part 1 clined TMJ
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What are the parts of the TMJ?
Mandible
Maxilla
Temporal
Sphenoid
Hyoid
Fibrocartilaginous Disk
2 Divisions of the TMJ
● Jaw;supportsthelowerteeth
● Largest & strongest bone in the face
● Suspended below maxilla by muscles and ligaments that provide both mobility and stability
MANDIBLE
Parts of the Mandible?
Condyle
Coronoid Process
A part of the mandible:
○ Posterior ramus
○ Articulates with the temporal bone
CONDYLE
A part of the mandible:
○ Anterior ramus
○ Attachment for temporalis and masseter
Coronoid process
● Contains 32 permanent teeth along with the mandible
MAXILLA
What are the parts of Maxilla?
Superior border
Inferior border
A part of maxilla:
Forms the nasal cavity and floor of each orbit
SUPERIOR BORDER ○
A part of maxilla
○ Forms the palate and the alveolar ridges
● INFERIOR BORDER
● Houses the mandibular fossa which is divided into two surfaces
TEMPORAL
What are the parts of the Temporal?
Articulating surface
Nonarticulating surface
A part of the temporal:
○ Made up of concave mandibular fossa and a convex articular eminence
ARTICULATING SURFACE
A part of the temporal:
○ Consists of a very thin layer of bone and fibrocartilage that occupies much of the superior and posterior walls of the fossa
● NONARTICULAR SURFACE
● The greater wings of the sphenoid bone form the boundaries of the anterior part of the middle cranial fossa
SPHENOID
● “Skeleton of the tongue”
● U-shaped bone serving as attachment for infrahyoid muscles
HYOID
● Found between articulating surface of the temporal bone and the mandibular condyle
FIBROCARTILAGINOUS DISK
What are the 2 divisions of the TMJ?
LOWER COMPARTMENT
Borders: mandibular condyle and inferior surface of the disk
Where osteokinematic spin(rotation) occurs
UPPER COMPARTMENT
Borders: mandibular fossa and superior surface of the articular disk
Allows translation of the disk and condyle
What division is this of the TMJ?
Borders: mandibular condyle and inferior surface of the disk
Where osteokinematic spin(rotation) occurs
lower compartment
What division is this of the TMJ?
Borders: mandibular fossa and superior surface of the articular disk
Allows translation of the disk and condyle
UPPER COMPARTMENT
○ A synovial, condylar, modified ovoid, and hinge type joint formed between the articular eminence of the temporal bone, the intra-articular disk, and the head of the mandible
○ Articulating surfaces covered with fibrocartilage
○ A tri joint complex
● TEMPOROMANDIBULARJOINT
Resting pack position of TMJ
Mouth slightly open, lips together, teeth not in contact
Closed pack position of TMJ
Teeth tightly clenched
Capsular pattern of TMJ
Limitation of mouth opening
Enumerate the ligaments of the TMJ
[CTSS]
CAPSULAR LIGAMENT (JOINT CAPSULE)
TEMPOROMANDIBULAR (LATERAL) LIGAMENT
SPHENOMANDIBULAR LIGAMENT
STYLOMANDIBULAR LIGAMENT
What ligament is this of the TMJ?
○ Surrounds the entire joint
○ Provide proprioceptive feedback
CAPSULAR LIGAMENT(JOINT CAPSULE)
What ligament is this of the TMJ?
○ Restrains movement of the lower jaw
○ Also resists rotation and posterior displacement of the mandible
● TEMPOROMANDIBULAR (LATERAL) LIGAMENT
What ligament is this of the TMJ?
○ Serves as a suspensory ligament of the mandible during wide opening
● SPHENOMANDIBULAR LIGAMENT
What ligament is this of the TMJ?
○ Act as “guiding” restraints to keep the condyle, disc, and temporal bone firmly opposed
● STYLOMANDIBULAR LIGAMENT
What are the muscles of the TMJ?
TEMPORALIS
INTERNAL (MEDIAL) PTERYGOID
MASSETER
EXTERNAL (LATERAL) PTERYGOID
What muscle is this of the TMJ?
○ Action: mouth closing (mandibular elevation) and side-to-side grinding of the teeth
● TEMPORALIS
○ Action: (bilateral) assists temporalis and masseter with mouth CLOSING
○ (Unilateral) DEVIATION OF MANDIBLE to the opposite side
○ Assists lateral pterygoid and temporalis in the PROTRUSION of the mandible
● INTERNAL(MEDIAL)PTERYGOID
○ Action: mouth closing occluding the teeth during mastication
● MASSETER
○ Action: mainly chewing
○ Jaw opening (mandibular depression)
○ Deviation of the mandible to the opposite side
● EXTERNAL (LATERAL) PTERYGOID
TMJ BIOMECHANICS
The TMJ has 3 DOF
PRIMARY ARTHROKINEMATIC MOVEMENTS:
_____
_____
_____: Gliding, translation, or sliding movement
_____: Rotation or hinge movement
TMJ BIOMECHANICS
The TMJ has 3 DOF
PRIMARY ARTHROKINEMATIC MOVEMENTS:
Rotation
Anterior translation
UPPER CAVITY: Gliding, translation, or sliding movement
LOWER CAVITY: Rotation or hinge movement
What are the phases in Mouth Opening (Mandibular depression)?
EARLY PHASE (ROTATION > TRANSLATION)
LATE PHASE (TRANSLATION > ROTATION)
What phase is this?
