The Circulatory System: Blood Outline Part 3
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Hemostasis
cessation of bleeding
hemorrhage
excessive bleeding
Platelets are fragments of
megakaryocytes
normal platelet count=
130,000 to 400,000 platelets per microliter
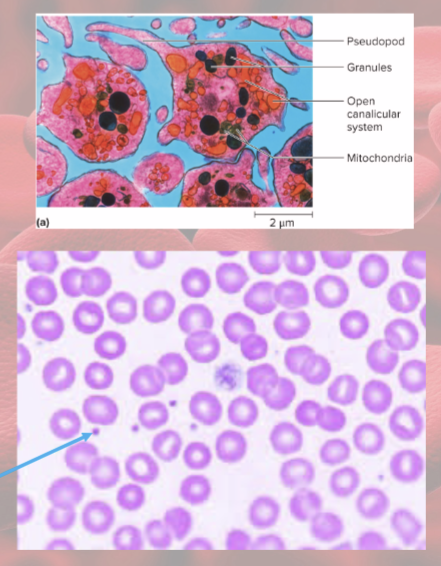
Platelet functions
secrete vasoconstrictors- help reduce blood loss
form platelet plugs to seal small breaks
secrete procoagulants (clotting factors) to promote clotting
initiate formation of clot dissolving enzyme
secrete growth factors—stimulate mitosis to repair blood vessels
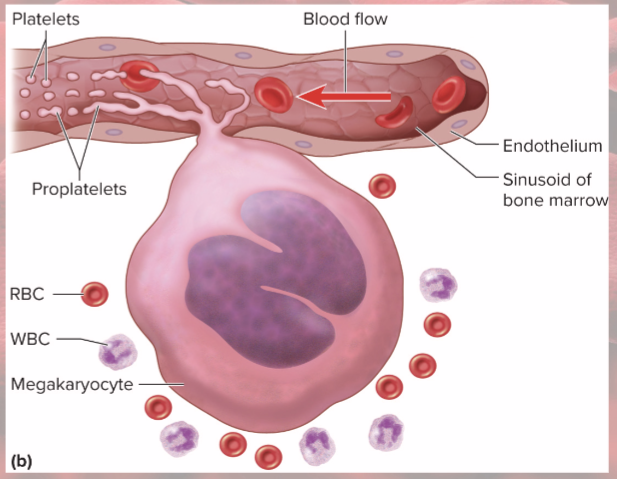
Thrombopoiesis
(platelet production)
stem cells become megakaryoblasts
Megakaryoblasts
replicate DNA without dividing
form gigantic 100 um cells (megakaryocytes)
Megakaryocytes
in bone marrow adjacent to blood sinusoids
tendrils of cytoplasm (proplatelets) protrude into blood sinusoids: blood flow splits off fragments called platelets
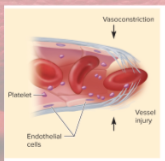
Vascular Spasm (step 1 of hemostasis)
prompt constriction of broken vessel
most immediate protection against blood loss
platelets release serotonin (vasoconstrictor)
pain and smooth muscle injury prompt quick constriction
buys time for other 2 clotting pathways
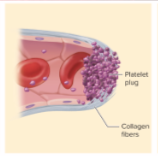
Platelet Plug formation (step 2 of hemostasis)
normally prostacyclin (platelet repellent) coats endothelium
but…
broken vessel exposes collagen
platelets grow pseudopods (tendrils of platelet)—stick to damaged vessel; pseudopods contract and draw walls of vessel together forming platelet plug
platelets degranulate, release:
serotonin- vasoconstricts
Thromboxane A2- promotes platelet aggregation, degranulation, and vasoconstriction
Positive feedback cycle active until break in small vessel seals
Coagulation (clotting, step 3 of hemostasis)
most effective defense against bleeding
conversion of fibrinogen (ogen=precursor to something else) to fibrin threads to form framework of clot
Procoagulants (clotting factors)— usually made by liver; present in plasma
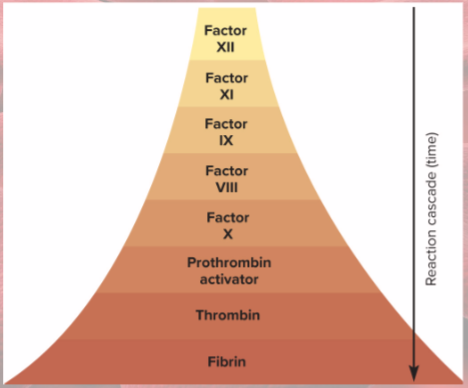
activate one factor, it activates next.. reaction cascade
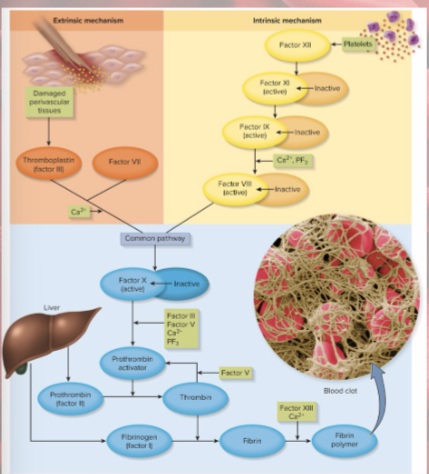
extrinsic pathway
