2(d) Reactivity series
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
order the metals in terms of reactivity
(anagram)
Please Send Lions, Cats, Monkeys, And Cute Zebras Into Hot Countries, Signed Gordon
Potassium
Sodium
Lithium
Calcium
Magnesium
Aluminium
Carbon
Zinc
(chromium)
Iron
(nickel, tin, lead)
Hydrogen
Copper
(mercury)
Silver
Gold
(platinum)
when metals react with water, what products do they form?
metal + water → metal hydroxide + hydrogen
what happens when potassium, sodium, lithium, and calcium react with water?
potassium: reacts violently
sodium: reacts quickly
lithium: reacts less strongly
calcium: reacts less strongly
what are the equations for potassium, sodium, and lithium reacting in water?
2 K(s) + 2 H2O(l) → 2 KOH(aq) + H2 (l)
2 Na(s) + 2 H2O(l) → 2 NaOH(aq) + H2 (l)
2 Li(s) + 2 H2O(l) → 2 LiOH(aq) + H2 (l)
what is the equation for calcium reacting in water?
Ca(s) + 2 H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq) + H2 (g)
what happens when iron, magnesium, and zinc react with water?
very slow reactions
iron rusts slowly
what common dilute acids can be reacted with metals?
sulfuric acid
hydrochloric acid
when a metal reacts with an acid, what products are formed?
metal + acid → salt + hydrogen
where does a metal have to be in the reactivity series to be able to react with a dilute acid?
above hydrogen
which common metals are used to react with dilute acids?
magnesium
zinc
iron
what are the equations for when magnesium, zinc, and iron react with dilute sulfuric acid?
Mg(s) + H2SO4 (aq) → MgSO4 (aq) + H2 (g)
Zn(s) + H2SO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + H2 (g)
Fe(s) + H2SO4 (aq) → FeSO4 (aq) + H2 (g)
TIP: the metal ions have a charge of 2+, and SO4 has a charge of 2-, which makes it easy to remember why they are used
what are the equations for when magnesium, zinc, and iron react with dilute hydrochloric acid?
Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Fe(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
TIP: the metals ions have a charge of 2+, and Cl has a charge of 1-, which makes 2 the magic number for the acid
what is a metal displacement reaction?
when a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal in a compound
what are 2 examples of metal displacement reactions?
reacting a metal with a metal oxide by heating
reacting a metal with an aqueous solution of a metal compound
describe the reaction of magnesium and copper (II) sulfate (2 details)
the blue colour of the solution fades as colourless magnesium sulfate forms
copper coats the surface of the magnesium and forms a solid metal, which falls to the bottom of the beaker
what are the conditions needed for iron to rust?
water + oxygen
describe an experiment to investigate the conditions for rusting
3 test tubes with iron nails in them
the first has air and water
the second has water but no air (boiled water with a layer of oil on top)
the third has air but no water (calcium chloride to remove water)
the first rusts, the other two do not
what are the three methods of preventing rust?
barrier methods
sacrificial protection
galvanising
how do barrier methods prevent iron from rusting?
what are some examples of barrier methods? (4)
what cons are there to this method?
prevent iron from coming into contact with water and oxygen
paint, oil, grease, electroplating
if coatings are washed away/scratched, the iron is exposed
because rust is porous, if iron starts to rust, it also starts to corrode internally
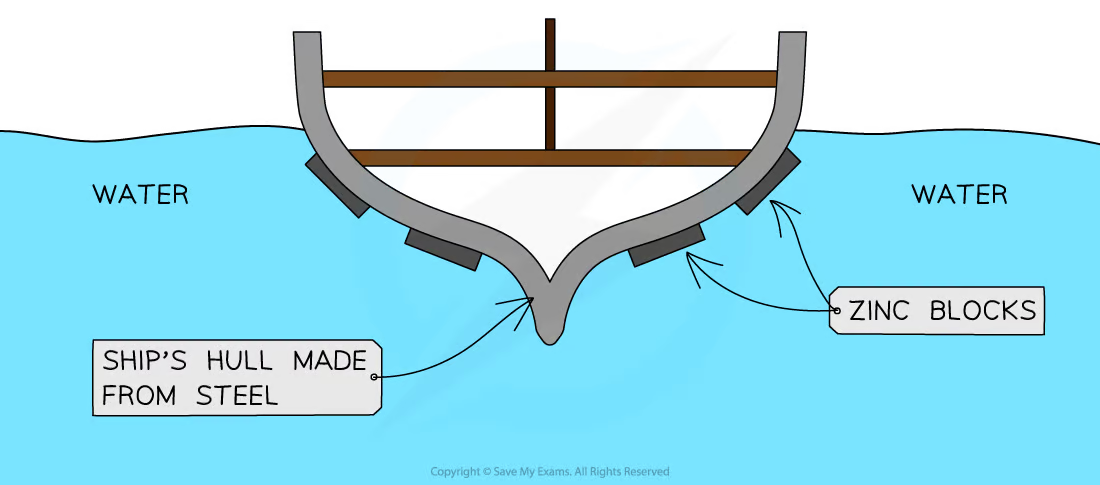
how does sacrificial protection prevent iron from rusting?
where is this type of rust prevention used?
what cons are there to this method?
a more reactive metal (commonly zinc) is attached to a body of iron
the more reactive metal oxidises and corrodes before the iron
ship hulls
the zinc bars have to be replaced before they corrode fully
how does galvanisation prevent iron from rusting?
what type of method is this?
what pros are there to this method?
iron is coated with a layer of zinc, either by electroplating or dipping the object into molten zinc
ZnCO3 is formed when the zinc reacts with oxygen and CO2 in the atmosphere
the ZnCO3 protects the iron
barrier method
if the coating is scratched, the iron is still protected due to sacrificial protection
define oxidation and reduction (not in terms of electrons)
oxidation: when a substance gains oxygen
reduction: when a substance loses oxygen
what type of reaction is one where oxidation and reduction occurs?
a redox reaction
what is the equation for the reaction between zinc and copper oxide? (Zn + CuO)
Zn + CuO → ZnO + Cu
Zn + CuO → ZnO + Cu
what is the oxidising agent in this reaction?
what is the reducing agent in this reaction?
Cu is the oxidising agent, because it supplies oxygen
Zn is the reducing agent, because it takes oxygen
what is the equation for magnesium + copper sulfate in terms of ions? (Mg + CuSO4)
Mg(s) + Cu2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) + Cu(s)
Mg(s) + Cu2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) + Cu(s)
identify the spectator ions in this equation and turn it into an ionic equation
Mg(s) + Cu2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) + Cu(s)
spectator ions appear unchanged on both sides of the equation
Mg(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + Cu(s)
to form an ionic equation, remove the spectator ions
Define oxidation and reduction in terms of electrons
oxidation is loss
reduction is gain
(OILRIG)
Mg(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + Cu(s)
split this ionic equation into two half equations
which element is oxidised and which is reduced?
which element is the oxidising agent and which is the reducing agent?
Mg → Mg2+ + 2e-
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu
Mg is the oxidised, and is the reducing agent
Cu2+ is the reduced, and is the oxidising agent
describe an experiment to investigate metals reacting with dilute acids
what should the results show?
Method:
wear safety goggles (acids)
add 5cm3 of dilute sulfuric acid to 3 test tubes
add a magnesium ribbon to the first, iron filings to the second, and zinc turnings to the third. try and keep their volumes similar
record your observations and test for any gases given off with a lit splint
repeat with dilute HCl
Results:
The results should show that, ranked in reactivity order: Mg > Zn > Fe