Board study guide
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
169 Terms
Which of the following is an accurate difference in scoring pediatric respiratory event related arousals (RERAs) from adult RERAs?
Pediatric rules require 50% or more reduction in flow. Pediatric rules require flattening of the flow waveform and snoring or labored breathing. Pediatric rules do not require an arousal to score a RERA.
Sleep spindles have a frequency of
12-14 H7.
What is the minimum AHI to be diagnosed with OSA?
.5/hr.
An oxygen desaturation is at least a (n)
.3-4% drop in 02 saturation levels.
In normal sleep architecture, stage 2 makes up approximately
40-50% of total sleep time
Average volume-assured pressure support focuses on maintaining which aspect of the respiratory process?
Tidal volume delivery
Which EKG arrhythmia is characterized by multiple and uniform P waves occurring between each QRS wave?
Atrial flutter is characterized by multiple uniform P waves occurring between each QRS complex.
What is the clinical term for bed wetting?
Enuresis is the clinical term for bed wetting.
What is the minimum recording time for a study?
6 hours
Narcolepsy first manifests itself in
.adolescence/young adulthood.
Which of the following medications is NOT used to treat PLMS?
.GABA antagonists.
Which of the following disorders involves sudden or gradual onset of loss of language and is characterized by nocturnal multifocal spikes and spike-wave discharges?
.Landau-Kleffner syndrome.
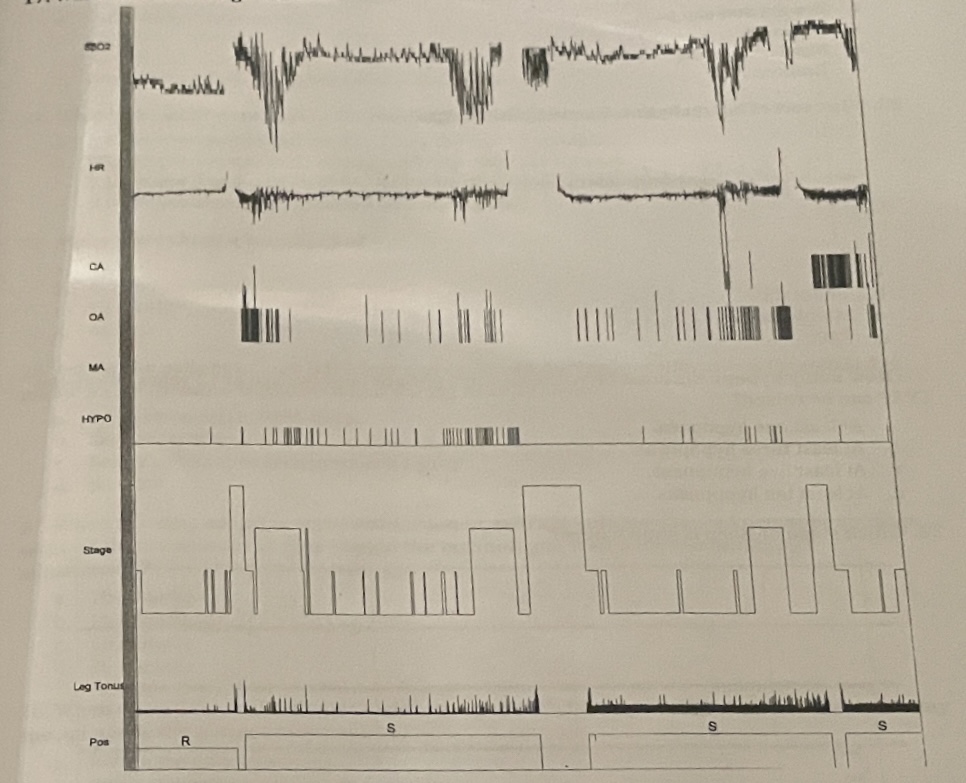
What does this image indicate?
REM-dependent apnea.
Sinus bradycardia is characterized by all of the following EXCEPT
a regular pulse of less than 50-60 beats/min with P waves in front of QRS complexes.
What is the most common side effect of proper CPAP use?
.Nasal congestion.
How many hypopneas must be witnessed in a patient over the age of twelve years before the CPAP can be raised?
At least three hypopneas.
All of the following locations on the body must be monitored during a PSG EXCEPT for
.P4-A1.
What is the BEST explanation for how a differential amplifier works?
