SEHS UNIT 4.1 - Neuromuscular function
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
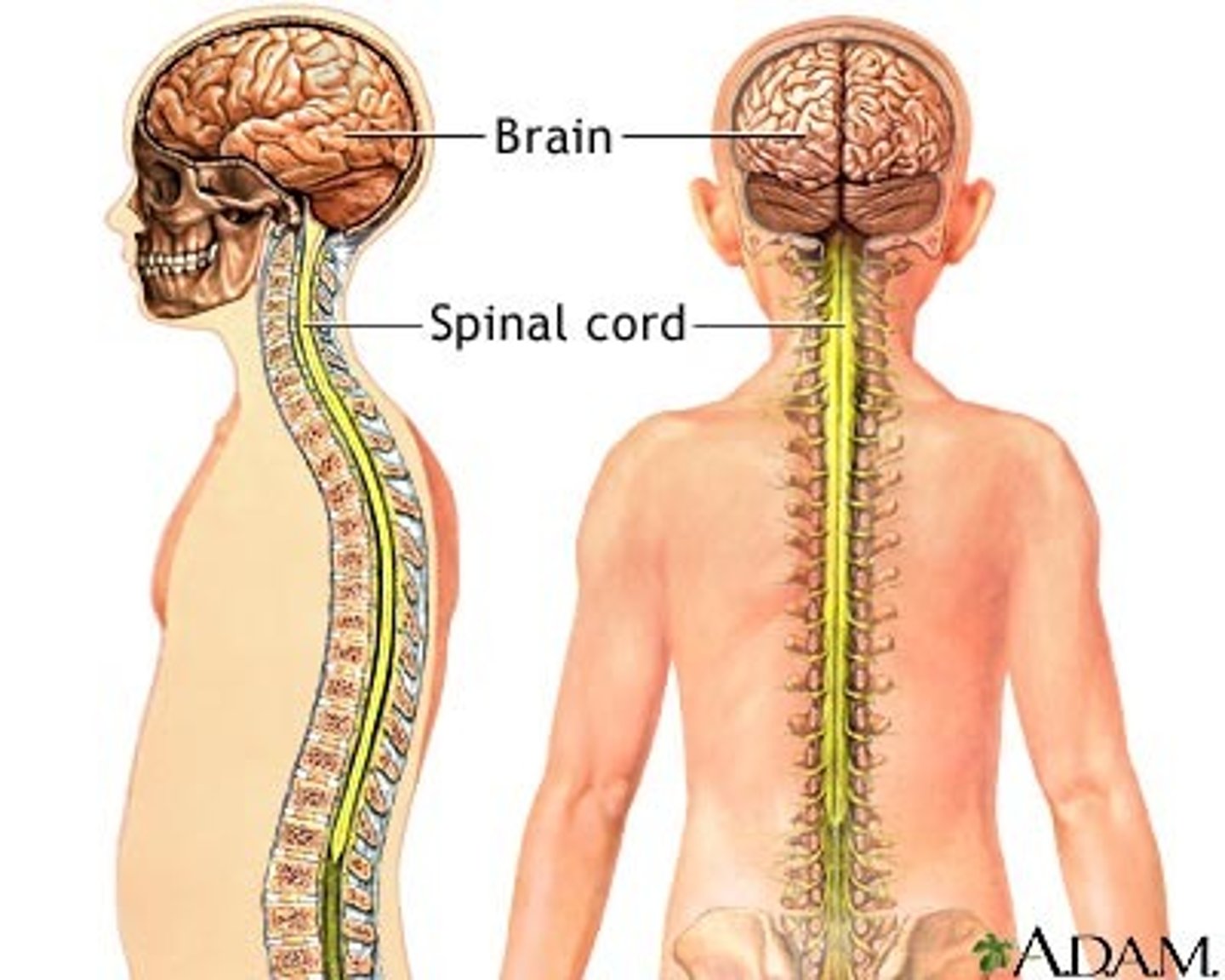
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord
