Vertebrates 2 - Amphibians
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
ostei vs chond meaning
osteichthyes - boney
chond - cartilage
Swim Bladder - who, function, similar to…
*key innovation of boney fish
flotation device (neutral buoyancy)
regulate gas
homologus to tetrapod lungs (lung is the synapomorphy…one became swim bladder other more developped lung)
two mechanism of gas regulation with swim bladder
gulp air from surface and ‘burp out’ to sink down
gland in bladder that regulates gas internally
Why Tetrapod moved to land
devonian droughts (~400 mya)
high competetion
low dissolved o2
new food resources on land … no predators (insects were there)
3 water and 1 land differences
avaible water and moisture and o2 in water
stability of temp in water
density of medium (kept shape of blobfish) in water
move UV radiation outside
Advantages of Resperating Terristrially
air has higher o2 concentration and gases diffuse faster into body (bc more availbility)
lung evolution
ventral pockets formed off esophogus
used as a supplemental respritory device - still use gills but do this if oxygen insufficient or are at surface…
think about why we choke…lung and airway are connected to same tube where food goes
Problems of Land (4)
Water needed (stay moist and for fertilization and larval development)
Air is less dense than water (require skeletal support and muscles and then more energy and o2)
More variable air temp (need to be able to regulate)
UV radiation more intense - need physical protection or behaviour change
Tiktaalik evidence
from 375 mya
aquatic organism that sometimes went out on land
has homolgus structures to our hand