It takes two sources and amplifies only the different voltages
Alpha waves have a frequency of
8-13 Hz
Asking the patient to look left/right and up/down during biocalibrations is intended to mimic which common situation found during healthy sleep?
The natural eye movement pattern during REM sleep.
When titrating adaptive servoventilation or average volume-assured pressure support, what minimum amount of time should the technologist wait between parameter adjustments?
20 minuets
When should the technologist review the patient's history and become familiar with any special needs the patient may have?
Before the patient arrives
In an EKG the P wave represents
Atrial contraction
When periodic limb movements of sleep are scored as events which of the following is false?
An event requires four or more consecutive leg movements, with the interval between movements ranging from 5-90 seconds.
What must be done each time a technologist enters the patients bedroom?
Document it in the study
What is the required amplitude for the negative deflection found in a k complex in order for it to count in scoring as stage N2 sleep?
No amplitude requirement for K-complexes.
The technician's duties include all of the following EXCEPT
giving an interpretation of the study to the patient.
A premature P wave in the EKG is referred to as a
PAC
Which of the following neurotransmitters is increased during the awake state; decreased during stages 1, 2, and 3 non-REM sleep; and absent during REM sleep
Norepinephrine:
A confisional arousal will manifest itselfas
disorientation and nonresponsiveness to environmental stimuli:
How many apneas should be witnessed in a patient 12 years or older before the PAP pressure is increased?
2 apneas
An alternating BEG pattern seen during quiet sleep in a newborn infant, consisting of both high- and low-voltage activity is termed
trace alternant.
An oral device treats sleep apnea by
prilling the patients lower jaw forward thereby opening the upper airway.
Ifa signal has a sensitivity of 7 V/mm and the deflection is 10 mm what is the voltage?
70 uV
Which form of supplemental oxygen delivery should be used during CPAP titrations?
Low flow
Central sleep apnea is characterized by which of the following?
Absence of chest wall and abdominal movements during apneic periods.
What is the difference between Sp02 and Sa02?
They both measure the amount of hemoglobin in the patient's blood that is saturated with oxygen, but SaOzis the more accurate reading.
SpOz stands for oxygen saturation as measured by a pulse oximeter. SaOz stands for oxygen saturation as measured by an arterial blood gas.
What percentage distance is Fpz. from Fz?
10%
One criterion for scoring pediatric obstructive sleep apnea is that, compared to baseline, there is a 90% or greater decrease in amplitude for at least what percentage of events?
90%
What is the minimum number of hours that an overnight nocturnal polysomnogram (PSG) should last in order to obtain adequate data?
Six
What should the technologist do if the patient awakens and complains that the pressure is too high?
Restart pressure with one that the patient subjectively feels comfortable.
In normal sleep architecture, REM makes up approximately
25-30% of total sleep time
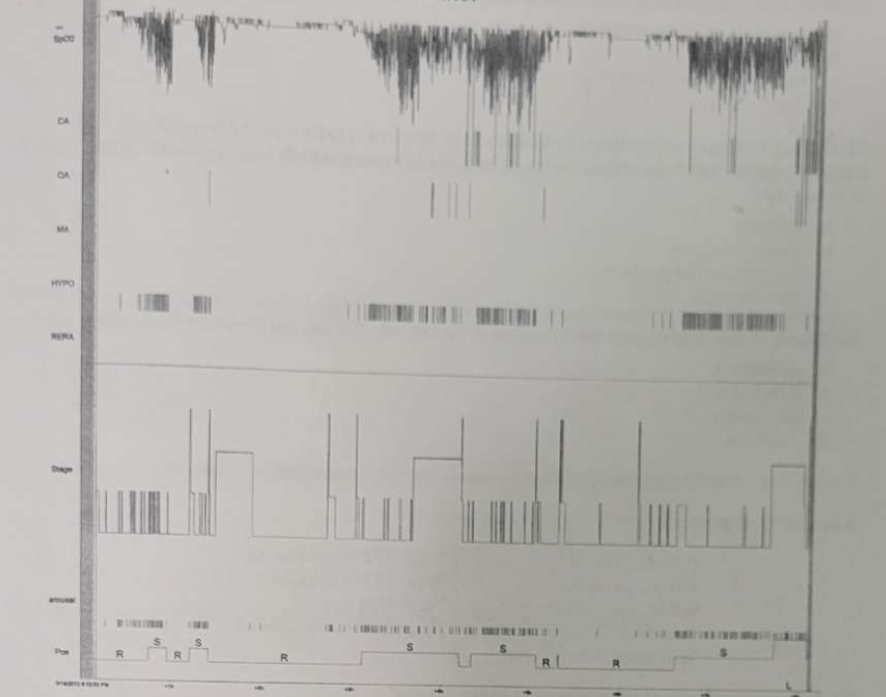
What does this raw data trend report indicate?
