macroeconomics chapters 13-17
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:17 PM on 12/22/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
1
New cards
labor force equation
number of employed + number of unemployed
2
New cards
unemployment rate
number of unemployed / labor force
3
New cards
what makes someone considered out of the labor force?
when a person stops looking for work
4
New cards
frictional unemployment
unemployment that occurs when people take time to find a job or are transitioning between jobs
5
New cards
structural unemployment
unemployment that occurs due to changes in the structure of the economy, resulting in significant loss of jobs in industries
6
New cards
cyclical unemployment
unemployment that occurs due to recessions and depressions
7
New cards
what happens to the wage rate when there is an excess supply of labor?
the wage rate will fall until a new equilibrium is reached. everyone who wants a job at a lower wage rate will have one.
8
New cards
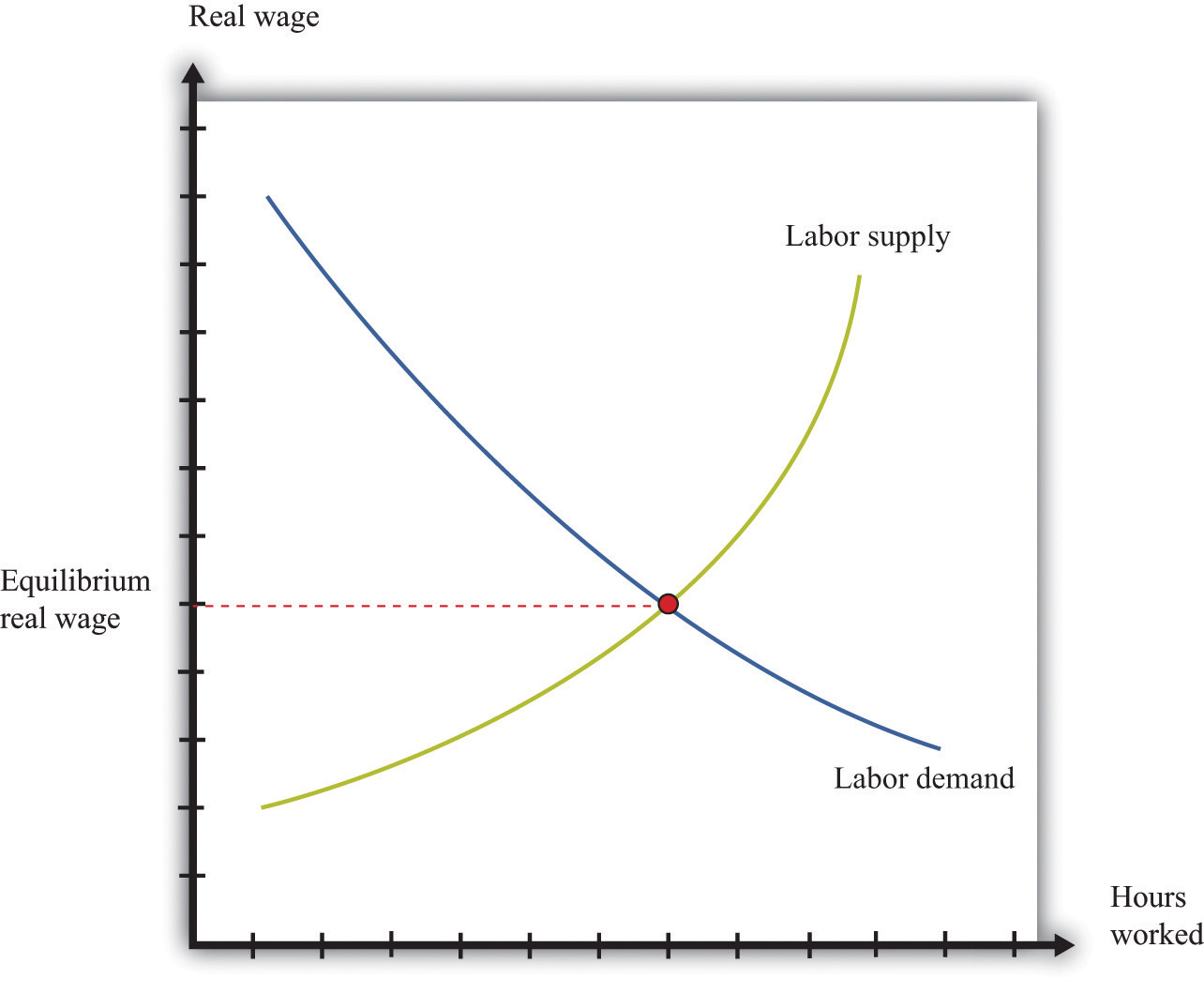
labor demand curve
a graph that illustrates the amount of labor that firms want to employ at each given wage rate
9
New cards
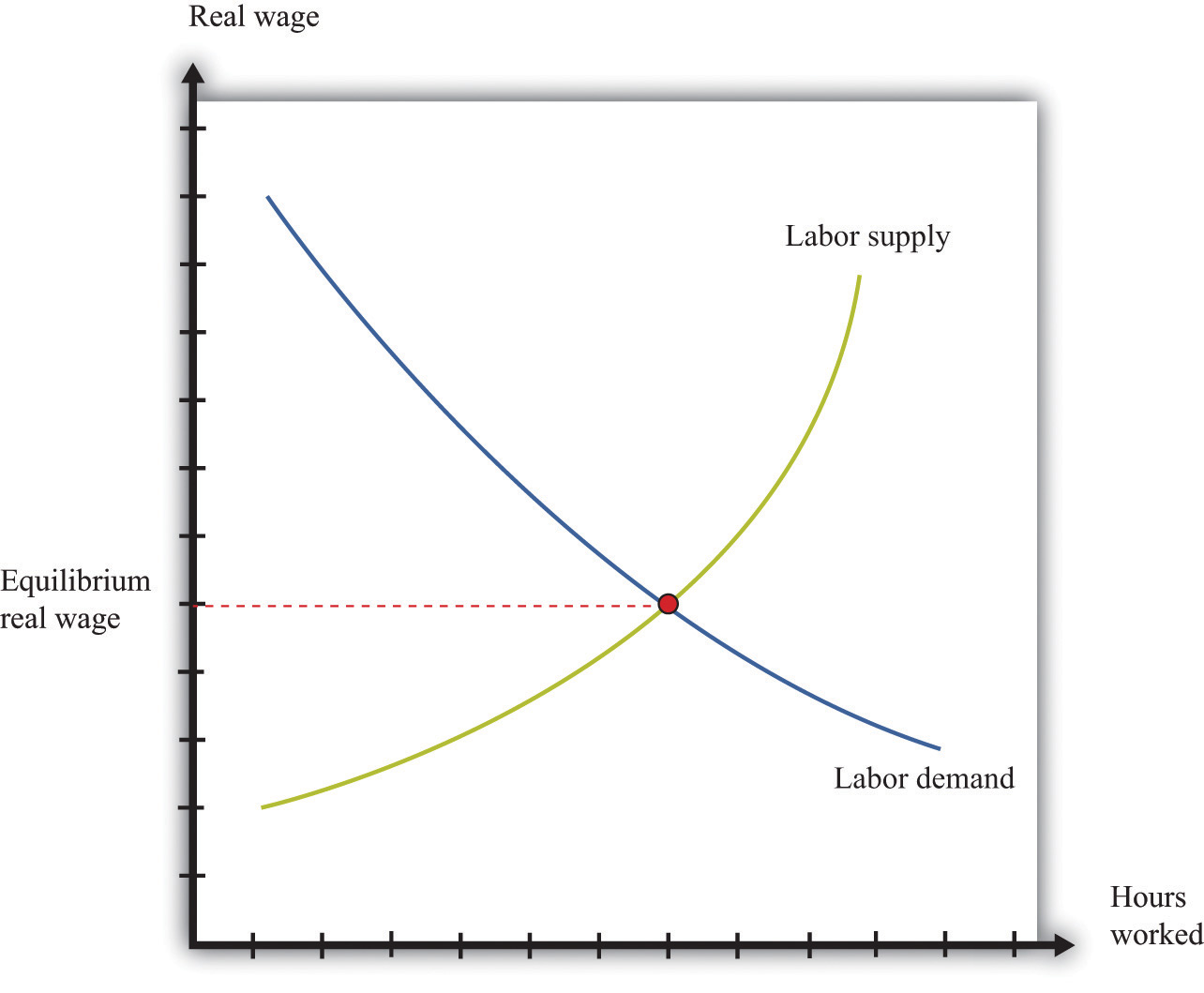
labor supply curve
a graph that illustrates the amount of labor that households want to supply at each given wage rate
10
New cards
what happens at equilibrium with the labor supply and labor demand curve?
