Test 6 - Complex Animals - Arthropods
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2025-07-29
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What does artho mean
joint
what does poda mean
foot
What percentage of animals are arthropods
80%
What percentage of arthropods are insects
76%
Are arthropods closer related to humans or insects, why
insects because they are also segmented
6 classes of arthropods
Chilipoda, Insecta, Diplopoda, Arachnida, Maxillopoda, Malacostraca
Example of chilipoda
centipedes
example of insecta
all 6 legged
example of diplopoda
milipedes
examples of arachnida
spiders, mites, scorpians
Examples of maxillopoda
barnicles
examples of malacostraca
lobsters, shrimp, crab
Describe arthropod body cavity status and symmetry
coelomate, bilateral
Arthropods known to be the first animals to..
live in air
Describe athropod appendages
joint appendages, moveable legs, antennae, claws, mouthparts, etc, made of hard segments connected by flexible joints.
How are exoskeletons made
chitin secreted by epidermis
three body regions of arthropods
head, thorax, abdomen,
How do arthropods respire
body surface, gills, trachea, or book lungs
open or closed circulatory system
open
well developed sensory organs like…
compound eyes, trympanum (drum like ears), antenna (touch, smell & chemical reception)
Describe digestive system
complete, mouth, specialized organs, anus
dioecious or hermaphroditic
dioecious
internal or external fertilization
internal
describe nervous system
developed, dorsal brain connected by a ring and double ventral nerve cords
what environments do they live in
marine, freshwater, terrestrial, aerial
insecta exoskeleton made of..
chitin
insecta head segmented into…
6, with sensory antennae and compound eyes
insecta thorax with…
segmented legs & possibly wings
insecta abdomen segmented into
11 segments which house most of the digestive, respiratory, excretory, and reproductive systems
insecta respires through…
a system of internal tubes and sacs that lie directly next to the circulatory system, (tracheal system with spiracles)
insecta circulatory system…
is open
insecta: sexual or asexual, internal or external
sexual, internal
insecta: direct or indirect development
indirect: hatched from eggs, most as they grow in size
excretion through
Malpighian tubules
body cavity status of anthropods
coelomate
germ layers
3
symmetry
bilateral
nervous system?
brain, ganglia, ventral nerve cord
Malacostraca: head and thorax are often…
fused into cephalothorax
Malacostraca: what are maxillipeds
Modified appendages near the mouth
Help manipulate food and bring it to the mouth
Malacostraca: what are antennules
Small, paired sensory appendages on the head. Used for balance, smell, and touch
Malacostraca: difference between antennules and antennae
Antennules
Shorter
Mainly used for balance and chemical sensing
Often biramous
Antennae
Longer
Primarily used for touch and sometimes smell
Usually uniramous
Malacostraca: head includes…
6 segments with antennules, antennae, & mouthparts with appendages called maxillipeds
Malacostraca: 8…
thoracic segments (between head and abdomen, each segment bears a pair of legs, houses muscles and structures for locomotion and sometimes respiration)
Malacostraca also known as
crustaceans
Malacostraca: cephalothorax is almost completely covered by a…
carapace (part of exoskeleton)
Malacostraca: 6…
abdominal segments often used for swimming
Malacostraca: eyes are..
compound stalked or sessile.