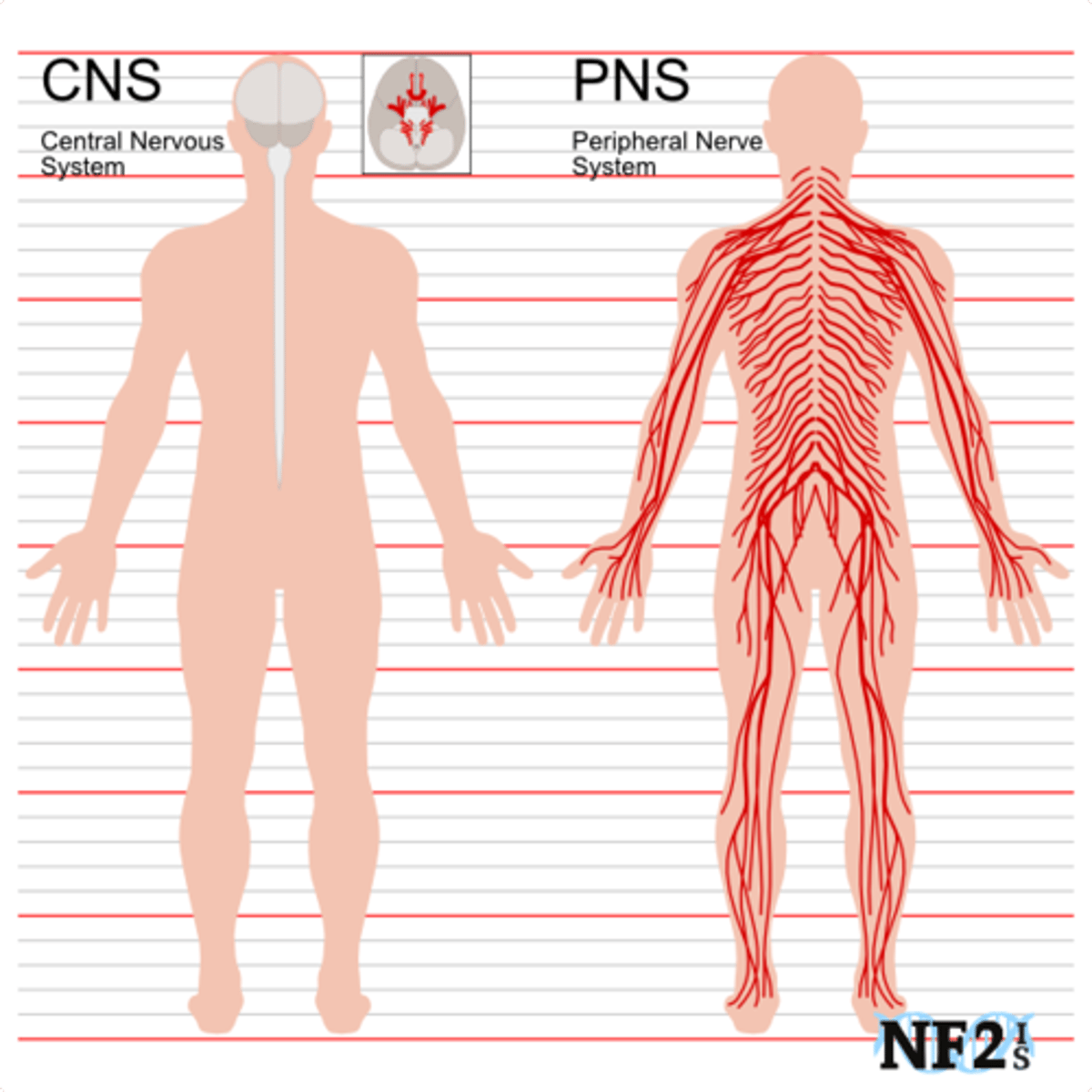
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Connects the brain and spinal cord to the muscles, organs and senses in the periphery of the body
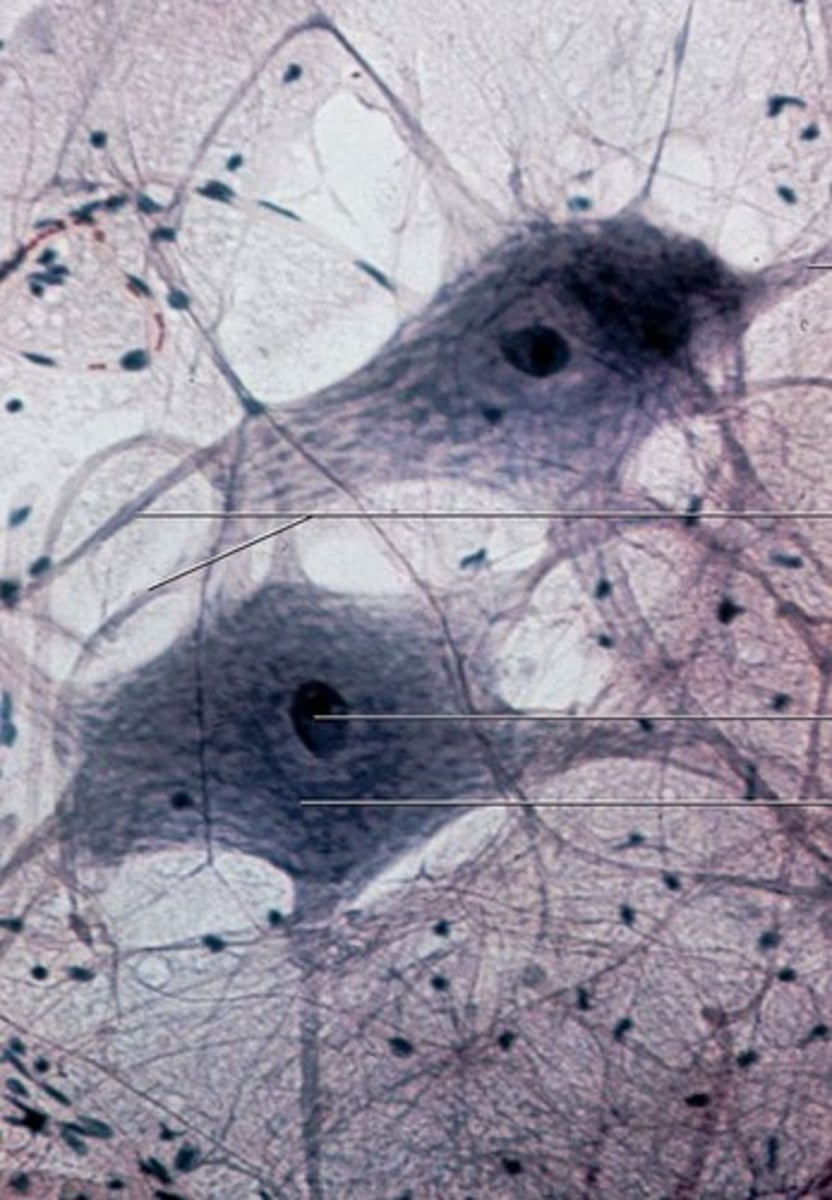
