da meow bio/biochem
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
what kind of cells have cell walls?
ALL prokaryotic cells
SOME eukaryotic cells
what cells have peptidoglycan?
Bacteria, specifically prokaryotic cells, comes w cell wall
neurotransmitter pathway pre-post ganglion for sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons
SYMPATHETIC: ACh, norepinephrine
short, long
PARASYMPATHETIC: ACh, ACh
long, short
total gametes produced in a single cycle of spermatogenesis and oogenesis
spermatogenesis:
4 haploid sperm cells
oogenesis:
1 haploid ovum, 2-3 polar bodies
what is transformation
Transformation is the process by which a cell takes up foreign DNA from its environment, resulting in genetic change. This mechanism is commonly observed in bacteria.
what is transduction
Transduction is the process by which a virus transfers genetic material from one bacterium to another, facilitating genetic variation and adaptation. This mechanism often involves bacteriophages, which infect bacterial cells.
what is conjugation
Conjugation is the process by which two bacteria connect and transfer genetic material through a direct physical connection, often via a sex pilus. This process promotes genetic diversity and can involve plasmids.
can include f factor (fertility plasmid)
disulphide bond are present in which protein structure(s)?
tertiary and quaternary
dehydration synthesis
formation of peptide bond by removing water
western blotting
separate proteins based on size and charge
vmax=
vmax = kcat[e]
size exclusion chromatography separates molecules by
LARGE molecules = cannot go through pores = EASILY pass through column
SMALL molecules = get stuck in pores = SLOWLY pass through column
pH range of an amino acid using henderson hasselbach equation
pH = pKa + log [deprotonated]/[protonated]
