Psychology 3 - 4
1/137
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
What sections is the brain divided into?
Hindbrain, Midbrain, Forebrain.
What systems is the Peripheral Nervous System made up of?
The Somatic Nervous System and The Autonomic Nervous System.
What is the Peripheral Nervous System?
All nerves that lie outside the brain and spinal cord.
What is The Somatic Nervous System?
Nerves that connect to voluntary skeletal muscles and to sensory receptors.
What are the nerve fibers in the Somatic Nervous System?
Afferent nerve fibers (Incoming) to the brain.
Efferent nerve fibers (Outgoing) from the brain.
What is the Autonomic Nervous System?
Nerves that connect to the heart, blood vessels, smooth muscles, and glands.
What two divisions lie within the Autonomic Nervous System?
Sympathetic Division and Parasympathetic Division.
What is the role of the Sympathetic Division? Give an example.
Mobilizes the body’s resources for emergencies.
Ex: Fight or Flight
What is the role of the Parasympathetic Division?
Give an example.
Conserves bodily resources.
Ex: There is no danger so the body is operating as normal.
What is The Central Nervous System?
Brain and Spinal Cord.
Where is the Spinal Cord and what is its function?
Starts at the base of the brain and goes down just below the waist.
Connects brain to the rest of the body through The Peripheral Nervous System.
Where is the brain and what is its function?
Fills the upper portion of the skull.
Contains billions of interacting cells that integrate info inside and outside of the body.
What is the function of Cerebrospinal Fluid?
Nourishes brain and provides protective cushion for it.
What lies inside the Hindbrain?
Medulla, Pons, and Cerebellum.
What is the function of The Medulla?
Controls largely unconscious unconscious but essential functions.
What is the Medulla considered to be?
Considered to be primitive because it does not have any higher brain function.
What is the function of The Pons?
Controls sleep and arousal.
What is the function of The Cerebellum?
Controls fine muscle movement and balance like typing and writing.
What is the function of the Midbrain?
Integrates sensory experiences.
Where does The Reticular Formation and what is its function?
Partially in The Hindbrain and partially in The Midbrain.
Regulates sleep and wakefulness.
What is the Forebrain and what lies inside it?
The largest and most complicated region of the brain.
Contains: The Thalamus, The Hypothalamus, The Limbic System, The Amygdala, The Cerebrum, The Cerebral Cortex, The Cerebral Hemispheres, The Corpus Callosum, and The Temporal Lobe.
What is the function of The Thalamus?
Structure through which all sensory info (except smell) must pass to get to the cerebral cortex.
What is the function of the Hypothalamus?
Regulates basic biological needs. (Hunger, Thirst, Temperature Control)
What lies within the Limbic System?
Not a defined area; Includes thalamus, hypothalamus, and amygdala.
What is the function of the Amygdala?
Where emotions (Fear) and Pleasure as stored.
What is the Cerebrum?
Largest, most complex part of the human brain.
What is the Cerebral Cortex?
Convoluted outer layer of The Cerebrum.
What are the Cerebral Hemispheres?
Right and Left halves of The Cerebrum.
What is the Corpus Callosum?
Structure that connects the two Cerebral Hemispheres.
What is the function of The Temporal Lobe?
Processes info related to hearing and some aspects of language.
How are experiences and brain structure related?
Aspects of experience can sculpt features of Brain Structure.
What can lead to Neural Reorganization?
Damage to incoming Sensory Pathways or destruction of Brain Tissue.
What can The Adult Brain do?
Generate New Neurons.
What is Neurogenisis?
The formation of New Neurons.
What problem occurs if the Corpus Callosum is severed?
Hemispheres communicate with the Corpus Callosum, so if it is severed the two halves don’t communicate.
What is the primary function of the Left Hemisphere?
Involved in Verbal Tasks. (Language, Writing, Mathematics)
What is the primary function of the Right Hemisphere?
Involved in Spatial Tasks. (Art, Music, Creativity)
How does The Right Hemisphere of the brain function if The Corpus Callosum is severed?
The Right Brain can see an object, but can’t say what the object is.
How does The Left Hemisphere of the brain function if The Corpus Callosum is severed?
The Left Brain can read a word and recognize the word, but cannot draw the word.
How are the two hemispheres wired to the body?
What goes to The Right Hemisphere goes to the left side of The Body and what goes to The Left Hemisphere goes to the right side of The Body.
What is the Endocrine System comprised of?
Hypothalamus, Pituitary Gland, Thyroid Gland, Thymus Gland, Adrenal Gland, Pancreas, Kidneys, and Reproductive Organs.
What is the relationship between The Hypothalamus and The Pituitary Gland?
