AP Macroeconomics Semester 1 Exam MCQ
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
please stop. i can't take it anymore. whyyyy.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What is shown on a production possibilities curve?
A graph that shows that if all resources are being used efficiently that you can only produce more of one good by producing less of another good.
What do tariffs cause?
A decrease in demand for a product
What is a comparative advantage?
Being able to produce an item at a lower opportunity cost than another economy.
What is an absolute advantage?
Being able to produce more of an item than another economy
When do both countries have a comparative advantage in trade?
As long as the opportunity costs are different.
Why do individuals and nations engage in trade?
Specialization of production
Each country has a comparative advantage (lower opportunity cost) in producing one item
What is a change in demand?
When a variable other than price changes. The entire demand curve itself shifts left or right
What is a change in quantity demanded?
When price changes. Movement occurs along the demand curve.
An increase in price causes a decrease in (blank)
A decrease in price causes an increase in (blank)
When is a good a substitute or compliment based on whether demand curve shifts left or right after a change in price?
Substitutes: if price & demand have a positive relationship
If Jiffy peanut butter price goes up, I buy more Great Value peanut butter (and vice versa)
Compliments: If price & demand have an inverse relationship
If price of cereal goes down, I buy more milk (and vice versa)
Which curve changes and in what direction if there’s a change in input prices?
If input prices increase, supply shifts left
If input prices decrease, supply shifts right
Where is market equilibrium found?
Where quantity supplied = quantity demanded
What are effects on equilibrium price and quantity when supply or demand curve shifts?
When any curve shifts right: quantity increases
When any curve shifts left: quantity decreases
Demand shifts: price & quantity change the same way
Supply shifts: price & quantity change opposite ways
Supply & Demand shift the same way: quantity changes, price ambiguous
Supply & demand shifts opposite ways: quantity ambiguous, price changes
How do households receive most of their income?
Earned by selling labor (called wages)
What are examples of investment spending?
Tools
Machinery
Equipment used by businesses
What is an example of an intermediate good?
A good that is used to make a final product (ex: wood for a toy box)
What is NOT included in GDP
Black Market Transactions
Volunteer Work
Financial Assets
Used Goods
Intermediate Goods
Transfer Payments
What is the difference between nominal wages & real wages?
Nominal wages: the actual dollar amount you're paid
Real Wages: wages adjusted for inflation
What are the classifications and types of unemployment?
Unemployed: Not currently working, actively looking for a job (ages 16+)
Frictional: Being in between jobs
Structural: More people looking for work than jobs available
Cyclical: Unemployment due to a recession
Discouraged: People who would like to work, but have given up looking
What are effects on unemployment and real GDP during a recession?
Unemployment increases and real GDP decreases
What is inflation?
An increase in price level
What is deflation?
A decrease in price level
What is disinflation
A slower increase in price level
What are effects on planned investment spending from change in interest rates?
High interest rates: Planned investment spending decreases
Low interest rates: Planned investment spending decreases
Why is SRAS upward sloping?
Because wages are sticky in the short run
What is the slope of LRAS and its relationship with the x-axis?
LRAS is vertical and touches the x-axis at potential output
What is stagflation?
Increased unemployment & inflation at the same time
What are short-run changes on a graph of AD and SRAS given a change in one of the curves?
SRAS shifts if economy self corrects
AD shifts due to policy changes or changes in consumer spending, investment spending, or exports (C,I, or X)
What are long-run self corrections for a recessionary or inflationary gap?
SRAS shifts right in a recessionary gap due to lower wages
SRAS shifts left in an inflationary gap due to higher wages
When does a recessionary or inflationary gap occur by definition or from a graph?
Recessionary Gap: output is less than potential output (LRAS right of equilibrium)
Inflationary Gap: output is greater than potential output (LRAS left of equilibrium)
How can expansionary or contractionary fiscal policy be used?
Expansionary: decrease taxes, increase government spending, increase transfer payments
Contractionary: increase taxes, decrease government spending, decrease transfer payments
What was the book and author who transformed the way economists looked at Macroeconomics?
John Maynard Keynes wrote “The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money” in 1936
What is the concept of how the money multiplier occurs?
Real GDP always changes by more than the change in taxes or government spending
What is the equation for multiplier from a change in government spending?
1/(1-MPC)
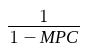
How do you reduce financial risk?
Buy a variety of financial assets (stocks, bonds, loans, bank deposits)
What is the GDP equation?
C+I+G+(X-M)=GDP
C: Consumer spending
I: Investment spending
G: Government spending
X: Exports
M: Imports
What is the relationship between reserve ratio (rr) and the money multiplier and how do you solve a calculation knowing one of them?
1/rr=money multiplier
If given a new amount of demand deposits, multiply by the
money multiplier to see how large the economy can grow
Which institution in the U.S. determines the size of the monetary base and regulates the banking system?
The Federal Reserve
What is the monetary policy tool that involves buying & selling government bonds?
Open market operations
What is the federal funds rate?
the rate banks charge each other for loans
What is the discount rate?
the rate that the Federal Reserve charges banks for loans
Why is the demand curve for loanable funds is downward sloping?
Businesses increase investment spending as interest rates decrease.
What is the crowding out effect?
When an increase in the federal budget deficit causes a decrease in investment spending due to higher real interest rates.
How can the Federal Reserve use expansionary or contractionary monetary policies?
Expansionary: in recessionary gaps to increase the money supply and shift AD right
Contractionary: inflationary gaps to decrease the money supply and shift AD left
How can monetary policy affect AD on a graph?
Expansionary monetary policy: AD shifts right
Contractionary monetary policy: AD shifts left
What is the belief of the classical model regarding a change in the money supply?
An increase in the money supply leads to just inflation with no change in output.
What is shown on a Short-Run Phillips Curve?
An inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation
Interpret a graph of a Short-run Phillips Curve
AD shifts right: upward movement along SRPC
AD shifts left: downward movement along SRPC
SRAS shift left or expected inflation increases: SRPC curve shifts up
SRAS shift right or expected inflation decreases: SRPC curve shifts down
When does a trade surplus occur?
when exports are greater than imports
When does a trade deficit occur?
when imports are greater than exports
What causes a currency to appreciate compared to another currency?
When a currency costs more for another currency to buy 1 of it
If people demand more of a product from that country
What causes a currency to depreciate compared to another currency?
When a currency costs less for another currency to buy 1 of it
If people demand less of a product from that country
Tariffs cause a decrease in demand for a product