Quaternary
2.58Ma
Neogene
2.58-23.03 Ma
Paleogene
23.03-66Ma
Cenozoic
End 66 Ma (Quaternary, Neogene, Paleogene)
Cretaceous
66-145Ma
Jurassic
145-201.3 Ma
Triassic
201.3-251.9Ma
Mesozoic
66-251Ma (Cretaceous, Jurassic, Triassic
Paleozoic
251-541Ma (COSDMPP)
Ordovician
443.8-485.4Ma
Cambrian
485.4-541Ma
Precambrian
541-4600Ma (Proterozoic, Archean, Hadean)
Proterozoic
541-2500Ma
Hadean
4000-4600Ma
Sedmentology
Process oriented
Straitigraphy
Spatial and Temporal variations
Principals of Stratigraphy
Steno
Superposition
Original Horizontality
Original Lateral Continuity
Superposition
in anysequence of undisturbed strata, oldest layer at bottom, and successively younger layers are successively higher
Original Horizontality
states that sedimentary layers were deposited nearly horizontal and parallel to Earth’s surface
Original Lateral Continuity
At the time of depotion, strata extened cont in all directions until they termintated by thinning at the edge of the basin, ended abruptly at a barrier to sedimentation, or graded laterally into a different sediment type
Uniformitarianism
Principle that processes acting upon Earth today have also operated in the geologic past
Fossil (biotic succession
principle that body fossils occur in strata in a definite determinable order
cross cutting relationships
states that a rock unit, sediment body, or fault that cuts another geologic unit is younger than the unit it was cut
Walther’s Law
facies that are found today in vertical sequence are the product of a series of depositional environments which lay laterally adjacent to eachother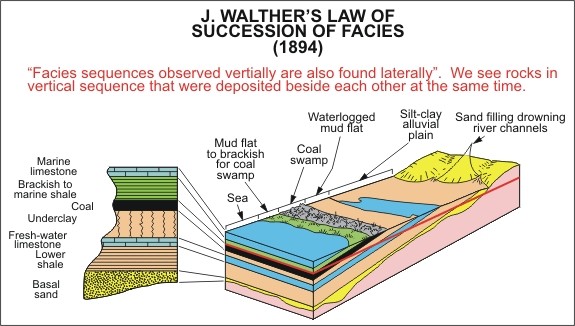
What is info is preserved in sedimentary rocks
Tectonics(internal)
Climate(external)
Sediment Routing System
tectonics+climate=erosions+deposition
Physical weathering
abrasion
insolition(thermal fatigue) and exfoliation
frost wedging and exfoliation
root-wedging
salt-wedging
transport
Chemical weathering
dissolution
hydrolysis
oxidation and reduction
Goldich Stability Series
What controls sedimentation?
amount of material available (erosion)
space available (accommodation space)
preservation potential
why is sed/strat important?
host most natural resources (oil,gas,water)
preserve Earth’s geological history
significant for energy resources, environment, economy
How much of Erath’s exposed rocks are sed
70%
Reynold’s Number
Froude Number
Fr<1
Subcritical
Fr>1
Supercritical
Re>>2000
Turbulent
Re<500
Laminar
Flow Regimine Diagram
Hjulstrom Diagram
How does a particle settle back down?
Function of viscosity, size, shape and density of particles
Stoke’s Law
a single solide sphere settling in a fluid has a terminal settling velocity which is uniquely related to the diameter
Implications of stoke’s law
high density minerals settle more rapidly than low density minerals
slow moving, high viscous fluids can transport courser grained materials more easily than less viscous materials
How do we describe sed rocks?
texture
composition
sed structures
Sandstones
classified according to grain size and composition
Conglomerate
classified according to clast size and composition
composed of >30% of clasts
Pebble size
4-64mm
Cobble size
64-264mm
Boulder size
264+mm
Granule size
2-4mm
Wentworth scale
Laminar flow
flows smooth and streamlined
Turbulent Flow
flows irregular and chaotically
Phi Scale
phi=-log2(d)
fine size: positive
course size : negative
What 3 things affect grain shape
form
roundness( angularity)
surface texture
sorting
measure of the range of grain sizes presnt and the magnitude of the spread around the mean size
Why is grain size and sorting important?