Positional-related apnea.
Which is the LEAST important reason for the technician to make a note of any medication the patient has taken in the last 6 hours?
Certain medications can affect the recording device's accuracy.
Sleep efficiency is defined as
the ratio of the percentage of time spent sleeping to the time spent in bed.
Bright light therapy is used to treat all of the following EXCEPT
Restless leg syndrome
During healthy respirations in NREM sleep, the brain relies on the hypoxic drive to trigger breaths. The hypoxic drive triggers a breath when which blood gas increases sufficiently?
Oxygen partial pressure.
Which of the following is best used to prep the site for an electrode on the scalp?
10-20 paste.
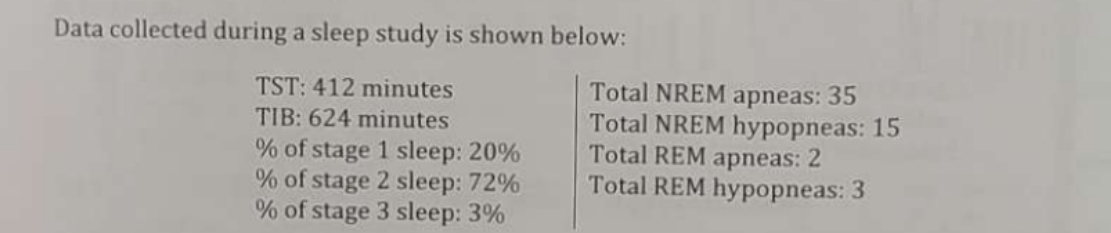
What percentage of the study was spent asleep?
66%
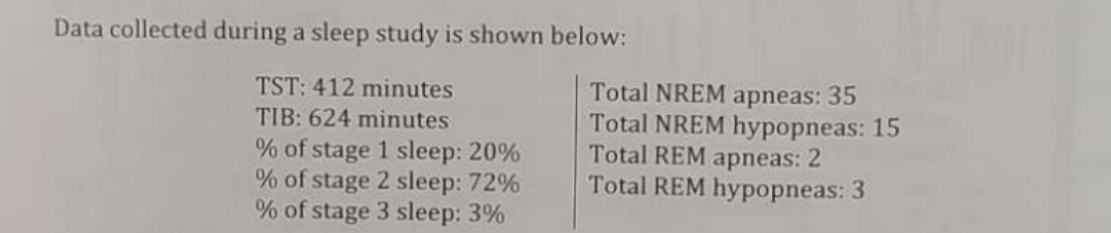
What is the amount of time, in hours, the patient was asleep (rounded to the nearest tenth of an hour)?
6.8 hrs.
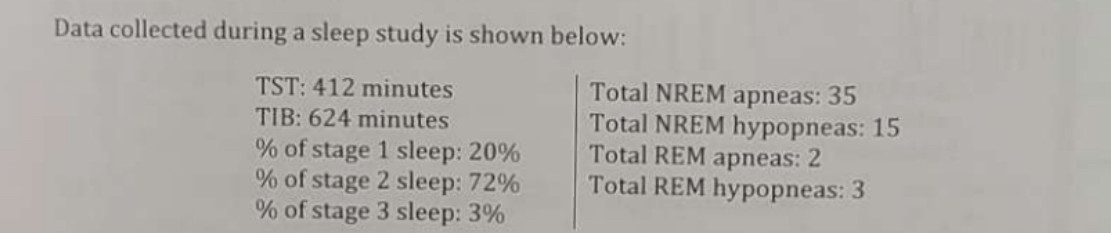
What is the amount of time, in minutes, spent in stage 1 sleep (rounded to the nearest minute)?