people who are not working have chosen not to work that that market wage, so there is always full employment.
11
New cards
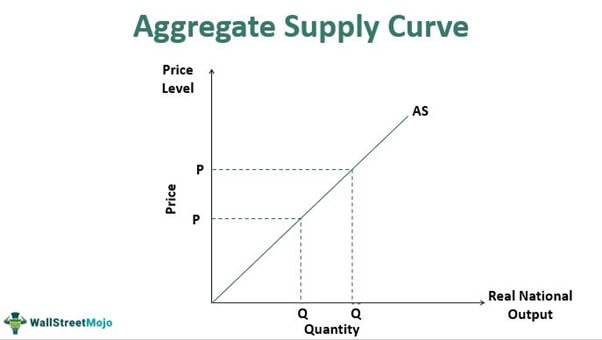
what happens to the aggregate supply curve when there are no sticky wages?
the aggregate supply curve is vertical
12
New cards
if there are no sticky wages, monetary and fiscal policy have [blank] effect on real output.
no
13
New cards
what happens to wages when the labor demand curve shifts to the left?
the wage decreases
14
New cards
three common arguments for the existence of frictional or structural unemployment
efficiency wage theory \n imperfect information \n minimum wage laws
15
New cards
imperfect information
firms may not have enough information at their disposal to know what the market-clearing wage is
16
New cards
minimum wage laws
laws that set a floor for wage rates, that is, a minimum hourly rate for any kind of labor
17
New cards
efficiency wage theory
the productivity of workers increases with the wage rate. firms are incentivized to pay wages above the market-clearing rate
18
New cards
imperfect information
firms may not have enough information at their disposal to know what the market-clearing wage is
19
New cards
minimum wage laws
laws that set a floor for wage rates, that is, a minimum hourly rate for any kind of labor
20
New cards
sticky wages
the downward rigidity of wages as an explanation for the existence of unemployment
21
New cards
social or implicit contracts
unspoken agreements between workers and firms that firms will not cut wages
22
New cards
relative-wage explanation of unemployment
An explanation for sticky wages (and therefore unemployment): If workers are concerned about their wages relative to other workers in other firms and industries, they may be unwilling to accept a wage cut unless they know that all other workers are receiving similar cuts.
23
New cards
explicit contracts
employment contracts that stipulate workers' wages, usually for a period of 1 to 3 years
24
New cards
cost-of-living adjustments (COLAs)
contract provisions that tie wages to changes in the cost of living. the greater the inflation rate, the more wages are raised
25
New cards
inflation rate
the percentage change in the price level
26
New cards
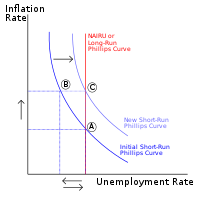
phillips curve
a curve showing the relationship between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate
27
New cards
on the aggregate supply curve, there is a positive relationship between the [blank] and [blank]
price level (P) ; income (Y)
28
New cards
what kind of relationship is on the phillips curve?
negative
29
New cards
on the phillips curve, as the unemployment rate decreases, what happens to the price level?
