2.2 - Biological Molecules
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Why do you handle TLC with gloves?
So the amino acids on your hands don't contaminate the results
What's the stationary phase?
Silica gel
TLC Process
1) A spot of mixture is placed on chromatography paper and left to dry
2) The chromatography paper is then suspended in solvent. Solvent must be below the pencil line or the amino acid will dissolve into the solvent
3) Lighter amino acids with a smaller R group will travel further up the chromatogram as there will be less resistance
4) Spray with ninhydrin to see the amino acids
Calculating Rf value

Iodine Test for Starch
1) Add iodine to test solution
2) If starch is present, then there is a colour change from brown to blue/black
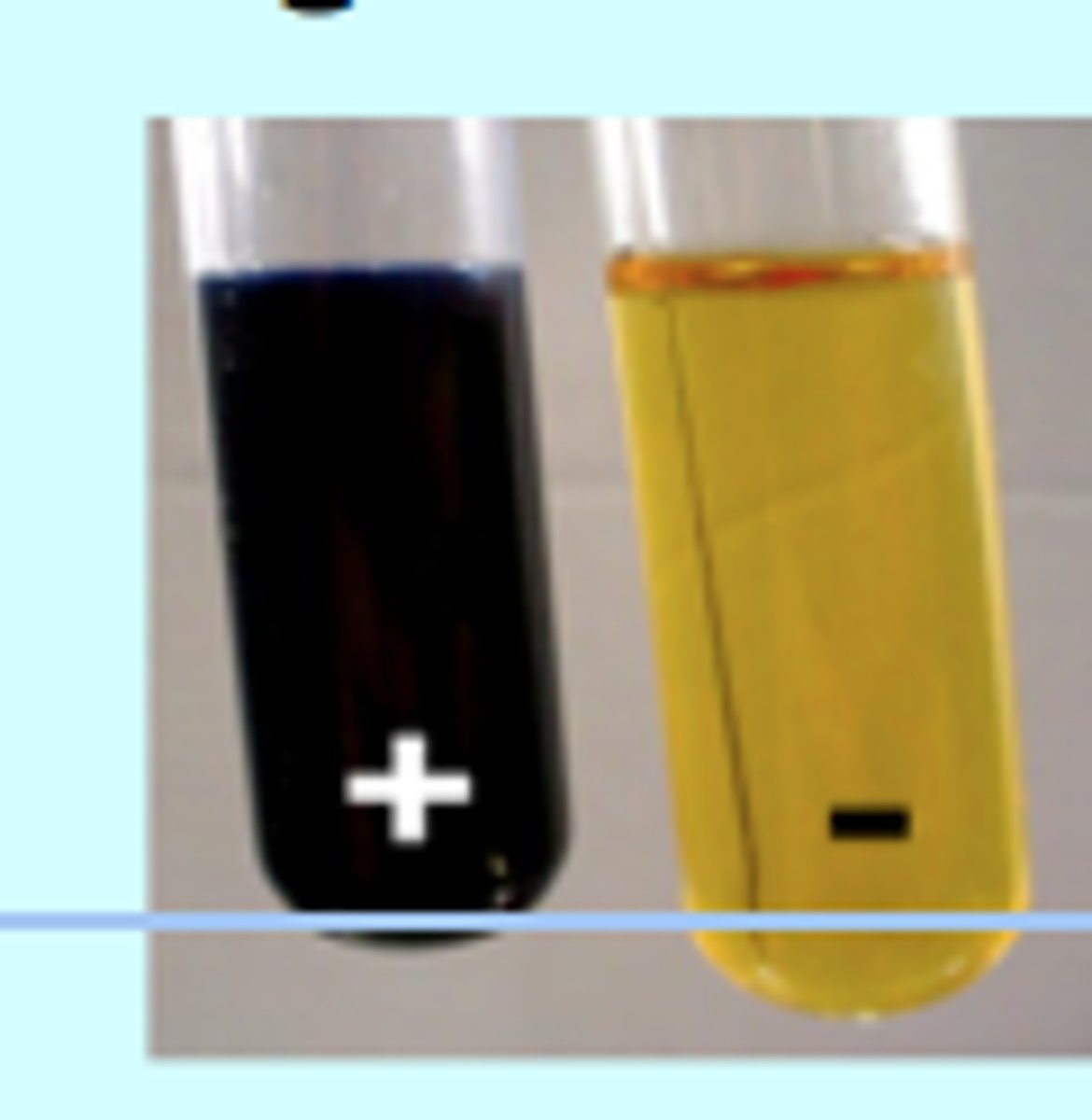
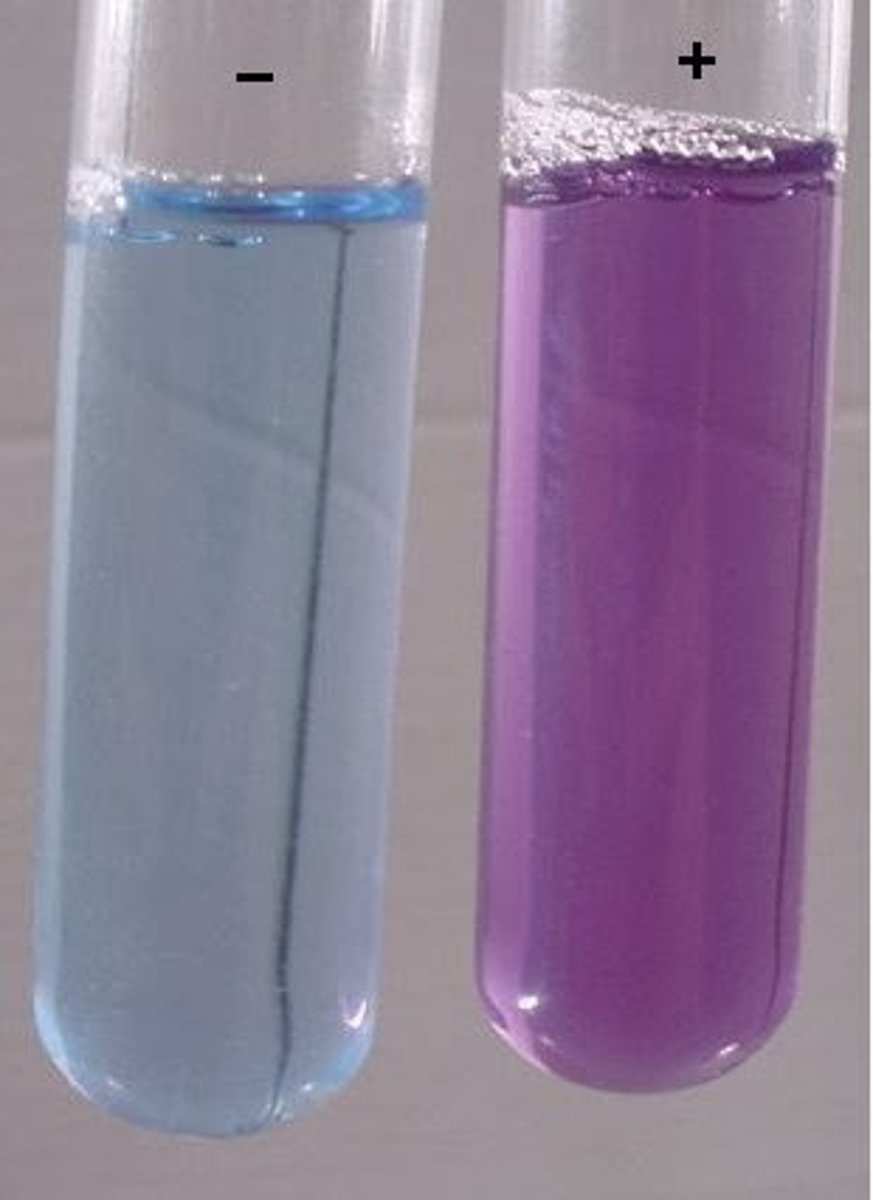
Biuret Test for Proteins
1. Add biuret to test solution
2. If there is a colour change from blue to lilac, protein is present

What are reducing sugars?
Sugars that act as a reducing agent
Example of reducing sugars:
Glucose
Lactose
Galactose
Fructose
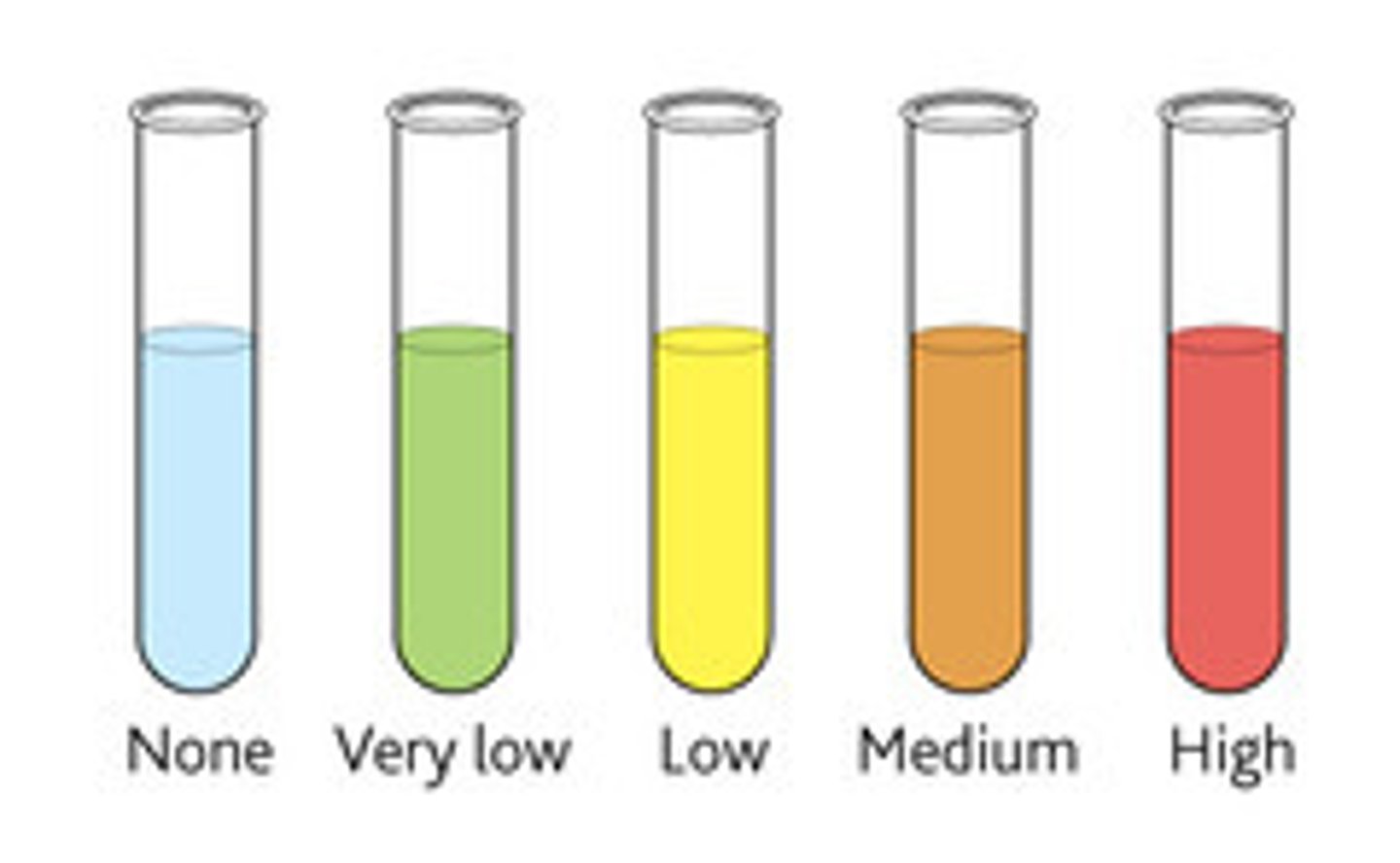
Benedict's Test for Reducing Sugars
1) Heat the same volume of sugar with the same volume of benedict's reagent in a thermostatically controlled water bath
2) If the reducing sugar is present, a yellow, green, orange, or brick red colour appears. The greater the concentration of the reducing sugar, the greater the colour change.
3) If there's no reducing sugar present, it remains blue

What are non-reducing sugars?
Sugars that cannot donate electrons and thus don't reduce Benedict's reagent.
Example of non reducing sugar
Sucrose
Benedict's Test for Non-Reducing Sugars
1) Heat the same volume of sugar with the same volume of benedict's reagent in a thermostatically controlled water bath
2) If no colour change, then heat with acid (HCl)
3) Add excess NaOH
4) Heat sample with benedict's reagent in a thermostatically controlled water bath
5) Non reducing sugar present if a yellow, green, orange, or brick red colour appears
Using colorimetry when testing for Reducing Sugars
1) Heat the same volume of sugar solution with the same volume of benedict's reagent in a thermostatically controlled water bath
2) If the reducing sugar is present, a yellow, green, orange, or brick red colour appears.
3) Filter out precipitate into a cuvette
4) Calibrate the colorimeter by setting it to 0 using a blank
5) Use a red filter
6) Measure the absorbance
7) Plot a calibration curve
8) Use the calibration curve to find the concentration of the unknown glucose concentration
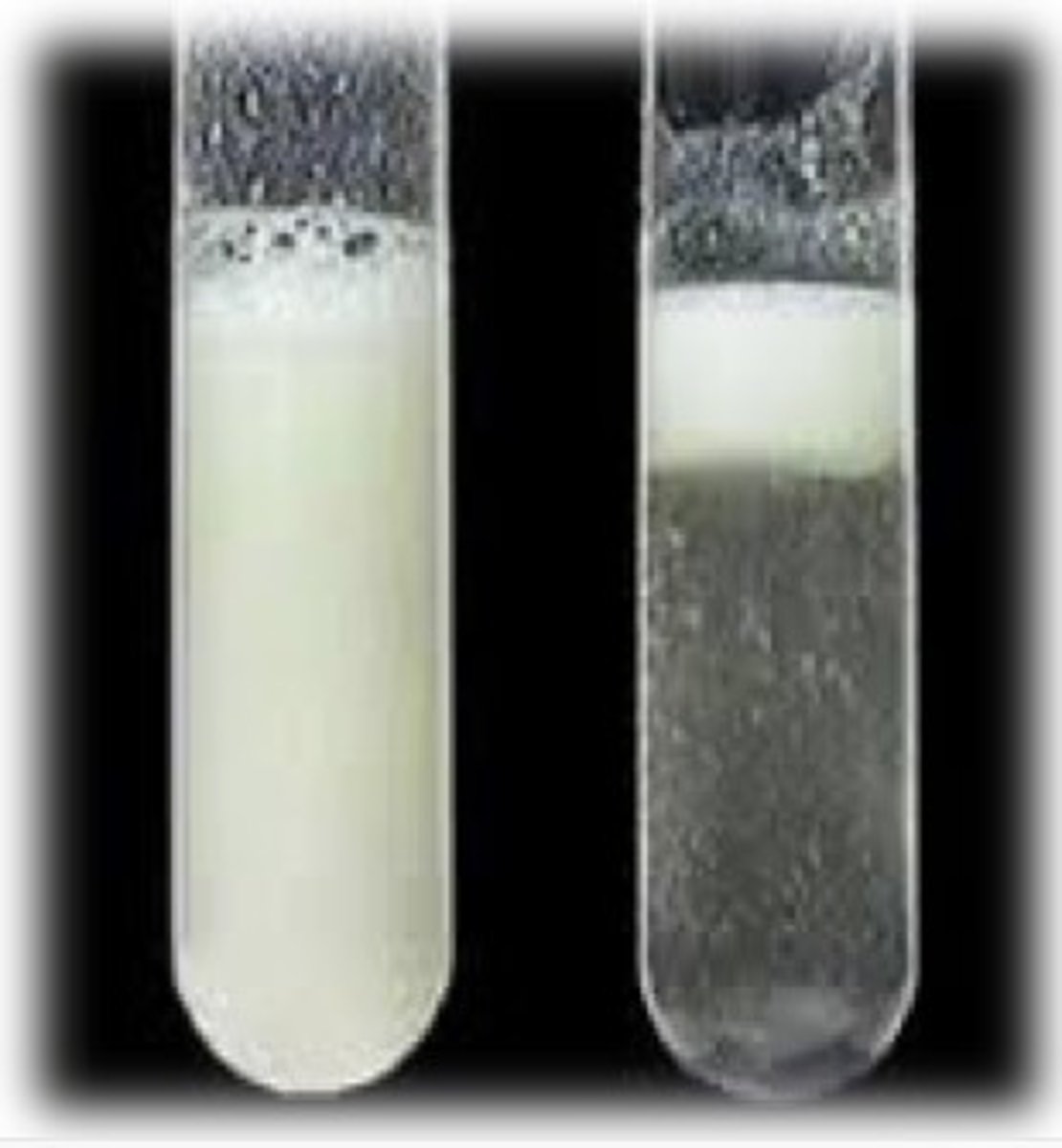
Emulsion Test for Lipids
1) Add a few drops of ethanol
2) Shake
3) Pour over water
4) If lipids are present, you will get a white emulsion
Name all cations:
Ca²⁺
Na⁺
K⁺
H⁺
NH⁴⁺
Ca²⁺ is used in
Muscle contraction
Synapses
Bohr effect
Na⁺ is used in
Nerve impulses
Selective reabsorption
K⁺ is used in
Nerve impulses
H⁺ is used in
Translocation
Chemiosmosis
Photosynthesis
Respiration
Coenzymes
NH⁴⁺ is used in
Nitrogen cycle
Name all anions
NO₃⁻
HCO₃⁻
Cl⁻
PO₄³⁻
OH⁻
NO₃⁻ is used in
Nitrogen cycle
HCO₃⁻ is used in
Bohr effect
Cl⁻ is used in
Bohr effect
PO₄³⁻ is used in
DNA
RNA
Phospholipids
ATP
OH⁻ is used in
Photosynthesis
Fibrous proteins are strong so...
