Biology 1.5 Plant Structure
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
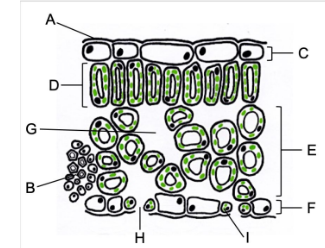
Identify the structures of the leaf labelled in the diagram below.
A - waxy cuticle
B - vein
C - upper epidermis
D - palisade layer
E - spongy layer
F - Lower epidermis
G - air-filled space
H - stoma
I - guard cell
How is the waxy cuticle adapted to its function?
Waterproof to reduce water loss.
Transparent, allowing light to reach the palisade layer.
How is the palisade layer adapted to its function?
It receives the most light, so it contains the greatest concentration of chloroplasts.
Describe the structure of the upper epidermis.
Transparent, allowing light to reach the palisade layer.
How is the spongy layer adapted to its function?
Contains many air spaces to allow the diffusion of carbon dioxide to chloroplasts in the palisade layer for photosynthesis.
Also contains some chloroplasts.
Describe how the lower epidermis is adapted to its function.
Contains many stomata to allow gas exchange.
What are stomata?
Pores found in the lower epidermis of the leaf that allow for gas exchange.
What are guard cells?
Specialised cells surrounding the stoma that change shape to control the size of the pore.
What are the veins?
Contain xylem and phloem.
Form a large network to deliver water and remove glucos