it increases, since it is moving closer to capacity output
30
New cards
![the aggregate demand curve shifts to the [blank] if there is a positive relationship between price wage and income.](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1e4e246004ba4acebba7140bdc99a02e.jpeg)
the aggregate demand curve shifts to the [blank] if there is a positive relationship between price wage and income.
right
31
New cards
the aggregate supply curve shifts to the [blank] if there is a negative relationship between price wage and income.
left
32
New cards
what does it mean for the relationship between price wage and income if both the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curve are shifting?
there is no systematic relationship
33
New cards
the phillips curve will shift to the [blank] if inflationary expectations increase
right
34
New cards
the phillips curve will shift to the [blank] if inflationary expectations decrease
left
35
New cards
natural rate of unemployment
the unemployment that occurs as a normal part of the functioning of the economy. sometimes taken as a sum of frictional unemployment and structural employment
36
New cards
how is the phillips curve formed if the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the long run?
it is also vertical
37
New cards
in the long run, the phillips curve corresponds to...
the natural rate of unemployment
38
New cards
NAIRU
non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment
39
New cards
what happens to the change in inflation rate if the actual unemployment rate is below the NAIRU?
the change in the inflation rate will be positive and accelerates
40
New cards
what happens to the price level changing rate if the unemployment rate is equal to the NAIRU
there is no change in the rate
41
New cards
stock
a certificate that certifies ownership of a certain portion of a firm
42
New cards
capital gain
an increase in the value of an asset
43
New cards
realized capital gain
the gain that occurs when the owner of a asset actually sells it for more than he or she paid for it
44
New cards
yield to maturity formula
c/1+i, c/(1+i)^2, c/(1+i)^3… c/(1+i)^n, f/(1+i)^n
45
New cards
what happens to the current stock price as the expected future dividends increase?
the price increases as well
46
New cards
the price of the stock is equal to...
the discounted value of its expected future dividends
47
New cards
dow jones industrial average
an index based on the stock prices of 30 actively traded large companies. the oldest and most widely followed index of the stock market performance
48
New cards
nasdaq (national association of securities dealers automated quotation system) composite
an index based on the stock prices of more than 5000 companies traded on the nasdaq stock market.
49
New cards
standard & poor's 500 (s&p 500)
an index based on the stock prices of 500 of the largest firms by market value
50
New cards
hyman minsky
stability breeds instability
51
New cards
stabilization policy
describes both monetary and fiscal policy, the goals of which are to smooth out fluctuations in output and employment and to keep prices as stable as possible
52
New cards
time lags
delays in the economy's response to stabilization policies
53
New cards
recognition lag
the time it takes for policymakers to recognize the existence of a boom or a slump
54
New cards
implementation lag
the time it takes to put the desired policy into effect once economists and policymakers recognize that the economy is in a boom or a slump
55
New cards
response lag
the time it takes for the economy to adjust to the new conditions after a new policy is implemented; the lag that occurs because of the operation of the economy itself
56
New cards
there is a lag between the time a fiscal policy action is initiated and the time [blank]
the full change in gdp is realized
57
New cards
response lags are longer for monetary policy or fiscal policy?
monetary
58
New cards
deficits in recessions are
temporary and do not impose any long-run problems
59
New cards
deficits at full employment are
able to have negative long-run consequences
60
New cards
gramm-rudman-hollings act
passed by the us congress and signed by president reagan in 1986, this law set out to reduce the federal deficit by $36 billion per year, with a deficit of zero slated for 1991
61
New cards
automatic stabilizers
revenue and expenditure items in the federal budget that automatically change with the economy in such a way as to stabilize gdp
62
New cards
automatic destabilizers
revenue and expenditure items in the federal budget that automatically change with the economy in such a way to destabilize gdp
63
New cards
life-cycle theory of consumption
a theory of household consumption: households make lifetime consumption decisions based on their expectations of lifetime income
64
New cards
permanent income
the average level of a person's expected future income stream
65
New cards
in early working and retirement years, people consume [blank] than they earn
more
66
New cards
in between early working and retirement years, people [blank] to pay off [blank] from borrowing and to accumulate savings for retirement
save; debts
67
New cards
substitution effect of a wage rate increase
a higher wage leads to a larger quantity of labor supplied
68
New cards
income effect of a wage rate increase
people with higher income will spend some of it on leisure by working less, since leisure is a normal good.