....so provide structural roles
Properties of Fibrous proteins
Insoluble in water
Very strong and tough
Why are fibrous proteins insoluble in water?
Contains a high proportion of amino acids with hydrophobic R groups
Why are fibrous proteins very strong and tough?
Due to many cross bridges between polypeptide chains
Examples of fibrous protein
Keratin
Elastin
Collagen
Keratin
Hair and nails
The more disulphide bridges in the keratin, the stronger it is

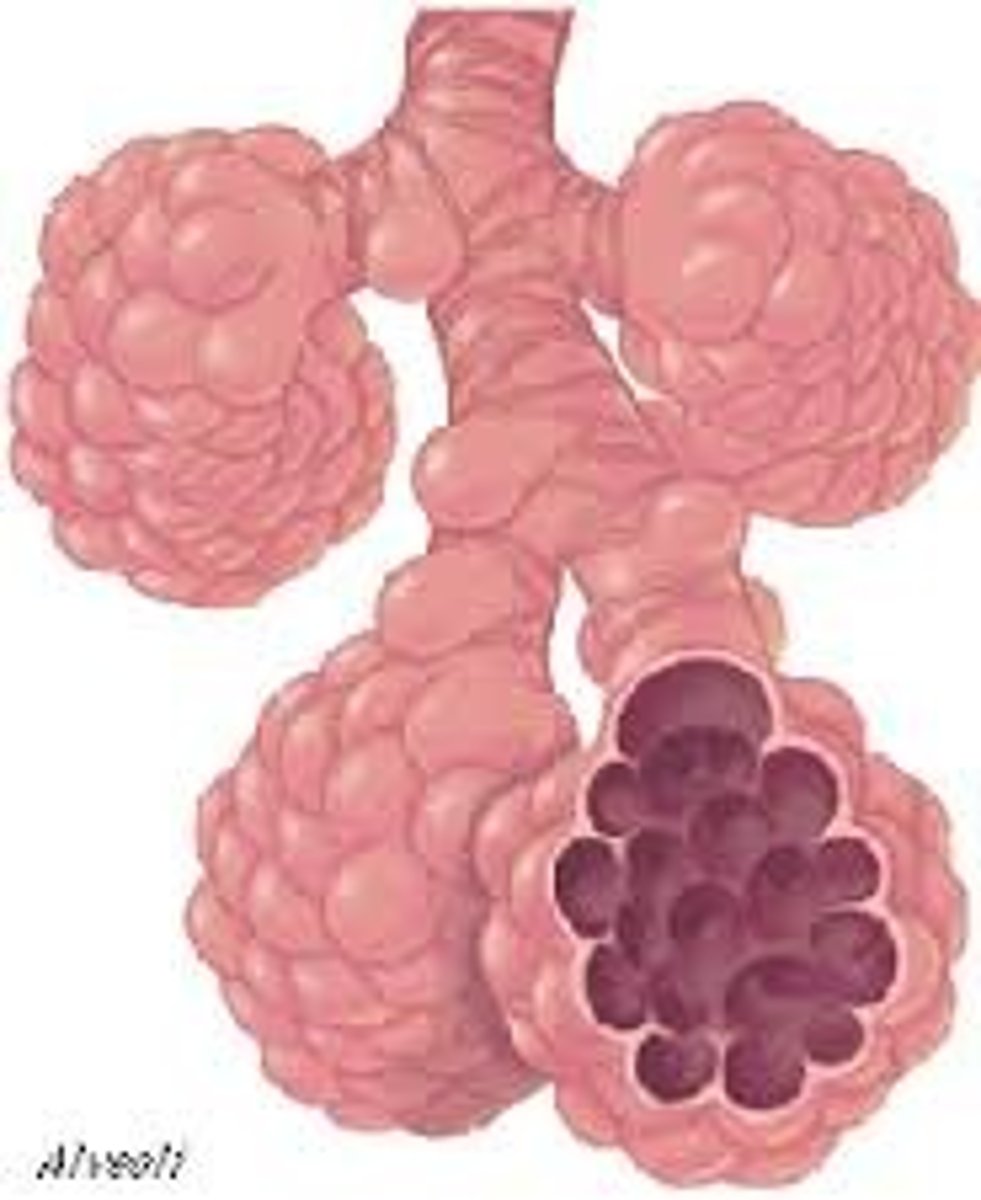
Elastin
Alveoli
Recoils after being deformed
Collagen
Skin
Flexible but doesn't stretch

Properties of globular proteins
- Compact, 3D globular shape
- Soluble in water
- Conjugated proteins have a prosthetic group
Why are globular proteins soluble in water?
They have amino acids with hydrophobic R groups orientate to the inside of the protein
It means they can be easily transported around organisms and be involved in metabolic reactions
What is a prosthetic group?
A non protein component that is tightly or permanently bound to the enzyme
Examples of globular proteins
Haemoglobin (conjugated protein)
Insulin
Catalase (conjugated protein)
Haemoglobin
- Conjugated Protein
- Can change shape
- Quaternary structure with 4 polypeptide chains. These chains are globin proteins, with 2 α-globins and 2 β-globins
- The 4 globin subunits are held together with disulphide bonds, arranged so that the hydrophobic R-groups face inwards and vice versa
- Each globin subunit has a prosthetic haem group containing Fe²⁺
Insulin
- Specific fixed shape
- Consists of 2 polypeptide chains, held together by 3 disulphide bridges
Catalase
- Conjugated protein
- Specific fixed shape
- Intracellular enzyme
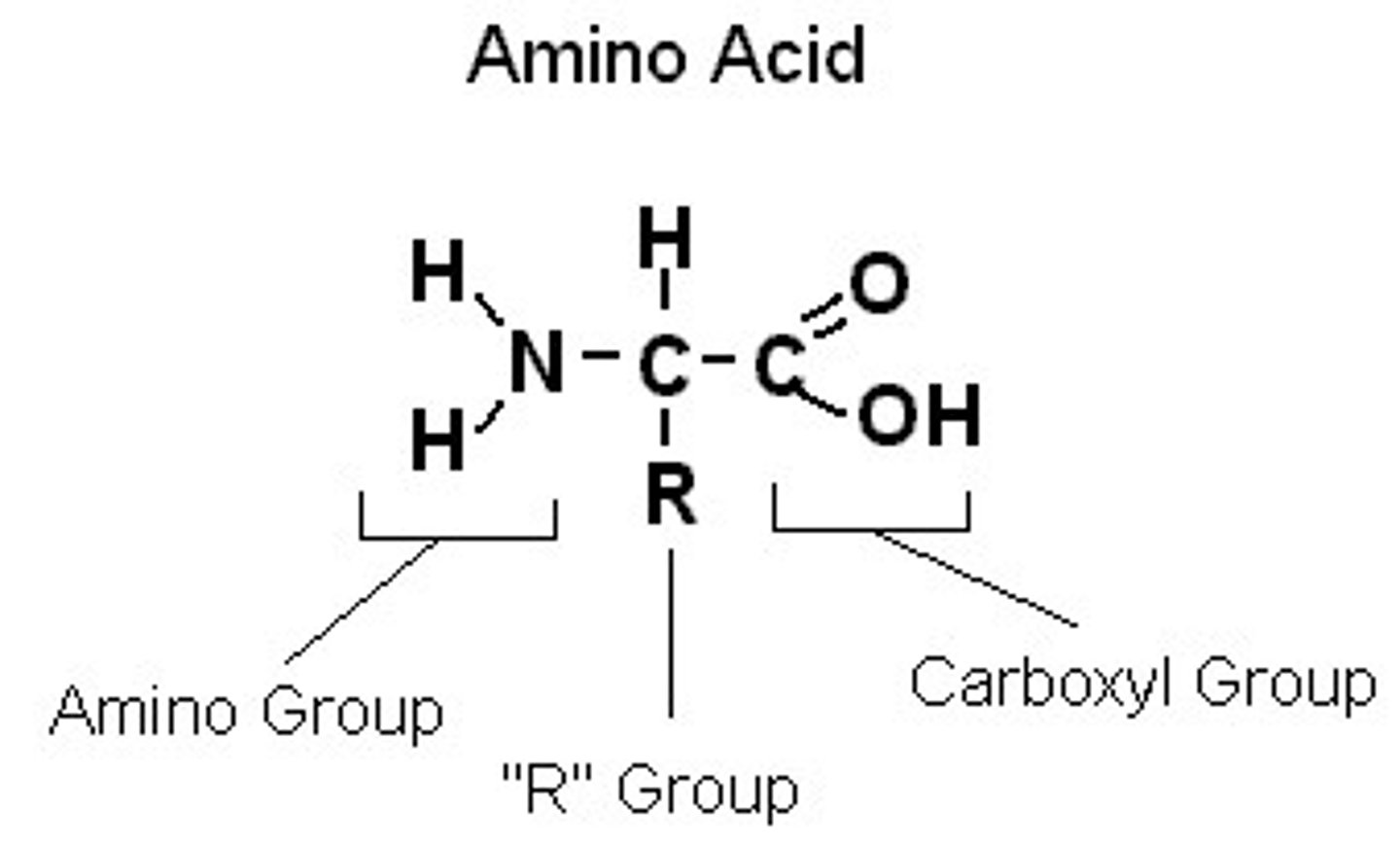
Structure of Amino Acid
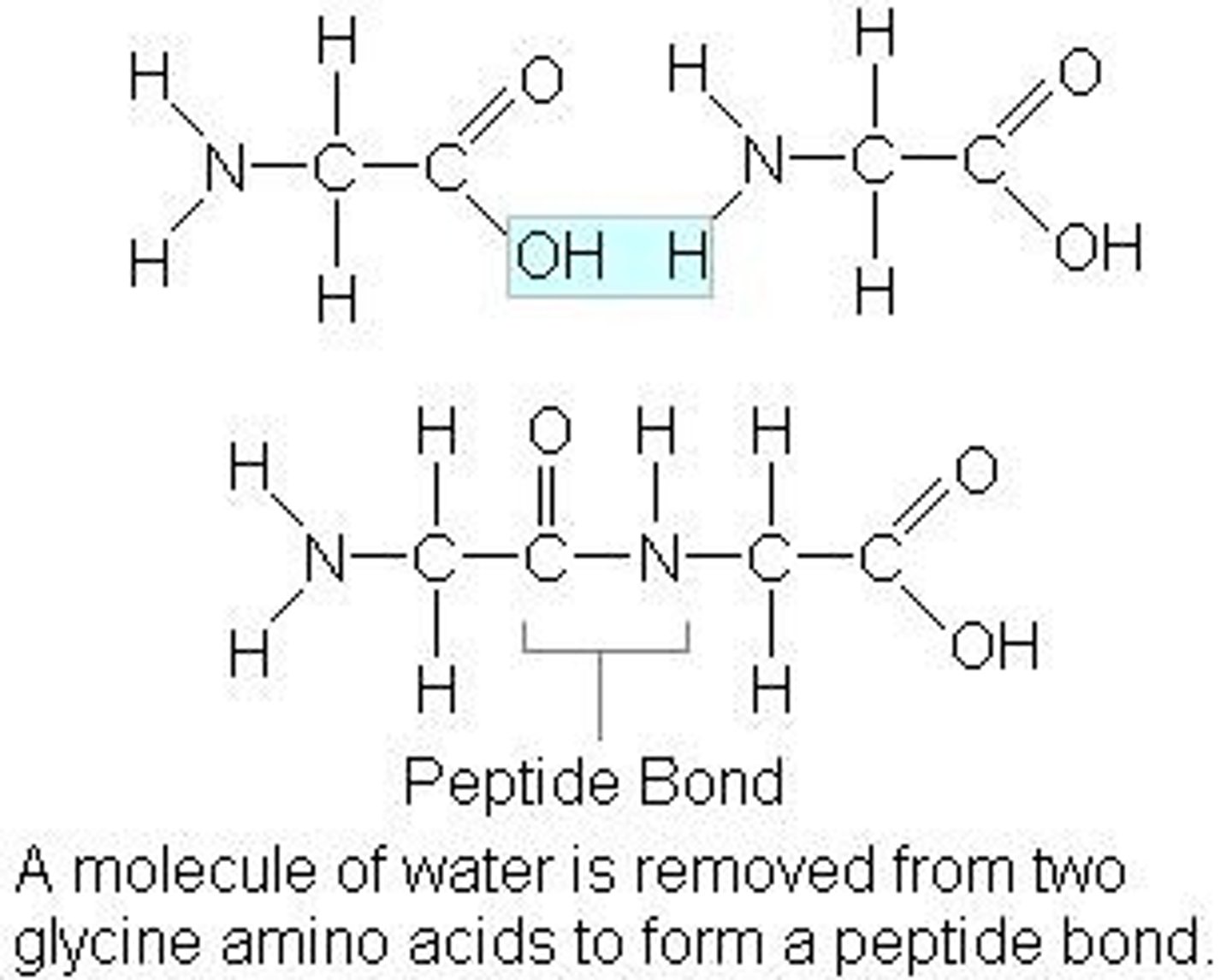
Dipeptide Formation Reaction
2 amino acids join together to form a dipeptide
A molecule of water is removed
- Ensure to circle the OH and H reacting, and label the peptide bond, and write in the H2O molecule removed
Primary structure
The sequence of amino acids bonded by peptide bonds

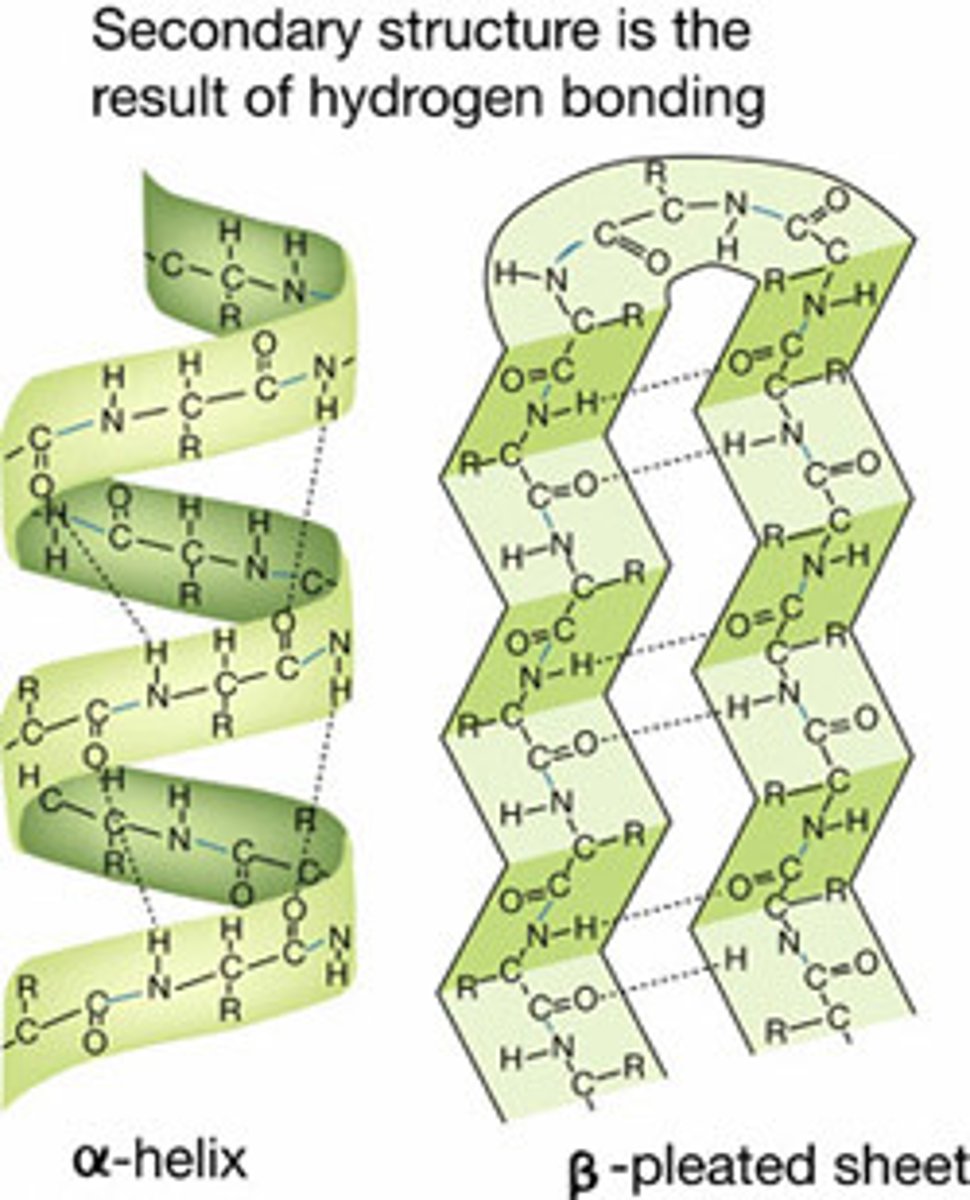
Secondary structure
Folding of the polypeptide chain.