6.9 hours
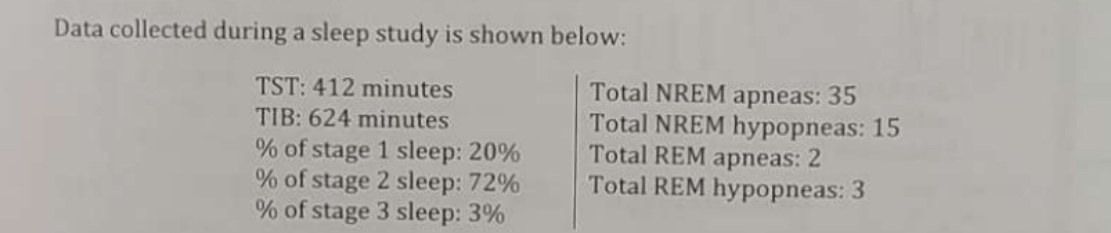
What is the amount of time, in hours, spent in stage 2 sleep (rounded to the nearest tenth of an hour)?
4.9 hours
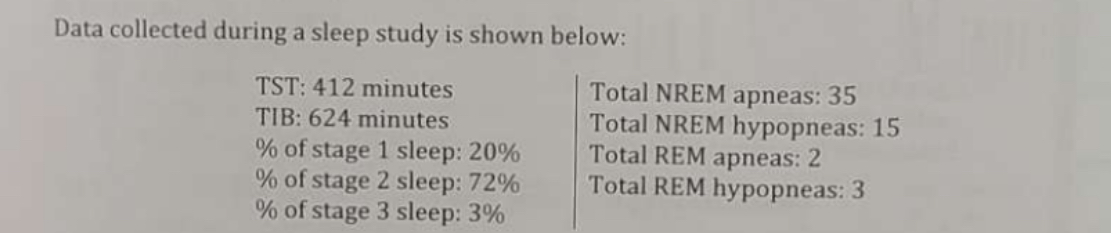
What is the total NREM sleep time in minutes (rounded to the nearest tenth of a minute)?
391.4
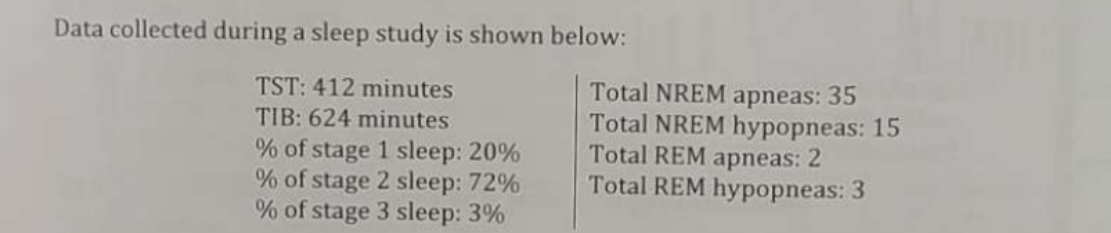
What is the amount of time, in minutes, spent in REM sleep (rounded to the nearest tenth of a minute)?
296.0 minutes.
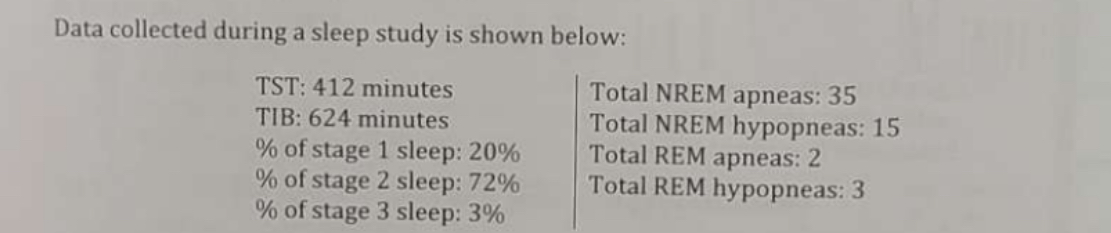
What is the total NREM AHI (rounded to the nearest tenth per hour)?
7.6/hr.
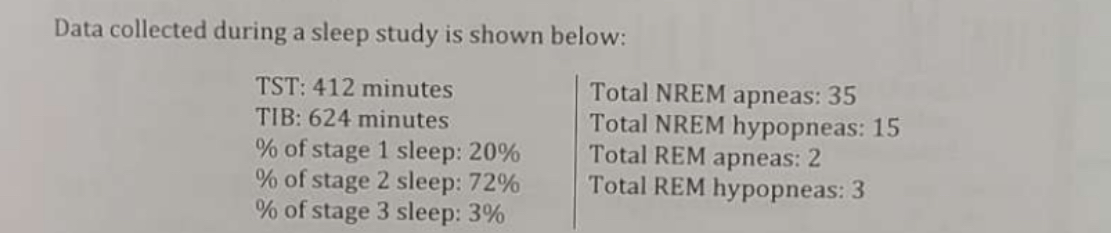
What is the total REM AHI (rounded to the nearest tenth per hour)?