69
New cards
nominal wage rate
the wage rate in current dollars
70
New cards
real wage rate
the amount the nominal wage rate can buy in terms of goods and services
71
New cards
nonlabor, or nonwage, income
any income received from sources other than working-- inheritances, interest, dividends, transfer payments, and so on
72
New cards
an unexpected increase in wealth or nonlabor income leads to...
a decrease in labor supply
73
New cards
substitution effect of interest rate and consumption
a rise in the interest rate leads you to consume less and save more
74
New cards
income effect of interest rate and income
a fall in the interest rate leads to a fall in interest income when
75
New cards
unconstrained supply of labor
the amount of a household would like to work within a given period at the current wage rate if it could find the work
76
New cards
constrained supply of labor
the amount a household actually works in a given period at the current wage rate
77
New cards
keynesian theory
current income determines current consumption
78
New cards
factors that affect household consumption and labor supply decisions
current and expected future real wages \n \n initial value of wealth \n \n current and expected future nonlabor income \n \n interest rates \n \n current and expected future tax rates and transfer payments
79
New cards
animal spirits of entrepreneurs
a term coined by keynes to describe investors' feelings
80
New cards
accelerator effect
the tendency for investment to increase when aggregate output increase and to decrease when output decreases, accelerating the growth or decline of output
81
New cards
excess labor, excess capital
labor and capital that are not needed to produce the firm's current level of output
82
New cards
adjustment costs
the costs that a firm incurs when it changes its production level (administration costs of laying off employees or the training costs of hiring new workers)
83
New cards
inventory investment
the changes in the stock of inventories
84
New cards
desired, or optimal, level of inventories
the level of inventory at which the extra cost (in lost sales) from lowering inventories by a small amount is just equal to the extra gain (in interest revenue and decreased storage costs)
85
New cards
factors that affect firms' investment and employment decisions
firms' expectations of future output \n \n wage rate and cost of capital \n \n amount of excess labor and excess capital on hand
86
New cards
productivity or labor productivity
output per worker hour
87
New cards
okun's law
the short run the unemployment rate decrease about 1 percentage point for every 3% increase in real gdp
88
New cards
discouraged-worker effect
The decline in the measured unemployment rate that results when people who want to work but cannot find jobs grow discouraged and stop looking, thus dropping out of the ranks of the unemployed and the labor force.
89
New cards
effects that decrease the size of the multiplier
automatic stabilizers \n \n interest rate \n \n response of the price level \n \n excess capital and excess labor \n \n inventories \n \n people's expectations about the future
90
New cards
output growth
the growth rate of the output of the entire economy
91
New cards
per-capita output growth
the growth rate of output per person in the economy
92
New cards
labor productivity growth
the growth rate of output per worker
93
New cards
catch-up
the growth rates of less developed countries will exceed the growth rates of developed countries, allowing the less developed countries to catch up
94
New cards
convergence theory
the idea that gaps in national incomes tend to close over time
95
New cards
advantages of backwardness
the phenomenon of less developed countries leaping ahead by borrowing technology from more developed countries
96
New cards
aggregate production function
An equation that shows the relationship stating that total gdp depends on the total amount of labor used and the total amount of capital used
97
New cards
diminishing returns
as labor increases, less and less output will be added by each new worker
98
New cards
foreign direct investment (fdi)
investment in enterprises made in a country by residents outside that country
99
New cards
as the quality of labor increases through more education, the labor productivity...
increases
100
New cards
embodied technical change
technical change that results in an improvement in quality of capital