Held in place with hydrogen bonds
Alpha helix or beta pleated sheets
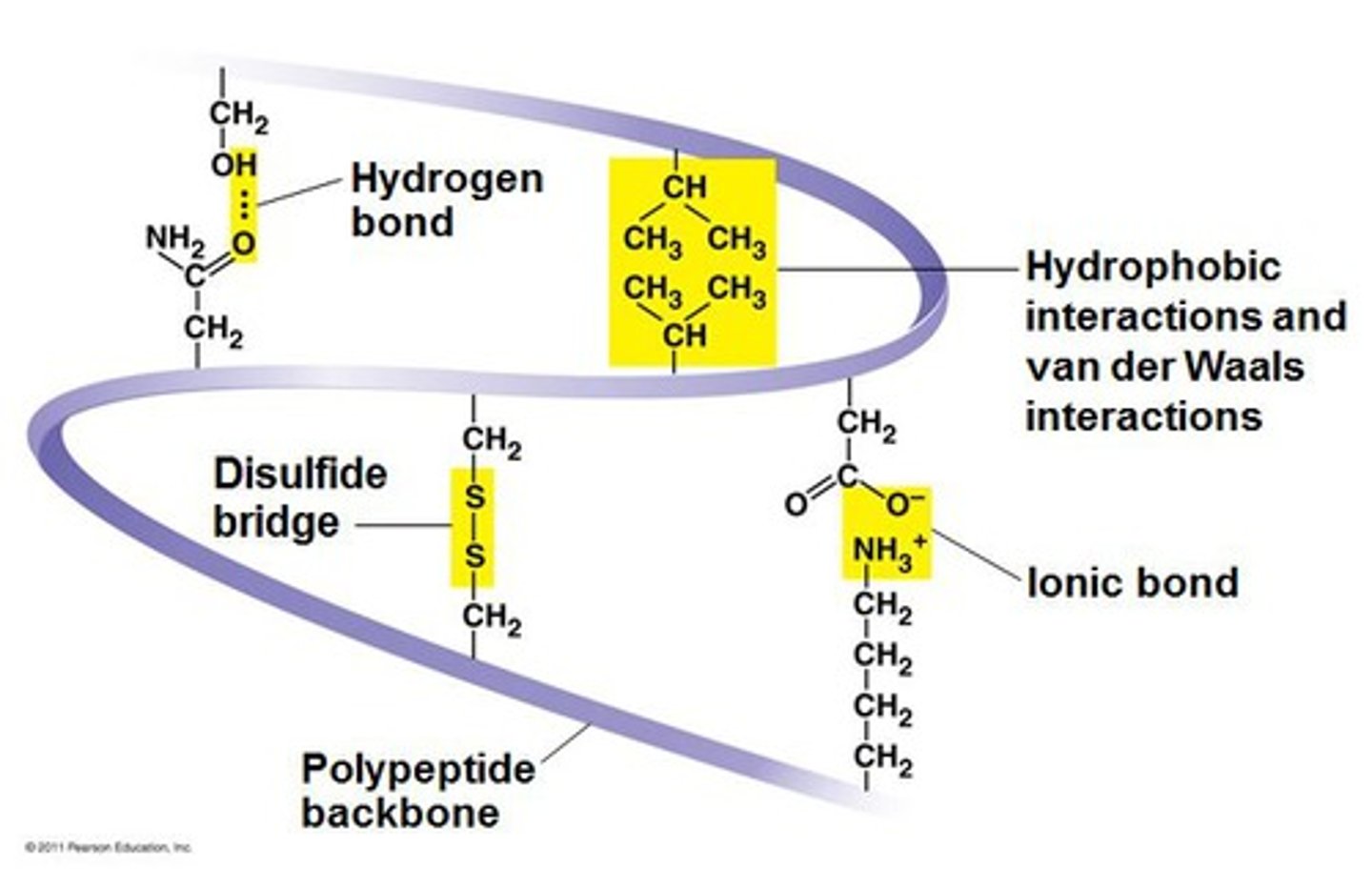
Tertiary structure
Further folding of the polypeptide chain
Held in place with:
- Hydrogen bonds
- Disulphide bridges
- Ionic bonds
- Amino acids with hydrophobic R groups orientated to the centre of the protein, amino acids with hydrophilic R groups orientated towards the outside of the protein
Quaternary structure
More than 1 polypeptide chain
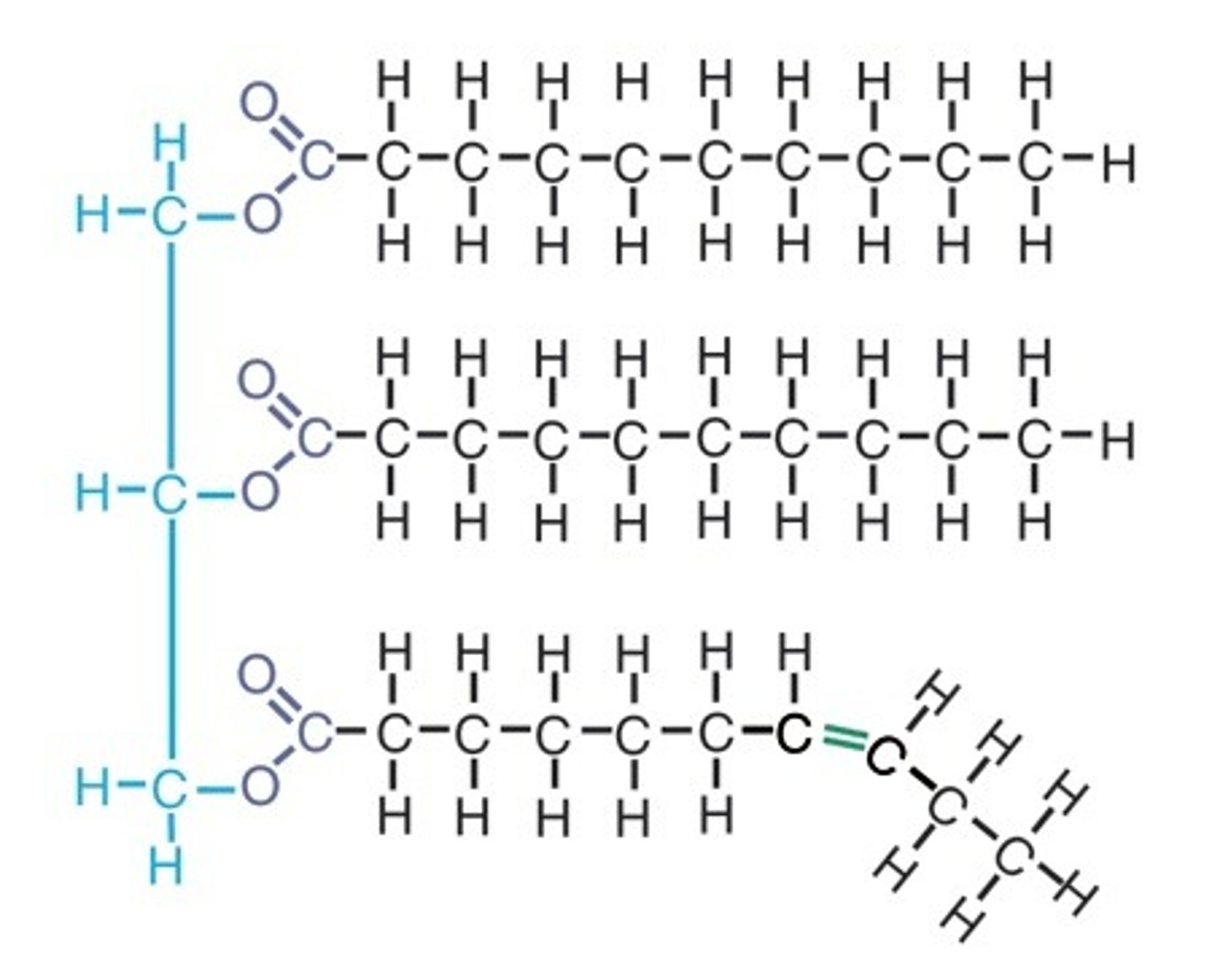
Unsaturated triglyceride
Cannot lie as close to another unsaturated triglyceride, therefore creating a less dense substance (such as oil)
