ANSC 1319 Exam 2
1/133
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I made this flashcard for our Exam 2 on Monday, Nov 4th. If you have Dr. Anderson for class, it should be super helpful!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
animal growth
increase in body size; muscle, fat, bones
Hyperplasia
increase in cell number
Hypertrophy
increase in cell size
Anabolism
BUILDUP of body tissues
Catabolism
BREAKDOWN of body tissues
chronological growth
increase in tissue size associate with age
Physiological growth
increase in tissue size associated with maturity
Growth measurement
- Measuring growth
- we measure growth for slaughter and breeding
- objective: can do with objective- Yuler grid scale, which provides a precise way to measure size
- subjective: done by a person - structure proper movement
Objective measurement
animal weight, loin eye area, and backfat thickness
Subjective measurement
visual appraisal
ADG( average daily gain)
measures growth rate
(weight2 - weight1) / (time2- time1)
WDA ( weight per day of age)
- Weight / age in days
- Poultry for standard market weigh 4.7-4.9lbs in 52d
- swine record as days 230lbs or ADG
- cattle use weight at 205d of age
growth curve
Relatively slow from conception to birth
Rapid from birth to after puberty
Slows as animal approaches maturity
growth curve phases
prenatal- prior to birth
Ovum- fertilization to attachment to the uterine wall
Embryonic- 25-45 days depending on species, cell differentiation, little growth (hyperplasia)- cell type
Fetus- 60-70% of BFW occurs here (hyperplasia and hypertrophy) - cell size
Preweaning
Birth to weaning.
Growth Dependent upon:
Mothers milk production
Genetic potential
supplement nutrition
Post Weaning
Weaning to maturity/ slaughter.
Puberty- resources available
Rapid growth early, followed by slowing and fattening ad they reach maturity
what happens to growth if an animal fattens to early
will not attain their full postweaning potential. Early fattening can prevent max development of skeleton and muscle tissues
post weaning gain is dependent upon
genetic potential
Sex
previous nutrition
environment
nutrition
Hormones
chemical messenger controlling growth and development.
Hormones are secreted from endocrine glands
Somatotropin
-Growth hormone produced by anterior pituitary
-Regulates bone and muscle development, milk production.
-can increase protein deposition by 30% and decrease fat deposition by 45%
BST(Bovine Somatotropin Hormone)
Increase milk production in dairy cows
PST(Porcine Somatotropin)
produces more protein and less fat
Thyroxine
thyroid: regulate metabolism
-Secreted by the thyroid gland around the throat
-Regulates metabolism which controls protein synthesis therefore lean tissues and animal body weight.
-Requires iodine w/o it the animal losses weight and muscle and bone growth are impaired.
Androgens
-Responsible for male secondary sex characteristics
-Also have dramatic effect on bone and muscle growth in both sexes.
-Testosterone is the major androgen that is produced in the testis of males, adrenal glands of females and males.
-Puberty marks increased growth rate
-Males have a more rapid growth rate than females because the testes produce more androgens than the adrenal do in females
Estrogen
-Secreted by the ovaries
-Development of reproductive tract in females
-Tend to increase fat deposition
-Responsible for female secondary sex chararacteristics
Glucocorticoids
-produced by adrenals
-used for nutrient utilization and energy release
-if glucocorticoids are not present, animal tend to suffer from severe weight loss
Factors influencing growth
-Genetic Potential
-mothers milking ability
-sex
-nutrition
-antibiotics/probiotics
Ionophores
-across lipid membrane
-Rumensin, Bovatec, Monensin
-Act as antibiotics to certain bacteria in the rumen.
MGA- Melengestrol acetate
-birth control for heifers
-Fed to heifers in feedlots
Anabolic growth implants
-Repartioning agents (more protein, less fat)
-Ralgro, synovex, revalor, finaplix
factors influencing growth
-physical environment/housing: shelter, flooring, animals per pen, sound, climate.
-compensatory gain: very rapid growth- occurs when animals go from an energy-deficit to an energy-rich diet
- if deficit occurs after about 7 mo of age in cattle, can catch up quickly, but prior to 7 mo, effects are long lasting.