The Hypothalamus controls The Pituitary Gland.
What is the function of The Pituitary Gland?
It’s the Master Gland and tells the other glands how to function.
What is the function of The Endocrine Glands?
To Secrete Hormones into the Blood Stream.
What is the function of The Thyroid Gland?
Controls Digestion (Turns Food into Energy).
What is the function of The Thymus Gland?
Controls The Production and Maturation of Immune Cells.
What happens when The Thymus Gland doesn’t function properly?
A person with an improperly functional Thymus Gland will have an Immune Disease.
What is the function of The Pancreas?
Regulates the amount of Sugar in the Blood.
What happens when The Pancreas doesn’t function properly?
A person with an improperly functional Pancreas will have a disease like Diabetes.
What is the function of The Kidneys?
Removes Waste from The Body.
What is the function of The Reproductive Organs?
Produce Estrogen and Testosterone.
What is the relationship between Sight and Light Waves?
What we see travels in light waves.
What do Wavelengths Determine for sight?
Color (Hue).
What does Amplitude Determine?
The brightness or dullness of color.
What does Purity determine?
The Saturation of color.
What are the Characteristics of Light Waves?
Wavelengths, Amplitude, Purity.
What structures make up The Eye?
Cornea, Iris, Pupil, Lens, Retina, Optic Nerve, Cones, Fovea, and Rods.
What is The Cornea?
A Transparent window at the front of The Eye.
What is the Iris?
A colored Ring of Muscle surrounding The Pupil. (It is Blue in Color)
What is the function of The Lens?
Soft Tissue capable of Adjustments that facilitate accommodation, which determines Visual Focus.
What is The Retina and what is its function?
Neural Tissue Lining the inside back surface of The Eye.
Absorbs light, Processes Images, and sends Visual Info to The Brain.
What is the function of the Optic Nerve?
A collection of Axons that connect The Eye to The Brain light signals turned into Nerve Impulses.
What is the function of The Cones?
Plays a role in Daylight Vision and Color Vision.
What is The Fovea?
A tiny spot in the Center of The Retina.
What is the function of The Rods?
Plays a role in Night Vision and Peripheral Vision.
What is Nearsightedness?
Occurs when The Eye is too long and the Focus of Light falls in front of The Retina. Distant Objects are blurry.
What is Farsightedness?
Occurs when The Eye is too short and the Focus of Light falls behind The Retina. Close Objects are blurry.
What is Dark Adaptation?
Process where Eyes become more Sensitive to light in Low Illumination.
What is Light Adaptation?
Process where Eyes become less Sensitive to light in High Illumination.
How does Info get Processed in The Retina?
Light strikes Rods and Cones. The Light goes through Bipolar and Ganglion Cells. Signals go to The Optic Nerve and depart The Eye through The Optic Disk. Axons leave the back of each eye from The Optic Nerves which travel to The Optic Chasm. Visual Input Arrives in Primary Visual Cortex in Optical Lobe.
What is Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic Theory?
The Human Eye (Retina) has three types of Receptors with Sensitivity to Wave Lengths of Red, Blue, and Green.
What do followers of Trichromatic Theory believe?
That any Color can be created by combining Light Waves of The Three Primary Color (Red, Blue, and Green).
That when Light stimulates Combination of These Cones, we can see other Colors.
Ex: Color TV.
What is Opponent Process Theory?
Color Perception depends on Receptors that make Antagonistic responses to Three pairs of Colors.
What do followers of Opponent Process Theory believe?
Complementary Colors and Afterimage.
What are Complementary Colors?
Pair of Colors that produce Gray Tones when mixed.
What is Afterimage?
Visual Image that persists after a Stimulus is removed.
What is Reversible Figure?
A Drawing compatible with two different Interpretations that shift back and forth.

What is Perceptual Set?
Readiness to perceive Stimuli in a particular way.