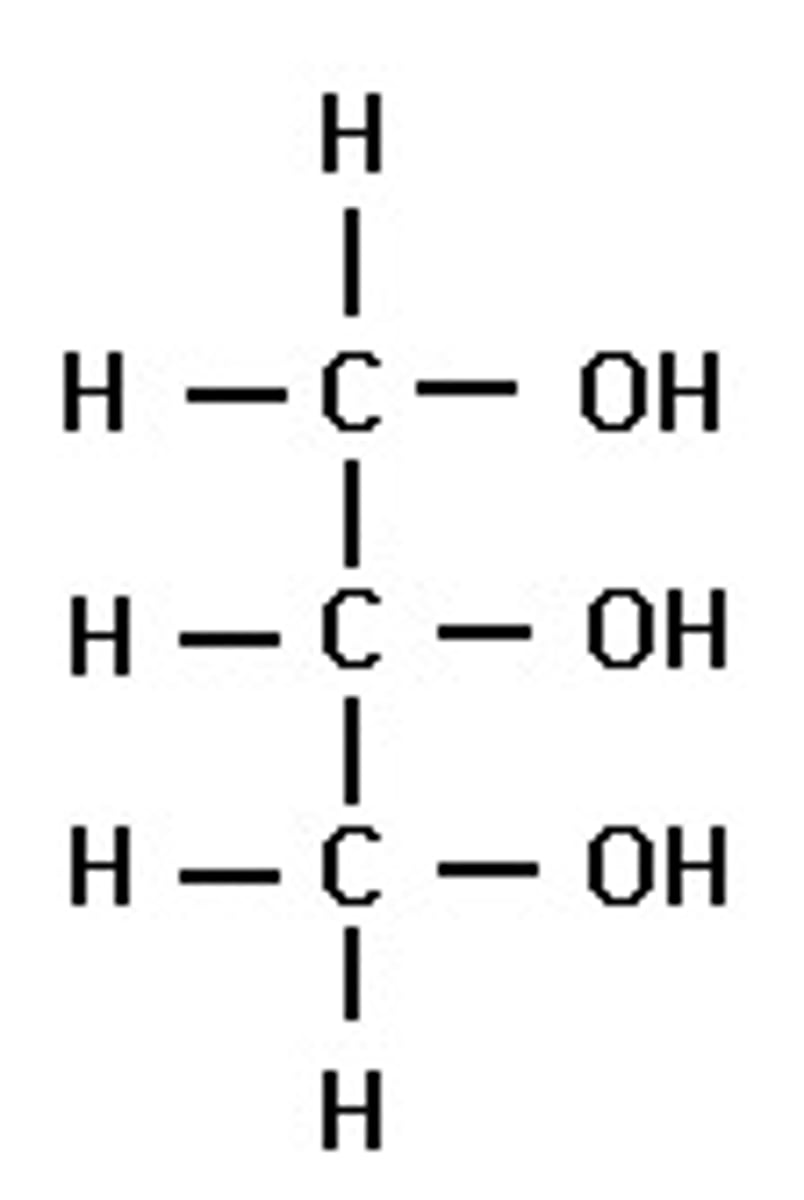
Glycerol structure
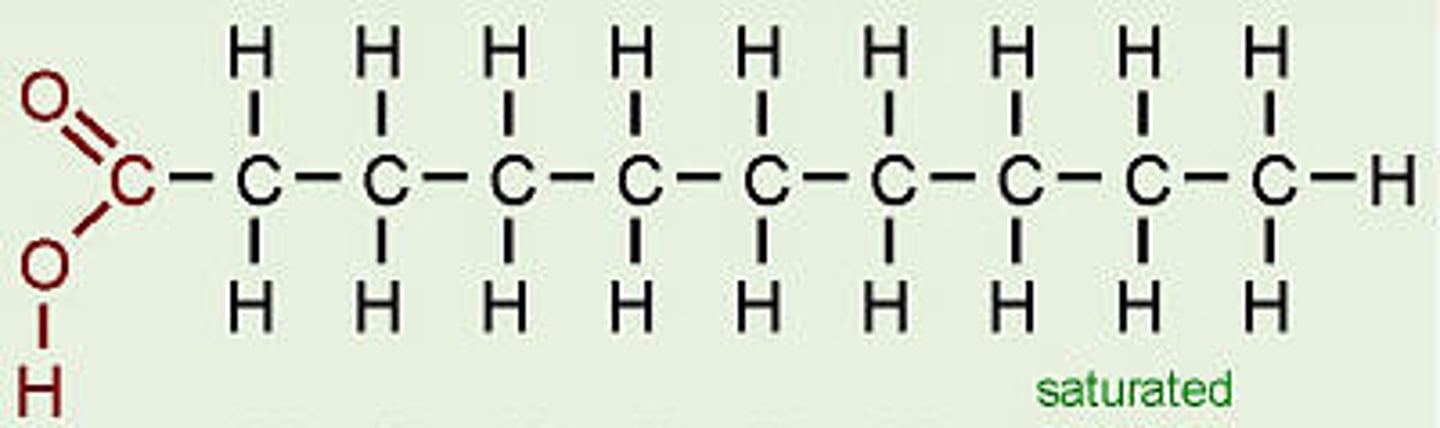
Fatty acid structure
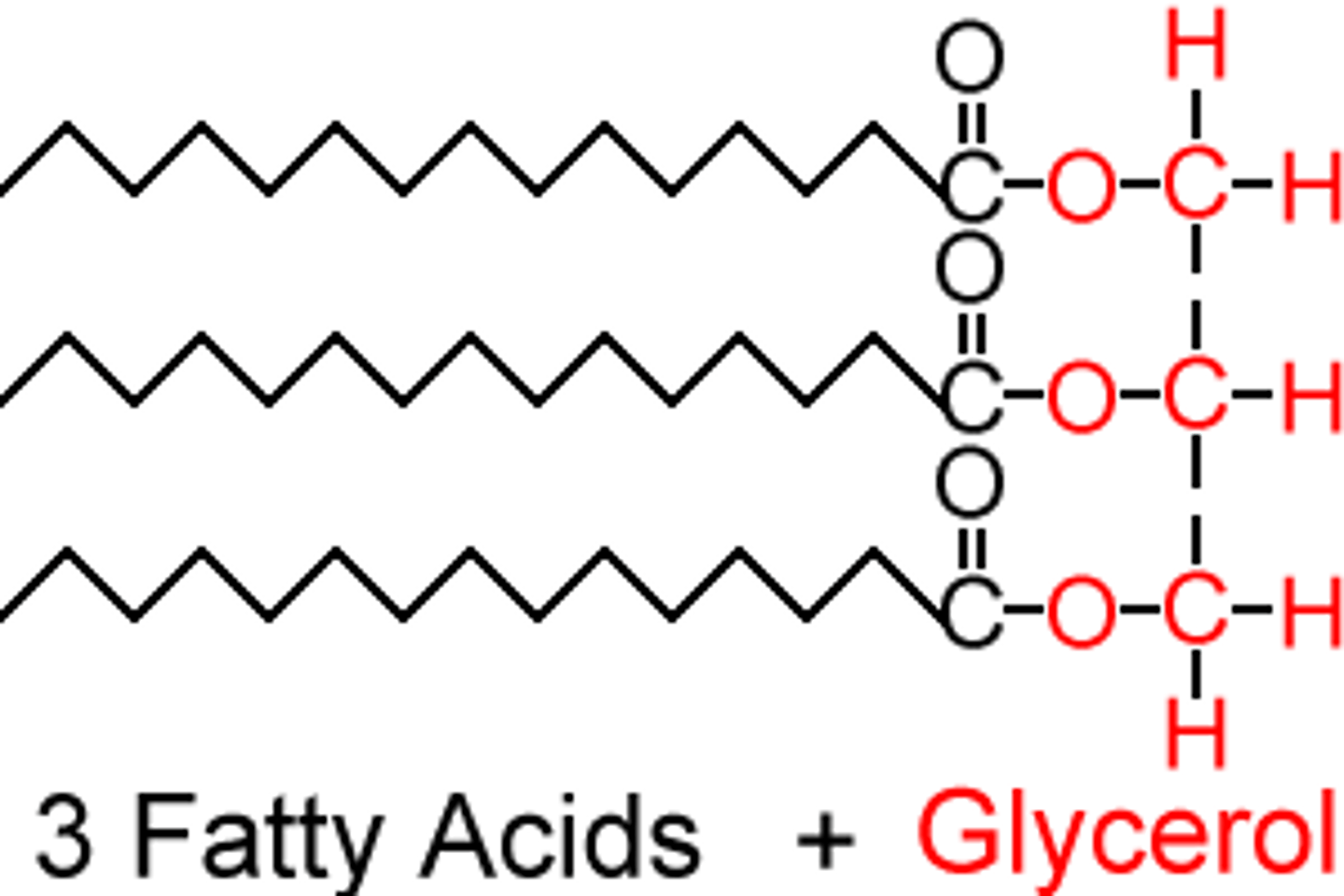
Triglyceride Structure
Ester bond joining the 3 Fatty Acids to the Glycerol
3 H₂O molecules removed in condensation reaction
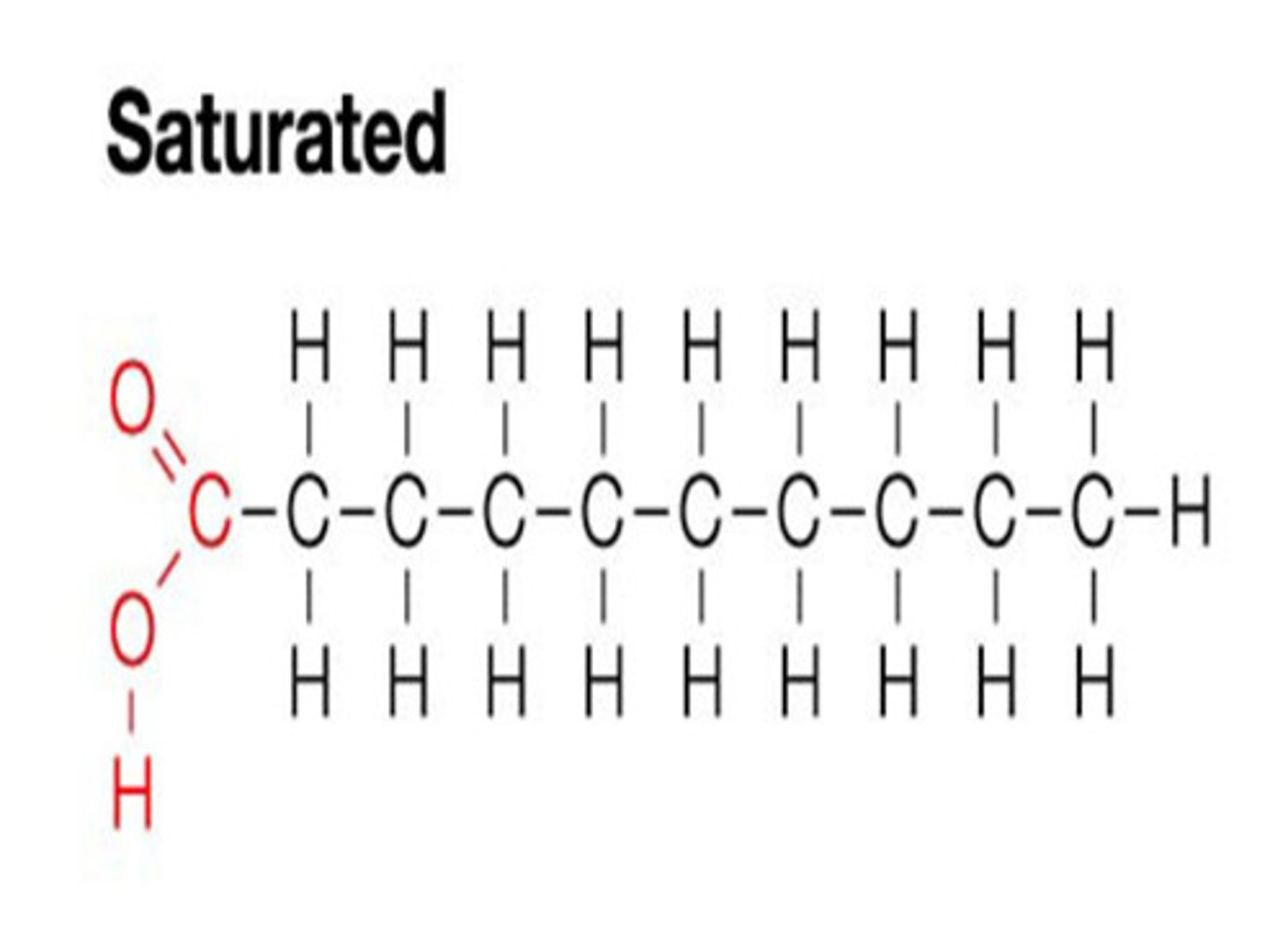
Saturated fatty acid chains
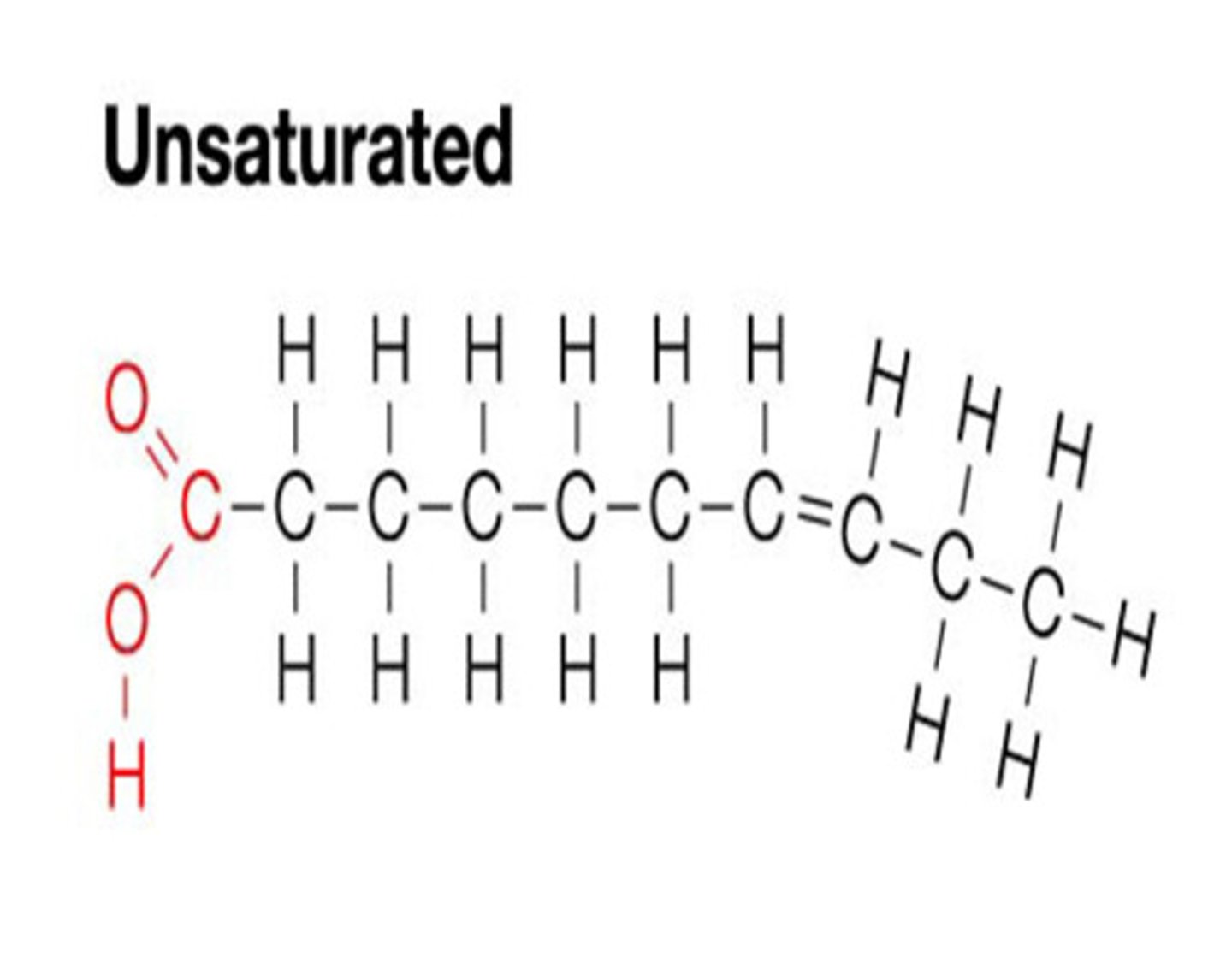
Unsaturated fatty acid chains
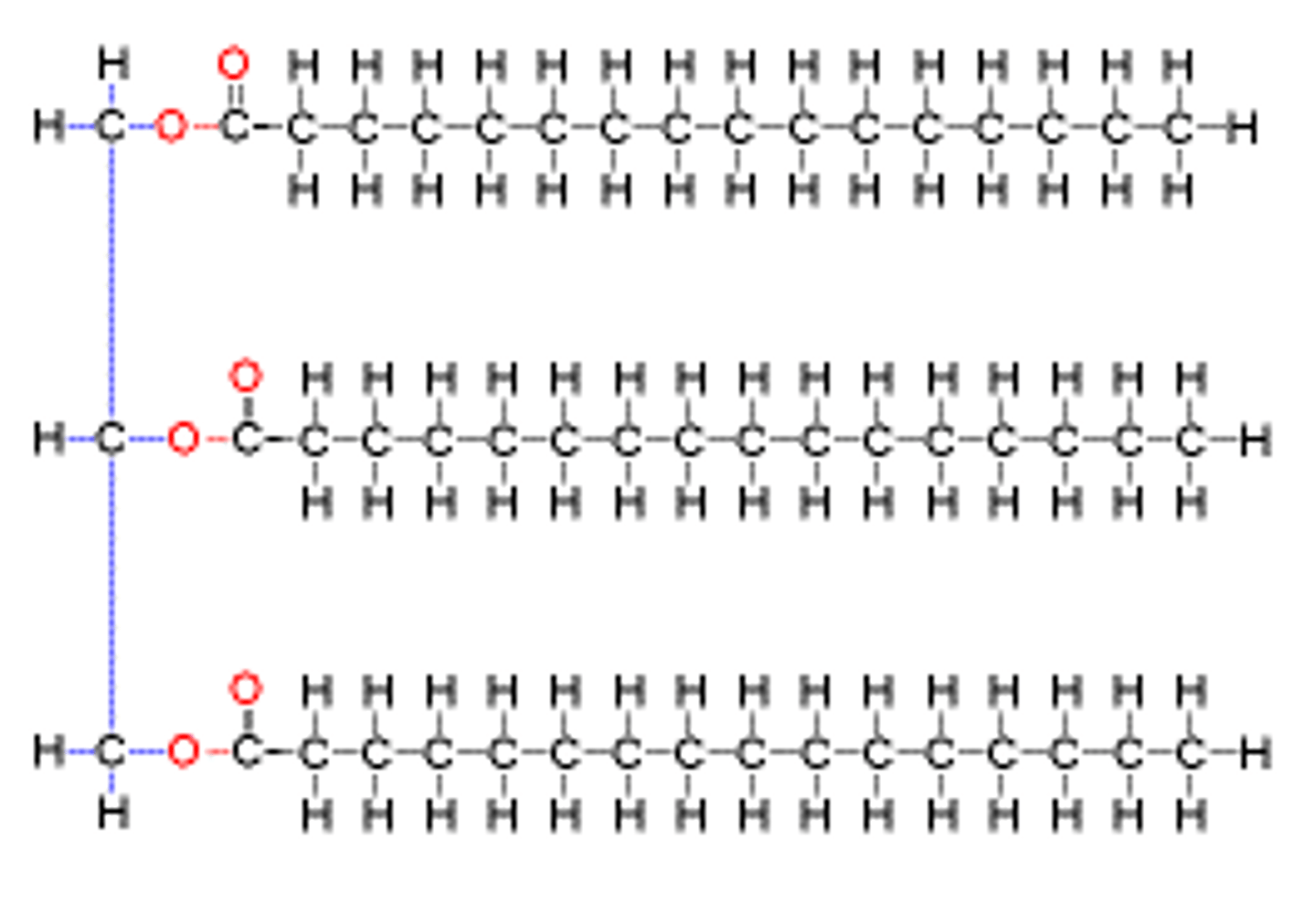
Saturated triglyceride
Creates lard, margarine
What's the function of triglycerides?
