CH 12: Muscle
1/145
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physiology Exam 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
146 Terms
A graded whole muscle contraction is produced in vivo primarily by variations in
a. the strength of the fiber’s contraction
b. the number of fibers that are contracting
c. both of these
d. neither of these
b. the number of fibers that are contracting
The series-elastic component of muscle contraction is responsible for
a. increased muscle shortening to successive twitches
b. a time delay between contraction and shortening
c. the lengthening of muscle after contraction has ceased
d. all of these
d. all of these
Which of these muscles have motor units with the highest innervation ratio?
a. Leg muscles
b. Arm muscles
c. Muscles that move the fingers
d. Muscles of the trunk
c. Muscles that move the fingers
The stimulation of gamma motor neurons produces
a. isotonic contraction of intrafusal fibers
b. isometric contraction of intrafusal fibers
c. either isotonic or isometric contraction of intrafusal fibers
d. contraction of extrafusal fibers.
b. isometric contraction of intrafusal fibers
In a single reflex arc involved in the knee-jerk reflex, how many synapses are activated within the spinal cord?
a. Thousands
b. Hundreds
c. Dozens
d. Two
e. One
e. One
Spastic paralysis may occur when there is damage to
a. the lower motor neurons
b. the upper motor neurons
c. either the lower or the upper motor neurons
d. neither the upper not lower neuron
b. the upper motor neurons
The _________ of a muscle is on the bone that moves when the muscle contracts, while the ______ is on the bone that is relatively immobile when the muscle contracts
insertion; origin
What are the columns of muscle produced by the extension of the epimysium into the body of the muscle called?
Fascicles
What is the connective tissue sheath that surrounds each fascicle?
Perimysium
What is the motor end plate?
A specialized part of the sarcolemma near the neuromuscular junction
The site of attachment of a muscle to the bone that it moves is its ________
insertion
The A band in muscle is predominantly ______
myosin in thick filaments
What is the fibrous connective tissue sheath that extends around the muscle?
Epimysium
The fascicles are _____
connective tissue that divides the body of a muscle into columns
Which of the following change during contraction?
The H band gets smaller
The I band gets smaller
Each fascicle is surrounded by a connective tissue sheath known as the ________
perimysium
Which of the following must be present to allow a muscle fiber to relax?
a) Acetylcholine
b) Sodium
c) Calcium
d) ATP
d) ATP
The specialized region of the sarcolemma of a muscle fiber at the neuromuscular junction is called the ______ _____ ______
motor end plate
When a muscle is at rest, the majority of the active sites for myosin binding on the actin molecule are covered by the protein _______
tropomyosin
Actin
is a protein involved in muscle contraction
What is the function of troponin in muscle contraction?
To move/lever tropomyosin off the active site of actin so that myosin can bind to it
The ________ is a fibrous connective tissue sheath that surrounds a whole muscle
epimysium
When is calcium used during contraction?
To bind to troponin and allow for the movement of tropomyosin
When ATP is added to a contracted muscle fiber, what happens?
The muscle fiber can relax
Most of the calcium in skeletal muscle cells is stored in the _________ ________
sarcoplasmic reticulum
In order for actin to bind to myosin, the active sites on the actin molecule must be uncovered. This involves the movement of tropomyosin by the protein _________
troponin
A muscle will _________ if the tension it develops is greater than or equal to the load it is under
shorten or contract
Before actin and myosin can bind, _______ binds to troponin C causing a conformational shape change that pulls tropomyosin off the F-actin's active site
calcium
The response when a muscle is stimulated with a single electric shock of sufficient voltage is a ________
twitch
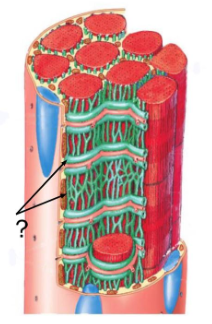
The web-like structure labeled in the diagram is the ________ _________
sarcoplasmic reticulum
What type of contraction occurs when your biceps brachii flexes to pick up a book?
a) Titanic
b) Isometric
c) Isotonic
d) Eccentric
c) Isotonic
Where is most of the calcium stored in a relaxed muscle fiber?