Ichthyostega
from 365 mya
first tetrapod on land
strong boney structure
proper lung evolved more efficient circulatory system
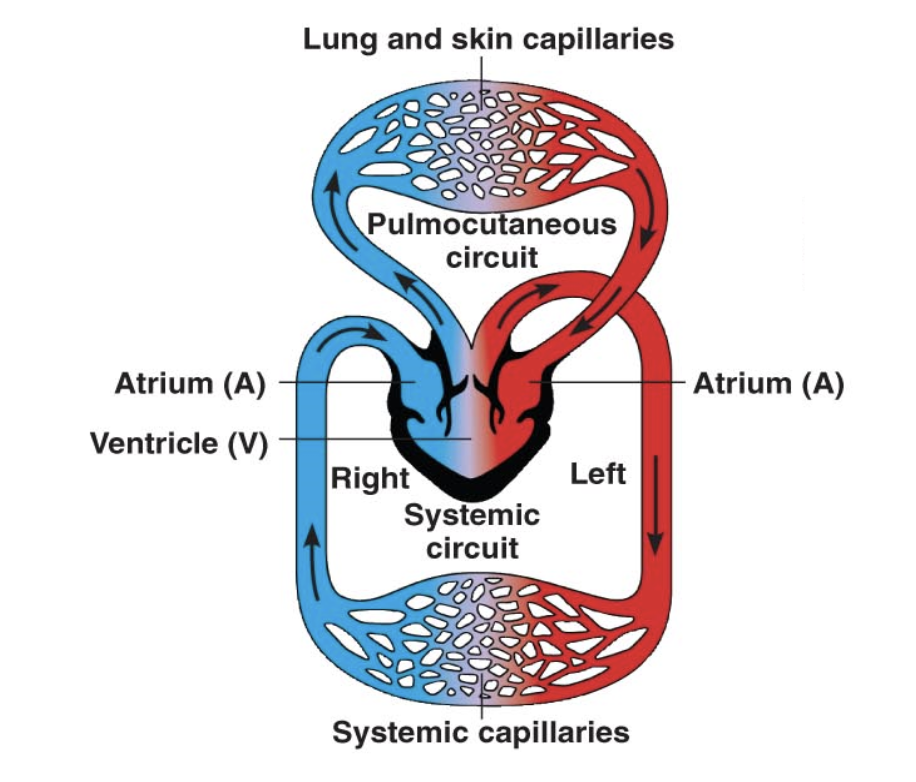
amphibian circulatory system and PROS and CONS
3 chambered heart (2 atrium, 1 ventricle)
blood oxygenated in lungs and skin
double circuit circulation
PRO: blood under higher pressure
CON: blood is mixed
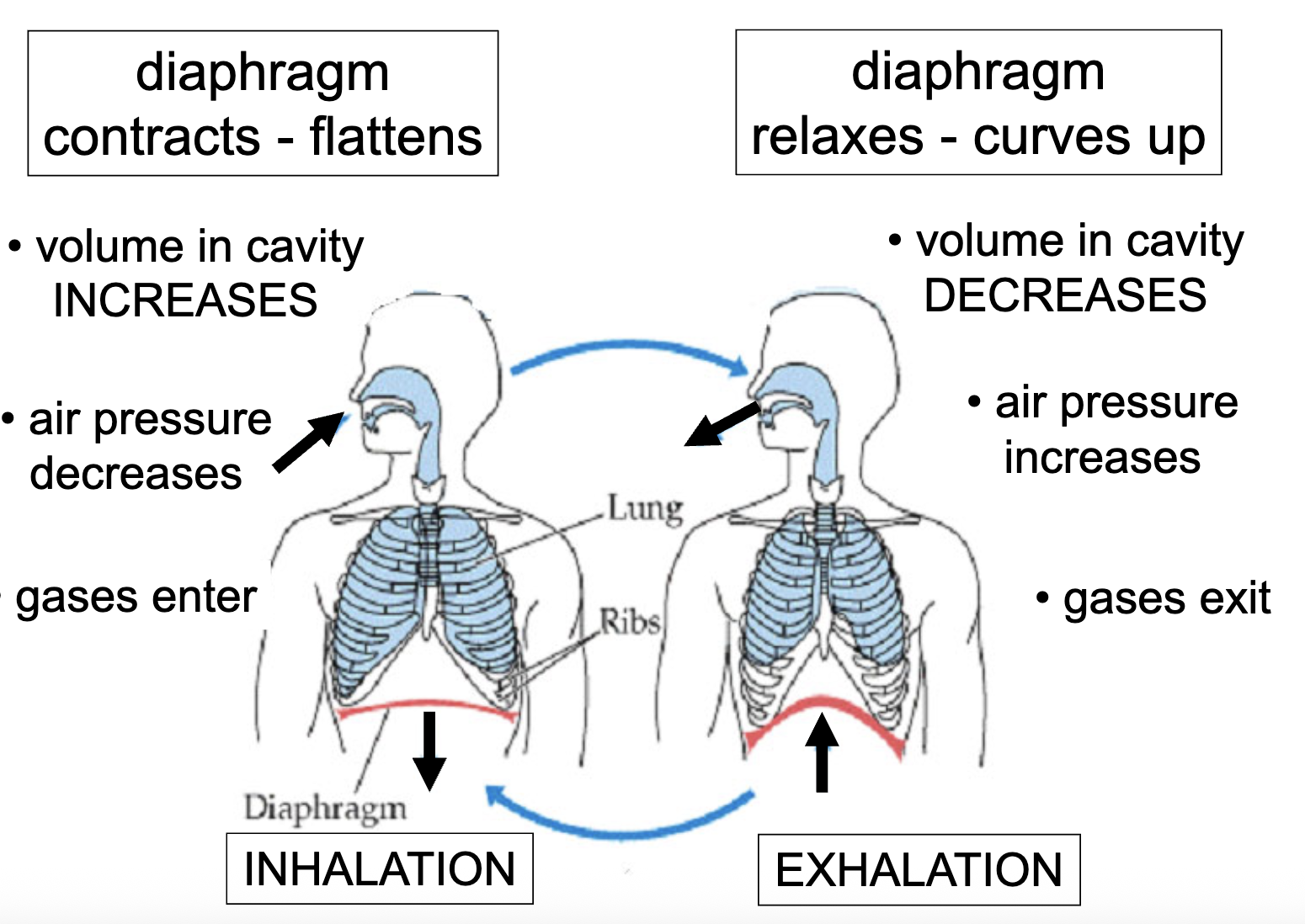
2 Mechanisms of Breathing
apply boyles law of volume and pressure
Negative Pressure breathing (humans) **presure decreases first
Positive Pressure breathing (amphibians) - 2 stroke process
Process of Amphibian breathing
air drawn into nostrils with mouth and glottis closed…causing a pressure increasew
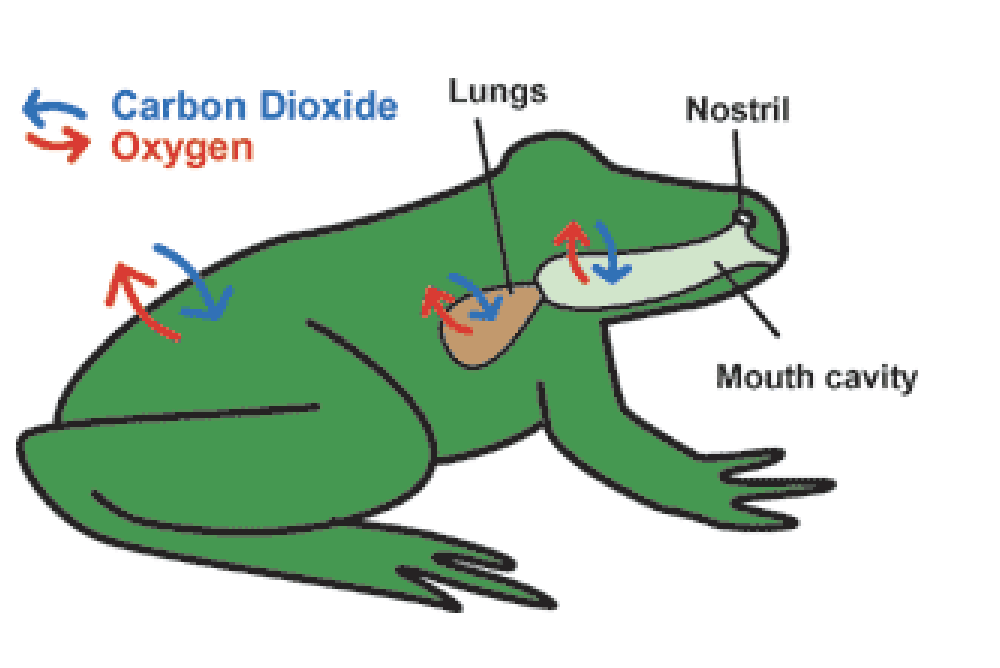
nostrils close, glottis opens and air forced into lungs
Amphibian Traits and Diversity
6000 species
1st tetrapods
freshwater and terristrial (still depend on water)
smooth, moist skin (no scales/glands)
have teeth
have tadpoles!
2 Life Stages of Amphibians
**key innovation
larvae (tadpoles)
have gills, 2 chambered ❤ herbivores, then undergo metamorphsis
adults
have lungs, 3 chambered ❤ , carnivores
3 Groups of Amphibians
Salamanders (Urodela)
internal fertilization…males drop off sperm and females collect
some never leave water
Frogs and Toads (Anura)
most diverse
typically loud courtshipcalls
Caecilians (not a real group but he thinks should be)
loss of apendages
internal fert
eat skin off mom
Parental Investment Strats of Amphibians
range…most provide little parental care…some a lot with reproductive oddities from carrying tadepoles on back to in stomach