factors released by damaged tissues begin cascade
intrinsic pathway
factors in blood begin cascade (platelet degranulation)
coagulation extrinsic pathway
initiated by tissue thromboplastin (factor III) from damaged tissues
combines with VII to activate X
calcium required
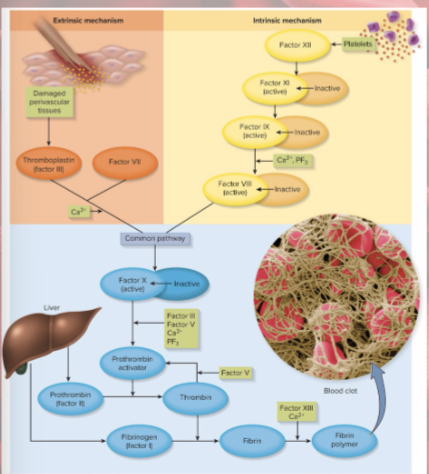
Intrinsic pathway
initiated by Factor XII from platelets
cascade to factor XI to IX to VIII to X
calcium required
Rapid clotting
each activated cofactor activates more molecules in next step of sequence
Prothrombin activator
converts prothrombin to thrombin
Thrombin!
converts fibrinogen to fibrin
Positive feedback when thrombin speeds up formation of
prothrombin activator (which converts prothrombin to thrombin that converts fibrinogen to fibrin)
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
stimulates fibroblasts and smooth muscle cell mitosis—repair damaged vessel
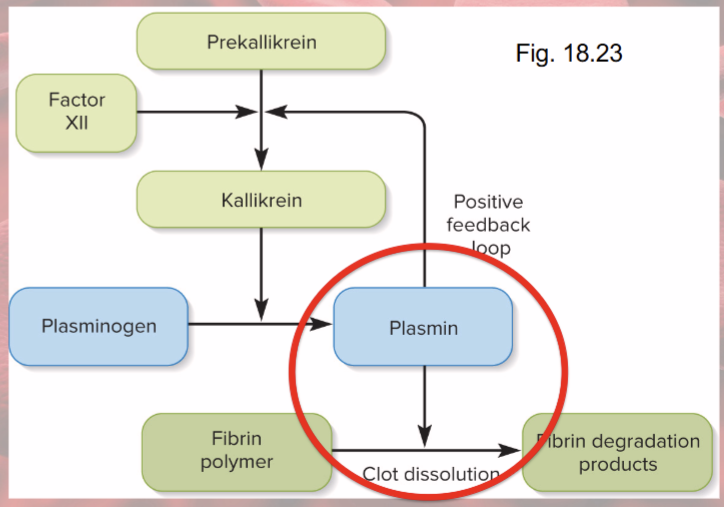
Fibrinolysis
dissolution of clot
factor XII speeds up formation of kallikrein enzyme
kallikrein converts plasminogen into plasmin = fibrin-dissolving enzyme
Platelet repulsion (prevents inappropriate clotting)
platelets do not adhere to prostacyclin-coated endothelium
2 natural anticoagulants
Heparin (from basophils) interferes with formation of prothrombin activator (makes thrombin which then makes fibrin)
Anti-thrombin (from liver) deactivates thrombin
clotting disorders
deficiency of any clotting factor can shut down coagulation cascade (can’t clot)
Hemophilia
family of hereditary diseases characterized by deficiencies of factor
Hemophilia A and B vs C
sex-linked recessive vs autosomal
Thrombosis
abnormal clotting in unbroken vessel (overclotting)
thrombus=clot
Embolus
thrombus (clot) that travels in blood
Pulmonary embolism
clot from legs may travel to lungs
Infarction
tissue death
may occur if clot blocks blood supply to heart (MI) or brain (stroke)
coumarin, warfarin=
vitamin K (required for formation of clotting factors) antagonists (prevents clots)
aspirin suppresses
thromboxane A2 (makes platelets sticky) (prevents clots)
3 things for dissolving clots
Streptokinase: enzyme that dissolve clots in coronary vessels
Tissue Plasminogen Activator (TPA): faster and more specific (given to people who have had a stroke)