ONLY in ionizable amino acids: HER DYCK
reducing sugars: monosaccharides vs disaccharides
MONO = always
DI = ONLY if 1 of the anomeric carbons is not involved in a glycosidic bond
tollens test (silver mirror)
positive = aldehydes present
make COOH
function of PFK-2 in relation to glycolysis n gluconeogenesis. (mention PFK-1 and Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase)
converts: F6P —> F-2,6-bisphosphate
this ACTIVATES glycolysis = allosterically regulate PFK1
INACTIVATE gluconeogenesis = stop F-1,6-bisphosphatase (RLS)
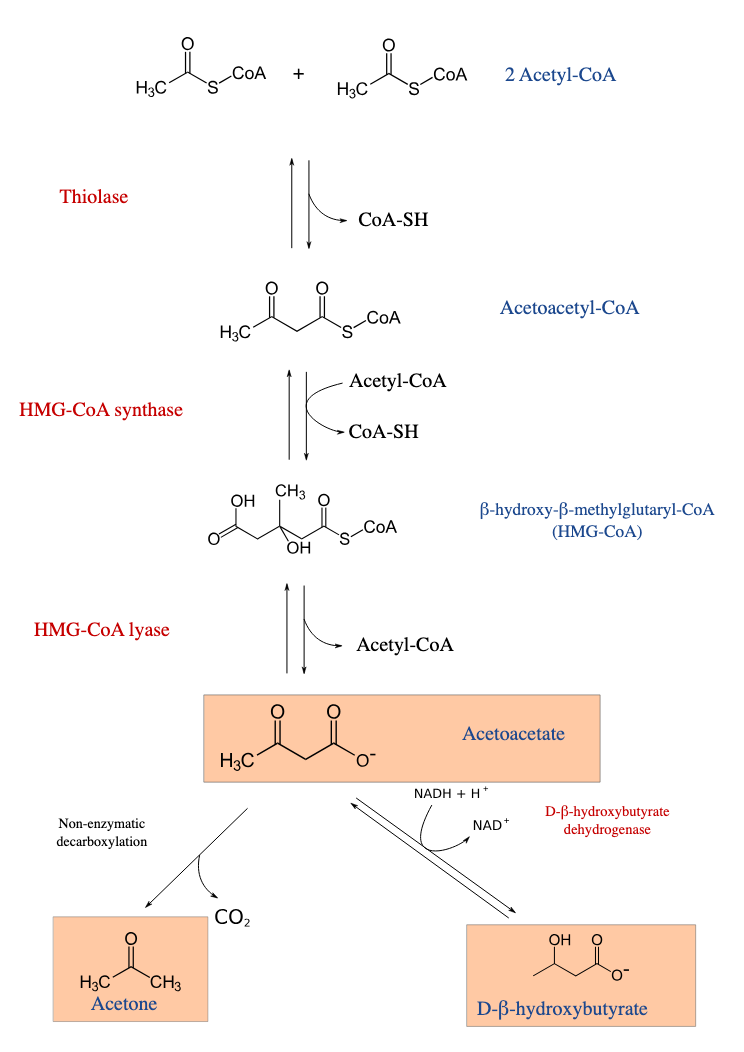
explain ketogenesis
2 a-CoA —> via thiolase —> acetoacetyl-CoA
via HMG-CoA synthase —> HMG-CoA (adding another a-CoA)
via HMG-CoA lyase —> acetoacetate
can do one of two things: decarboxylate to ACETONE
reduce to β-hydroxybutyrate
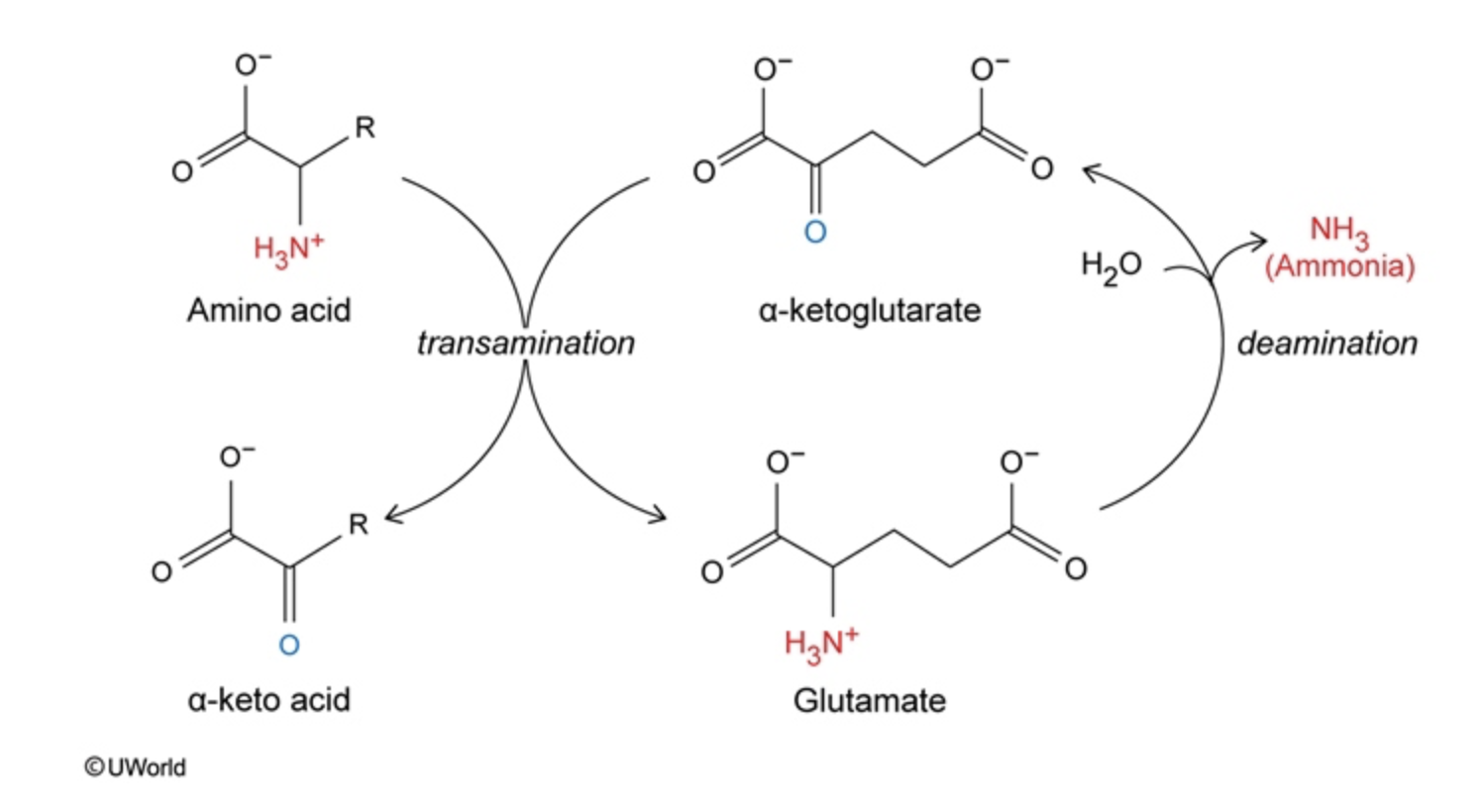
transamination pathway
amino acid + alpha ketoglutarate —> alpha keto acid + glutamate
give amino group from amino acid to alphaketoglutarate, give a carbonyl to amino
e.g. alanine n pyruvate, aspartate n OAA
what conditions will cause the LONGEST reannealing time for DNA
long strands
LOW pH = h-bond ACCEPTORS protonated, HIGH pH = h-bond DONORS deprotonated
ionic strength: LOW [salt] = LOW stability
ATCG hydrogen donors and acceptors
AT or AU = 1 donor n 1 acceptor each
CG = GUANINE 2 donors (give) 1 acceptor, cytosine 2 acceptors 1 donor
difference between structure of ribose vs deoxyribose pentose sugars
RIBOSE = OH at 2’ carbon
DEOXYRIBOSE = H atom at 2’ carbon
what direction does dna polymerase move
moves 3’ to 5’
makes strands 5’ to 3’
what does it mean if exonuclease activity is only 3’ to 5’ on growing strand
means nucleotide bases on 3’ are repaired, not 5’ end
endonuclease vs. exonuclease
ENDO = cut into middle of backbone, break phosphodiester bonds. dimers, mismatch repair
