BIO - Invertebrates 1&2 - Intro to Animals and Sponges
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
metazoa def and relevance and stats
multicellular and eukaryotic animals, point on circle tree of life where diverges to this…then takes up 2/3 of life evolutionary tree
89% of all species - possibly because they evolved more mechanisms for nutrience (mobility)
8.8 mil eukaryote species
Distinguishing Charecteristics of Animals vs other life forms (3 main)
# of species
Evolutionary Age (600 mya)
Biomass (take up 1% compared to plants with 82%) - because of wood!
other charecteristics:
mode of nutrition
mode of reproduction (sexual)
Biomass def
how much mass group takes up on earth
‘the mass of living biological organism in a given area or ecosystem @ a given time’
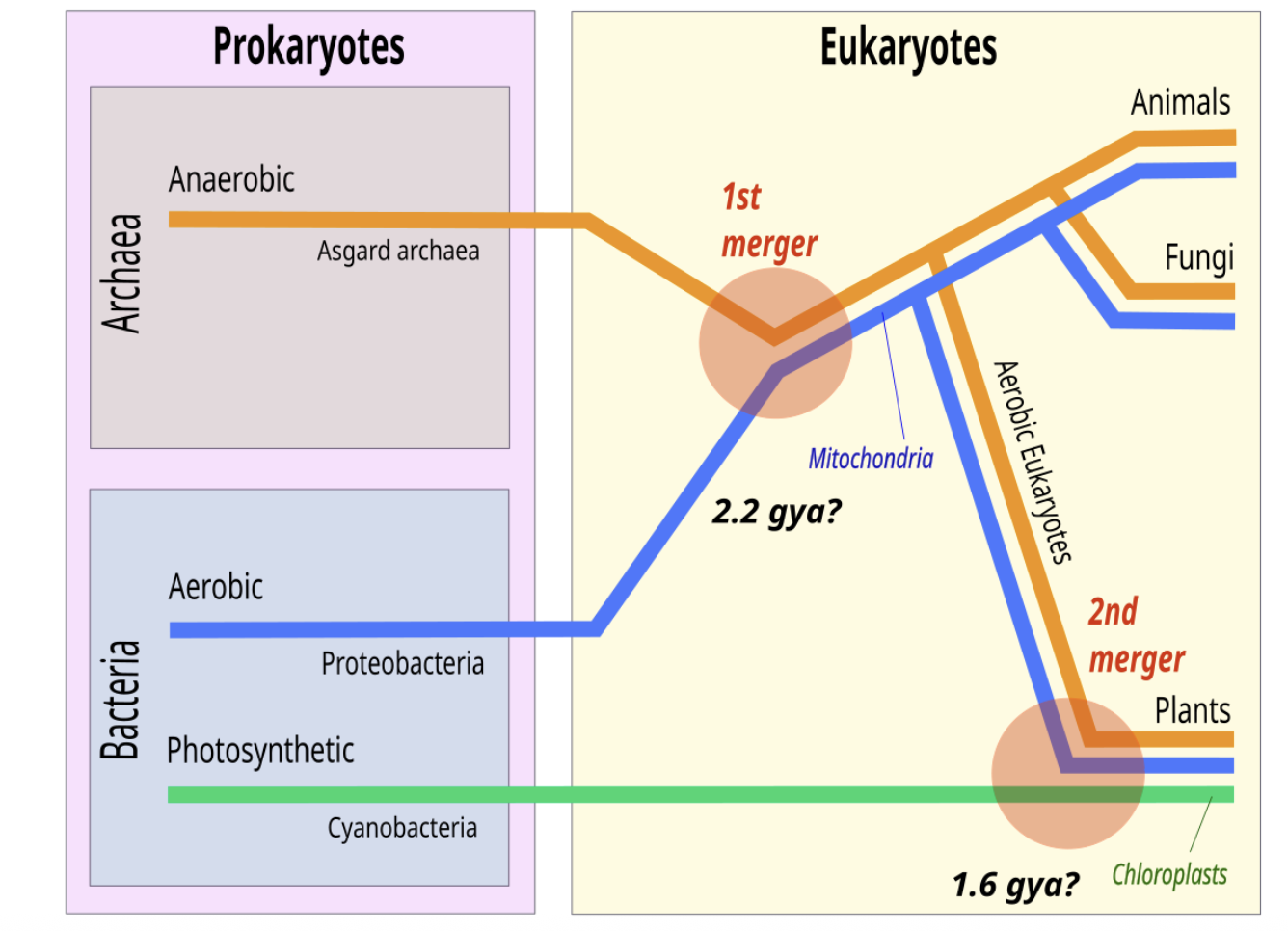
2 merger symbiogensis
1st merger (archea and bacteria) - makes eukaryotes
2nd merger (cynaobacteria and eukaryotes) - makes plants
choanoflagulates (who are they, traits)
animal sister group
*recall from og opistkonts clade
evidence from molecular phylogentics (studying relationships with molecular data)