Terminal cisternae of SR
In order for a muscle to contract and shorten, the tension produced by the muscle must _______ the load on the muscle
be greater than
The elastic structures of muscle and tendons, called the ________ __________ __________ must be pulled tight before a muscle contraction can result in shortening
series elastic component
Which of the following will not increase the strength of a muscle contraction in a normal healthy muscle?
a) Frequency of stimulus
b) Size of the motor neuron axon innervating the fiber
c) Diameter of the fiber
d) Increasing the number of fibers stimulated
e) Initial resting length of fiber
b) Size of the motor neuron axon innervating the fiber
During muscle contraction, the majority of ATP is used:
a) or Ca2+ transport during contraction
b) by actin for moving tropomyosin
c) for Ca2+ transport during relaxation
d) by myosin ATPase for contraction
d) by myosin ATPase for contraction
Which of the following are examples of isotonic contractions?
a) Picking up a pencil
b) Trying to lift a car but not succeeding
c) Picking up your leg during walking
a, c
For the first 45-90 seconds of moderate to heavy exercise, skeletal muscles obtain energy:
anaerobically
In muscle, ATP is used:
a) for calcium transport back to the sarcoplasmic reticulum
b) by troponin for moving tropomyosin off of actin's active sites
c) by myosin ATPase to break the bond between actin and myosin
d) by myosin ATPase to energize the myosin cross bridge
e) by calcium release channels to increase sarcoplasm calcium concentrations
a, c, d
When a skeletal muscle experiences a reduction in its ability to produce tension during exercise, the muscle has undergone _________
fatigue
Which of the following will be true of a trained endurance athlete?
a) Lower lactate threshold
b) Increase in aerobic capacity
c) Decreased number of type IIX fibers within muscle
d) Decrease in number of type IIA fibers within muscle
b, c
Satellite cells:
a) proliferate in response to muscle damage
b) are a type of myostatin
c) are stem cells
d) are neuroglial cells that aide in muscle signaling
e) differentiate into myoblasts
a, c, e
What effects will endurance training have on skeletal muscle?
Increase the amount of myoglobin
Increase the number of mitochondria
Improved efficiency in extracting oxygen from the blood
In skeletal muscle, stem cells, also known as ________ cells, located between the myocyte sarcolemma and the basal lamina are activated after injury and fuse with the damaged muscle cell
satellite
Which of the following statements about motor neurons are true?
a) The activation of the gamma neurons enhances the stretch reflex.
b) Alpha motor neuron stimulation of the intrafusal fibers results in the phenomenon called "active stretch" of the spindles.
c) Only stimulation by alpha motor neurons can cause muscle contraction resulting in skeletal movements.
d) Gamma motor neurons conduct faster than alpha motor neurons.
a, c
In muscle, ATP is used:
a) by myosin ATPase to break the bond between actin and myosin
b) for calcium transport back to the sarcoplasmic reticulum
c) by troponin for moving tropomyosin off of actin's active sites
d) by calcium release channels to increase sarcoplasm calcium concentrations
e) by myosin ATPase to energize the myosin cross bridge
a, b, e
Upper motor neurons usually stimulate alpha and gamma motor neurons simultaneously in a process known as ______
coactivation
Lower motor neurons:
a) are interneurons in the brain
b) facilitate or inhibit skeletal movements via their effect on other neurons
c) are the final common pathway in control of skeletal muscle
d) have cell bodies located in the brain stem or spinal cord
c, d
A _____ is an involuntary, stereotypical reaction to a specific stimuli
reflex
Coactivation in muscle involves the simultaneous stimulation of both the _______ and _______ motor neurons so that a muscle can contract while also providing information about its length to the CNS
alpha; gamma
The pyramidal tracts of the brain involved in motor neuron control include the ________, while the extrapyramidal tracts include _______
lateral & ventral corticospinal tracts; reticulospinal tracts
Which types of muscle have sarcomeres and are striated?
skeletal and cardiac
How is contraction initiated in cardiac muscle?
A pacemaker region depolarizes
A reflex:
a) is voluntary
b) produces the same result no matter the original strength of the stimuli
c) is involuntary
b, c
The tracts of the brain involved in motor control of the skeletal muscle include:
extrapyramidal and pyramidal tracts
Skeletal muscle
a) striated, innervated in motor units, multinucleate
b) striated, myogenic, intercalated disks
c) unstriated, no sarcomeres, myogenic
a) striated, innervated in motor units, multinucleate
Cardiac muscle
a) striated, innervated in motor units, multinucleate
b) unstriated, no sarcomeres, myogenic
c) striated, myogenic, intercalated disks
c) striated, myogenic, intercalated disks
Smooth muscle
a) striated, myogenic, intercalated disks
b) striated, innervated in motor units, multinucleate
c) unstriated, no sarcomeres, myogenic
c) unstriated, no sarcomeres, myogenic
Which of the following are true of cardiac muscle but not of skeletal muscle?
a) Undergoes excitation contraction coupling
b) Contracts in motor units
c) The entire myocardium contracts as a unit
d) Signal to contract is passed between cells via gap junctions
c, d
How does smooth muscle differ from skeletal muscle?
The thin filaments in smooth muscle cells are much longer
Smooth muscle does not have sarcomeres.