EXO = only remove LAST nucleotide, e.g. DNA polymerase correcting as it goes
telomeres n ____ are made of _____
centromeres
made of heterochromatin (tightly condensed complex of DNA wrapped tightly around histones)
native, reducing, n non-reducing SDS page
REDUCING: using DDT, it reduces disulfide bonds and breaks quaternary structure
NONREDUCING: disulfide bonds intact, breaks quaternary structure, use polyacramide gel
NATIVE: disulfide bonds intact, quaternary structure intact, separates proteins by mass, charge and polarity
histones are rich in these 2 amino acids
arginine R
lysine K
makes histone POSITIVE so it can attract NEGATIVELY charged DNA
methylation = HETEROCHROMATIN, brings closer together
acetylation = EUCHROMATIN, unwinds histone
during repolarization, Na+…
Na+ INACTIVATION gates = closed, prevents reentry into membrane
K+ channel = open, ions leave cell membrane
peptide hormones
FLAT PEG, receptors ON cell membrane, soluble in water but cannot cross phospholipid bilayer
posterior pituitary neurohormones
NOT typical glandular cells, derived from NEURAL tissue at ectoderm
made in hypothalamus, stored into neurosecretory neuron axons going into PP, released by exocytosis into blood
neutrophils
usually in blood circulation
phagocytosis of bacterial cells, INNATE immune system
basophils
histamine
help mast cells, anti allergen
eosinophil
release toxins that kill bacteria/parasites, lead to tissue damage
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm results
ECTODERM: nervous system, hair, skin, nails, anus, mouth
MESODERM: bones, muscles, circulatory system, urinary/reproductive
ENDODERM: digestive n respiratory systems, epithelium lining
stop codons
UAG
UGA
UAA
RBC vs. WBC leukocytes location of production
RBC = renal cortex kidney
WBC = bone marrow
____ anchor MUSCLE to BONE
tendons