Consumer Attributes
-consumption of red meat has declined
-traditionally family has changed
-less than 30 min on meal prep
-dislike "leftovers"
Quality grading
expected palatability.
-the palatability indicating characteristics of the lean is referred to as the quality grades
Yield grading
how much meat
system developed to estimate the yield of closely-trimmed boneless, retail cuts that can be obtained from the round, Iion, rib, and chuck.
4 grades for carcass
USDA prime- highest marbling
USDA choice
USDA select
USDA standard- least marbling
USDA 1
52.3% or more BEST
most muscular leaneast
USDA 2
52.3-50.0%
USDA 3
50.0-47.7%
USDA 4
47.7-45.4%
USDA 5
45.4% or less HORRIBLE
Fastest light muscled
Pork Grading
first evaluate quality
-acceptable
-unacceptable
Secondary evaluate yield
-US No. 1,2,3,4
-muscle score
-last rib fat thickness
PSE- unaide to hold water, thickness not thick enough
Aging
Dry aging occurs while the beef is hanging in a refrigerated cooler
10-28 days after harvest and prior cutting
moisture evaporates from the muscle creating a greater concentration of beefy flavor.
Natural enzymes break down proteins and therefore tenderize the meat
Niche marketing
Differentiating the product for a segment of the buying public
-unsatisfied with conventional supplies
-consumer willing to pay a premium
-grass fed
-locally raised
-Hormone free
-organic
-All natural
geographic concentration
-largest concentration of cattle and lamb feeding in on the great plains and western corn belt
-desirable climate (dry and low humidity)
-proximity to grain supply
-sparse population and more open space
feeder cattle efficiency
-as cattle begin to fatten, rate of gain decrease, feed efficiency gets poorer
feeder cattle
southern region supplies about 50% of all beef feeders
breeds have changed dramatically over the past several decades.
Meat Breeds
Greater yield
Large frame
lean muscle tissue
improved feed efficiency
MEAT PRODUCTION
Dairy/ prolific Breeds
bred for
-milking ability
-mothering ability
-weigh of calf at weaning
-made of milk
weaning- coming off milk
feeder lambs
Sheep are generally divided into 3 groups
-mutton type
- wool type
-prolific type
mutton type
bred for
-Fast growth
-lean muscle tissue
large frames
hamp and sufflock
wool type
bred for
-wool quantity or quality
-staple length
-fineness
-yield
-ramboulet
prolific breeds
bred for
-increased number of offsprings
-mothering ability
-milking ability
feeder pig
-born weighing 3-5lbs
-weaned at three weeks
-slaughter weight= 230-250 lb
- many operations are farrow to finish
-large increase inn vertical integration of swine rasing
farrowing
High capital cost
high labor requirements
finishing
lower investment cost
lower labor
lower margins
higher volume required
Maternal breeds
Number of piglets
mothering ability
milking ability
terminal breeds
bred for
-leanness
-muscle mass
-growth rate
-feed efficiency
genotype
genetic make up of an animal
phenotype
characteristics that an animal shows
genetic and the environment together
crossbreading
mating animals of different breeds
get good genes
why we crossbreed
dominance helps production, the good gene is most likely to be dominant
Bulls effects of animal sex
gain at high rates
high percentage of lean
high feed efficiency
more aggressive
slaughter prior to 15 mo
-higher testosterone- gain quicker more feed
cows effects on animals
only class of beef animal that increases in price per lb as the weight goes up
fed primarily for the ground beef market
decrease palatability
steer effect of animal sex
grain at high rates
fatten (palatable meat)
marketable
purchase steers that are well muscled, not overly fat, large frammed, youthful
Genetic/ Environmental Interaction
Genotype + Environment = phenotype
Think of the genotype as a genetic potential
Phenotype is actual results
To maximize or optimize animal performance
-Modify the environment
-Reduced heat/cold
-Alter air movement
-Affect radiation
Animals body temp
Horses- 100.0f
cow- 101.5
pig- 102.5
sheep- 102.5
poultry 106.0
heat loss and production
Constant body temperature= heat produced + received - lost
Heat increases from last
Metabolism, muscle, activity, exercise, solar radiation, etc
Radiation
transmitted of energy inform of issue
conduction (touching)
losing heat through touching
convection (flow/wind)
transfer heat to water taken by wind
Thermoneutral zone
comfort zone
temperature at which an animal can produce at its maximum
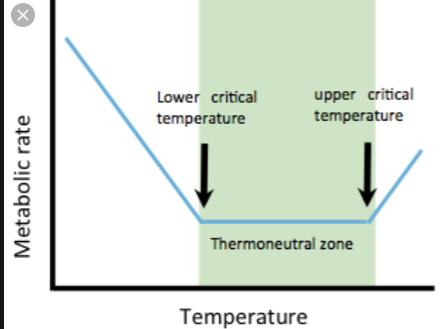
different for each individual animal
brahman are more tolerant of heat stress than british breeds
british and continental breeds are more tolerant of colder temps
energy intake increases or decreases as temp is altered
Thyroid gland and temperature acclimation in animals
thyroxine levels increase in cold temps to increase metabolic rate, and make us feel warmer.