(stalked eyes allow the crustacean to pull them in for protection or see in many directions, Mr. krabs)
Malacostraca: 5 pairs of…
walking legs, some with modified pincers
Malacostraca: 2 chambered…
stomachs
Malacostraca: central…
nervous system
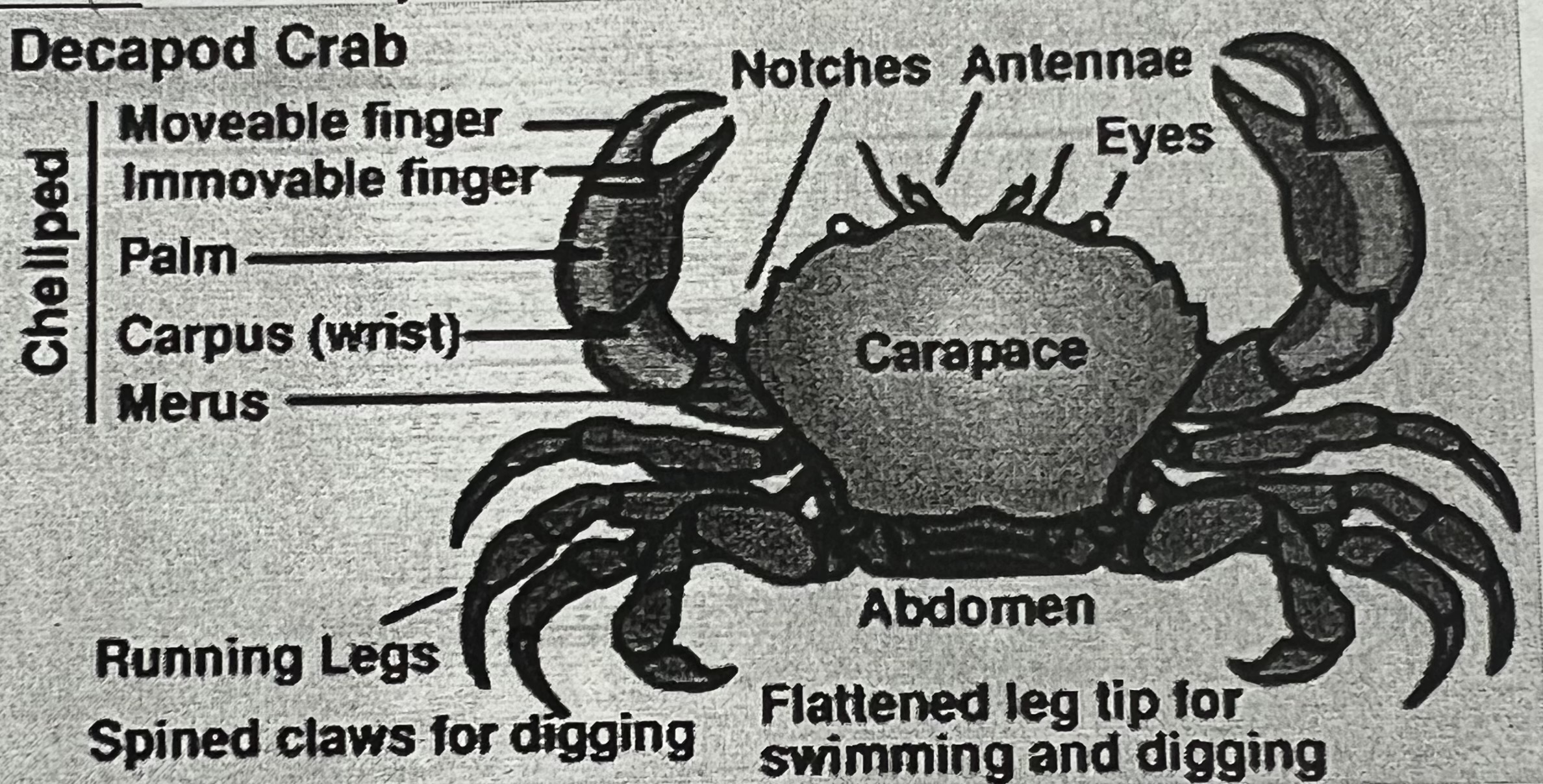
Label all the parts of this decapod crab and list the functions.
Cheliped (claw/first leg) parts:
Movable finger: Opens and closes to grasp or cut prey.
Immovable finger: Fixed part of the claw; works with movable finger to pinch.
Palm: Main gripping area; holds food or fights.
Carpus: Joint segment allowing movement of the claw.
Merus: Upper limb segment; provides strength and leverage.
Other Body Parts:
Notched chela (claw edge): Helps grip slippery prey or dig.
Antennae: Detects touch, chemicals, and vibrations in water.
Eyes (compound, stalked): Wide field of vision; detect motion and light.
Carapace: Hard shell protecting organs and gills.
Abdomen (reduced & tucked under): Holds reproductive organs; helps in swimming for some species.
Running legs (4 pairs): For walking and scuttling.
Spines/claws on legs: Aid in digging, anchoring, and defense.
Flattened leg tips: Adapted for swimming and digging into substrate.
Largest arthropod?
Japanese spider, leg span of 4 meters, 20 kg, life expectancy of 100 years
Ecological roles of arthropods
pollination
Production of honey, wax silk
Recycled biological materials to aid in producing topsoil
Part of food chain, (eat insects when food price is high)
Forms symbiotic relationships with other organisms: burrowing shrimp and Goby fish, shrimp is blind and cleans and digs a burrow, Goby fish touches shrimp when danger approaches.
