L 6
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
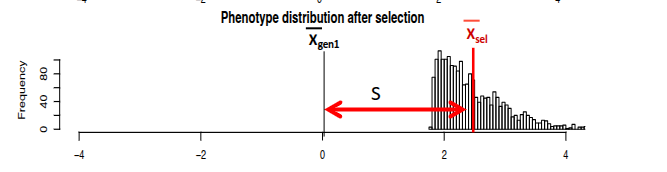
S, the selection differential, is
the difference caused by selection in mean phenotype
within a generation
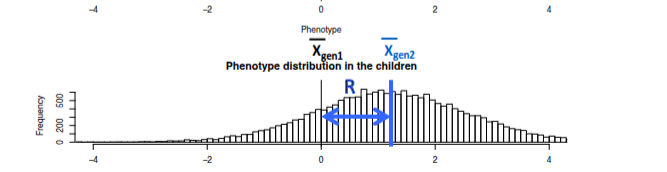
R, the selection response, is
the change in the trait mean across
successive generations
If none of the variation in a trait is
genetic (show equation)
No change in mean i.e. R = 0 * S
if all variation in a trait was additive genetic
variation
Then the transmission in the change
In mean would be (equation)
perfect, i.e. R = 1 * S
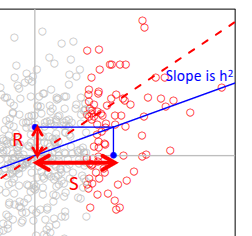
The breeder’s equation.
R = h2S
S – change in phenotypic mean in
parental generation due to selection
R- Response: change in mean in offspring
generation
h2- Narrow sense heritability,
Mean flowering time before selection: 60 days
Selection due to drought within one generation
moved the mean flowering time to 53 days
h2 = 1/2
R = ?
Predicted change in next generation
R = h2S
= ½ * (53-60)
= -3.5
breeders equation where we can apply the breeder’s equation over many
generations
n = generations
• Rn = n h2 S
Dwarfing of Red Deer on Jersey:
• Evolved from a mean weight of 200kg to 36kg.
• Within in 6,000 years.
• Generation time of red deer = 5 years
Assume h2 = 0.5 and that this is constant.
R (change in the trait mean)= 36kg - 200kg = -164 kg
n= 6,000/5 =1,200 generations
Rn/1,200 = -0.136 kg change across generations
Rn/n = -0.136 = 0.5 x S
-.136/.5
S = -0.27 kg per generation!
S is difference caused by selection in mean phenotype
within a generation