○ Mandibular condyle rolls anteriorly about the articular disc within the mandibular fossa (condylar anterior rotation), causing downward rotation of the mandible
○ Slight anterior translation of the mandible
● EARLY PHASE (ROTATION > TRANSLATION)
What phase is this?
○ Very little downward condylar rotation
○ Mandibular condyle slides anteriorly on the articular disc relative to the mandibular fossa
○ Movement puts tension on the articular disc
● LATE PHASE (TRANSLATION > ROTATION)
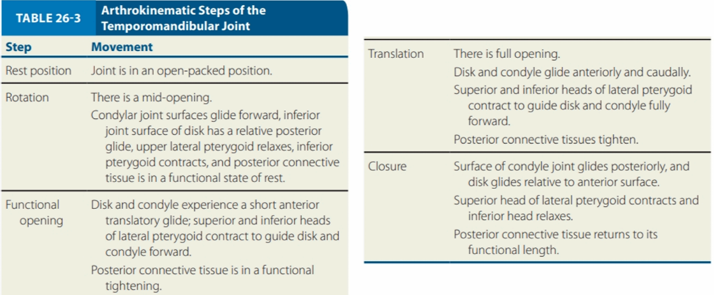
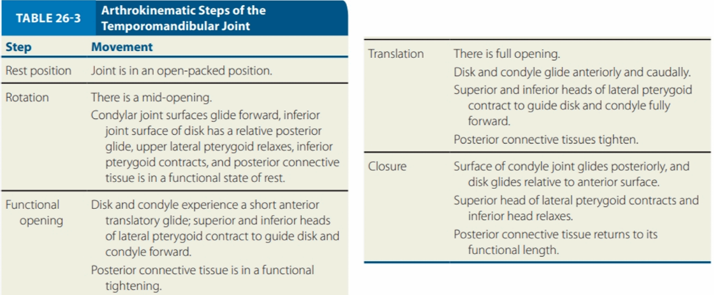
ARTHROKINEMATIC STEPS OF THE TMJ
Movement:
Joint is an open-packed position
Resting position
ARTHROKINEMATIC STEPS OF THE TMJ
Movement:
There is a mid-opening
Condylar joint surfaces glide forward, inferior joint surface of disk has a relative posterior glide, upper lateral pterygoid relaxes, inferior pterygoid contracts, and posterior connective tissue is in a functional state of rest
Rotation
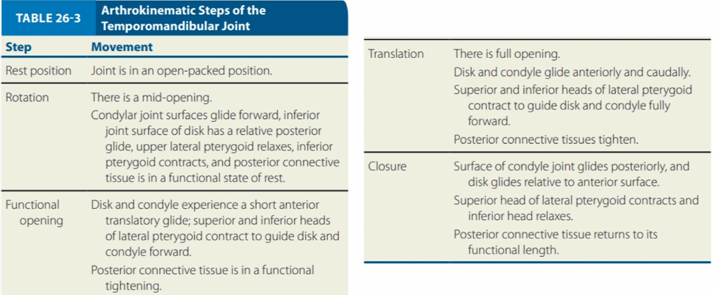
`
ARTHROKINEMATIC STEPS OF THE TMJ
Movement:
Disk and condyle experience a short anterior translatory glide; superior and inferior heads of lateral pterygoid contract to guide disk and condyle forward
Posterior connective tissue is in a functional tightening
Functional Opening
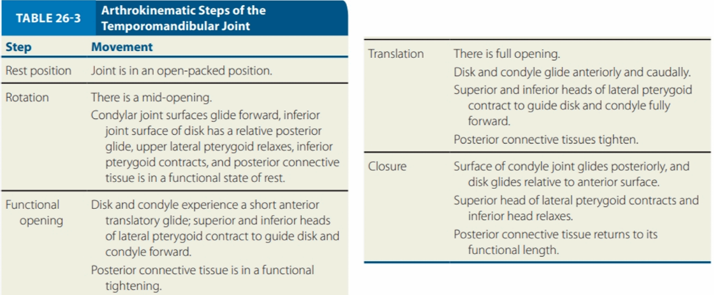
`
ARTHROKINEMATIC STEPS OF THE TMJ
Movement:
There is full opening
Disk and condyle glide anteriroly and caudally.
Superior and inferior heads of lateral pterygoid contract to guide disk and condyle fully forward
Posterior connective tissues tighten
Translation
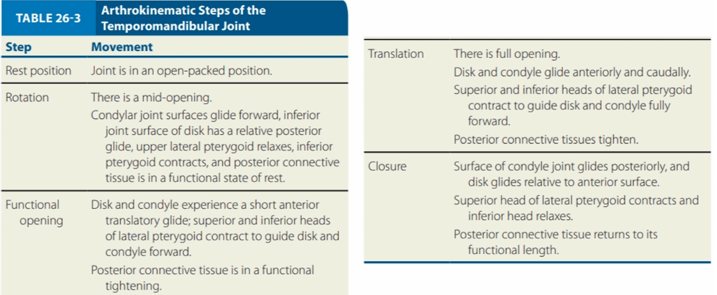
`
ARTHROKINEMATIC STEPS OF THE TMJ
Movement:
Surface of condyle joint glides posteriorly, and disk glides relative to anterior surface
Superior head of lateral pterygoid contracts and inferior head relaxes
Posterior connective tissue returns to its functional length
Closure