hyaline cartilage 4 fun facts
avascular n receives nutrients via surrounding fluids
endochondral ossificiation aka helps make bone (deposition), linear bone growth at epiphyseal plate in childhood
no nerves, lacks innervation
faciliatates joint movement
in bones: epipysis vs diaphysis, spongy vs compact bone
EPI: at the ends of long bones, surrounded by articular cartilage
DIAPH: hollow shaft aka medullary cavity filled w yellow bone marrow
SPONGY: has trabeculae, porous, red bone marrow
COMPACT: aka cortical, harder outer layer, beneath periosteum
despite beta sheets or alpha helix, secondary structures always have ____ bonds
HYDROGEN BONDS between amide n carbonyl
western blot steps
protein electrophoresis
protein transfer
addition of blocking protein
addition of primary antibodies, then secondary
fluorescence
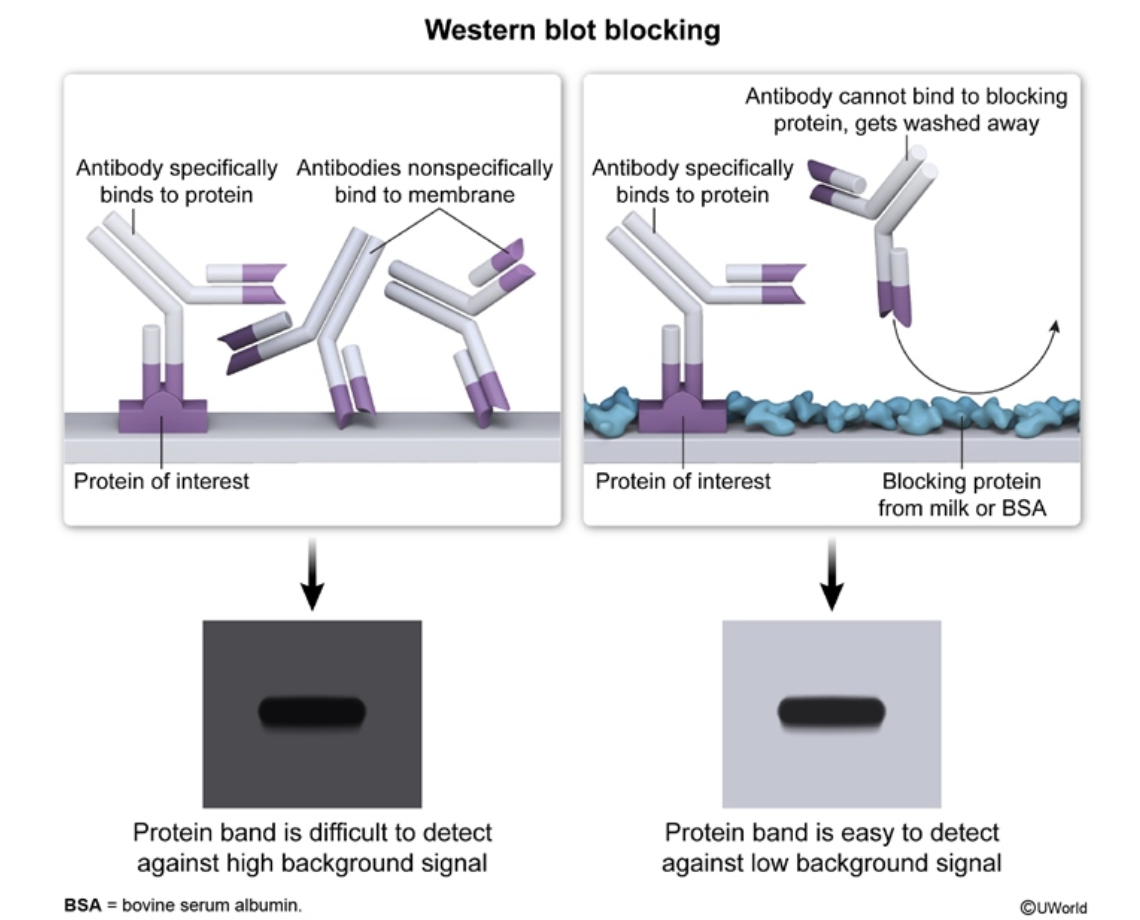
what is antibody blocking in western blot?
to prevent excess signal, you add blocking protein to the protein-binding membrane (to which you have transfered your desired proteins to) so the antibodies won’t do NONSPECIFIC protein binding
chaperone proteins
help fold proteins correctly
DECREASE protein aggregation
INCREASE solubility (e.g. hydrophobic in, hydrophillic out)
proteins with NEGATIVE charge at physiological pH have a ____ isoelectic point pI
LOW. since their net charge of 0 occurs are low pH so pI is low. more H+.
histone n gene expression
ACETYLATION = INCREASE
methylation = DECREASE (meth = bad for you)
3 reactions occurring at complex 2 of ETC
succinate oxidized to fumarate, reducing FAD+ to FADH2
FADH2 oxidized to FAD+ as electrons shuttled through iron-sulfur center
ubiquinone takes electrons from ^ centers = reduced to ubiquionol
stacking interactions between WHICH 3 amino acids can stabilize secondary protein structures?
AROMATIC (Y FW?)
