Carbon and Hydrogen Naming
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Organic Chemistry
Is the study of compounds that contain carbon
Carbon in Organic Chemistry
is important because of its unmatched chemical diversity. It can form strong bonds with itself and other elements, and it makes four covalent bonds.

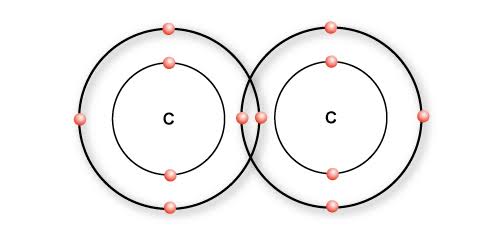
C–C Bonding
Carbon atoms bond strongly with other carbon atoms, allowing long chains or ring structures to form.
C–X Bonding
Carbon atoms bond well with atoms of other elements like hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Covalent Bonds
Chemical bonds where atoms share electron pairs. Carbon forms four of these, which adds to its bonding flexibility.
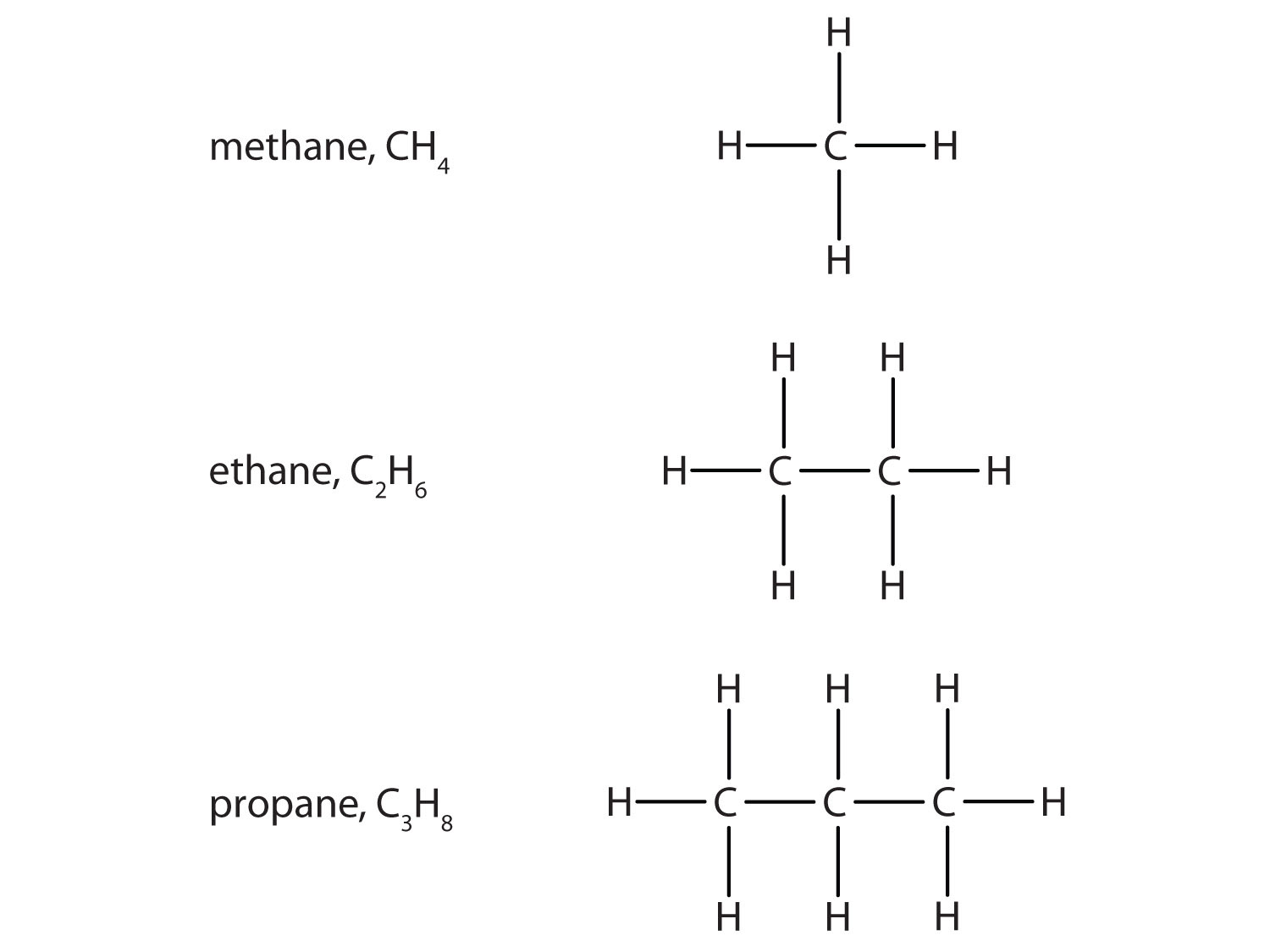
Molecular Formula
Shows the exact number of atoms of each element in a molecule. Example: C₃H₈