Neurons
Information messengers. They use electrical impulses and chemical signals to send information between the brain and the rest of the nervous system.
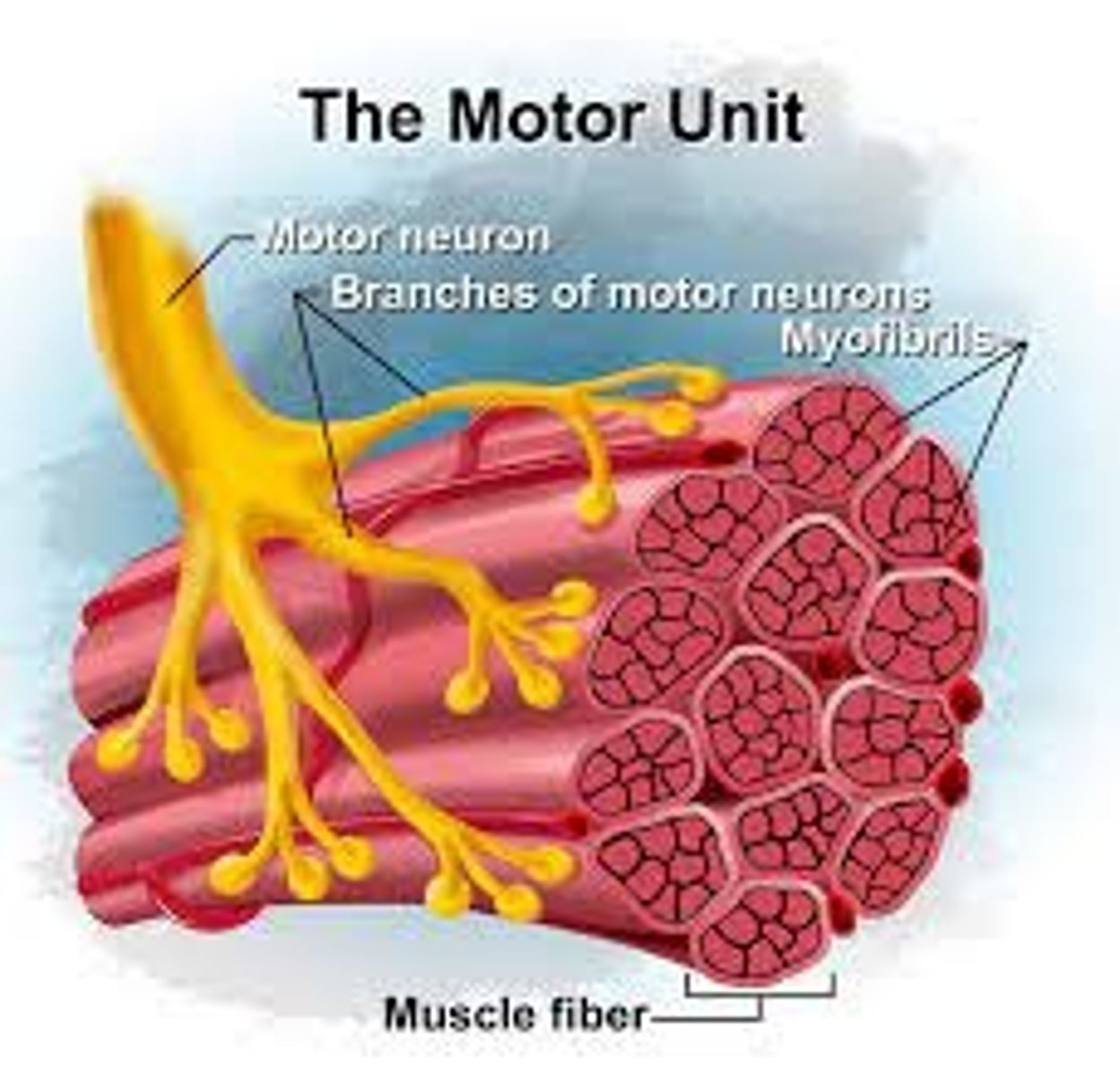