- Stores energy: they are used as a respiratory substrate and release water when broken down
- They are insoluble so they don't affect water potential
- Used to make hormones
- Water proofing
- Buoyancy
- Good at forming layers of insulation for warmth, or protective layers around organs or on nerves (like the myelin sheath)
- Aids fat absorption
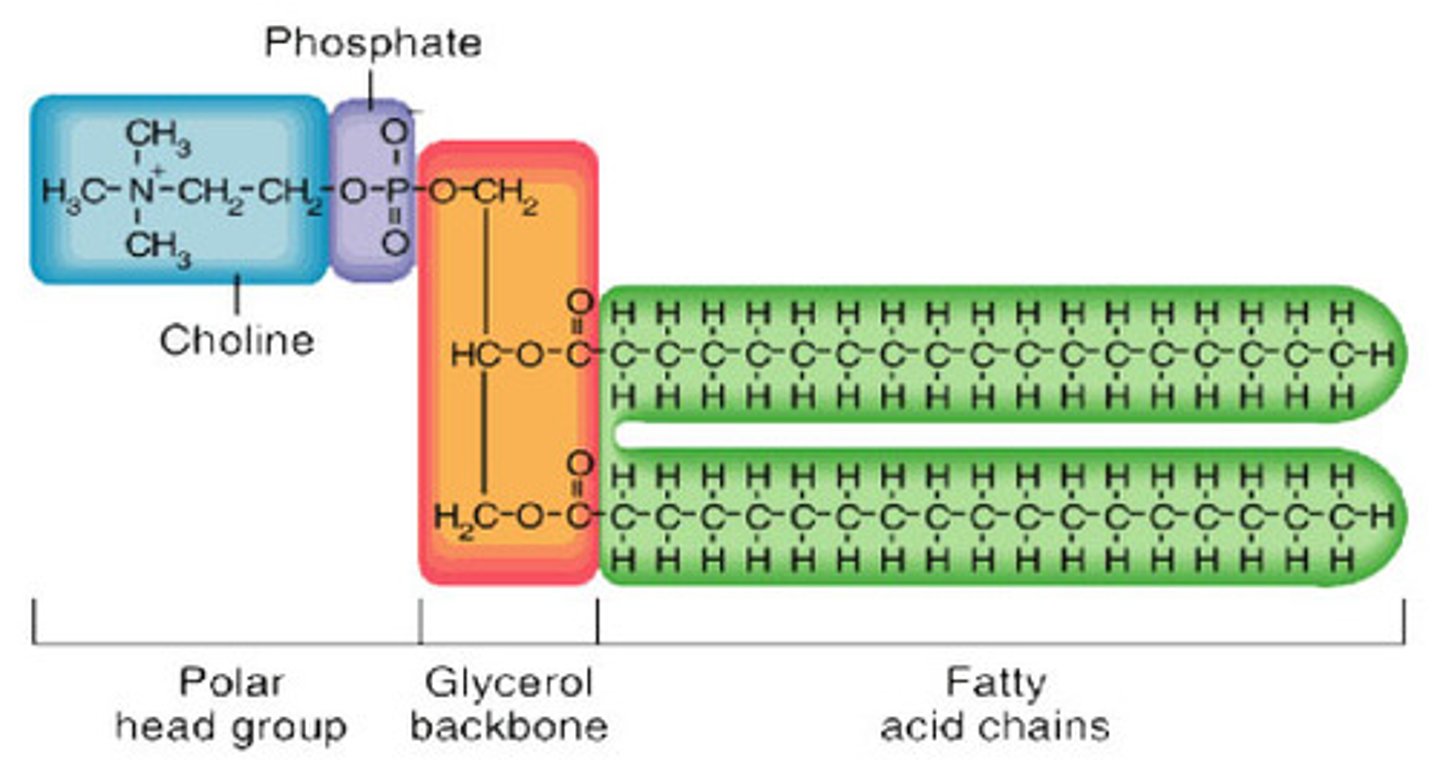
Phospholipid
Hydrophilic head
Hydrophobic tails
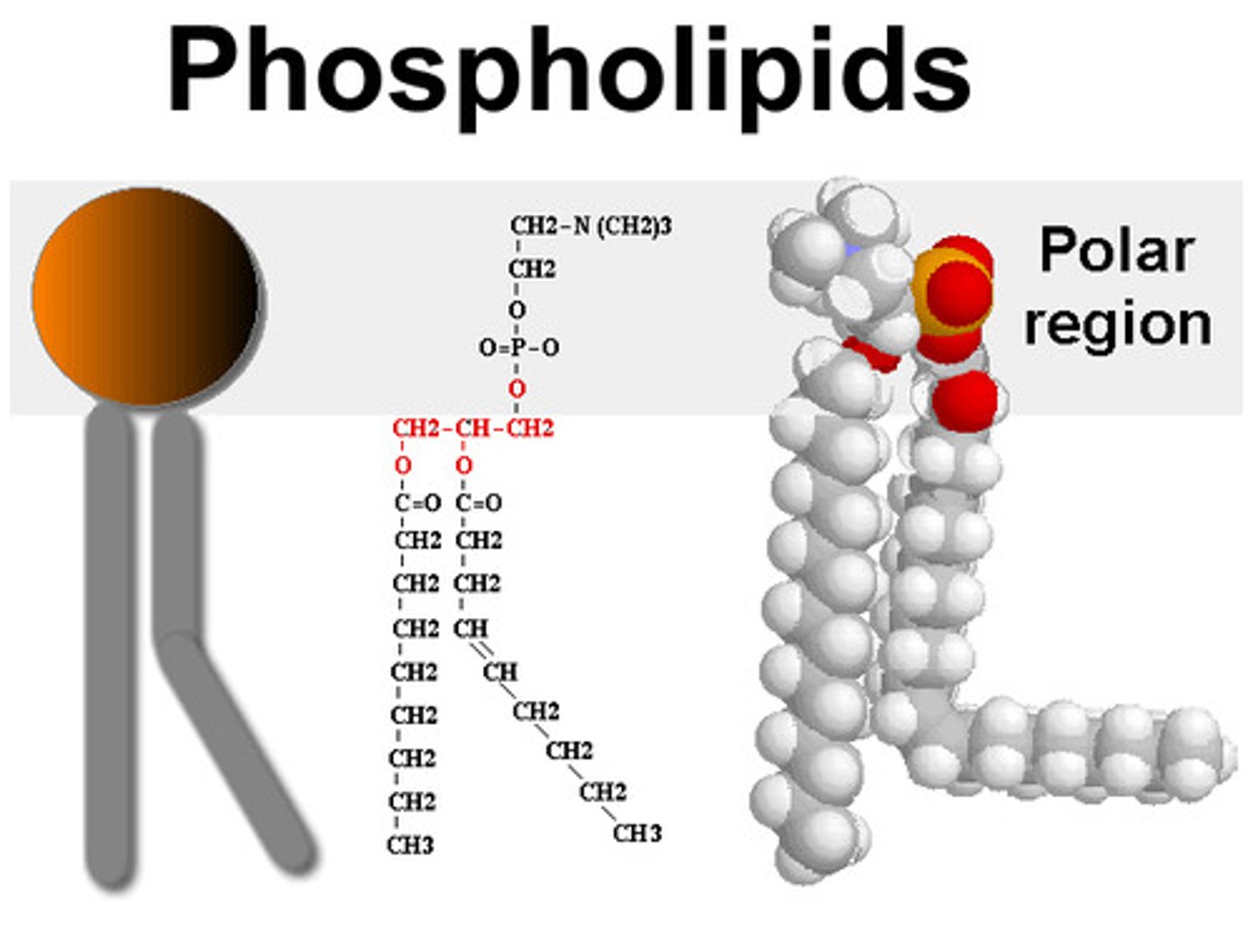
Phospholipid structure explanation
Similar to a triglyceride, but one of the fatty acids is replaced by a phosphate group
Fatty acids are non polar and insoluble in water (hydrophobic)
The phosphate group is polar and water soluble (hydrophilic). The hydrophilic heads orientates towards the water.
What do phospholipids form?
Phospholipid bilayer
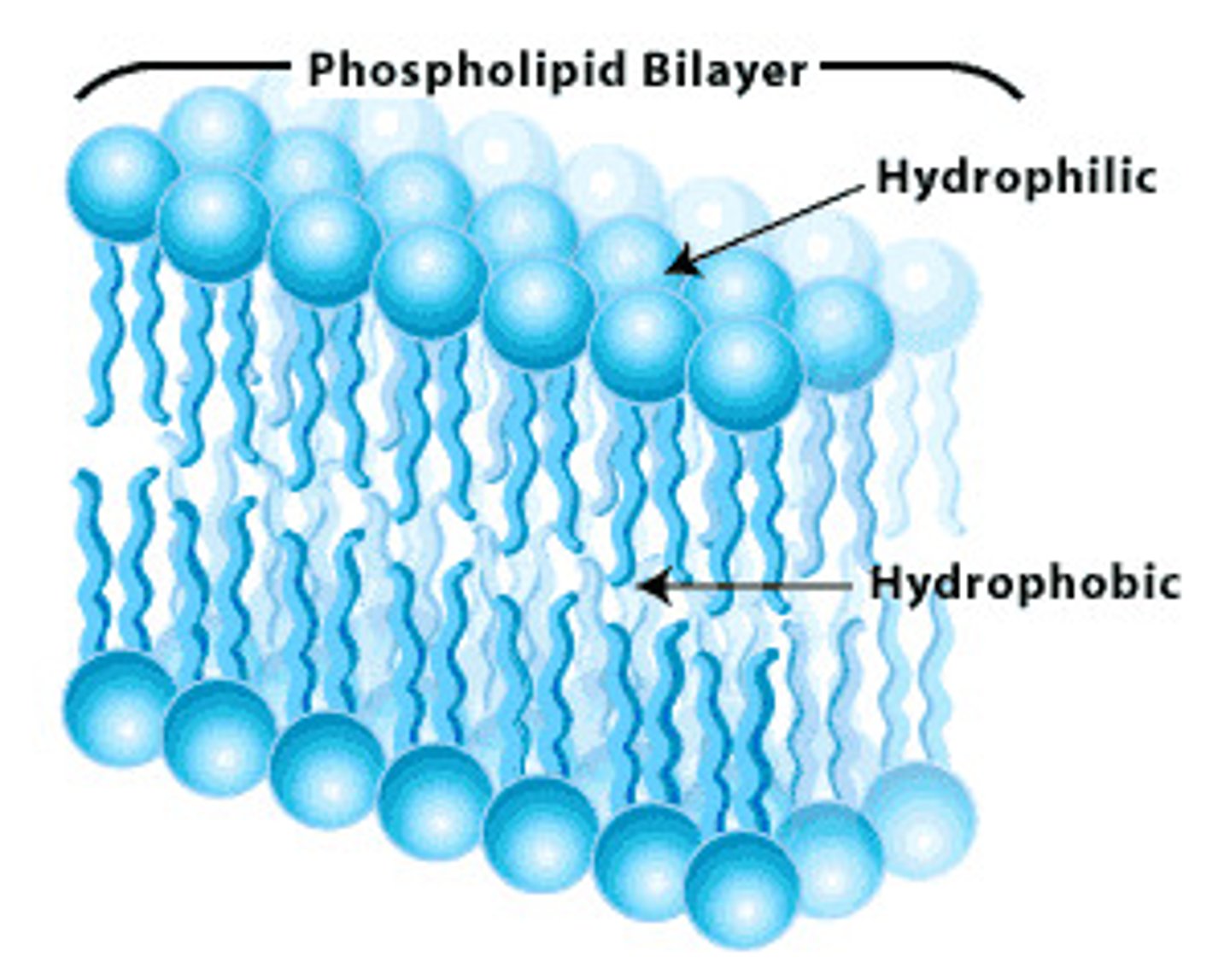
What does cholesterol do?
Cholesterol molecules form part of the cell membrane and regulates fluidity
How does cholesterol regulate fluidity?
Their small size and flattened shape allows them to fit between phospholipids and bind to their hydrophobic tails, making the membrane more rigid.
At low temperatures, cholesterol increases the fluidity of membranes
At high temperatures, cholesterol decreases the fluidity of membranes
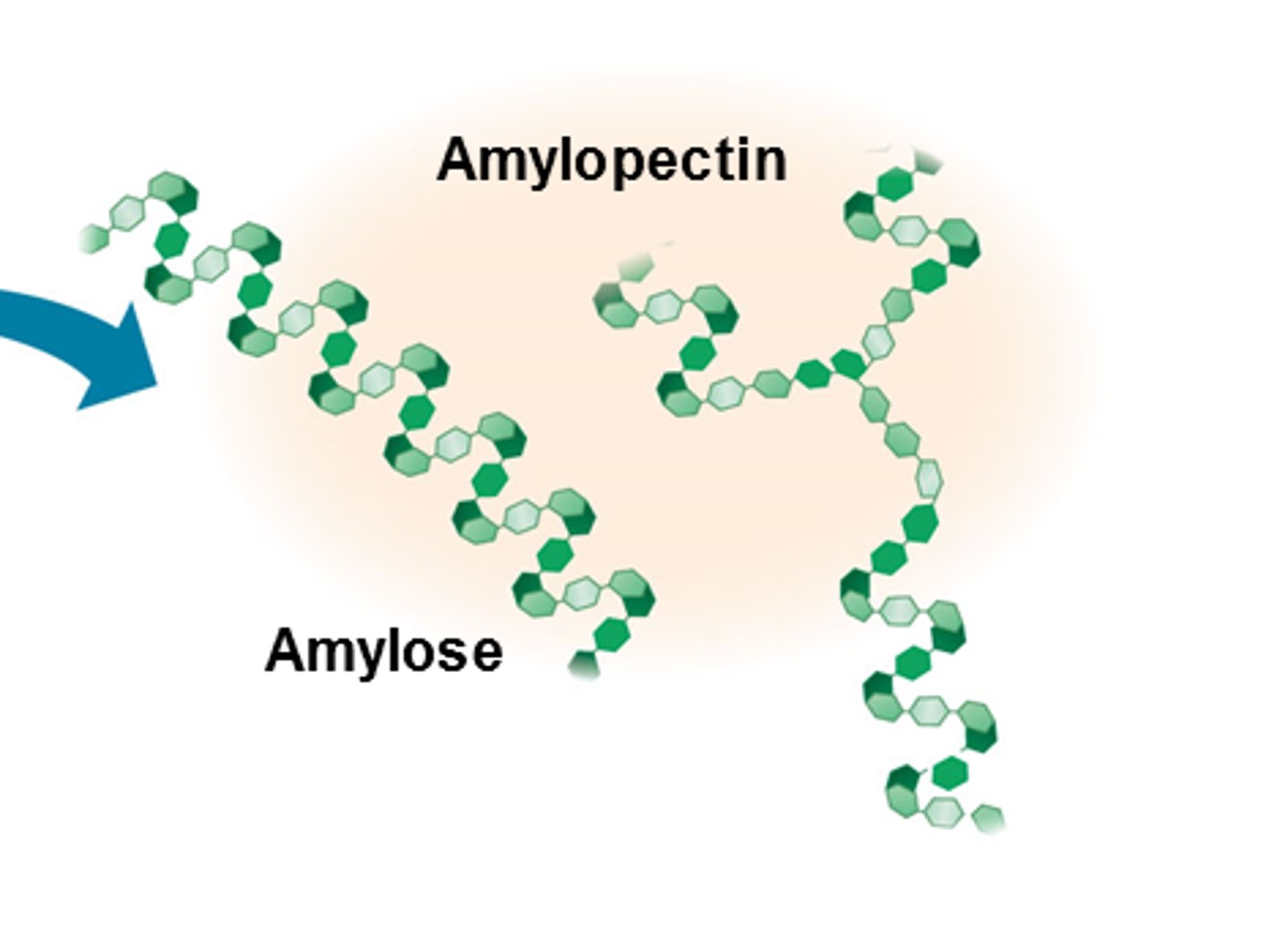
Starch is in plants and made up of what?
