Energy Systems - Unit 4
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
3 Energy Systems Fuel the Muscles
All energy in the body is derived from the breakdown of:
Carbohydrates
Fats
Proteins
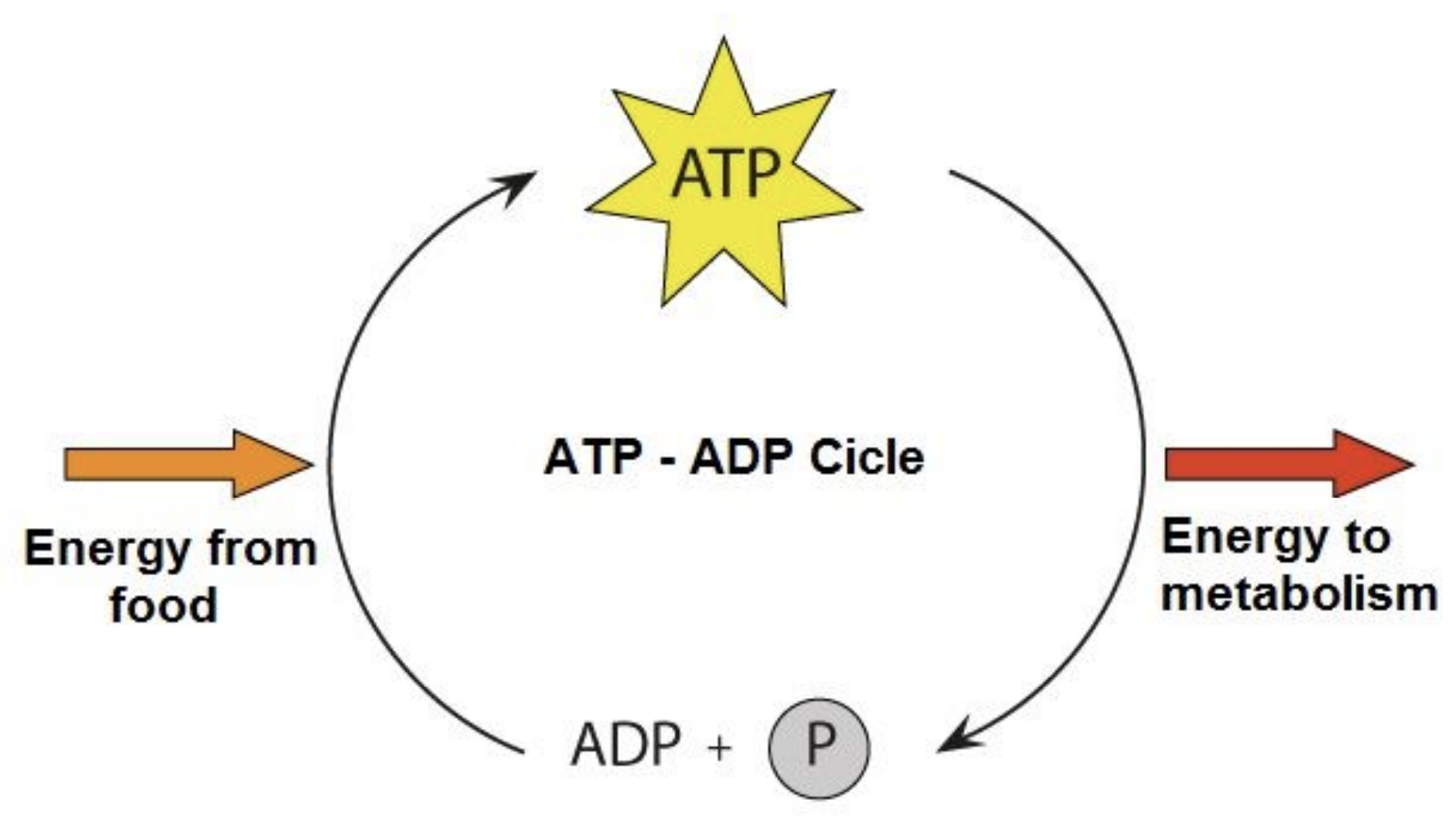
The breakdown makes ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
ATP
ATP is broken down into ADP and Phosphate (P)
Used as energy for working muscles
Allows actin and myosin to do their work
ATP is continually resynthesized
With more food
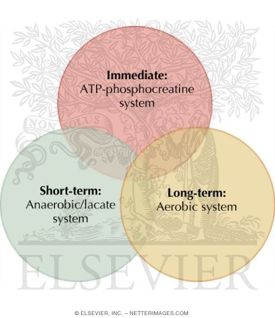
3 Energy Systems
The energy systems work together to release energy at different rates
Energy System #1: Anaerobic Alactic
Supplies: High Power Output Activities
Weight Lifting, sprinting,
Immediate high rate of energy production
Creatine Phosphate in muscles is used
The Phosphate is used to bond with ADP to make quick ATP
Produces a very high amount of energy for a really short duration
Runs-out when Creatine Phosphate stores run out.
High Intensity for 12 seconds
Medium Intensity for 30 seconds
Type 2 (fast twitch muscle fibres) contain a higher concentration of Creatine Phosphate
Energy System #2: Anaerobic Lactic
Provides ATP for muscular work at high intensities
30 seconds to 5 minutes
Breakdown of stored carbohydrates (glycogen)to make ATP
Uses glycolysis and produces pyruvic acid to be used by the mitochondria
If the mitochondria cannot process pyruvic acid fast enough, lactic acid will be produced
Lactic Acid will produce Hydrogen ions (H*)
Hydrogen ions hamper the function of the neuromuscular junctions (create muscle fatigue = muscle burn)
Anaerobic Threshold
Exercise intensity where lactic acid begins to accumulate in the blood
Discomfort and burning
The rate of lactic acid buildup can be decreased by decreasing the intensity (allowing the mitochondria to use up the excess)
Endurance Athletes
Remove lactic acid from muscles faster
Have more blood flow in their muscles
More exercise at higher intensities for longer
Ultramarathon
Energy System #3: Aerobic
Used for a large range of activities
Low intensity and low lactic acid levels
10 minutes to hours
Endurance type activities
Long distance running, swimming, biking
The mitochondria use food, water and oxygen to make ATP
Uses the Krebs cycle and the ETC (electron transport chain)
Makes large amount of ATP
Endurance Training
Increased blood flow which delivers more nutrients and oxygen
Increases number and size of mitochondria
The Oxygen Difference
System 1 alactic: 1 ATP per glucose
System 2 lactic: 2 ATP per glucose
System 3 aerobic: 36 ATP per glucose
VO2max - Maximal Aerobic Power
Maximum rate of oxygen that can be consumed to make energy in muscles
VO2max peaks at age 25
Working Together
The systems overlap and work together to provide energy at different intensities over different durations