AICE Environmental Management Review
1/349
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Complete Review Units 1-8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
350 Terms
Low income countries
GNI per capita of $1,145 or less
ex. Chad and Ethiopia
Lower middle income countries
GNI per capita $1,145-$4,515
ex Cube
Higher middle income countries
GNI per capita $4,516-$14,005
ex. Mexico and Iraq
High income Countries
$14,006 or above
ex. USA and Germany
Factors of HIC
good, clean water supply
stable government
buys raw materials and processes into more expensive product
imports cheaper than exports
good trade
Factors of LIC
income inequality
climate change
government conflict
lack of access to basic healthcare
Sustainability
The ability to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Renewable Resources
Light, air, soil energy, atmosphere, forests
How to protect renewable resources
Communities need to develop judicious land practices for both conserving ecosystems and enhance local economies as they maintain the equilibrium of the environment.
14 Points of sustainability
save energy - reduce carbon
eat less meat
use reuseable alternatives
go paperless
renewable energy
recycle reuse
grow fruits and vegetables
donate unused items
save water
buy fair trade products
drive less
do no waste food
wear sustainable clothing
use eco-friendly clothing products
3 states of water
solid-ice
liquid-water
gas-water vapor
How to change state of water
adding or removing heat energy
adding - energy in
removing - energy exits
Where does energy come from
Energy comes from the sun
Water cycle
the continuous movement of water into the air, onto the land, and back into the air over and over again.
Water cycle image
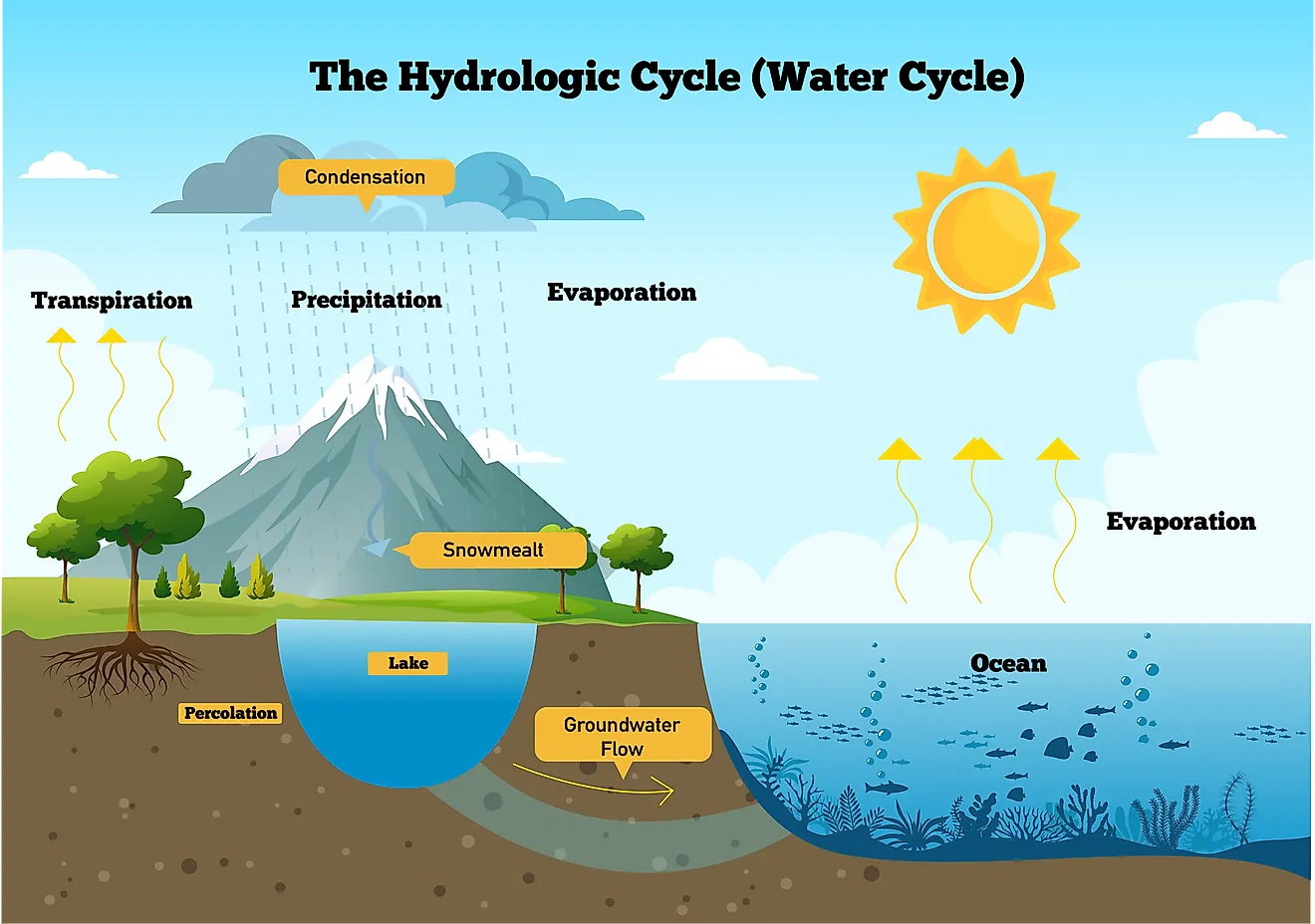
Condensation
water vapor in the air that gets cold and changes back into liquid forming clouds
Precipitation
solid or liquid water that falls from the air to the surface
ex. rain, snow, sleet, and hail
Interception
part of the rainfall that is intercepted by the earth’s surface and which subsequently evaporates
anything that becomes wet after rain
Infiltration
process by which precipitation of water soaks into subsurface soils and moves into rocks through cracks and pore spaces
More absorption(infiltration)
further away from ocean or collection
more surface runoff (infiltration)
closer to collection
Surface runoff
water that flows across land and collects in rivers, streams, and eventually the ocean
Groundwater flow
water located within the rocks below the earths surface
