar environmental conditions
B. individuals of 1 species occupying the same general area, utilizing the same space, resources & influenced by similar environmental conditions
C. individuals of 1 species occupying the same general area, utilizing different spaces, but the same resources & influenced by similar environmental conditions
B. individuals of 1 species occupying the same general area, utilizing the same space, resources & influenced by similar environmental conditions
true or false population ecology depends on how big the population is, how widely spread the population is and a combination of the two being how dense the population is
true
what is population density dependent on?
A. population size
B. population range
both
How do you add to a population?
births and immigration
How you subtract from a population?
deaths and emigration
true or false the lincoln-peterson estimate is when you mark an initial sample and then come back and take another sample counting the ones marked and the ones unmarked and finding your total population
true
firstsamplemarked/N=Markedsample/total#in2ndsample
true or false dispersion are patterns of spreading among individuals in a population
true
What are the 3 dispersion patterns?
clumped, uniform, random
what is demography?
A. the study of population statistics of a population and how they change overtime
B. the study of vital statisics of a population and how they change overtime
C. the study of dispersion statistics of a population and how they change overtime?
B. the study of vital statistics of a population and how they change overtime
life history strategies
the degree of investment in reproduction and survival over an organisms lifetime
true or false the components of life history are growth reproduction, defenses, and other adaptive traits that promote fitness
true growth reproduction, defenses, other adaptive traits that promote fitness
trade offs of life history components
can't do everything at once because energy is limited.
what is iteroparity
reproduce multiple times but separately, parental(smaller number of reproductive events) parental investment is high
What is semelparity?
Reproduction in which an organism produces all of its offspring in a single event with little parental investment.
true or false populations are not static
true
unlimited population growth(exponential, density independent growth)
assume a closed population with no immigration or emigration, only focuses on births and deaths
N
population size
B
# of births that occur in a time period
D
# of deaths that occur in a time period
b
per capita birth rate
d
per capita death rate
r
instantaneous per capita rate of increase
dN/dt=
rN or (b-d)N
if r is 0 whats the graph look like?
flat line at whatever the starting population is
true or false an r value that is positive will have a declining population
false it will be an increasing population
r-selected species
a species that has a high intrinsic growth rate, which often leads to population overshoots and die-offs
logistic growth model( density-dependent growth or limited growth)
true or false k represents the carrying capacity which is the upper boundary for population size that can be sustained over a relatively long time period.
true
factors that affect birth and death rate include what
predators, resources, disease, space, hiding spot
rmax
is the maximum per capita rate of increase
true or false organisms can overshoot there carrying capacity
true happens all the time and then it goes back down until it reaches carrying capacity
density dependent regulation can do what?
can affect deaths or births
if density doesn't matter what happens?
the graph will flatline
which of the following describe r selected species
A.
have low per capita growth rates(r), long generation times, low reproductive output, high parental investment, low juvenile mortality, often but not always regulated by density-dependent growth, selection tends to favor traits that are sensitive to population density, while the species is favored at high densities.
B.
have high values of r, short generation times, high reproductive output, low parental investments, often but not alway regulated by density-independent growth, maximizes reproductive success in uncrowded environments
have high values of r, short generation times, high reproductive output, low parental investments, often but not alway regulated by density-independent growth, maximizes reproductive success in uncrowded environments
which of the following describe k-selected species?
A.
have low per capita growth rates(r), long generation times, low reproductive output, high parental investment, low juvenile mortality, often but not always regulated by density-dependent growth, selection tends to favor traits that are sensitive to population density, while the species is favored at high densities.
B.
have high values of r, short generation times, high reproductive output, low parental investments, often but not alway regulated by density-independent growth, maximizes reproductive success in uncrowded environments
have low per capita growth rates(r), long generation times, low reproductive output, high parental investment, low juvenile mortality, often but not always regulated by density-dependent growth, selection tends to favor traits that are sensitive to population density, while the species is favored at high densities.
true or false humans and redwood trees are more of an r selected species rather than a k selected species
false they are more defined to be a k selected species because of the long lived generations
what is generation time
its the time it takes an individual from the time it is born to have a baby
what is a meta population?
is a spatially separated populations(subpopulations) that are linked by the dispersal of individuals
what are the locations of subpopulations called?
patches
what can cause patches to become unoccupied?
emigration, death, disease
what can causes patches to become occupied?
