Waves
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Waves transfer energy without transferring matter
Waves transfer energy without transferring matter
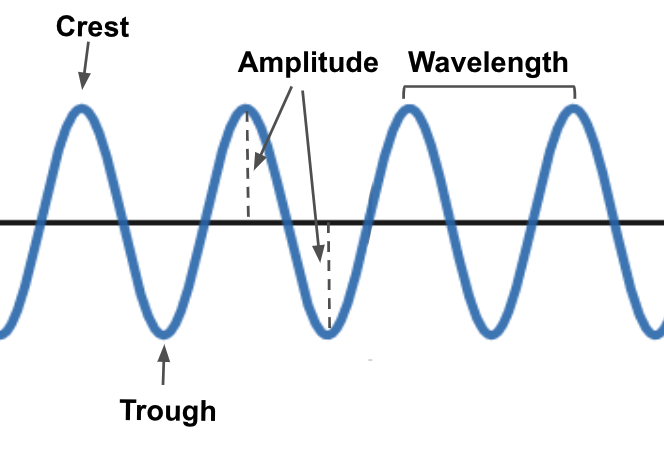
Parts of a wave
Crest - Highest point
Trough - Lowest point
Amplitude - height of a wave from its resting point
Frequency - Number of vibrations per second
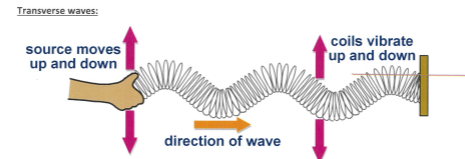
Types of Waves- Transverse wave
Coils move up and down
direction of wave is at a right angle
Transverse waves: electromagnetic radiation, water waves seismic S waves
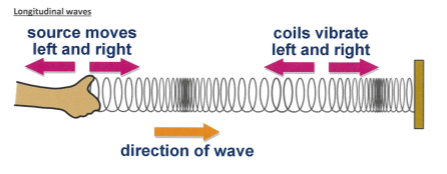
Types of Waves- Longitude wave
Coils move left and right
Direction of wave is parallel
Longitude waves: sound waves, seismic p waves
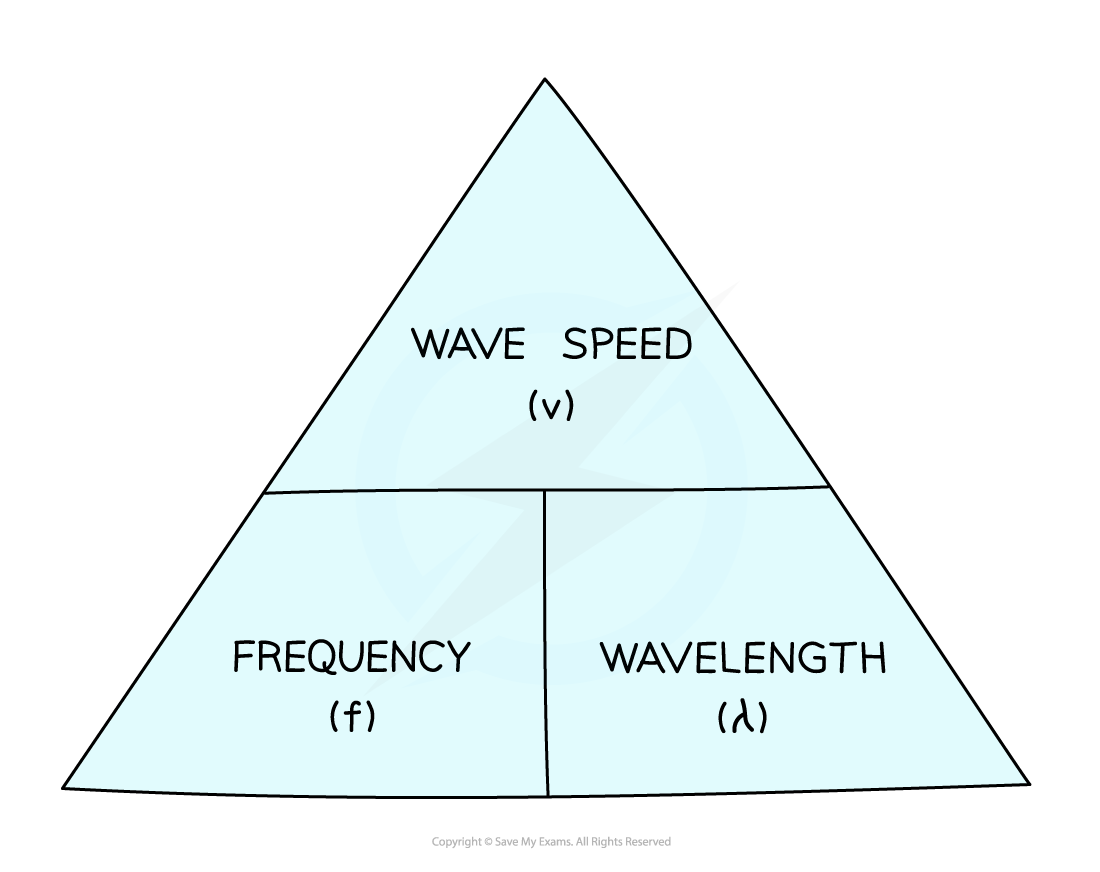
The wave equation
Wave speed: V measured in : m/s
Frequency: F measured in : hz- hertz
Wavelength: λ measured in : m
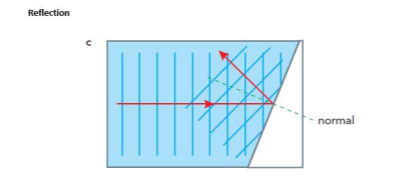
Reflection - waves
When a wave hits a barrier its reflected. reflection changes the direction of the wave. direction of the reflected wave depends on the angle of incidence