Amylose
Amylopectin
Amylose structure
- Unbranched and helix shaped (coiled)
- Only 1,4 α-glycosidic bonds
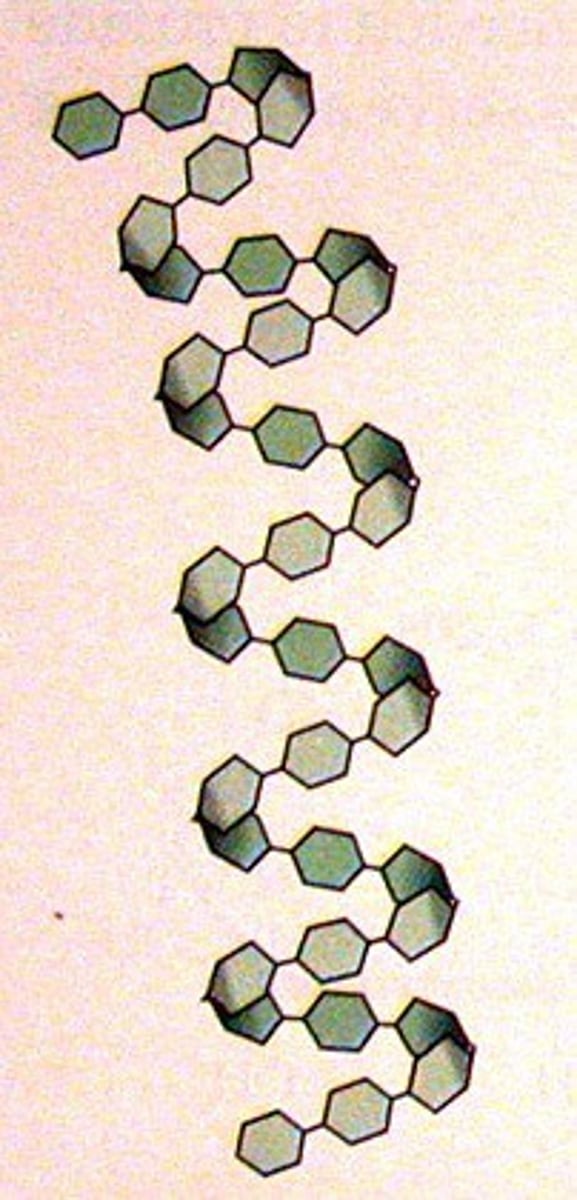
How does the coiled shape of amylose help?
Enables it to be more compact
Amylopectin structure
- Branched and uncoiled
- Has 1,4 and 1,6 α-glycosidic bonds
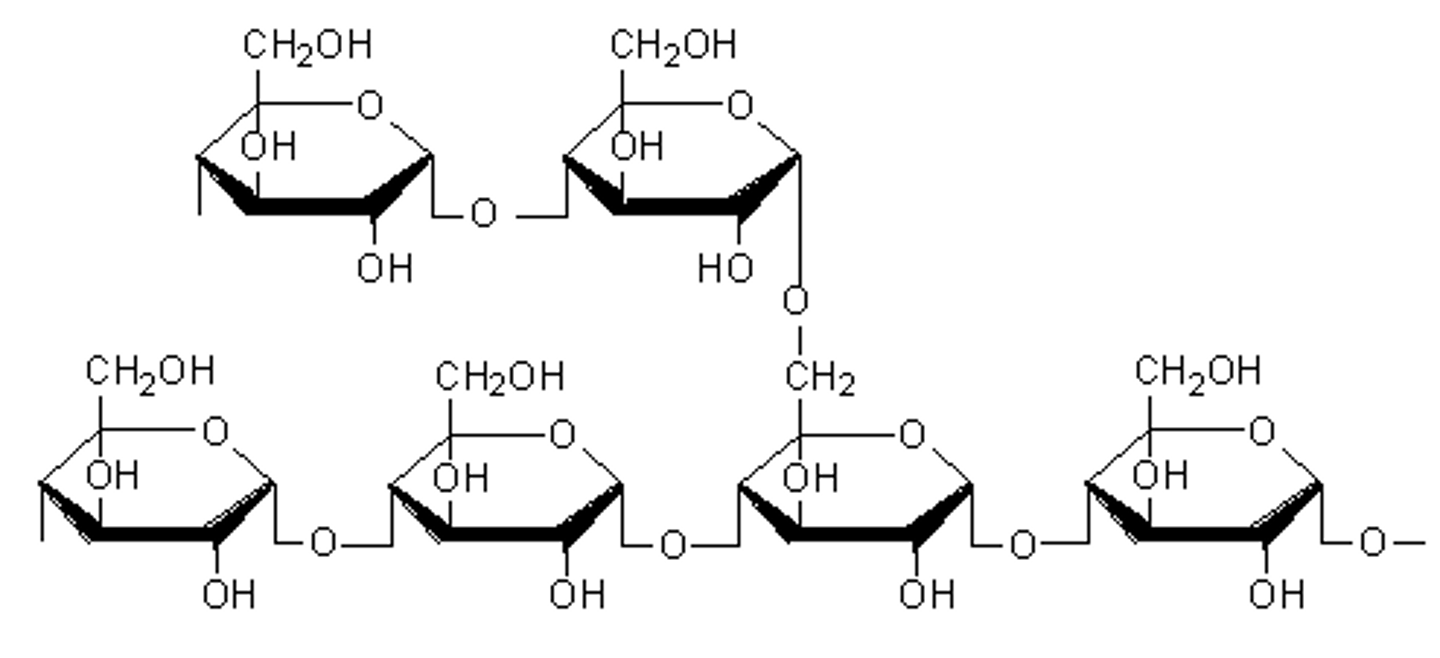
Why is the structure of amylopectin branched ?
The branches mean many glucose molecules can be easily hydrolysed for use during cellular aerobic respiration
Glycogen is in animals and is made up of what?
Alpha glucose subunits
Glycogen structure
- Branched molecule
- Has 1,4 and 1,6 α-glycosidic bonds
Do starch and glycogen dissolve?
No, therefore they don't affect the water potential.
Cellulose structure
- Unbranched
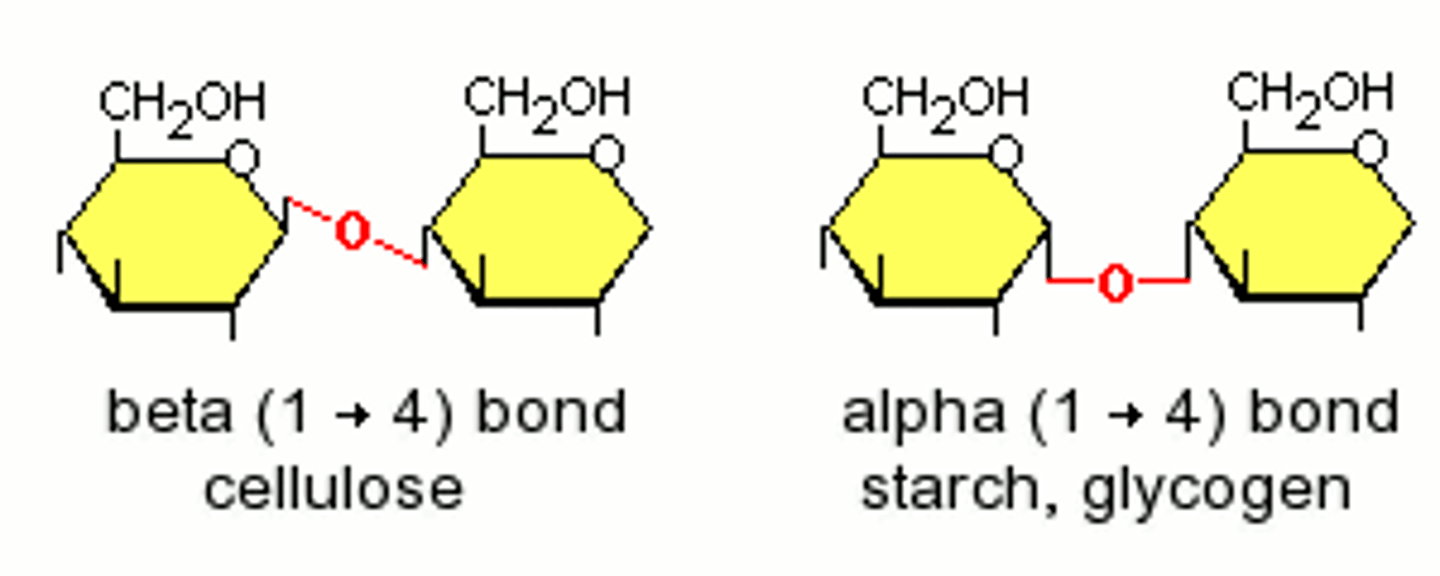
- 1,4 β-glycosidic bonds, that must be rotated 180° to each other
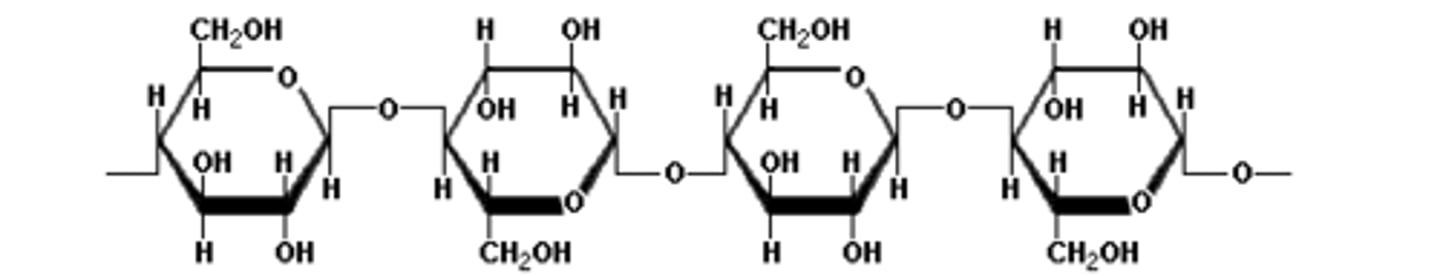
Beta glucose glycosidic bonds
They form beta pleated sheets between hydrogen bonds, which can form cross links to form bundles called microfibrils.
Larger microfibrils are called....
macrofibrils
Importance of cellulose structure:
Provides high tensile strength and make up plant cell walls.
Allows water to pass through, preventing the cell from bursting, determining shape.
Condensation reactions
Occurs when a water molecule is removed to form a covalent bond
Hydrolysis reactions
Occurs when a water molecule is added to break a covalent bond
Lipids are made up of
C H O
Proteins are made up of
C H O N S
Nucleic acids are made up of
C H O N P
Carbohydrates are made up of
C H O
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars form the monomer units
Disaccharides
Made of 2 monosaccharide molecules joined together
Polysaccharides
Made up of a long chain of monosaccharides.