migration
whats a source patch?
they are net exporters of individuals(r>0) high birth rate (b>d)
whats a sink patch?
net importers of individuals(r<0) high death rate (b
what speed is the human population growing?
exponential
hyperbolic
logistically
hyperbolic
what is an ecological footprint?
the amount of land and water area that is required by individual (or a population) to produce the resources they consume & absorb their wastes
True or false carrying capacity of humans can be defined as the maximum # of persons that can be supported in perpetuity in an area with a given technological level and set of consumptive habits
true
what is community
the assemblage of populations of different species that occur in the same place
what is competition?
when 2 or more species rely on similar limiting resources, they have negative effects on each other
true or false interspecific is competition between individuals of the same species
false that is for intraspecific
interspecific
competition between members of different species
competitive exclusion principle
that 2 species using the same limiting resource cannot coexist indefinetely
Niche
the abiotic and biotic conditions that a species needs to grow, survive, and reproduce
fundamental niche
The full potential range of the physical, chemical, and biological factors a species can use if there is no competition from other species.
realized niche
the range of abiotic and biotic conditions under which a species actually lives
niche (resource) partitioning
the use of limiting resources by different species in a community in different waysz
true or false dispersal can be defined as the amount an organism moves away from its place of birth
true
true or false biotic factors include interactions with light, temperature, water availability and wind
false thats for abiotic factors
true or false interactions between organisms can help or negate whether a species is in a particular place based on biotic factors
true
what three air masses pass through Wisconsin?
Arctic airmass, subtropical airmass, continental air mass
Prairies and Savannas rely on what abiotic factor to survive?
fire
What dominants most of wisconsin?
forests
what contributes a lot toward the making of pine forests
sandy soil
in northern WI communities what would you find?
north hard woods, pine and pine barrens
in southern WI communities what would you find?
prairies, oak savannah, southern mesic forest
which of these southern wisconsin comunities would be maintain by fire?
A. southern mesic forest
B. Hardwoods
c. Oak savannah
C
true or false climate is the prevailing conditions at a locality
true
whats the difference between weather conditions and climate?
climate happens are combined weathering events that happen over a decade while weather is what happens in days.
what causes the seasons?
The tilt of the earths axis
true or false less rain is accumulated towards the poles
true
When is a lake stratified?
during the summer and winter months
turnover is what
mixing water which happens in spring and autumn.
whats important about the thermocline?
this separates where some organism live
aquatic biomes affected by where light and temperature in aquatic relms
zonatin patterns
Literal zone
(close to shore)Area of a lake where plants at the bottom can get enough sunlight for photosynthesis
limnetic zone
farther from shore
benthic zone
the muddy bottom of a lake, pond, or ocean
photic zone
Portion of the marine biome that is shallow enough for sunlight to penetrate.
aphotic zone
dark layer of the oceans below the photic zone where sunlight does not penetrate
pelagic zone
open water above the ocean floor far far away
continental margins
shallow-water areas close to continents (edge of the continent of oceans)
true or false you will find no species in the tidal zones
false you will only find species that are able to tolerate the tides
intertidal zone
prominent and felt by organisms
Neuritic Zone
The area from low-tide to the edge of the continental shelf.
true or false an aquatic biome is a major life zone characterized by the physical environment
true
What are the aquatic biomes?