Through-flow
the movement diagonally downslope of water through soil
Evaporation
when the sun heats up liquid water and turns it into water vapor
Transpiration
Process by which plants lose water through the leaves → helps evaporation get water vapor back into the air
Ocean water in hydrosphere
97.2%
Non-ocean compartments in hydrosphere(%)
2.8%
Non-ocean compartments in hydrosphere
glaciers
groundwater
saline lakes and inland seas
soil moisture
stream channels
atmosphere
glaciers hydrosphere(%)
2.15%
Groundwater hydrosphere(%)
0.62%
Saline lakes and inland seas hydrosphere(%)
0.008%
soil moisture hydrosphere(%)
0.005%
stream channels hydrosphere(%)
0.0001%
atmosphere hydrosphere(%)
0.001%
5 factors of water cycle
recycles earth’s fixed supply of water
water remains chemically unchanged
changes physical state
powered by solar energy and gravity
works if we do not overload water systems
Interacting water compartments
distribution of water across the earth
residence time
the length of time water typically resides in a water compartment → water may reside in one compartment or stay there for eons
Avg residence time of water in oceans
about 3000 years before the water evaporates and enters the hydrolic cycle
Water compartment examples
Rivers and streams, wetlands, atmosphere, groundwater
Rivers and Streams
precipitation does not evaporate or infiltrate into the ground runs off the surface back towards sea
Wetlands
lush plant growth stabilizes soil and hold surface run-off allowing more aquifer infiltration
Atmosphere
among the smallest water reservoirs and has most rapid turnover rate
Groundwater
stored in slowly flowing and slowly renewed underground reservoirs called aquifers
Running water
streams, rivers, drainage basin
Stream
any channelized flow of water
river
a stream that has at least 1 tributary
drainage basin
land area that contributes to a river system
Atmosphere
protects us from the sun UV light and stores the oxygen we need to breathe → layer of gases occupying above the lithosphere
Atmosphere cycle image
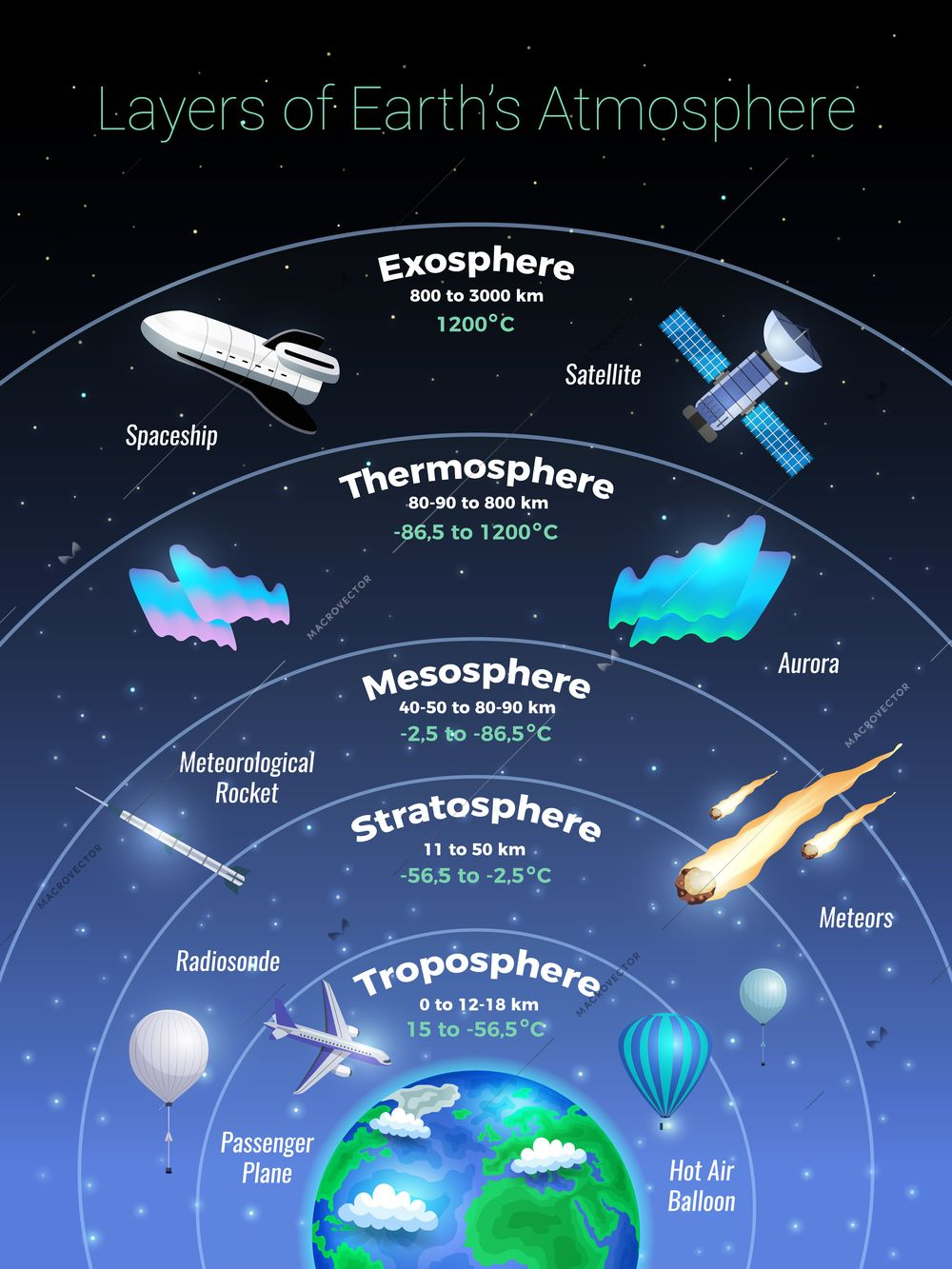
Atmosphere composition of gases
Nitrogen 78%
Oxygen 21%
Water vapor 0-4%
Carbon dioxide 0.037%
Argon 0.93%
4 layers of atmosphere
Troposphere
Stratosphere
Mesosphere
Thermosphere
Troposphere
lowest layer extending 10kms from crust
contains 99% of water vapor and 75% of atmospheric gases
weather occurs here
temp cools about 6.5`c per km of altitude
density of air particles decreases with altitude
Stratosphere
directly above troposphere 10-15kms above earth’s surface