Motor neurons
Nerves that carry info from CNS to the muscles signalling contraction/relaxation
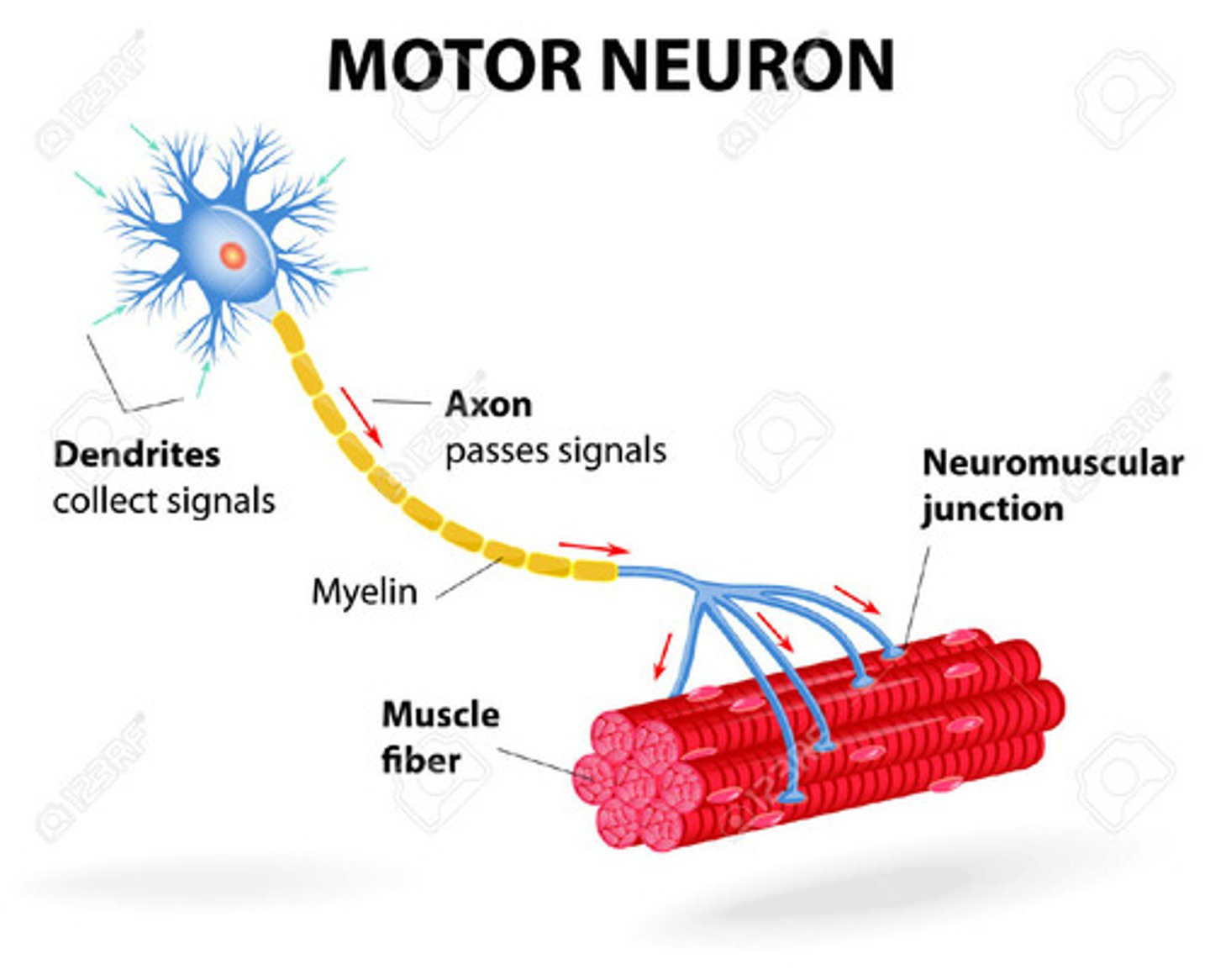
Neurotramsitters
Chemical messengers
Acetylcholine