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
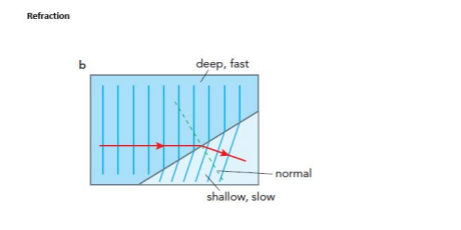
Refraction - waves
When waves move from one medium to another like deep water to shallow. They change speed. Causing the waves to change direction
deep to shallow - water slows down
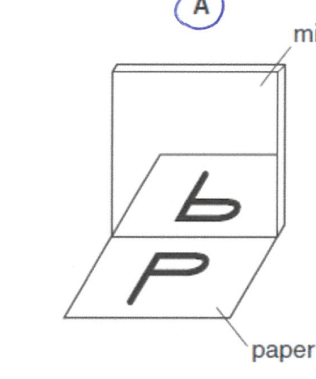
Images in a plane mirror
Images in a plane mirror are:
Virtual - can’t be touched
Upright - not upside down
Same size as object
Laterally inverted - Left and right is switched
Same distance from the mirror to object
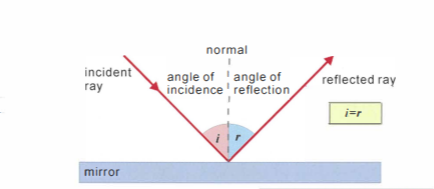
Plane mirror - angle of incidence and reflection
Angle of incidence = angle of reflection
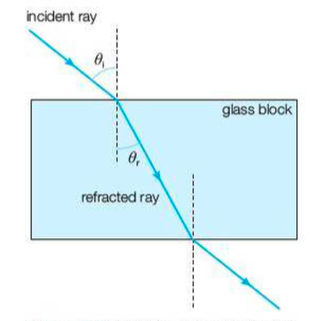
Refraction of light
The change in direction of a light ray passing from one medium to another
More dense medium - bends towards the normal
Less dense medium - bend away from normal
Sound waves travel fast in solids slow in gases
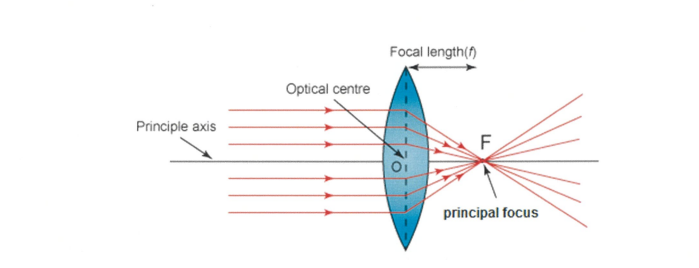
Lenses
Types of lenses : Converging, Diverging(convex)
Principal focus - the point at which parallel rays converge after passing through a converging lens