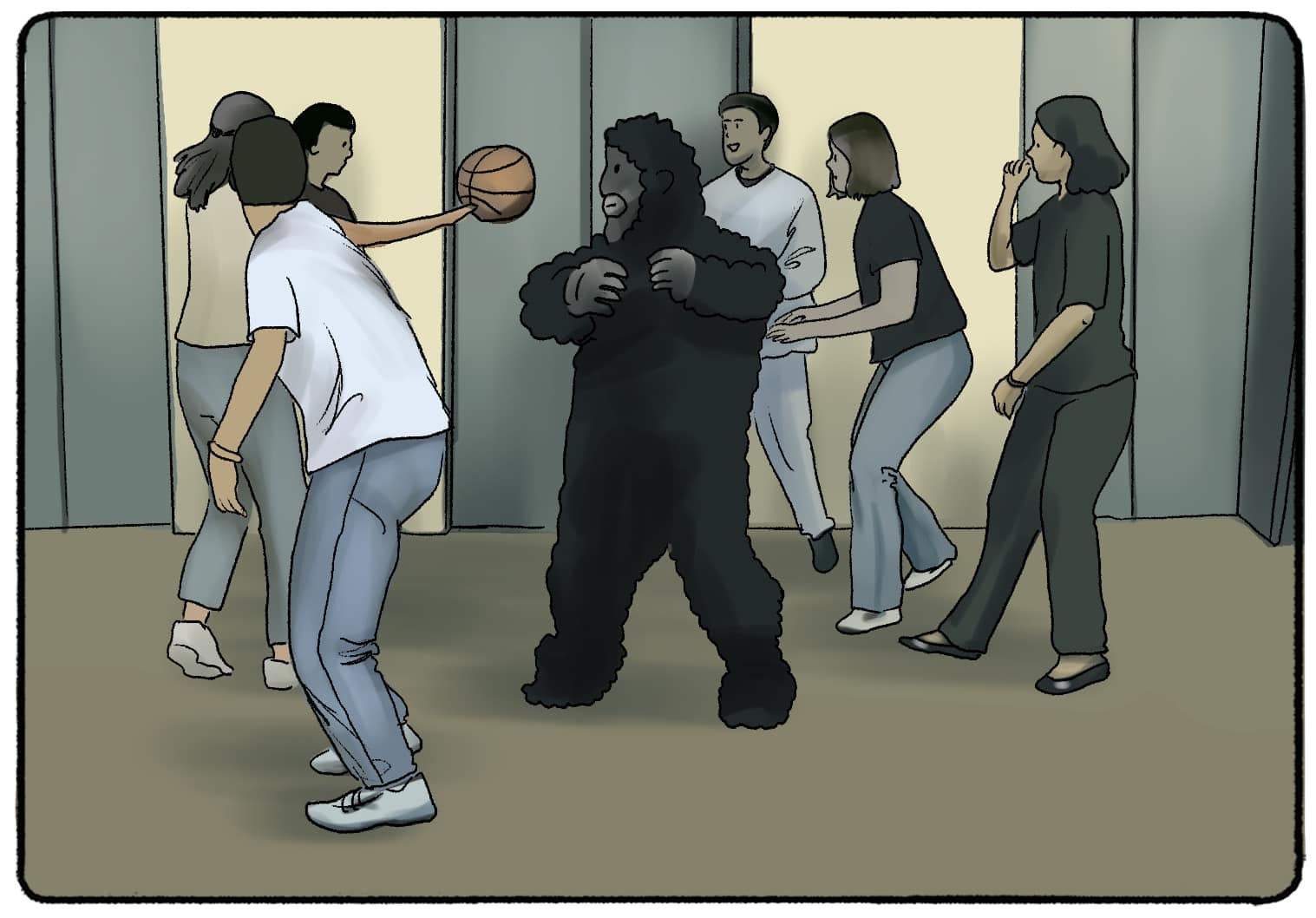
What is Inattentional Blindness?
Failure to see a fully Visible object in a Visual Display because your attention was some where else.

What are the Gestalt Principles?
Principle of Proximity, Principle of Closure, Principle of Similarity, Principle of Simplicity, Principle of Continuity, Principle of Phi Phenomenon, and Principle of Figure and Ground.
What is The Principle of Proximity?
Elements that are close together tend to be grouped together.
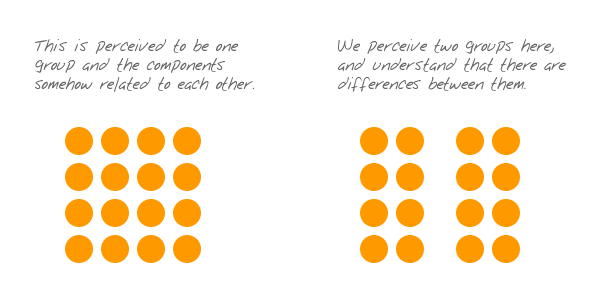
What is the Principle of Closure?
Viewers tend to supply missing elements to close or complete a Familiar Figure.

What is the Principle of Similarity?
Elements that are similar tend to be grouped together.
What is the Principle of Simplicity?
Viewers tend to organize elements in the simplest possible way.
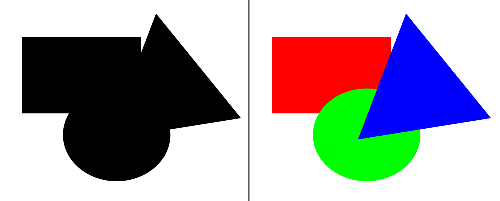
What is the Principle of Continuity?