The myosin in smooth muscle fibers is stacked perpendicular to the length of the cell.
Sarcomere
The functional unit of the muscle containing fibers
Repeating pattern from arrangement of thick and thin filaments between pair of Z lines
How do the H bands and I bands of the sarcomere differ?
The H bands contain only myosin, while the I bands contain only actin
How do the A and I bands change during muscle contraction?
The A band remains the same but slide closer together and the I band narrows
During contraction of a muscle, calcium ions bind to _________
troponin, sliding tropomyosin away and allowing myosin to bind actin
The bond between the actin and myosin head is broken when ________
an ATP molecule binds to the myosin head
Cross bridges form between _________
the actin filaments and the myosin heads
Sprinters working at 100% of their aerobic capacity for 45 seconds obtain most of their energy from _________
muscle glycogen
As a person engages in exercise over several hours, muscle glycogen stores _________
decrease, as exercising muscle utilizes both glucose and free fatty acids for energy
After 3 hours of exercise, what are the main sources of energy?
Blood glucose and plasma free fatty acids
What happens to the amount of plasma-free fatty acids used for energy as exercise continues?
They increase, as stored adipose tissue is hydrolyzed for energy
Where are most plasma-free fatty acids obtained from?
Hydrolysis of stored adipose tissue
Acetylcholine (ACh) is released from motor neurons and enters the ________________
synaptic cleft
Acetylcholine causes an end-plate potential by triggering the ________________
Acetylcholine causes an end-plate potential by triggering the ________________
Toxin that competitively binds to and prevents the opening of acetylcholine receptors located in the membrane of the motor end-plate
curare
The illness, _______ causes muscle paralysis by interfering with the release of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction
botulism
Botulinum toxin causes muscle paralysis because ________________
no acetylcholine enters the synaptic cleft
Facial wrinkles, such as glabellar or “frown” lines, appear with aging as a result of natural, repetitive muscle contractions. Botox® helps alleviate the appearance of these wrinkles by _________________
relaxing the facial muscles that cause the wrinkles
If there was a high concentration of acetylcholine within the synaptic cleft, but little to no response at the motor end-plate, you would expect ________________ to be the responsible neuromuscular-blocking agent
curare
The antidote that holds the most promise to counteract the effects of tubocurarine is one that ______________________
modifies acetylcholine receptors so that they bind acetylcholine stronger than tubocurarine
Hundreds of mutations have been identified in RyR1 that contribute to multiple muscular diseases. Assume that a new mutation was discovered that causes this receptor to continually remain open. Based on what you know about the function of this receptor, how would you expect this new mutation to impact contraction?
This mutation will increase levels of calcium in the sarcoplasm, which will induce continued muscle contraction
If it were possible to move the terminal cisternae further away from the T-tubules, it would _________________________
interfere with the signal required for the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Thin filaments connect to and extend from either side of a ___________. These thin filaments are composed largely of the myofilament __________
Z disc; actin
Myosin heads directly use ______________ to transition to their _____________________ conformation, which enables them ready to bind to actin
ATP; energized
The presence of calcium in the sarcoplasm is directly responsible for __________
exposing the binding sites on actin
Rigor mortis occurs after death because ________________
detachment of cross-bridges does not occur due to the lack of ATP
Myasthenia gravis represents a type of disease called ______
immune-mediated
In the case of _______ _______, antibodies are made that react with the ACh receptor of the muscle cell membrane
myasthenia gravis
The abnormal antibodies made by patients with myasthenia gravis interact with what portion of the motor endplate unit?
Acetylcholine receptors on the muscle cell membrane
A positive _______ _______ would indicate damage to upper motor neurons
babinski sign
What is a monosynaptic reflex?
A neuron path with one synapse
How would antibodies against ganglioside GM1 cause Albert’s symptoms?
Causes demyelination of motor neurons and loss of action potentials to muscles
Which endocrine gland in the body most closely regulates plasma calcium levels?
parathyroid glands
Increased plasma calcium levels will lead to a(n):
increased muscle tone
How do calcium channel blockers help to regulate blood pressure?
They relax the smooth muscle in the blood vessels causing dilation
Elevated creatine phosphokinase levels in the blood indicate there has been:
Muscle damage
Where are the nuclei located?
the cerebrum
Why does the shaking of the limbs tend to disappear when a patient is asked to throw a ball across the room?
The cerebellum is now being used for coordinating the motor movement
Which of the following pharmaceutical agents could help improve symptoms for a Parkinson's patient?
Dopamine agonist
______ _______ ______ is a disease which involves degeneration of the upper and lower motor neurons, leading to skeletal muscle atrophy and paralysis
Amyotropic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
What do most people die from with ALS within 5 years?
Respiratory failure