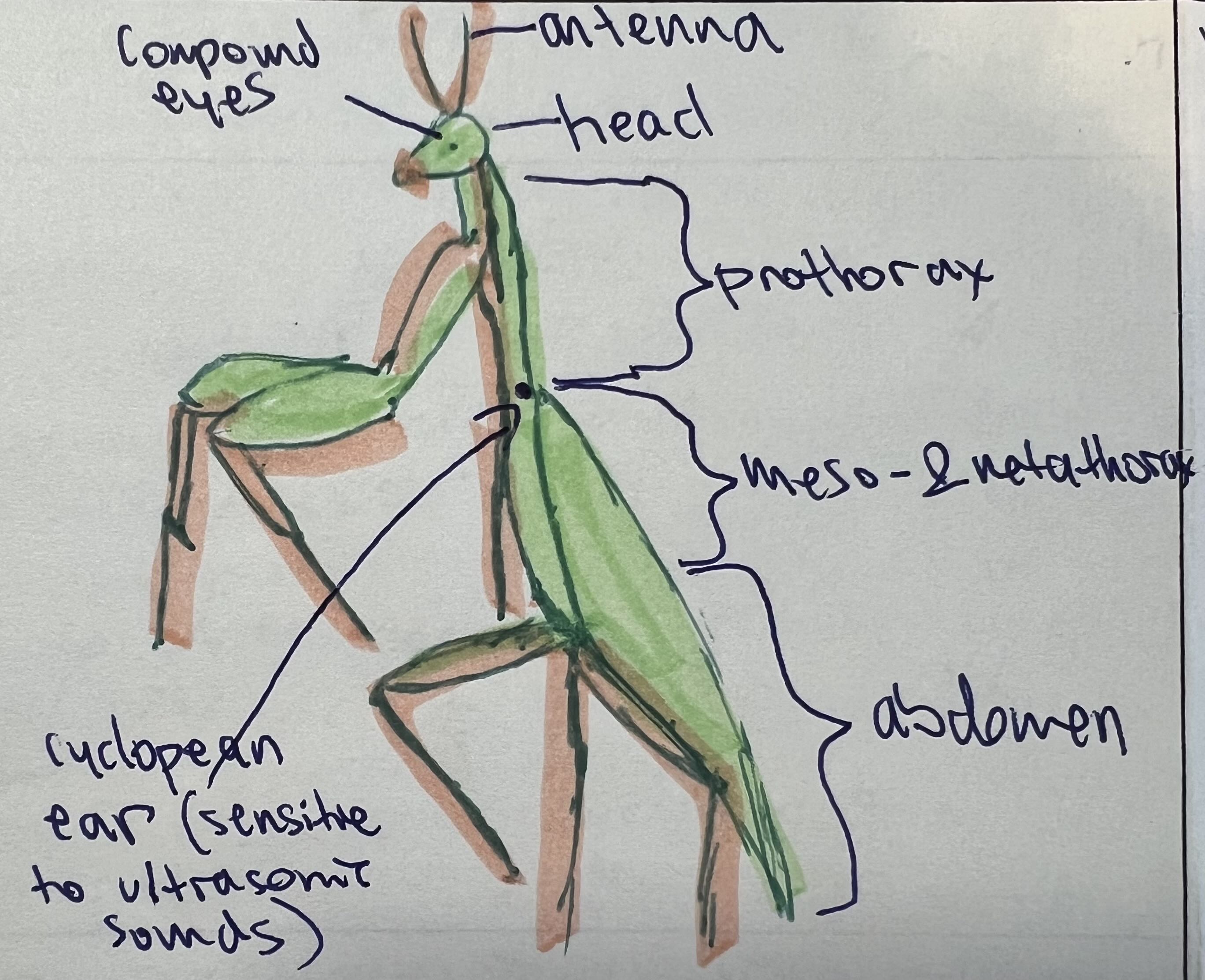
List the:
class
common name
respiration methods
circulatory systems
digestive system
nervous system
reproductive methods and system
habitat
For Hierodula patellifera
Class: Insecta
Respiration: Tracheal system (spiracles + tracheae)
Circulatory System: Open
Digestive System: Complete (mouth to anus)
Nervous System: Brain + ventral nerve cord + ganglia
Reproductive System: Sexual; dioecious; internal fertilization; lays eggs (ootheca)
Habitat: Terrestrial; warm, vegetated areas in Asia
Common Name: Giant Asian Mantis