Neurotransmitter released at the motor end plate which changes electrical impulse into a chemical signal
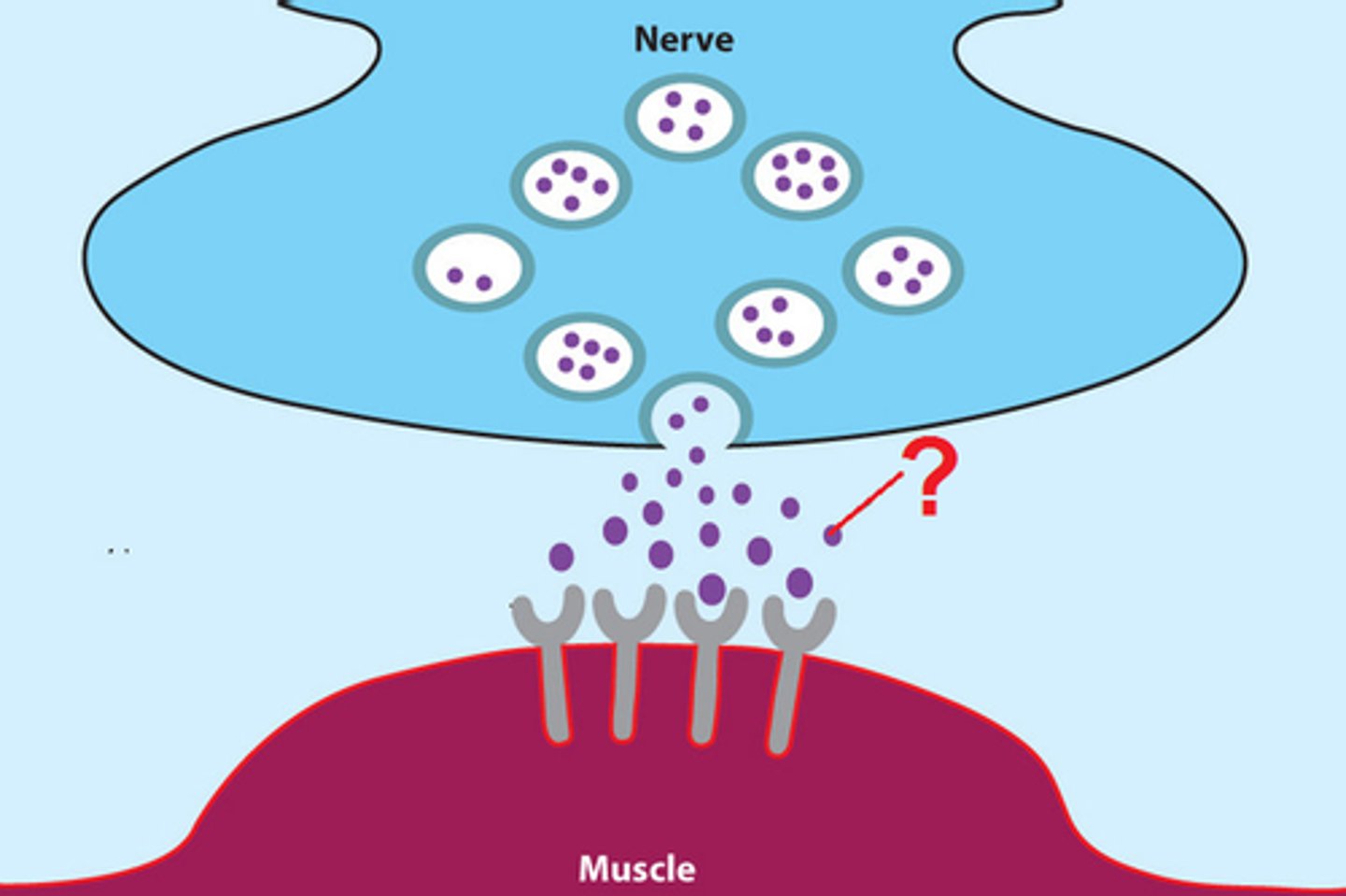
Cholinesterase
Enzyme which breaks down acetylcholine to return