Viewers tend to see elements in ways that produce continuation?

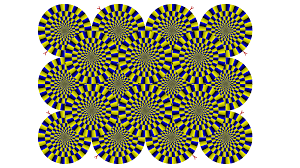
What is the Principle of Phi Phenomenon?
Illusion is created by presenting visual stimuli in rapid succession.
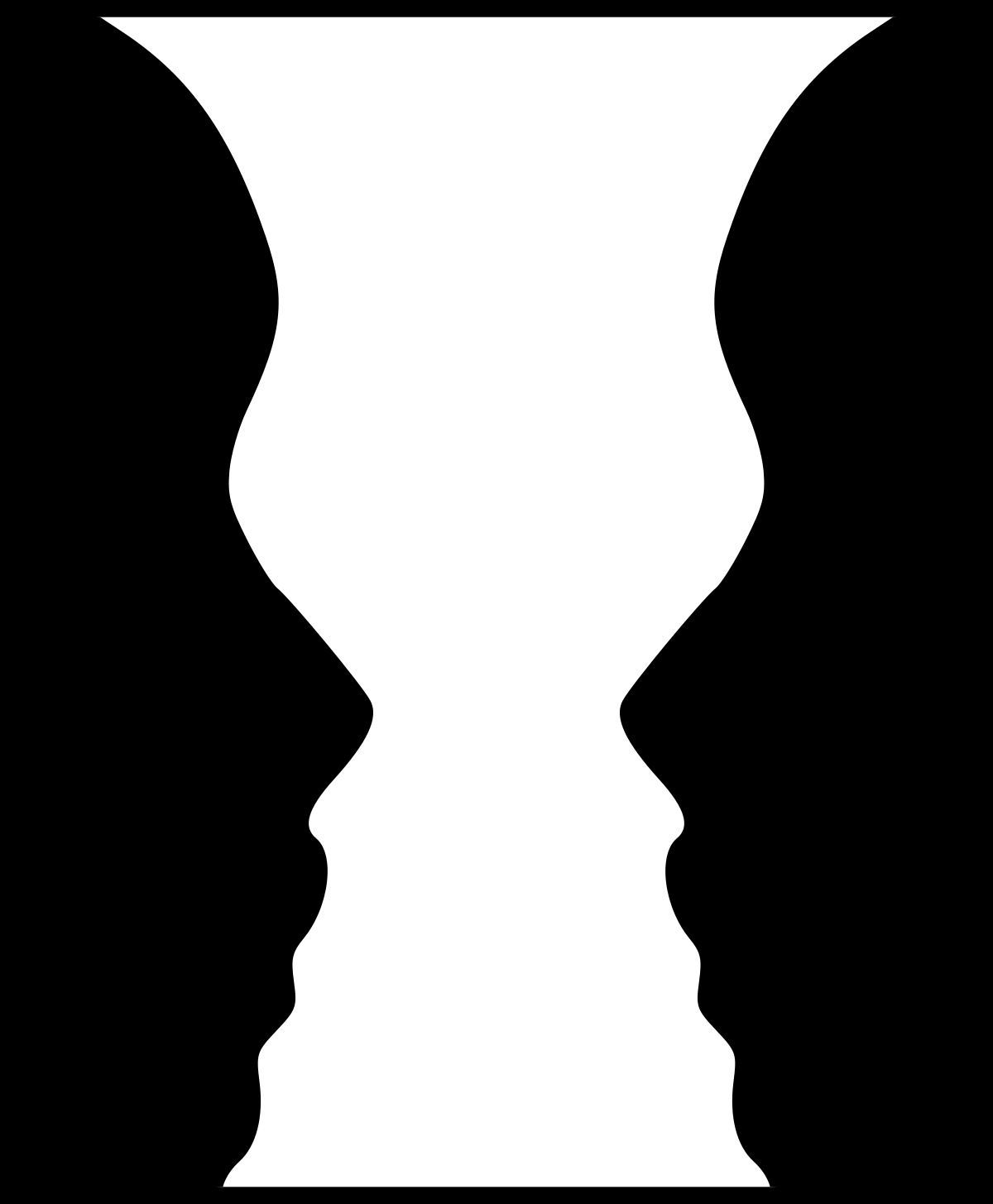
What is the Principle of Figure and Ground?
Whether you see a form as the thing being looked at or the background against which it stands.
What is Depth Perception?
Indicates How Near or Far an Object is.