Focal length - the distance between the centre of the lens and the principal focus
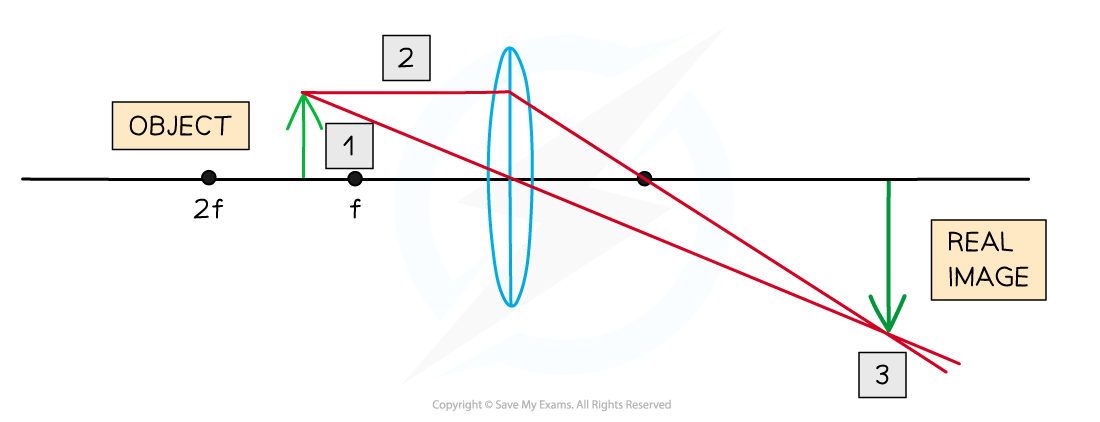
Start by drawing a ray going from the top of the object through the centre of the lens. This ray will continue to travel in a straight line
Next draw a ray going from the top of the object, travelling parallel to the axis to the lens. When this ray emerges from the lens it will travel directly through the principal focus f
The image is the line drawn from the axis to the point where the above two rays meet
When describing an image, consider if it is:
Real or virtual
Magnified (large) or diminished (smaller) - image larger or smaller than original
Upright or inverted
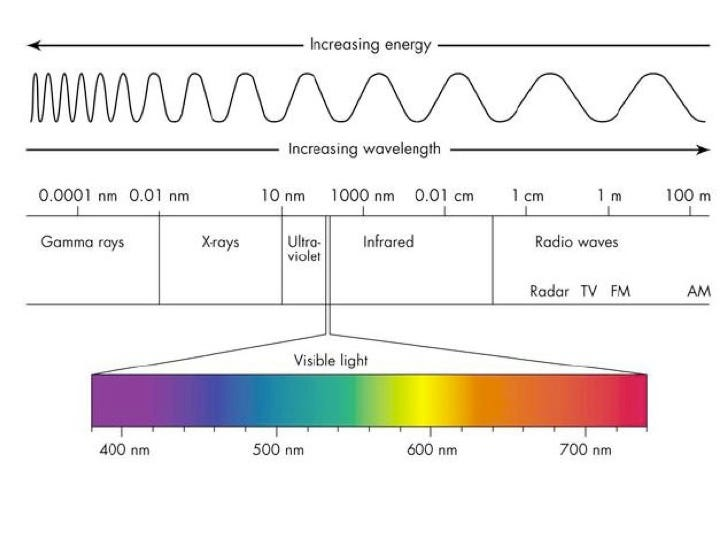
Dispersion of light
The dispersion on light is split into a spectrum because the sides of are not parallel it comes out in a different direction this is dispersion
This occurs because whiter light is a mixture of different colours, different colours have different waves lengths the longer the wave length the less light is refracted. red has the longest wavelength and lowest frequency.