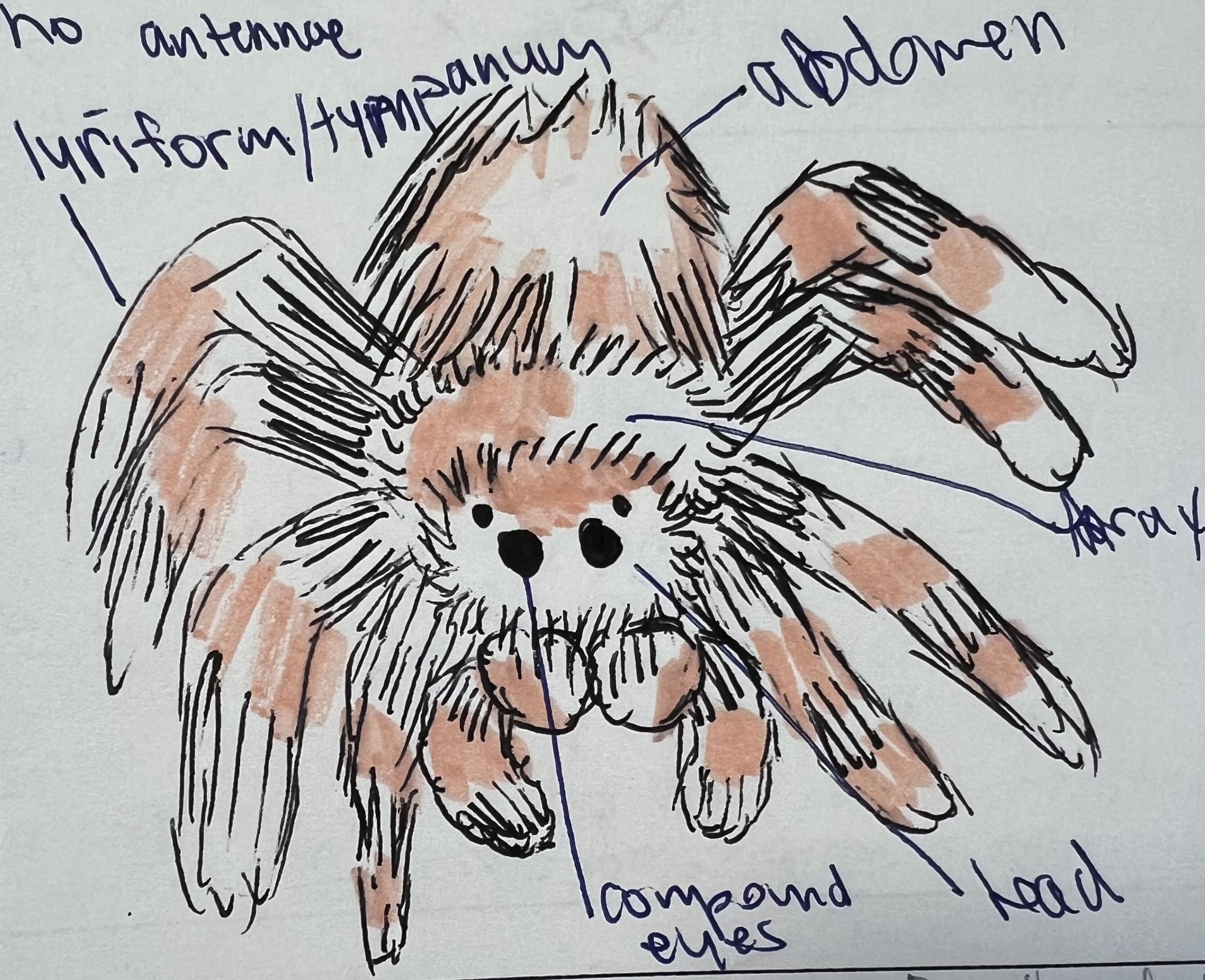
List the:
class
common name
respiration methods
circulatory systems
digestive system
nervous system
reproductive methods and system
habitat
For Brachypelma hamorii
Class: Arachnida
Respiration: Book lungs
Circulatory System: Open
Digestive System: External digestion followed by sucking liquefied food
Nervous System: Brain + ventral nerve cord
Reproductive System: Sexual; dioecious; internal fertilization via male pedipalps
Habitat: Terrestrial; burrows in dry forests/deserts of Mexico
Common Name: Mexican Red-Knee Tarantula