oceanic pelagic and benthic zones, intertidal zones, estuaries(salinity gradient), coral reefs, rivers, lakes
Name all of the terrestrial biomes
tundra, alpine, Taiga, coniferous forest, deciduous forest, grasslands, tropical rainforests, deserts, chaparral, savanna
terrestial biomes
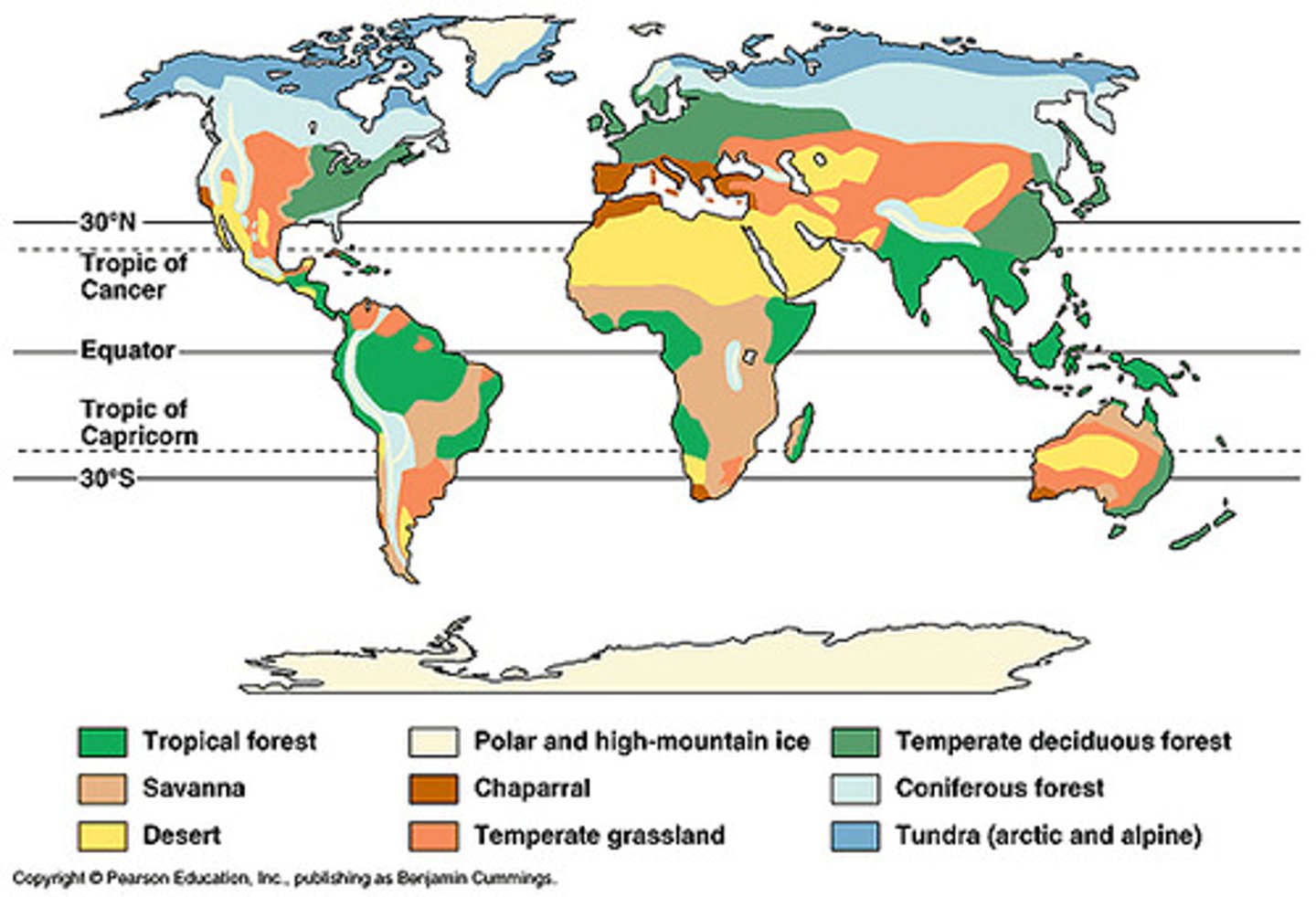
true or false increased elevation breeds a more wet cooler environment for plant life
true
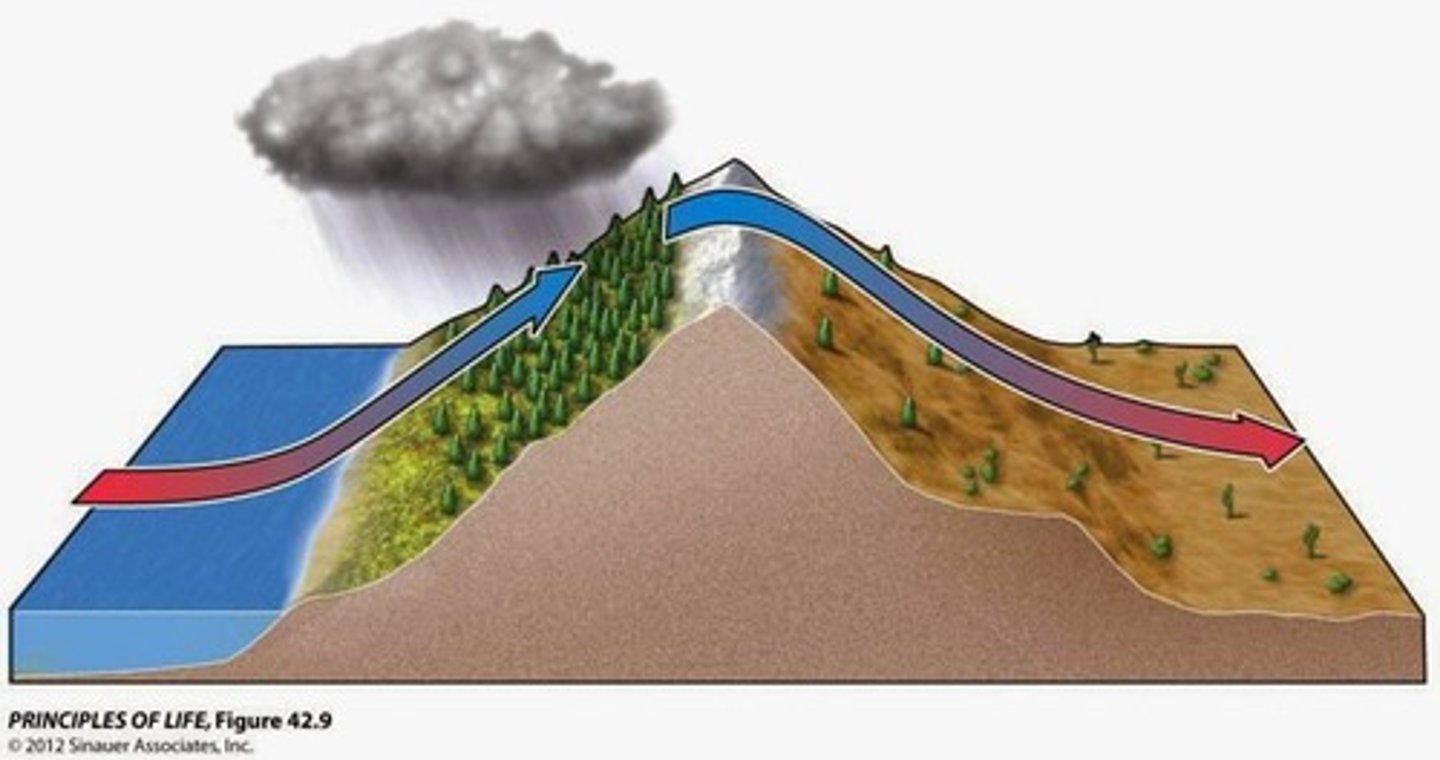
true or false rainshadows are characterized by cool wet water going up a hill and heating up over the mountain
false warm water goes up the hill and cools up and over the mountain
Rainshadow
a region having little rainfall because it is sheltered from prevailing rain-bearing winds by a range of hills.
true or false competition is a common demand by two or more organisms upon a limited supply of a resource; for example, food, water, light, space, mates, nesting sites. It may be intraspecific or interspecific.
very true
cryptic coloration
Camouflage; makes an organism difficult to spot.
aposematic coloration
A. type of mimicry in which a harmless species looks like a species that is poisonous or otherwise harmful to predators.
B. The bright coloration of animals with effective physical or chemical defenses that acts as a warning to predators
C. Evolution of two species, both of which are unpalatable and, have poisonous stingers or some other defense mechanism, to resemble each other
B.
what is Batesian mimicry
A. type of mimicry in which a harmless species looks like a species that is poisonous or otherwise harmful to predators.
B. The bright coloration of animals with effective physical or chemical defenses that acts as a warning to predators
C. Evolution of two species, both of which are unpalatable and, have poisonous stingers or some other defense mechanism, to resemble each other
A
Mullerian mimicry
A. type of mimicry in which a harmless species looks like a species that is poisonous or otherwise harmful to predators.
B. The bright coloration of animals with effective physical or chemical defenses that acts as a warning to predators
C. Evolution of two species, both of which are unpalatable and, have poisonous stingers or some other defense mechanism, to resemble each other
C
Herbivory
interaction in which one animal (the herbivore) feeds on producers (such as plants)
what is parasitisim
A. both organisms benefit
B.a symbiotic relationship in which one species benefits and in doing so the other is harmed.
C.type of symbiosis where one species is neither harmed nor helped, but inhibits growth of another species
D.A relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed
B