thyroxine levels decrease in hot weather to cool us
controlling heat stress
most cattle in the world are raised in the warmer climates
more parasites and diseases carried by parasites
foragers lower in protein and energy
In cattle, temperature above 85 degrees are usually considered stressful
shade
simple and effective
can reduce temperature by 10 degrees to 15 degrees
can reduced radiant and reflective energy up to 50%
Evaporation cooling
more effective in arid climates
helpful in humid climates
every 20 degrees increase in temp= doubling of water holding capacity in air.
need to wet the skin, not moisten the hair.
sprinklers are better than forages in livestock with hair/wool/feathers.
refrigerated cooling/air conditioning
expensive
cooling needs to be accompanied by reducing the humidity level.
cool air only on the head of a sow.
feed and water
-cool vs warm water: under heat stress with cooler weather.
-feed with high fiber generates more heat during the digestion process
-food intake increases with cold weather
-water intake increases with hot weather
controlling cold weather: largest concern for
swine
poultry
all young animals
breeds not adapted to cold climates
ventilation
-essential for confined livestock
-high humidity
-ammonia build up in houses
waste management
-all animals in confinement create manure concentration problems
proper flooring
manure management plans
environmentally safe and sound handling procedures
Keeping animals healthy
- lack of disease pressures
-absence of internal and external parasites (worms, lice, flies, etc.)
-adequate feed and water
-clean, comfortable surroundings
Unhealthy animals
-perform poorly
- lethargic
- dull eyes
- droopy ears
- separate themselves from the heard
- rough hair coat
injuries
injuries and be caused by other animals
by fences, facilities, weather
predators
coyotes and dogs. and others
Nutritional deficiencies causes
-low levels of nutrients
-prepared rations low in a key nutrient- Lysen in horses
-impaired absorption of a nutrient- calcium phosphate
-incomplete or blocked metabolism of a nutrient in the body cells.
-abnormal requirement for a nutrient
-failure of the animal to synthesize a nutrient
Vitamin A
primarily cattle and sheep- weak calves at birth
Vitamin D
all species-rickets, joint disease, osteomalacia
Phosphorus
all species- pica, poor growth, infertility
tend to eat weird things
Zinc
primarly swine- parakeratosis- has dry skin
dandruff
Manganese
primarily cattle- infertility
Metabolic disorders
the blockage of a metabolic pathway may cause a deficiency at the body cell, even though the ration is entirely adequate.
common metabolic disorders horse
-lactation tetany of mares- calcium deficiency: causes involuntary muscle contraction or seizures
-azoturia- sudden increase in muscular work or high carb diet: no blood flow with increased glycogen causes acid buildup
common metabolic disorder cattle
rumen acidosis- abrupt increase in ingestion of highly fermentable carbs
fat cow syndrome- excessive conditioning, especially during dry period
common metabolic disorder swine
Hypoglycemia- postpartum deprivation of milk
PSS (porcine stress syndrome)- heritable trait
common metabolic disorder sheep
pregnancy toxemia (ketosis)- impaired metabolism of carbs or advanced pregnancy stress
-energy comes from burning ketones bodies
-causes breath to smell of acetone (finger nail polish remover)
Toxin
a harmful chemical of animal or bacterial origin
Toxemia
an illness or malady caused by a toxin