Starch is a long chain of a-glucose molecules. It is used by plants as an energy store
α-glucose
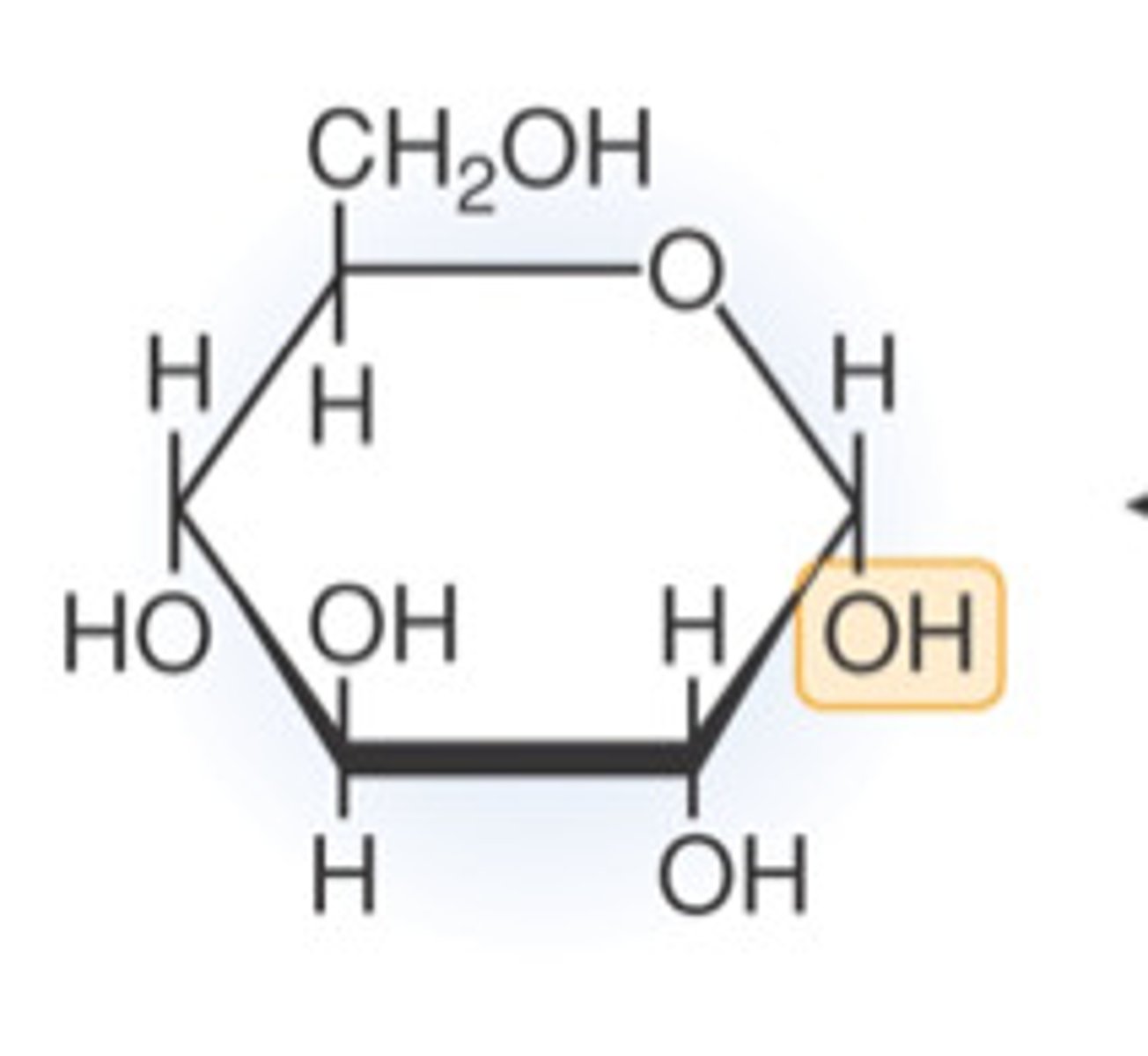
β-glucose
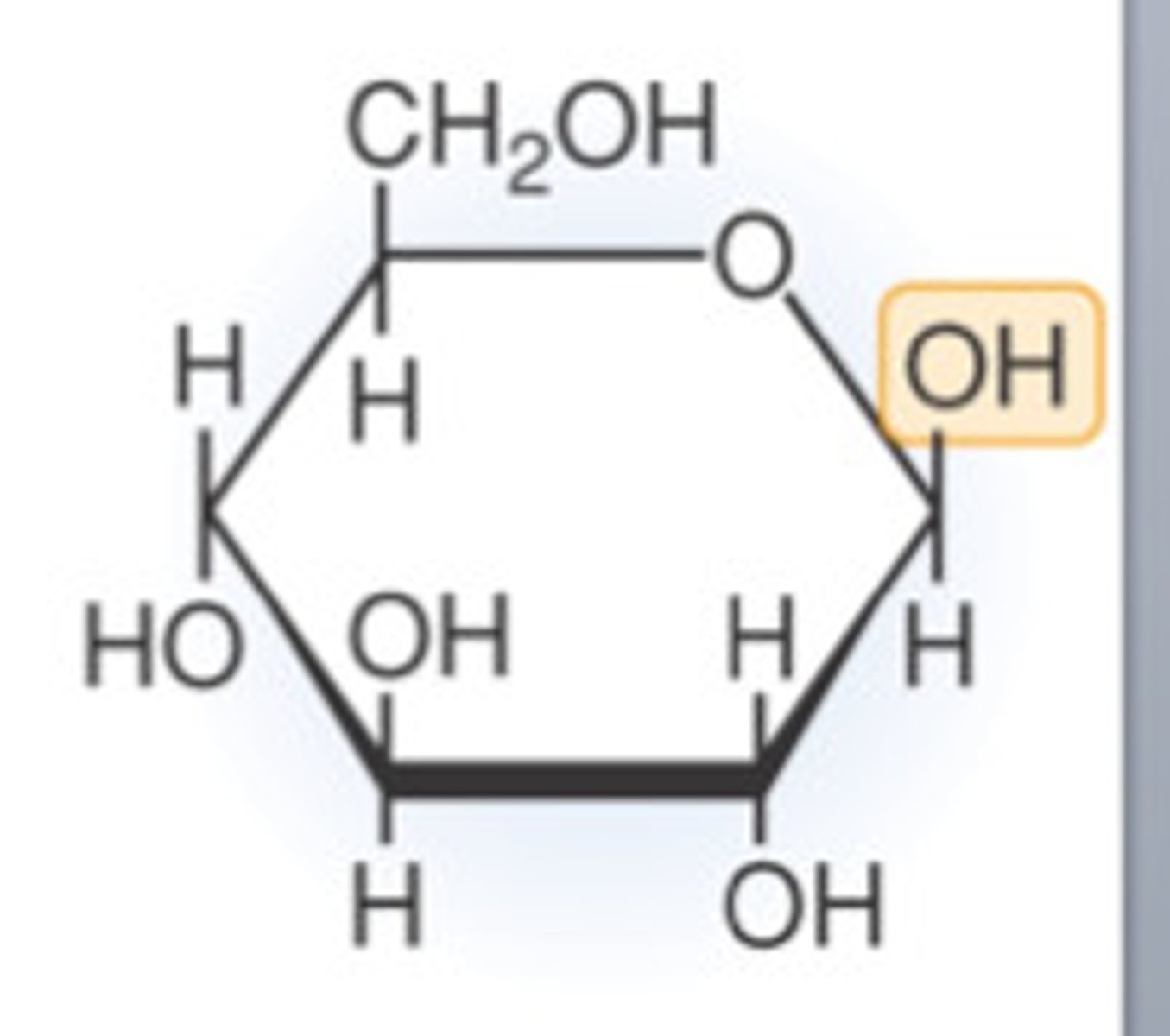
Ribose
- 5C sugar
- RNA

Disaccharide of Sucrose
α-glucose + fructose
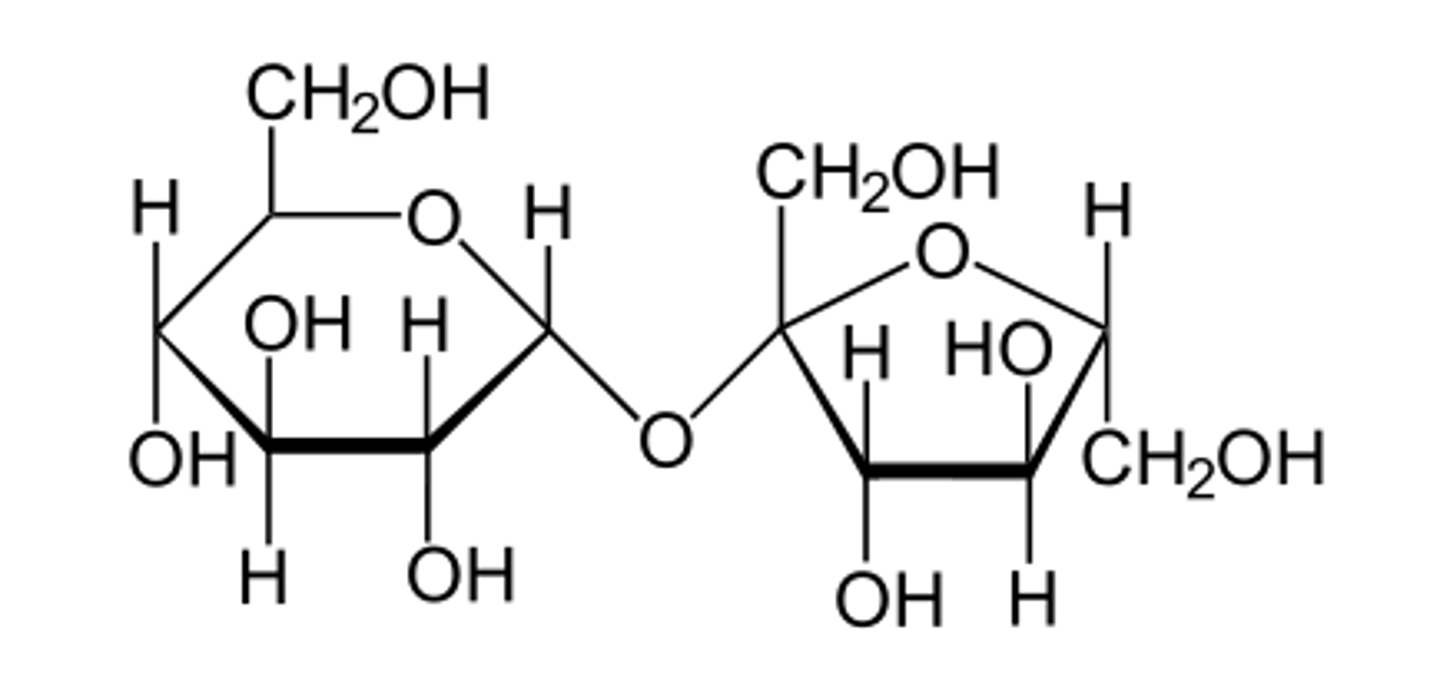
Disaccharide of Lactose
β glucose + Galactose
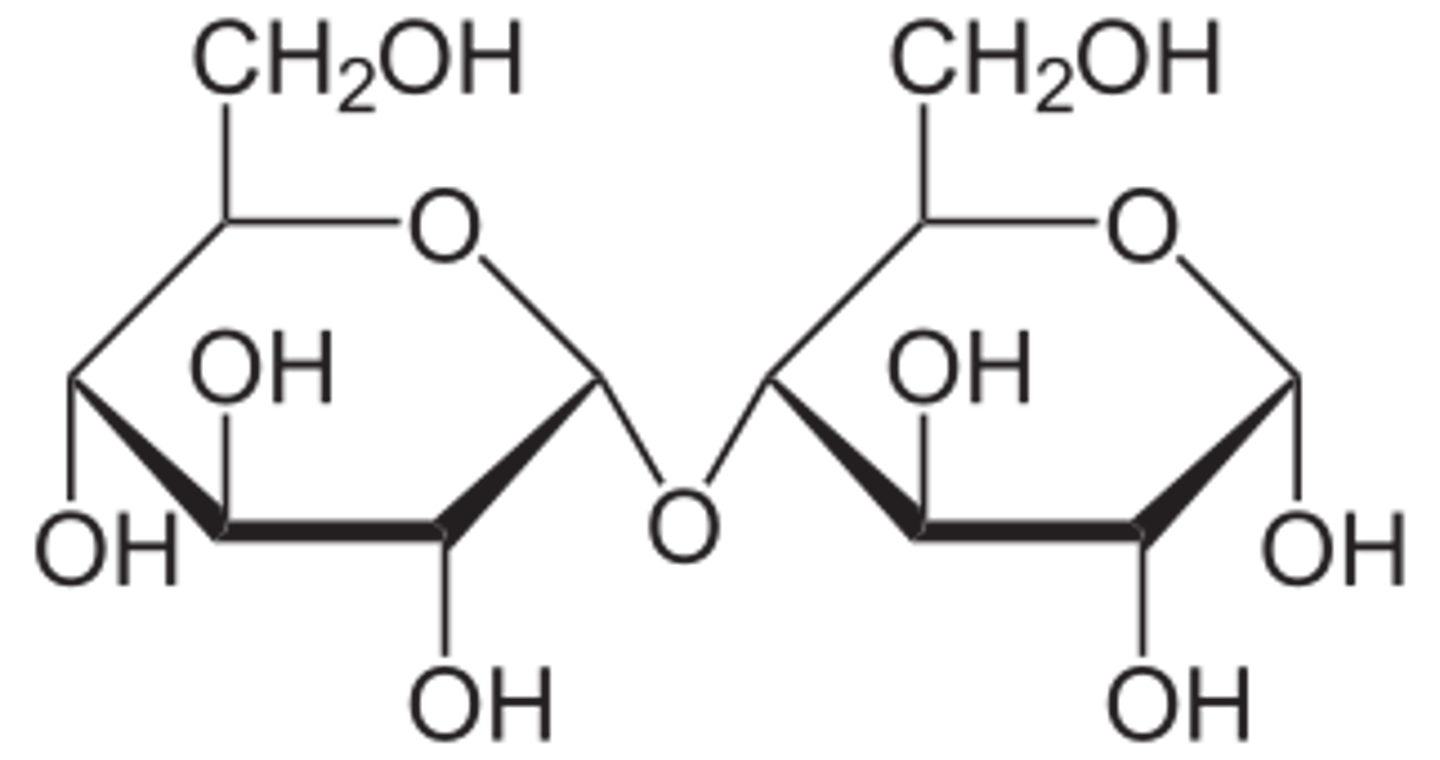
Disaccharide of Maltose
α-glucose + α-glucose
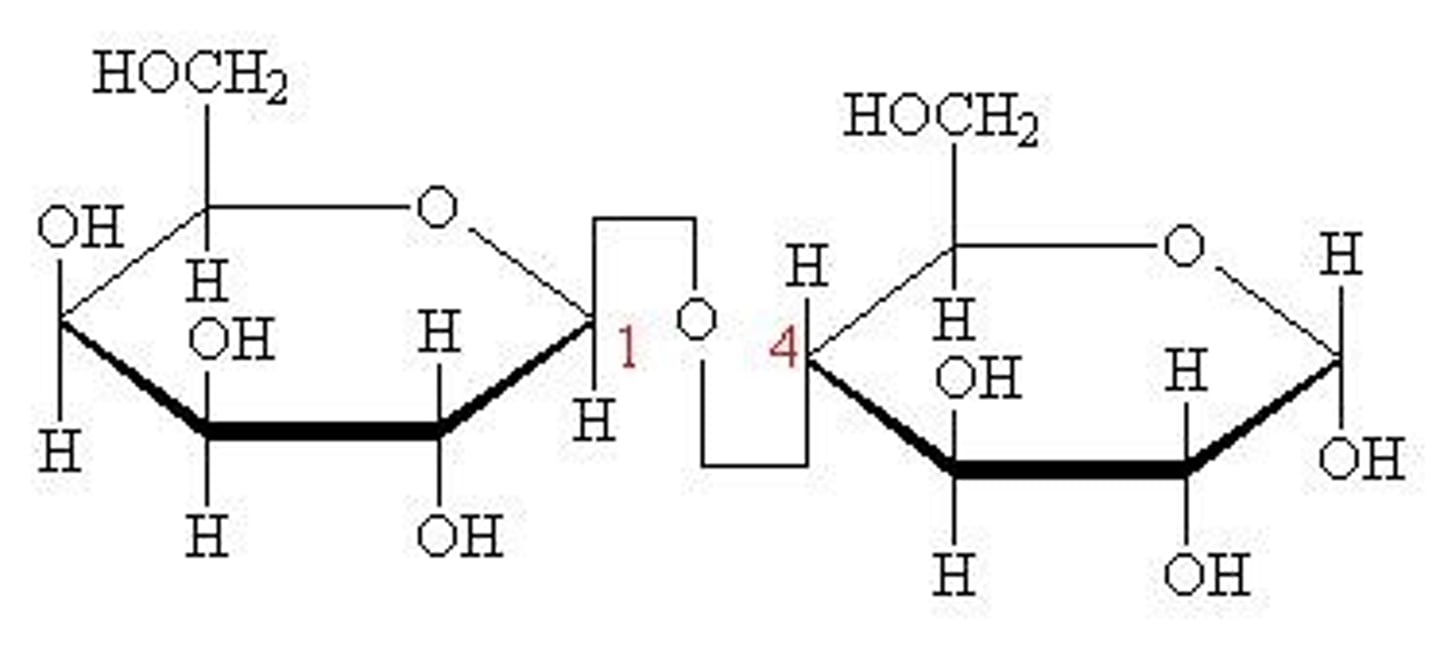
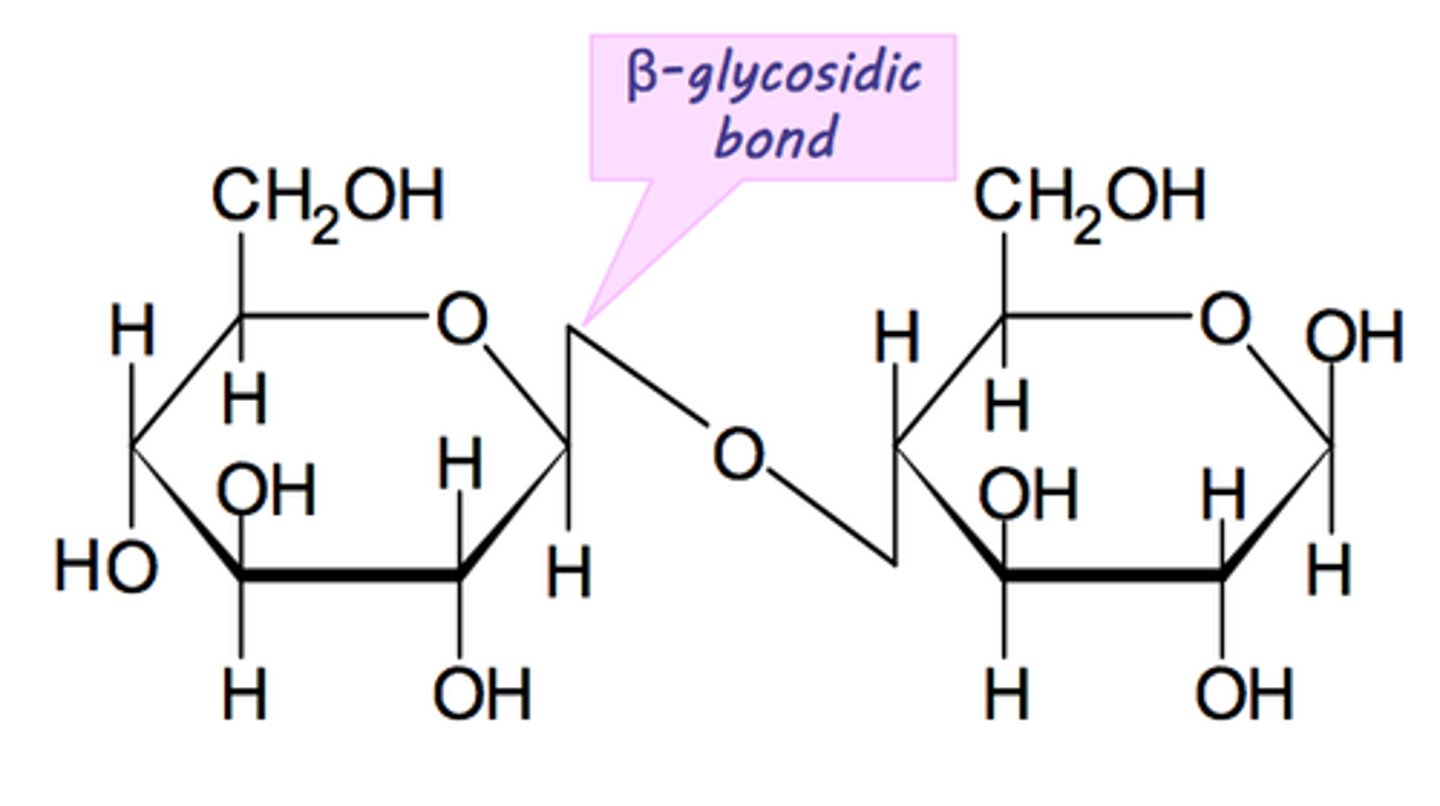
1,4 β-glycosidic bond
The molecule has to orientate it 180 degrees so that the OH on C1 on one β-glucose is next to the OH on the C1 of another β-glucose
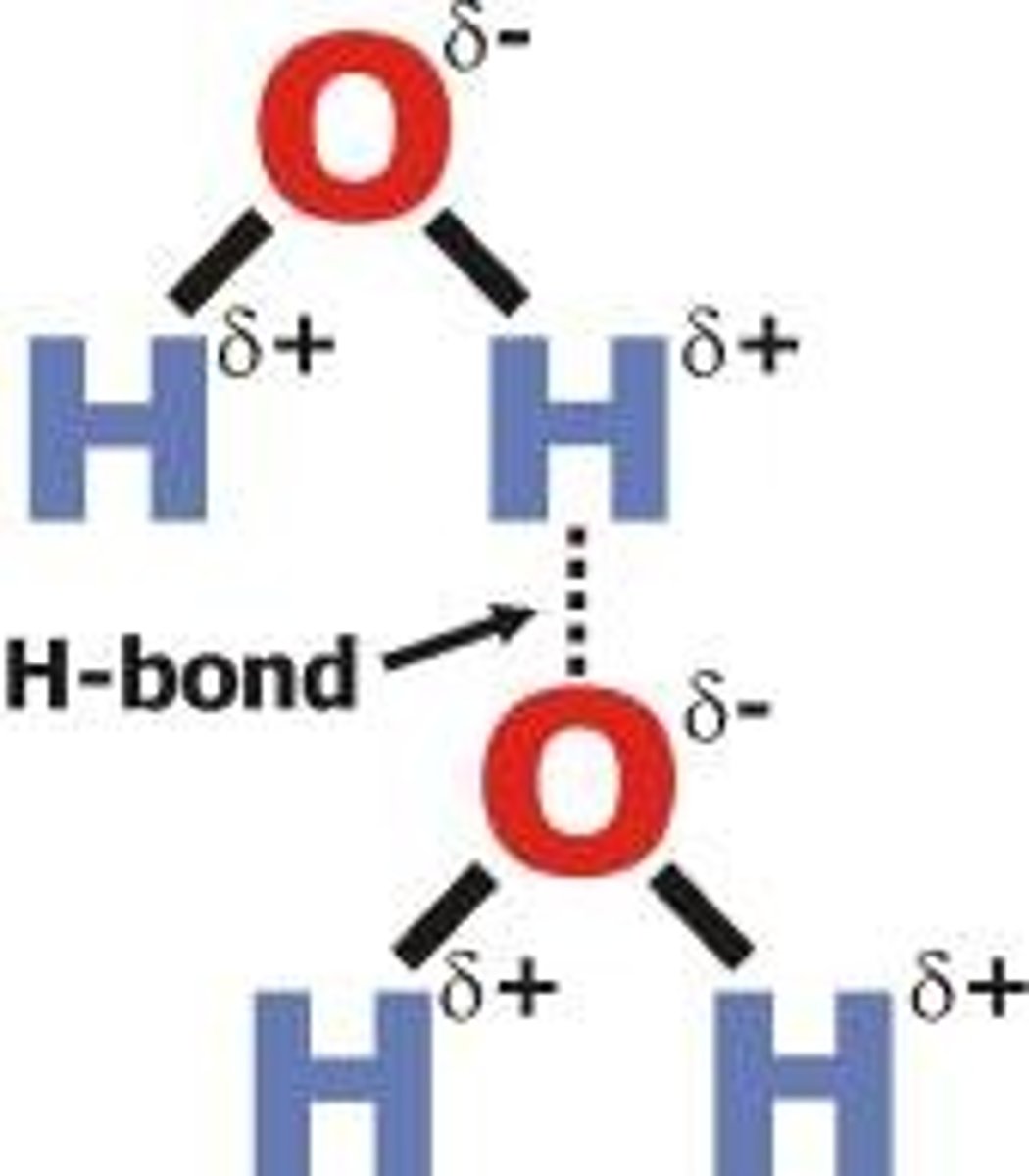
Hydrogen bonding in Water
Water is a polar molecule
Properties of Water
- High boiling point
- Ice is less dense than water
- Cohesion
- Adhesion
- Acts as a solvent
- Transport medium
- Cooling mechanism
- High specific heat capacity
- High latent heat of vaporisation
- Capillary Action
High boiling point
- Important for living organisms
- A lot of energy is needed to break the hydrogen bonds
- Creates stable water temperature for aquatic animals.
- Less energy is spent on temperature control

Ice is less dense than water
- Creates an insulating barrier. Water below the ice doesn't freeze, allowing organisms to move under water