Traits:
eukaryotic, heterotrophic, flagellated cells that form colonies *sponges resemble this
5 Animal Charecteristics
Eukaryotes
Heterotrophs (can’t make own food)
Multicellular - no cell walls
Mobile at some life stages
diplontic life cycle with diploid somatic cells - 2 sets of chromosomes
*none are unique to animals
Benefits of Multicellularity as a trait
specialized functions of cells (many different types of tissues)
grown in size
longer life span
Heterotrophic
‘different feeding’
use preformed organic materials as energy and carbon source - can’t make their own
various modes of feeding (parasites - thrive on other organisms without killing them, detritivores eat decayed organic material)
3 types of skeletons and who
Exoskeleton - hard external skelton provides rigid outercovering of body (arthropods, shelled-mollusks)
Endoskelton - rigid structure inside body that provides internal support (found in vertebrates, sponges and echinoderms)
Hydrostatic - fluid-filled cavities (coeloms) within the body, surrounded by muscles…simple movements…depend on humid environ (chidarians, worms, shell-less molluscks)
Ecdysozoans
animals that molt - get rid of exoskeleton to grow…all arthropods
Benefits of Mobility
enhances genetic diversity
less competetion
expands distribution range
‘unique traits of animals’
neurons and nervous system
muscles cells
germ layers
*problem is that these traits did not evolve at root of split between chaoloflagates and metazoa ALSO not all animals have this and loose it along the way…?
First Branching Point of Animals
sponges (system of pores and canals) and all other animals (ectoderm/endoderm)
Overview of Embryonic Development
fertilization of sperm and egg cells (n) → zygote formed as 1st diploid cell of next gen → embryo rapidly cell divides to develop)
Process of Embryonic Development
Clevage: cells rapidly multiple and forms blastomere → morula (solid ball)
Becomes hollow ball with 32/64 cells
Gastrulation: shell goes in to form 2 layers
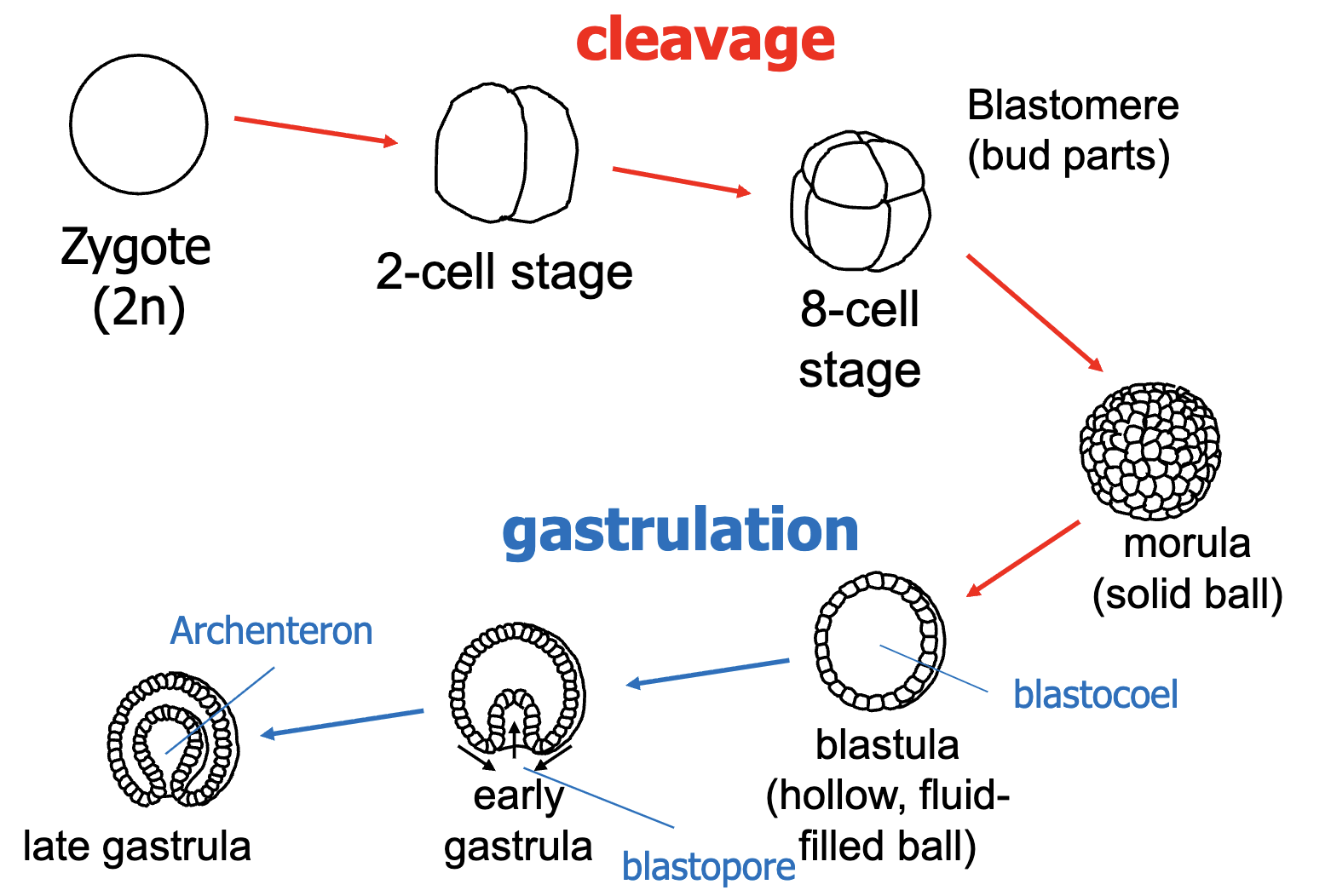
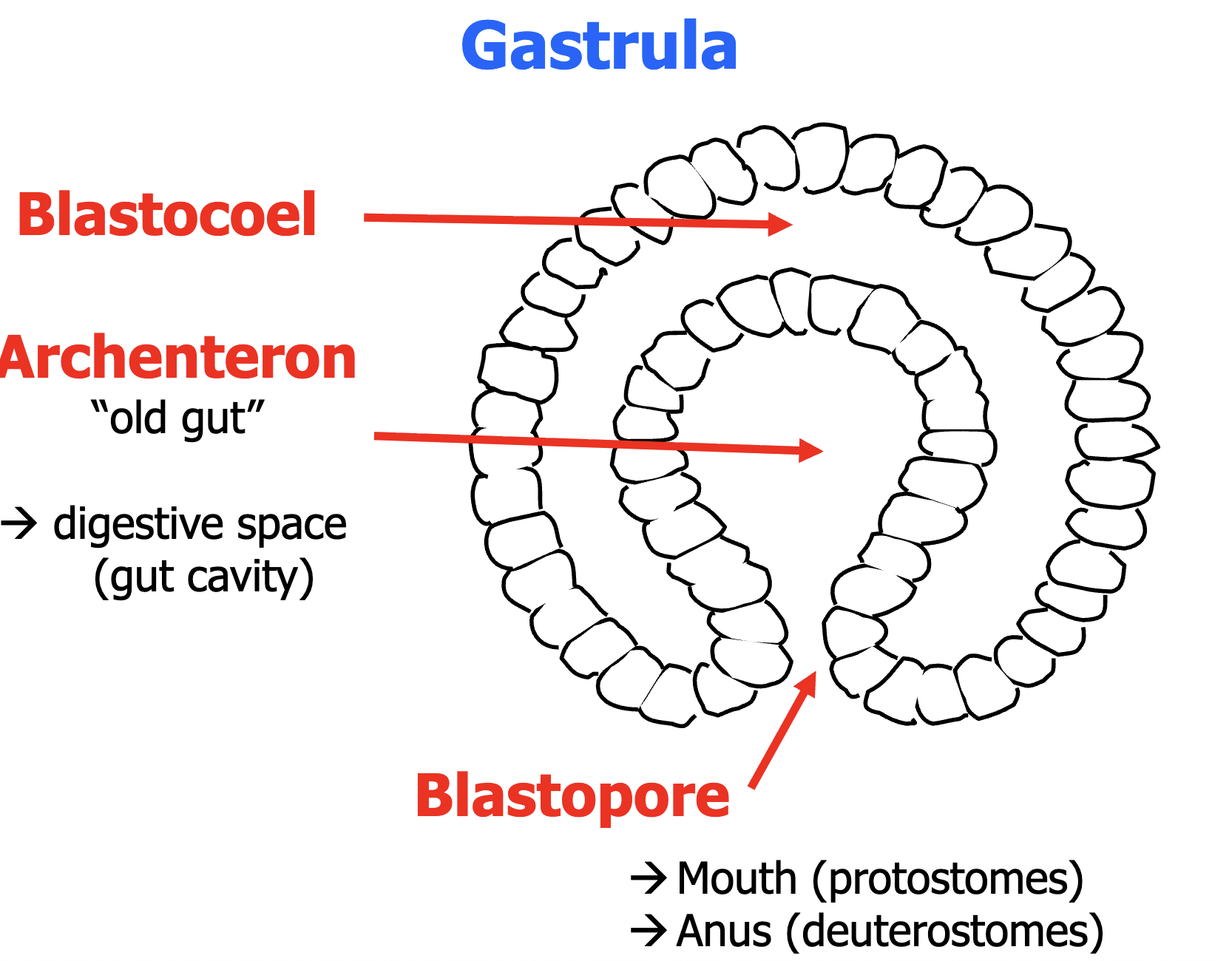
Parts of Gastrula
blastocoel - fluid inside
archenteron - digestive space/gut cavity
blastopore - mouth/anus
Germ Layers
…they become specialized
Ectoderm - outerlayer - becomes epidermus and nervous system
Endoderm - innerlayer - becomes digestive and respitory tracks
mesoderm ‘middleskin’ - becomes internal organs!: muscle, skeletal system, gonads **not all have this
Triploplastic vs Diploplastic
difference between having mesoderm or not
Sponge Traits
earliest animals to appear in fossil record
mostly marine (9000 species)
motile as larvae, sessile as adults
primitive features with no true tissues/organs
endoskeleton! - made of spicule (rigid support) and elastic fibre support network
Filter feeding mechanism
create current that pulls water through pores into atrium and then out osculum
2 types of sponges
high spongin conent ‘bath sponges’
high SiO2 ‘glass sponges’
Asexual Reproduction of Sponges (2)
Fragmentation - caused by waves or predators
Internal budding - clone of parent produced…lays dormant for a while until favourable conditions
Sexual Reproduction
sperm and egg cells found throughout sponge bc is a hermaphrodedite
explosion of sperm…sperm finds female part of another sponge
germinates and motile larvae released