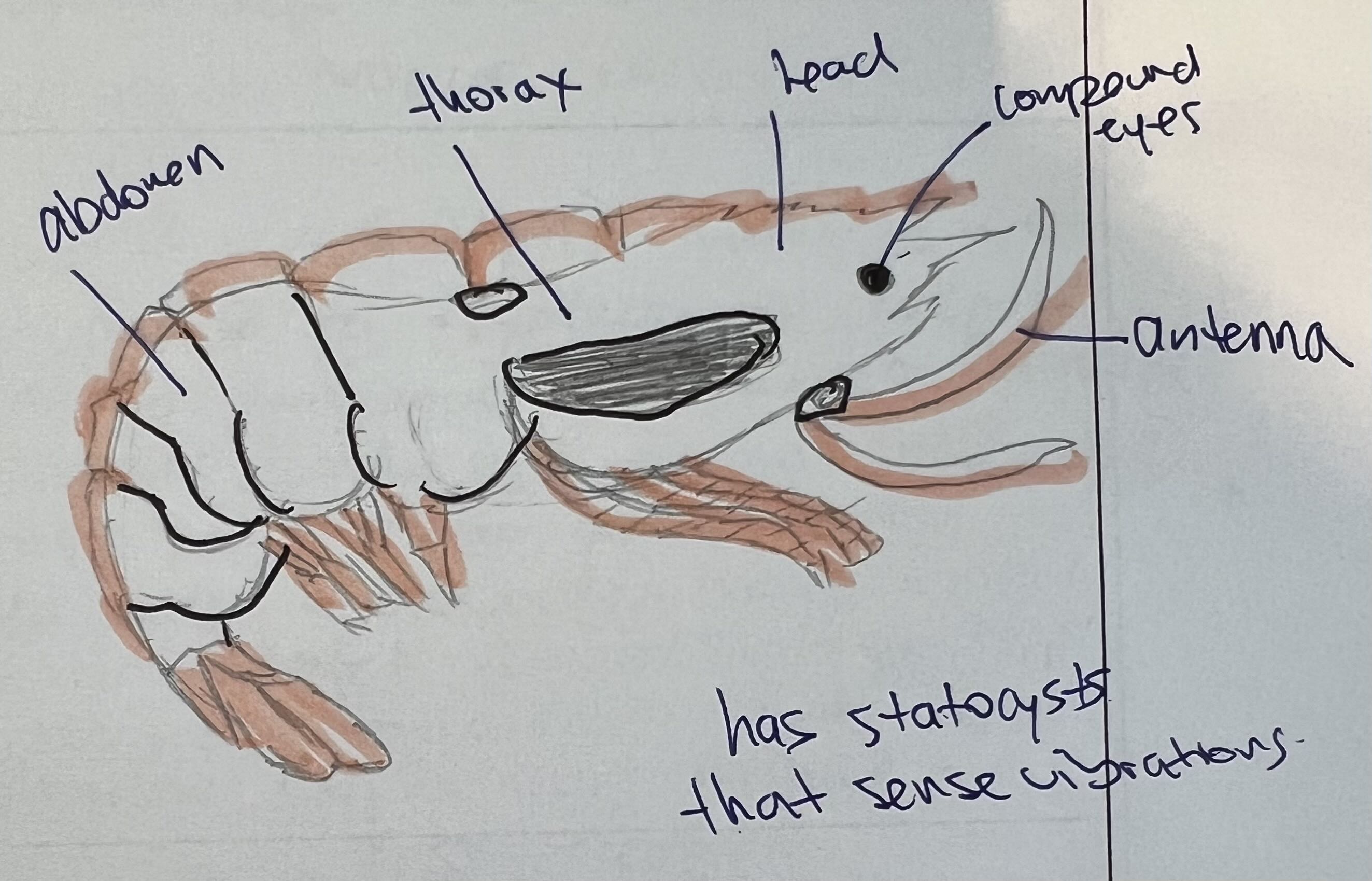
List the:
class
common name
respiration methods
circulatory systems
digestive system
nervous system
reproductive methods and system
habitat
For Penaeus vannanei
Class: Malacostraca
Respiration: Gills
Circulatory System: Open
Digestive System: Complete (with stomach, digestive gland, intestine)
Nervous System: Brain + ventral nerve cord + segmental ganglia
Reproductive System: Sexual; dioecious; external fertilization; indirect development
Habitat: Aquatic (marine); shallow coastal and estuarine waters
Common Name: Pacific White Shrimp