14.2/hr.
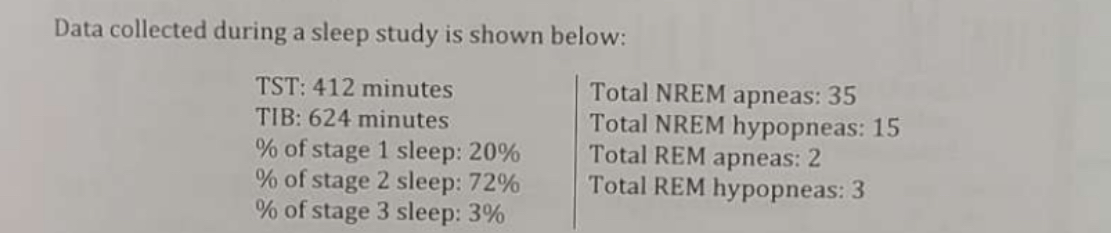
What is the total AHI (rounded to the nearest tenth per hour)?
8.1/hr.
A patient comes to the lab stating that she is to have a CPAP titration study. Her chart states that she is to have a diagnostic NPSG. What should the technician do?
Run the diagnostic NPSG.
Antidepressants suppress which stage of sleep?
REM
How can alcohol affect sleep?
Increase OSA.
In normal sleep architecture stage 1 makes up
~5-10% of total sleep time.
During a CPAP titration study a patient at a CPAP pressure of 15 cm who is still snoring and having hypopneas complains that the pressure feels too high and she cannot sleep. What should the technician do?
Switch to BiPAP of 15/11 cm and continue the titration.
For documentation purposes a technologist should record witnessing all of the following EXCEPT
patients' facial expressions.
In which study does a patient try to stay awake in a darkened room during daytime hours?
MWT
Heated humidity can possibly remedy which of the following conditions seen in some patients
Patient mouth-breathes because of nasal congestion.
Patient complains of dry throat or nose.
Which of the following is true of Cheyne-Stokes respirations?
Cheyne-Stokes breathing can occur with damage to the central nervous system (e.g., brain tumor, stroke, traumatic brain injury), hyperventilation, and heart failure.
Pulse oximetry during the respirations shows a wave-like waveform as saturation begins to rise during the apneic period and then falls after the periods of rapid respirations.
One criterion for scoring the respirations is the presence of consecutive cycles of a crescendo-to-decrescendo breathing pattern that lasts for a minimum of two consecutive minutes.
One criterion for scoring the respirations is the presence of consecutive cycles of a crescendo-to-decrescendo breathing pattern that includes three central apneas or central hypopneas per hour of sleep.
Cheyenne -Stokes breathing can occur with damage to the central nervous system (e.g., brain tumor, stroke, traumatic brain injury), hyperventilation, and heart failure.
Correct statements about data storage and transferring include all of the following Except
immediately delete the original data following the upload or transfer of the data.
78-year-old female who weighs 120 pounds and is 5'5" tall with a history of heart attack, stroke, and hypertension comes in complaining of headaches, memory loss, and daytime fatigue. She most likely has
central sleep apnea.
Which two points on the international 10-20 system of electrode placement are used to locate F3?
Fz and F7
If the right EOG lead is out and above the eye, when the patient looks right the left EOG channel will deflect
Up
The most commonly seen arrhythmia during a sleep study is
There is an up and down deflection.
Reasons to alert the physician of an immediate need to revive a patients study include all of the following except
sinus tachycardia.
The Berlin questionnaire (1996) asks about which of the following?
there is a periodic leg movement index of over 40.
All of the following statements are true about the changes seen from stage N2 to N3 EXCEPT
Snoring: presence, characteristics, frequency, impact on bed partner and others, and apneic episodes.
K-complexes are often seen
In stage 2 sleep
Stripping of the skin by the incorrect removal of tape is more likely in which group of patients?
The elderly
Obstructive apneas and hypopneas were initially cleared on CPAP, but the patient then began having central apneas. What should the technician do?
Continue to use CPAP, but reduce the pressure and monitor for resolution of the central apneas; considering alternatives if there is no resolution.