phenylalyine, tyrosine, tryptophan
amino acid that is favourable for beta turns
glycine
amino acid conductive to tight turns in beta sheets
proline
renin n blood pressure
in response to LOW bp = does vasoconstriction to INCREASE bp by inc. sodium n water absorption
good nucleophilic amino acid groups
hydroxyl
thiol
amine
Kd formula
= Kunbinding/Kbinding = Koff/Kon
measurements to determine protein thermal stability
activity assays, circular dichroism, heat capacity measurements
Kcat is impacted by [E]
FALSE
but equation: Kcat = Vmax/[E]
cat efficiency = Kcat/Km = Vmax*Km/[E]
adding more [S] or [E] impacts reaction velocity
enzyme, cuz more active sites
natural selection vs. gene flow
NS:
INC. survival, IMPROVED probability
BENEFICIAL alleles selected
GF:
inbound MIGRATION (e.g. AA goes to colony of aa and mates) = small populations BENEFIT = INC. genetic diversity
hardy-weinburg assumptions (5):
NO new mutations
NO natural selection
NO gene flow
RANDOM mating
LARGE population size
—> allele frequences usually do not change
adaptive radiation and impact
diversifies characteristics in a single species = diversifies population = improves fitness
kinase vs. phosphatase vs. phosphoryLASE
KINASE: p from ATP to substrate
TRANSFERASE
phosphaTASE: use h2o, break into free p (remove p)
HYDROLASE
phosphoryLASE: inorganic p to substrate
TRANSFERASE
Kcat and Vmax and lineweaver-burke plot relationship
at [E]tot constant, Kcat proportional to Vmax, even tho Kcat=Vmax/[E]
INC. slope = DEC. catalytic efficiency = Kcat/Km
but this also means… INC. slope = Km/Vmax
phosphodiester bond
5’ phosphate n 3’ hydroxyl
nuclear localization sequence
how proteins can enter nucleus
ubiquitination
marks proteins for degradation by a proteasome
rt-pcr can be used to_____
look at changes in protein expression at transcriptional levels
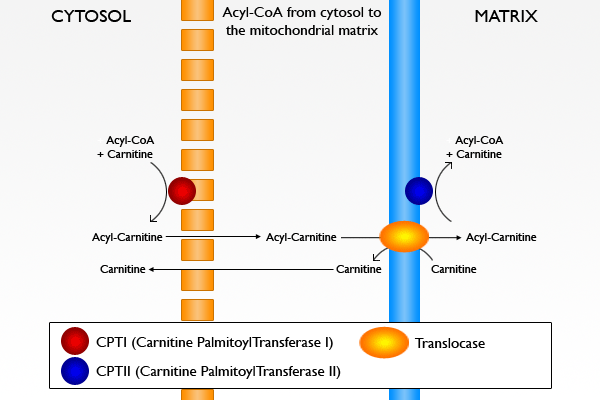
fatty acid activation n transport
autosomal dominant vs. autosomal recessive
DOMINANT:
only ONE copy of affected gene is required for condition to be expressed
RECESSIVE:
BOTH copies of affected gene are required for condition to be expressed
restriction enzyme sequences
PALINDROMIC sequence
osmotic vs. hydrostatic pressure
OSMOTIC:
think MOLAR… water moves INTO HIGH solute concentration
iB… interstitial to blood
HYDROSTATIC:
think STATIC aka PHYSICS aka PRESSURE
water moves from HIGH pressure to LOW pressure