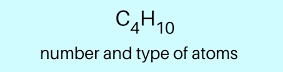
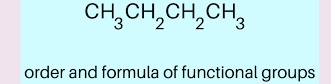
Condensed Structural Formula
A simplified way to write molecules where atoms are grouped and bonds are implied. Example: CH₃CH₂CH₃
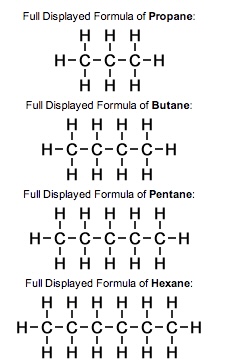
Skeletal Formula
Shows all atoms and bonds explicitly; used to visualize the full structure of the molecule.
Skeletal Formula (Line-Angle Structure)
Represents carbon chains as zigzag lines. Each corner or end point is a carbon atom, and hydrogen atoms are usually not shown.
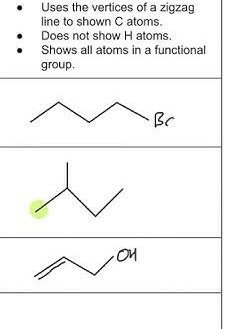
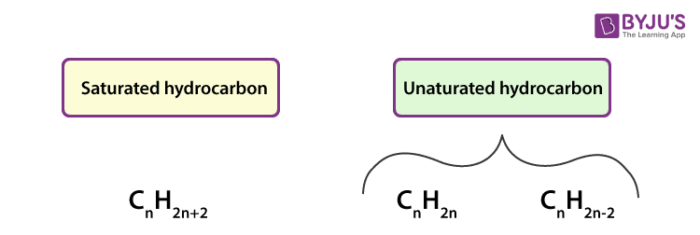
Hydrocarbons
Organic compounds made up of only carbon and hydrogen.
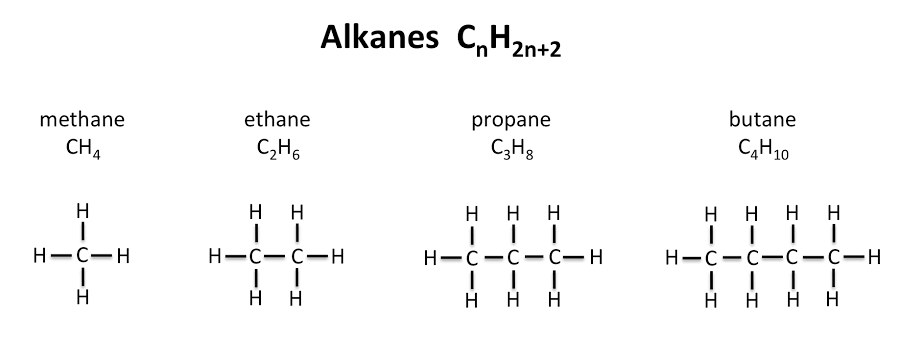
Alkanes (plAin and saturAted) CnH2n+2
Hydrocarbons with only single bonds between carbon atoms. They are saturated hydrocarbons.