temp gets warmer as you increase
density of air particles increases w/altitude
major home of OZONE gases
Ozone
ozone layer absorbs harmful rays from the sun
layer of 3 atom molecules that protects the earth from the sun’s ultraviolet radiation
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
Pollutants that destroy ozone
→ ozone has large hole over Antartica and a smaller one over the North Pole → currently closing by CFC reduction efforts
Mesosphere
extends from top of stratosphere to about 85kms above earth
coldest layer with little ozone
Meteors or rock fragments burn up here
Temp decreases with altitude
Density of air particles decrease with altitude
Thermosphere
thickets atmosphere layer between 85-500kms above earth
contains the auroras
very high temp
very little air particles
warmed as it filters out x-rays and gamma rays from sun
Shortwave radiation
Sun emits shortwave radiation b/c it is extremely hot and has a lot of radiation to give off
Longwave radiation
The earth emits longwave radiation b/c earth is cooler than the sun and has less energy to give off
→ once earth’s atmosphere, clouds, and the surface absorbs solar energy
Greenhouse effect
a natural process that warms the earth’s surface
when suns energy reaches the earth’s atmosphere some is reflected back, and the rest is absorbed and re-radiated by greenhouse gases.
Greenhouse gases
water vapor
CO²
methane
nitrous oxide
ozone
some artificial chemicals
Greenhouse process
absorbed energy warms the atmosphere and the surface of the earth
process maintains earth’s temp at around 33`c, warmer than it would be otherwise
Climate Change
a change in global climate patterns attributed largely to the increased levels of atmospheric carbon
Global warming
gradual increase in the overall temp of earth atmosphere by the greenhouse effect caused by increased gases
Climate change vs Global warming
GB - long term warming of the planet
CC - is broader range of changes(rising sea-levels, blooming times)
Ecosystems
the self sustaining structural and functional interaction between living and non-living components
Ecosystem components
solar radiation
disturbances
moisture
habitat
plant community
soil organisms
minerals
nutrients
Parts of an ecosystem
an ecosystem is made up of all living and non-living things in an environment
Population
A group of organisms of the same kind living in the same place
Community
all the population that lives in an ecosystem at the same time
Habitat
a place where plants and animals live
→ place where they can meet the needs
animals get food, water, shelter.