helicase, ligase, topoisomerase, DNA primase, DNA polymerase
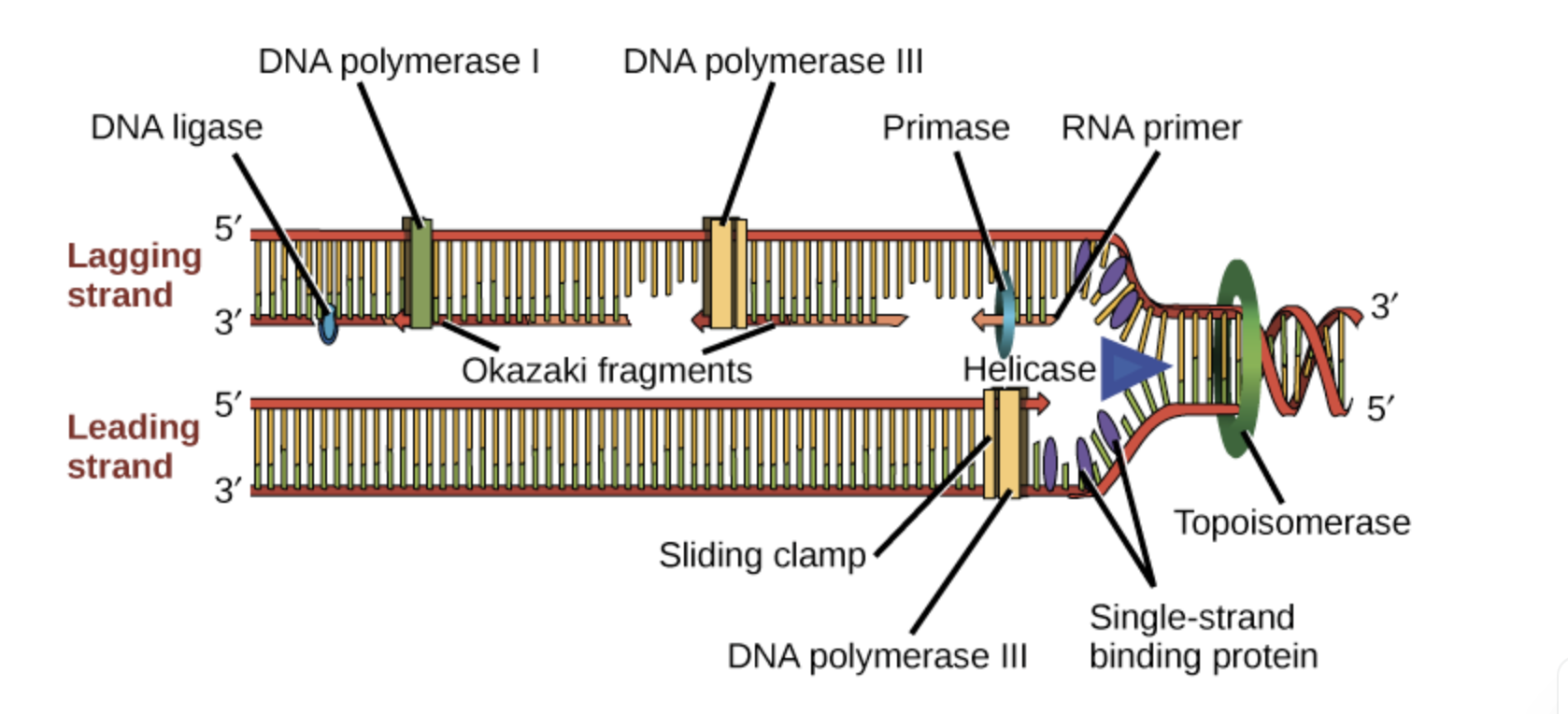
HELICASE: open DNA at replication fork, break hydrogen-bonds
LIGASE: seal okazaki fragments, create phosphodiester bond (P-O)
TOPOISOMERASE: prevent supercoiling
PRIMASE: makes RNA primase which is complementary to DNA strand, makes the start point for DNA polymerase
POLYMERASE: 3- goes from 5’-3’ extending primers to make new DNA, 1- repalces the rna primer spot
steroid vs peptide hormones
STEROID: cholesterol built, NOT soluble, NEED transport protein (think… people on steroids NEED assistance)
PEPTIDE: hydrophillic, NO transport protein, bind to receptors
during phosphorylation of tyrosine, what atoms attack what?
KINASE removes phosphate from ATP to phosphorylate the tyrosine
hydroxyl group from tyrosine… Hydrogen is taken OUT so tyrosine can become nucleophilic n ATTACH the phosphorus of the phosphate
why? well the Oxygen atoms on phosphate have the negative dipole so phosphorus is electrophillic
so… HYDROGEN of hydroxyl = EXCHANGED for PHOSPHATE on ATP
if an enzyme is continuous and upregulated, what happens to the half life of its product?
UPREGULATED = making more very quickly = LOWER half life = FAST regeneration rate
affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen n PO2 during exercise
INCREASE EXERCISE = DEcrease PO2 in muscle = DEcrease affinity for O2 = turn to anaeorbic after a certain period of time
native vs gel filtration… charge or no?
NATIVE = looks at electrophoretic mobility, length, conformation, n charge
GEL = NO charge. ONLY size
how does adding a negative molecule to a protein change its isoelectic point pI?
If you add negative weight (e.g., phosphoglycerol), you have to lower the pH (add more H⁺) to get the see-saw balanced again → pI DECREASES.
so… NEGATIVE add = counter w H+ = DECREASE pI
desmosomes vs gap junctions vs tight junctions
DESMOSOMES:
provide strength to anchor, TENSION, MECHANICAL stress
e.g. skin, muscle
GAP JUNCTIONS:
communication, ions n small molecules pass
e.g. heart/cardiac, smooth muscle
TIGHT JUNCTIONS:
prevent water n solutes to go through
e.g. blood brain barrier, skin, GI tract
large n small prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic subunits
PROKARYOTE: 50-30
think…the PROs ATE (8= 5+3)
eukaryote: 60-40
what is pI isoelectric point
ratio of cationic n anionic functional groups = 1