- Creates habitat for animals like polar bears on top of the ice.
- Fish can move under the water

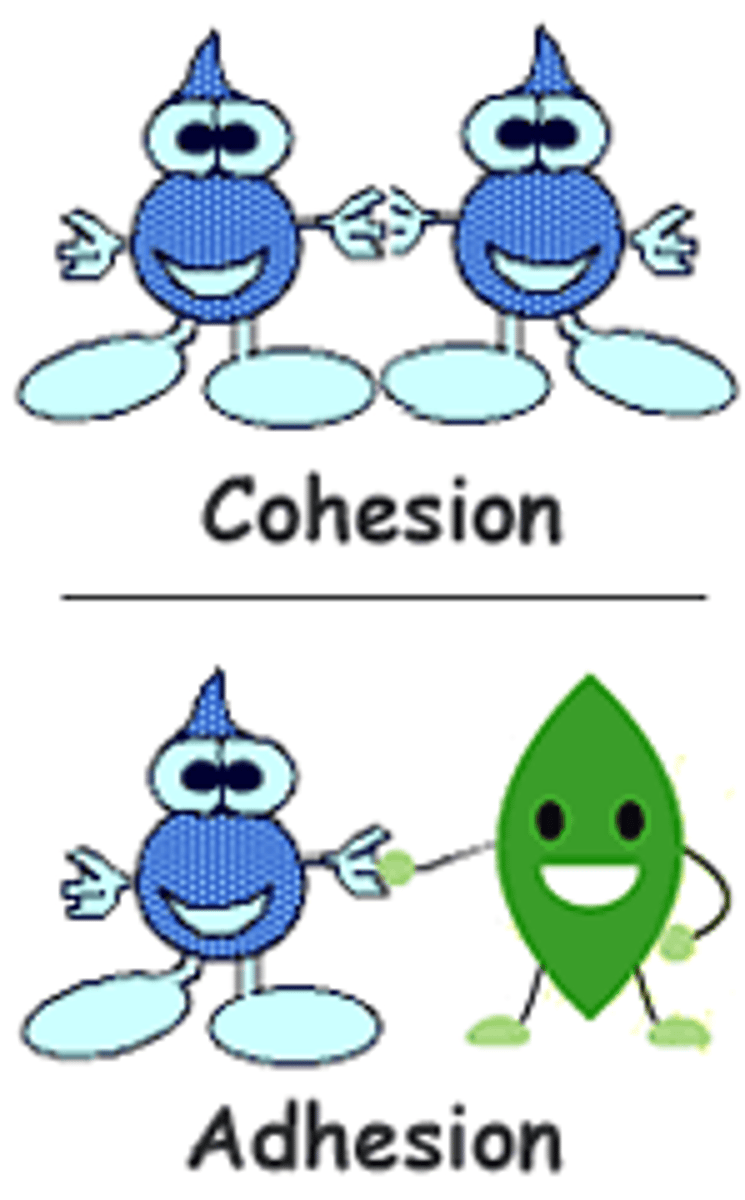
Cohesion
- Cohesion - hydrogen bonding in water
- Water moving through the xylem, creating high surface tension for insects like the water skater to walk on
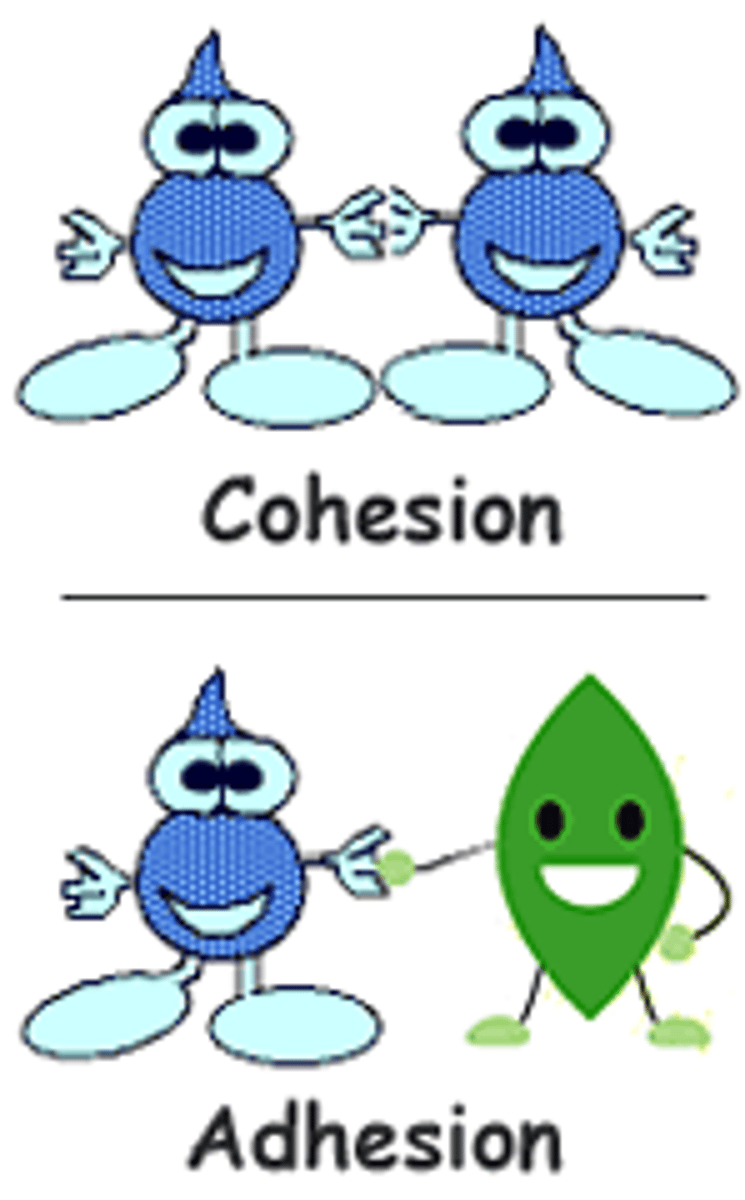
Adhesion
- Adhesion - Water attraction to other molecules/surfaces
- Water moving through the xylem
Acts as a solvent
- Water can act as a solvent, allowing mineral ions to be transported around plants and animals
- Substances dissolving in the blood stream
Transport medium
- Water is a transport medium, allowing the transport of soluble substances
- It transports substances around the body in blood, or around a plant
Cooling mechanism
- Evaporation is a cooling mechanism. The evaporating water takes heat away from the body
- Sweating in mammals or panting in dogs to cool them down

High specific heat capacity
- It takes a lot of energy to heat up water by 1°C
- This creates stable temperature
- Enzymes can work at their optimum temperature
- Gases remain soluble for aquatic organisms
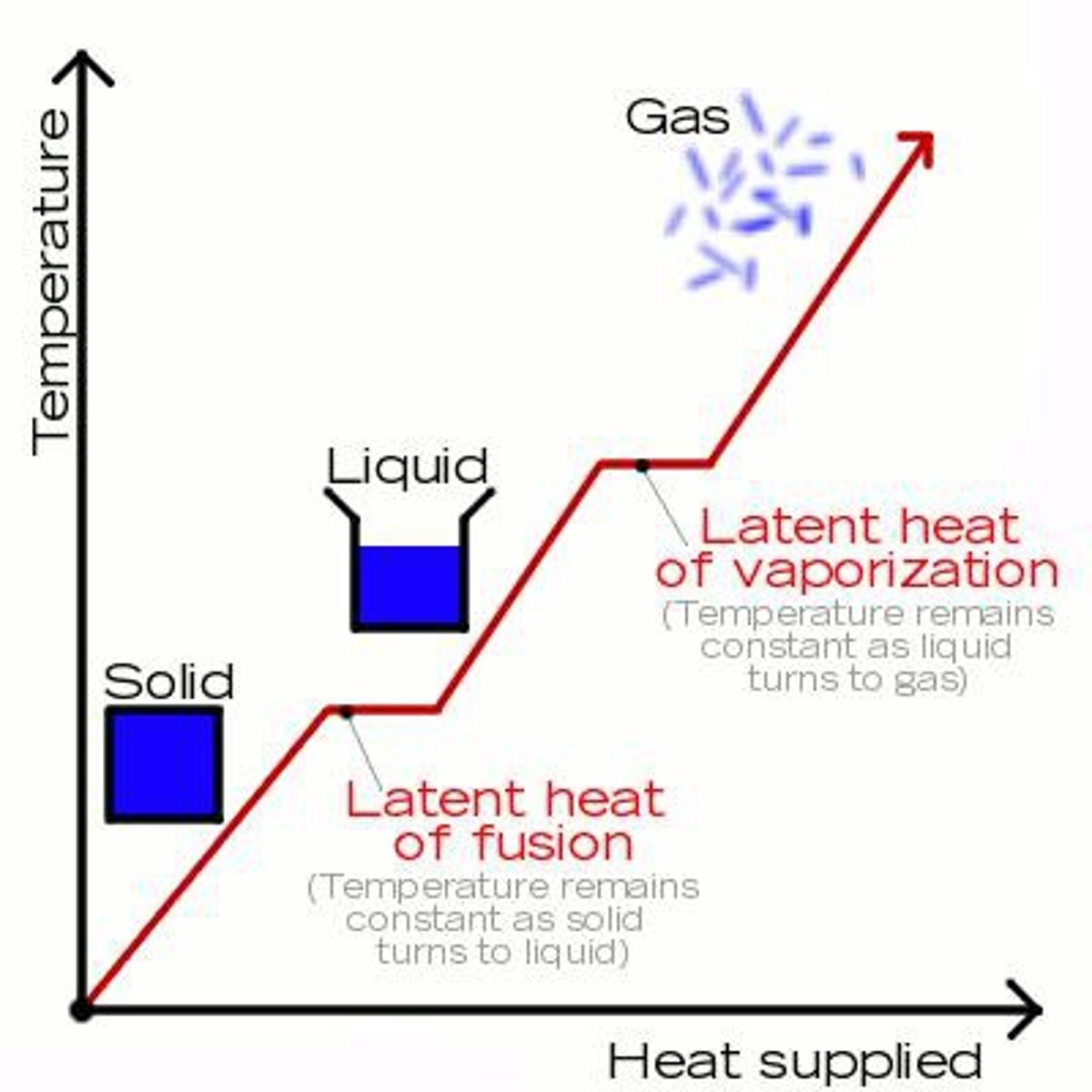
High latent heat of vaporisation
It takes a lot of energy to change water from a liquid to a gas form
Capillary Action
- Allows water to move up narrow vessels
- Water moving up the xylem in plants