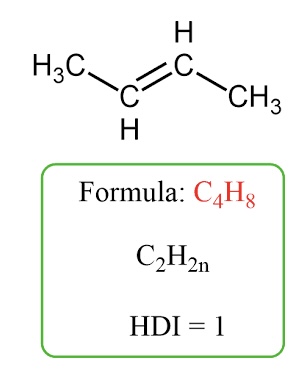
Alkenes (doublE bond) C2H2n
Hydrocarbons that contain at least one double bond between carbon atoms. They are unsaturated.
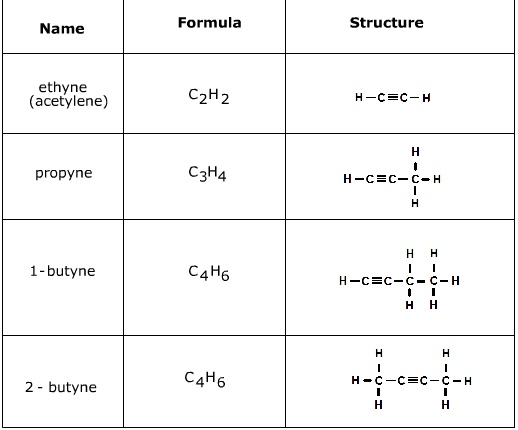
Alkynes
Hydrocarbons that contain at least one triple bond between carbon atoms. Also unsaturated.
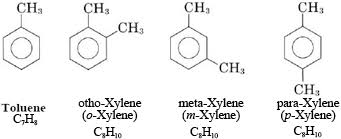
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons that contain benzene rings or similar ring structures with alternating double bonds (delocalized electrons).
Alkanes
Also called saturated hydrocarbons — they contain only single covalent bonds between carbon atoms.
Straight-Chain Alkanes (C1–C12)
My Energetic Parrot Bakes Pizza Holding Hot Orange Nuggets Daily (Under Dog)
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry - IUPAC Nomenclature (Alkanes)
A systematic way to name organic compounds.
Find the longest carbon chain → parent name
Add prefixes for branches/substituents
Use numbers to indicate positions
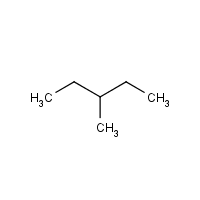
Substituent
A group of atoms (usually an alkyl group) that replaces a hydrogen on the carbon chain.
The suffix changes from -ane → -yl
Example: Propane → Propyl
Alkyl Group
A side-chain formed by removing one H from an alkane.
Examples:
• –CH₃ → methyl
• –CH₂CH₃ → ethyl
“-YL” = “you lost one hydrogen”
Naming Substituents (Steps)
Identify the longest chain
Number the chain from the end nearest a substituent
Name and number each substituent
Arrange names in alphabetical order
🧠 Hook: “L-C-N-A” = Longest, Closest, Number, Alphabetize
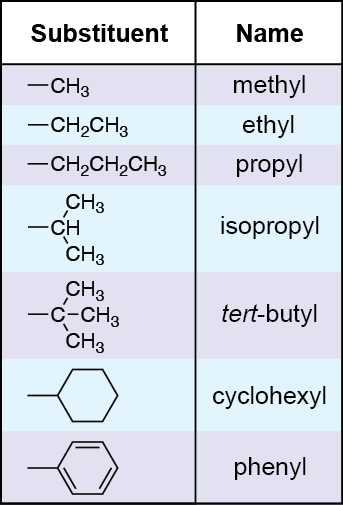
Example: 3-Methylpentane
• Longest chain: Pentane (5C)
• Methyl group on carbon 3
• Final name: 3-methylpentane
🧠 Name format: position-substituent+parent chain
Substituent Names (1–5 Carbons)
My Ex Played Basketball Poorly
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
Organic compounds that contain at least one double or triple bond between carbon atoms — not fully “saturated” with hydrogen.