immunity
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms





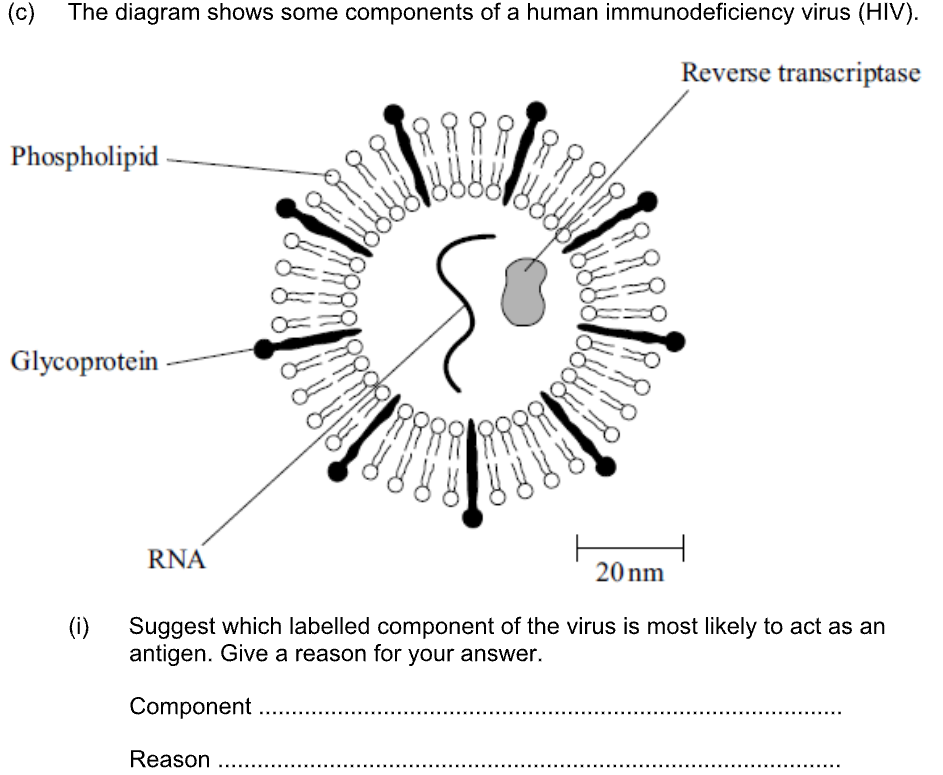




G. lamblia can attach itself with its sucker. Explain how this is an adaptation to living
in the intestines.
Enables organism to remain in area (of food source) / prevent its removal;
(ii) A vaccine can be used to produce immunity to HPV. Describe how memory
cells are important in this process.
(ii) Memory cells produced / remain / stored (from previous infection);
Rapid / secondary / greater response / many or more antibodies produced;
Destroys virus / antigen before it can cause harm / symptoms / cancer;
Give two ways in which a pathogen may cause disease when it has entered the
body
Produces toxins;
Damages cells / tissues / example given e.g. cell lysis;
Explain why these antibodies are referred to as monoclonal. ?
(i) (Antibodies) produced from a single clone of B cells / plasma cells;
Brucellosis is a disease of cattle. It is caused by bacteria. These bacteria can infect people who drink milk or eat dairy products from infected cattle. A test using monoclonal antibodies allows vets to identify cattle that are carriers. The carriers are cattle that carry the brucellosis bacteria but do not show any symptoms of the disease.
The tests using monoclonal antibodies allow vets to identify brucellosis while theyare still on a farm. Explain the advantages of this.
(Rapid) treatment of carriers / infected cattle / disease;
Can isolate / cull carriers / infected cattle / infected (dairy) products not sold /
consumed / tracked;
Reduces spread of disease / no need to kill / prevents the death of non-
infected animals;