Natural ecosystems
ponds, lakes, oceans, forests, grassland, desert, ets
are self regulating without much direct human interference or manipulation
Terrestrial ecosystems
grasslands, forests, desert ecosystems
Aquatic ecosystems
a. lentin (stagnant water)
→ lakes, ponds, etc
b. Lotic (flowing water)
→ river, ocean, sea, etc
Artificial ecosystems
a crop land, garden, aquarium, park, kitchen garden
Types of ecosystems
Deserts, grasslands, forest, saltwater, freshwater
Deserts
very dry
desert plants survive with very little water
Grassland
are dry, often flat areas of land that are not in the summer and cold in the water
they get more rain and snow then deserts, but less than most ecosystems
Forest
are places in which many trees grow
Saltwater
are oceans
oceans cover 3/4ths of the earths surface
→ more saltwater ecosystems than any other
Freshwater
rivers, ponds, lakes, and streams
lakes and rivers closely tied
→ some lakes are the source for some rivers
→ important rivers most often originate form lakes
→ some rivers ends lakes
Abiotic factors example
water
air
soil
sunlight
minerals
Biotic factors
are living or once living organisms in the ecosystem. these are obtained from the biosphere and are capable of reproduction
Biotic factors examples
animals
birds
plants
fungi
other similar organisms
Abiotic components of ecosystem
sunlight
temperature
precipitation
water or moisture
soil or water chemistry
Biotic components
primary producers
herbivores
carnivores
omnivores
detritivores
Function of ecosystem 1
the producers, the green plants, fix solar energy and with the help of minerals take from their soil where they grow, or aerial environment build up complex organic matter
Function of ecosystem 2
the animals eat up plants and other animals as food so energy is transferred through food to animals
Functions of ecosystem 3
when plants and animals die, their decomposers act on their dead bodies and decompose them into simple minerals like carbon dioxide, water, and minerals, which go back to air, water bodies, and soil where they were taken.
Processes of an ecosystem
energy enters the system in the form of sunlight or photons, which is transformed into chemical energy in organic molecules by cellular processes including photosynthesis, and cellular respiration and ultimately converted into heat energy.
Equilibrium
As the number of carnivores in a community increases, they eat more and more of the herbivores, decreasing the herbivore population. It becomes harder for carnivores to find food, decreasing the carnivore population. This keeps them at a stable equilibrium as they limit each other’s population.
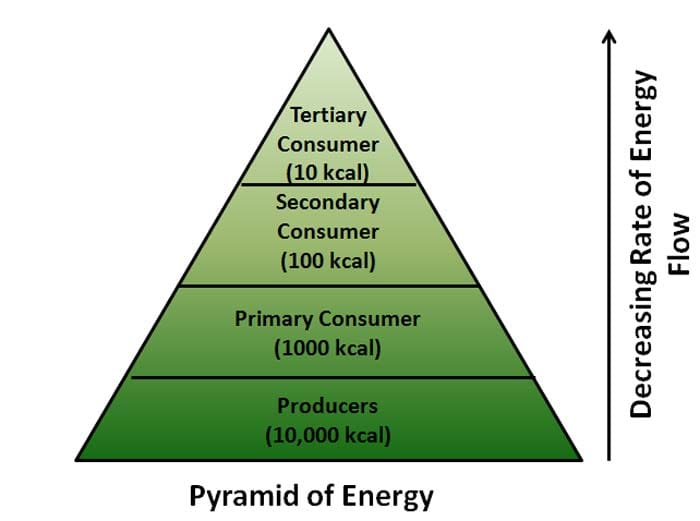
Biomass
Total living material of an organism.
pyramid of biomass describes the qualitive relationship between the producer and consumer.
gradual decrease of biomass from each trophic level
total biomass of producer is MORE than that of what follows
Pyramid of energy
Autotrophs
producers (energy from the sun)
self-feed
Photosynthesis equation
6CO² + 6H20 → C6 H12 O6 + 6O2
carbon + water → glucose + oxygen
Carbon
An element: 6 protons, 6 neurons, the basis of life on earth
found in all earth systems
carbon atoms repeatedly used on earth
Cycle between: atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, biosphere
Processes transfer carbon
photosynthesis
respiration
consumption
decomposition
combustion
weathering
dissolve/vaporize
fossilization
carbon in rocks and underground
deposits are released very slowly into the atmosphere
process takes many years and is usually caused by weathering
Ways food chains lose energy
90% is lost
metabolic heat(released during respiration)
through movement
in materials that the consumer does not process digestion
excretion