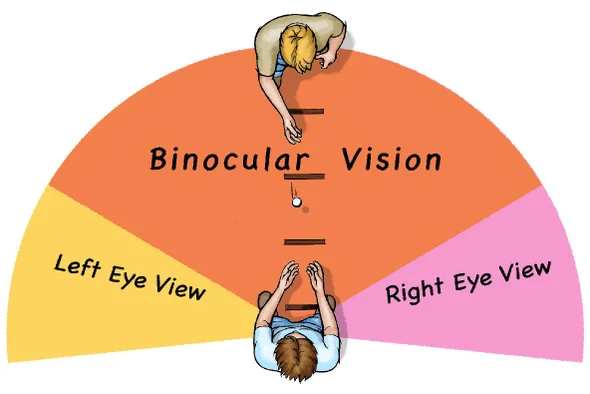
What are Binocular Depth Cues?
Cues about Distance due to differing Views of the two eyes.
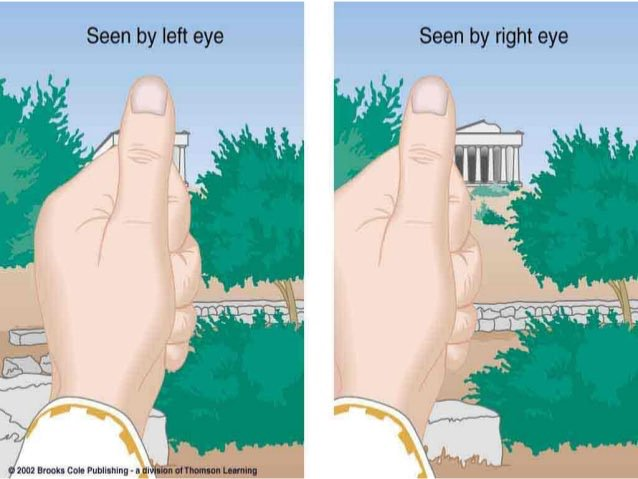
What is Retinal Disparity?
Objects with 25ft. project images to different locations on the right and left Retinas. (Different views of an Object).
Whare are Monocular Depth Cues?
Cues about Distance based on the image from either Eye by itself. (Relative Height, Relative Size, Shadows).
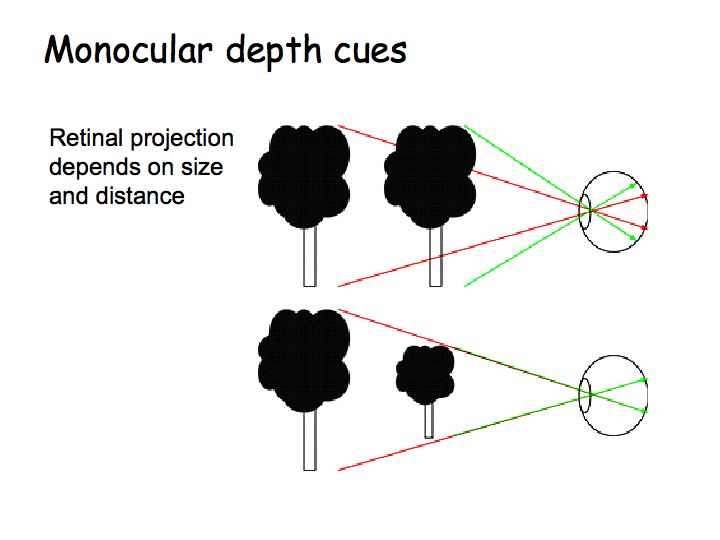
What are Pictorial Depth Cues?
Cues about distance given in a flat picture.

What are Papillae and how many are there?
Tiny Bumps on The Tongue with Taste Buds inside of them.
There are three types.
What are the four different tastes that tastebuds can recognize?
Sour, Sweet, Salty, Bitter.
How does taste get processed?
Taste Cells convert to neural impulses and sent to The Frontal Lobe.
How does smell get processed?
Travels from The Olfactory Cilia to The Olfactory Axons in the Olfactory Bulb where smell gets converted into neurons.
What is special about smell?
Smell bypasses The Thalamus and goes straight to the Temporal Lobe.
What is Psychical Stimuli?
Touch Consists of energy that comes in contact with skin, producing perceptions of tactile stimulation, warm, cold, and pain.
What is the relationship between The Thalamus and Nerve Fibers?
Nerve Fibers carrying info about tactile stimulation run through The Thalamus.
How does The Human Body’s pain warning system function?
Receptors are free nerve endings in the skin.
There are two pathways to The Thalamus. (One for life threatening pain and one for subjective pain)
Cognitive and emotional processes may block pain signals (Pain is Subjective)