Frequency goes is lowest at the top the lower you go the higher the frequency gets
Wavelength is highest at the top the lower you go the lower the frequency get
R
O
Y
G
B
I
V
Sound
Sound is caused by objects vibrating and air molecules moving backwards and forwards
Sound is a longitudinal wave its a series of compression and rarefactions
Humans can hear at the range of 20Hz to 20,000Hz
A medium is needed to transmit sound waves
hard surface reflect noise soft surface absorbs
Sound travels faster in solids than liquids and liquids is faster than gases
Measuring speed of sound
Use starting pistol to make a sound
Measure time take between firing the pistol and hearing the noise from 1km away
Divide distance by the time on watch
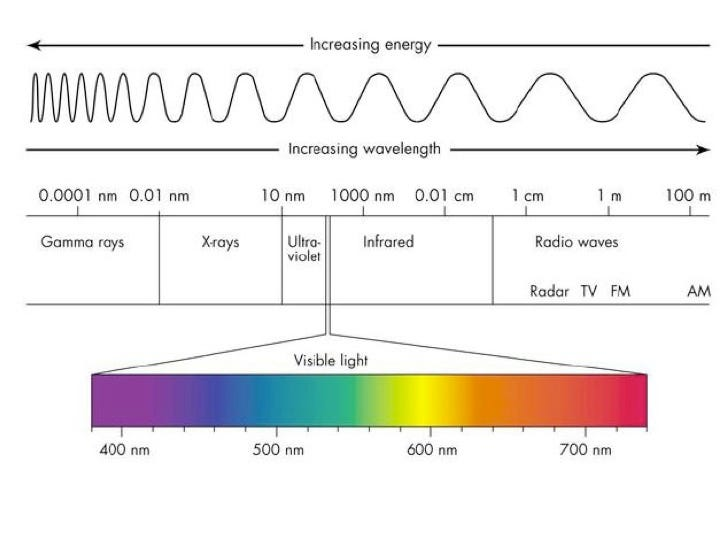
Amplitude and frequency affecting sound waves
Amplitude determines loudness, with higher amplitude resulting in a louder sound, while frequency determines pitch, with higher frequency corresponding to a higher pitch.
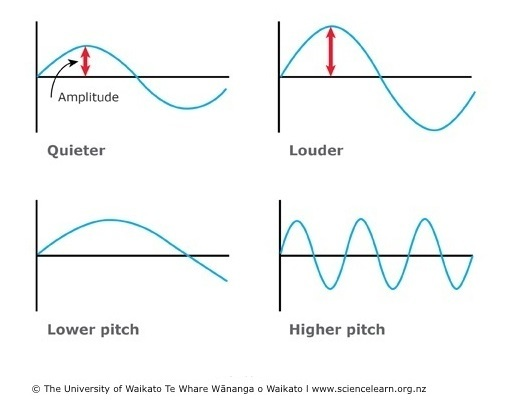
What is an echo
A reflection of a sound wave
Ultrasound
A sound with a frequency higher than 20,000 Hz
Compressions and rarefaction
Compression- Regions of higher pressure due to particles being closer together
Rarefaction- Regions of lower pressure due to particles being far apart
Electromagnetic spectrum
They are transverse waves which transfer energy
Can be reflected or refracted
Can travel through a vacuum at the same high speed
The electromagnetic waves in a vacuum travel at the speed of light - 3 × 10 to the power of 8
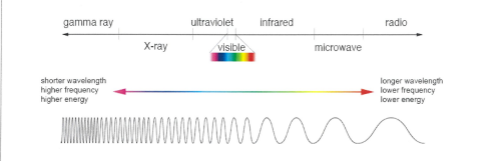
Application of regions of the electromganetic spectr