Give us info on physical processes and depositional environments
control oil and gas resivior quality (porosity and permeability)
control groundwater reservior volume
Grain orientation to determine flow direction
clasts supported
orthoconglomerate
when clasts are in contact with eachother and matrix is <20%
Matrix Supported
paraconglomerate
when matrix is >20%
polymictic conglomerate
made of clasts of different compositions
olimictic or monogenic
made of clasts of the same composition
conglomerate naming formula
support+clast type+avg size of clasts+conglomerate
Composition of sandstones
relative proportion of quartz, feldspars and lithics/rock fragments
imbrication
primary depositional fabric
QFL
l=lithics (<62micrometers
QFR
R=rock fragments include all polycrystalline lithic fragments (size bias)
Sediment gravity flows
sediment transported by the effect of gravity acting directly on the sediment or rock
Debris Flow
highly cohesice sediment water mixture drived by its own weight
initiate on slopes >10, flow on slopes <5
Debris flow deposit
poorly sorted
large range of grain size
mud matrix
lack internal layering
base may show evidence of shearing or scouring
either no grading, normal or reverse grading
Turbidity Currents
subaqueous
triggers: earthquake, storm, sediment failure, alignment slopes
turbulence causes sediment to become suspened
creates desnity contrast with surrounding water
flows stop when density contrast is reduced by settling
Turbiditty currents three main parts
head: concentration of courser particles, most intense turbulance, overhanging, velocity slower than body
body: uniform, steady velocity, velocity > haed velocity, feeds head, near uniform thickness, can be area of erosion or deposition
tail: thins rapidly away from body, becomes more dilute, area of deposition
What drives velocity on turbidity currents?
desnity contrast
Turbididte Bouma Sequence E
Massive Ungraded mudstone, possibel bioturbation, pelagic seds
Turbididte Bouma Sequence D
Lower flow regimes planar laminated siltstone
Turbididte Bouma Sequence C
Ripple laminated fine-grained sandstone, flame/convolute lamination
Turbididte Bouma Sequence B
Uper flow regime planar laminated medium grained sandstone
Turbididte Bouma Sequence A
Normally garded sandstone, course grains or rip-up clasts at the base scoured base
liquefied flows
concentarted dispersions of grains in which sedimenrt is supported by upward escape of flow of pore water or by injection of water from below
liquefied flow deposit
thick, poorly sorted sand
identified by fluid escape structures
Grain flow
occur on steep surfaces near angle of repose (30)
cohesion often causes cohesionless sediment to be piled up beyond angle of repose
grain-to-grain contact supports flow
most commonly observed in aeolian environments
deposits difficult to preserve
almost like billiards balls
Carbonate production
material for carbonate sediments is extracted from the dissovled load of the sea or other body of water
what controls carbonate production
light, pH, temperature and nutrients
main areas of carbonate production
carbonate platforms (non-reefs)
organic reef env
slope basin carbonates or carbonate ramps
mixed carbonate siliciclastic systems (non-reef)
light
most important control on skeletal carbonate precipitation because of the dominance of photo-autotrophic arganisms in carbonate productions
carbonate compensation depth
the water depth at which the rate of supply of calcium carbonate from the surface is equal to the rate of dissolution
What controls the CCD?
solubility of calcium carbonate is determined by temperature, pressure and dissolved CO2 in the water
in areas of high productivity, greater rates of supply makes the CCD deeper
increase pH
decrease CaCO3 solubility, deeper CCD, higher T, lower P
What does a Temp increase do to the CCD?
The CCD gets deeper
would you expect a shallower or deeper CCD in areas of upwelling
Deeper
Components of limestone
biogenic
non-biogenic
carbonate minerals (micrite and sparite)
Carbonate Minerals
calcite, aragonite, dolomite
carbonate grains: skeletal and plants
molluscs, stromatolites, nanoplanktos, cephalopods, corals, crinoids, coccoliths, oncoids
nonbiogenic constitients of limestone
ooids( speherical bodies of CaCO3 less than 2mm
poloids (fecal pellets) no cocentric structure
intraclasts- fragments of calcium carbonate material that has been partially lithified and then broken up and reworked to form clasts
carbonate mud- micrite
made of fine-grained calcium carbonate less then 4 micrometers across
they form by chemical precipitation of CaCO2 out of saturated wtaer
Sparry Calcite- sparite
course-grained calcite crystals that appear clear to translucent in plane light
Folk Sequence
relative abundance of 1. carbonate grains or allochems, 2. microcrystallline carbonate mud (micrite) and sparry calcite cement
Dunham Sequence
relative abundance of allochems and micrites or sparite, but does not consider ID of grain
How to decrease CO2
increase temp
decrease pressure
increase CO2 and lower solubility of CO2
photosynthetic organisms
inorganic precipitation
preference for calcite vs aragonite seas
Mg2+ rich seas favor aragonite