How many naps does an MSLT consist of?
4-5
REM behavior disorder is most often seen in
Makes over the age of 60
What is the time constant?
The amount of time it takes for a signal to fall to 37% of the original calibration amplitude.
Where must the conductive paste be placed in relation to the gold cup wire?
Inside the gold cup.
Cataplexy is
The loss of muscle tone that accompanies a strong emotion.
Following an arousal in stage N2 sleep, what must occur before stage N2 can continue to be scored?
Stage N1 must be scored until a K-complex or sleep spindle occurs again.
When performing a CPAP titration study, it is important for the patient to have which of the following?
All stages of sleep
Cheyne-Stokes breathing pattern is
A crescendo-decrescendo breathing pattern.
Pulse oximetry measures
arterial oxygen saturation (SpOz).
Actigraphy works by
recording movements throughout the day to determine sleep-wake patterns, sleep fragmentation, and body movements.
Upon arriving in the sleep lab, the technologist should first do which of the following?
Test the equipment for proper function.
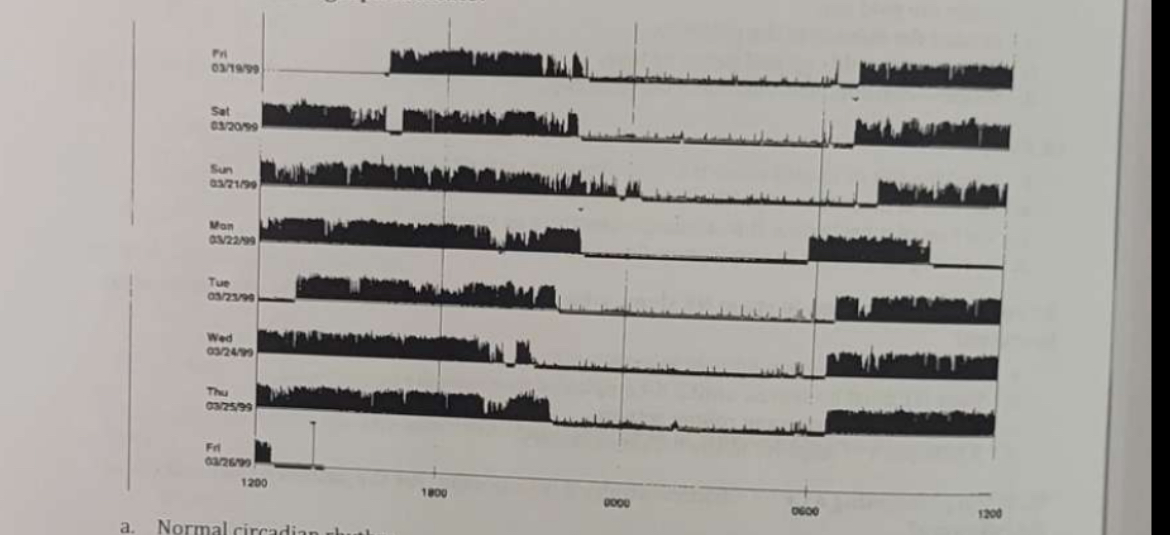
What does this actigraph indicate?
Normal circadian rhythm.
BiPAP S/T stands for
bilevel positive airway pressure spontaneous/timed.
Flow monitoring devices that may be used on patients during a sleep study include all of
the following EXCEPT
A transcutaneous carbon dioxide (CO2) monitor.
When optimal pressures of CPAP titration are reached, of what undesirable effect should the technologist be aware?
Severe hypoxia or hypercarbia.
How much sleep time must be between 2 apnea events?
There is no sleep time requirement.
In an ECG the T wave represents
ventricular repolarization.
If a tonic-clonic seizure event occurs in the sleep lab, the technologist is responsible for doing which of the following?
Raising bed rails.
Padding the patient to best prevent harm.
Keeping the study running and documenting all clinical movements and events
Which of the following actions must be completed following marking "lights on" and before the study
Perform equipment and biocalibrations
When fitting a patient with a CPAP mask, it is important to check that
there is no leak above clinical levels escaping from the mask.
According to guidelines from the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, what is required to run a multiple sleep latency test?
An overnight PSG recording
If the right EOG lead is out and above the eye, when the patient looks up the right EOG channel will deflect
Down
Which two channels on the PSG montage show the highest amplitude of slow-wave sleep?
F3-A2 and F4-A1.