neuron to resting state (repolarization)
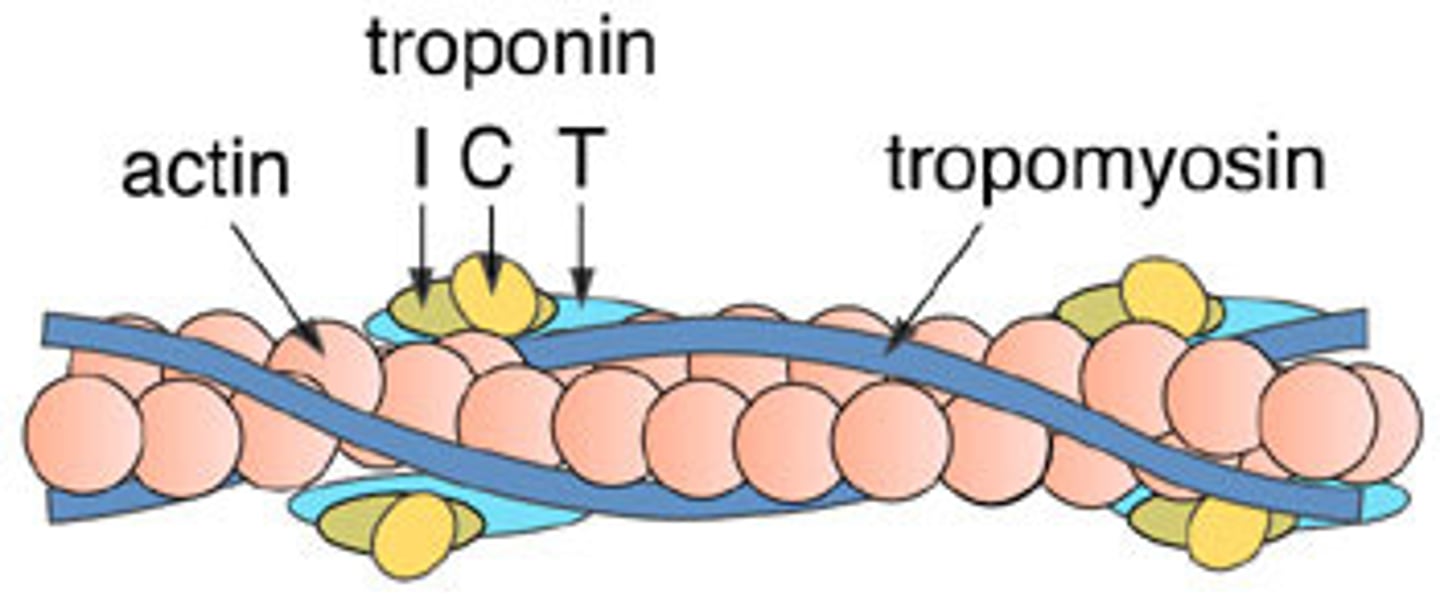
Actin
Thin myofilaments
Myosin
Thick myofilament
Tropomyosin
In relaxed muscle, blocks myosin from attaching to actin
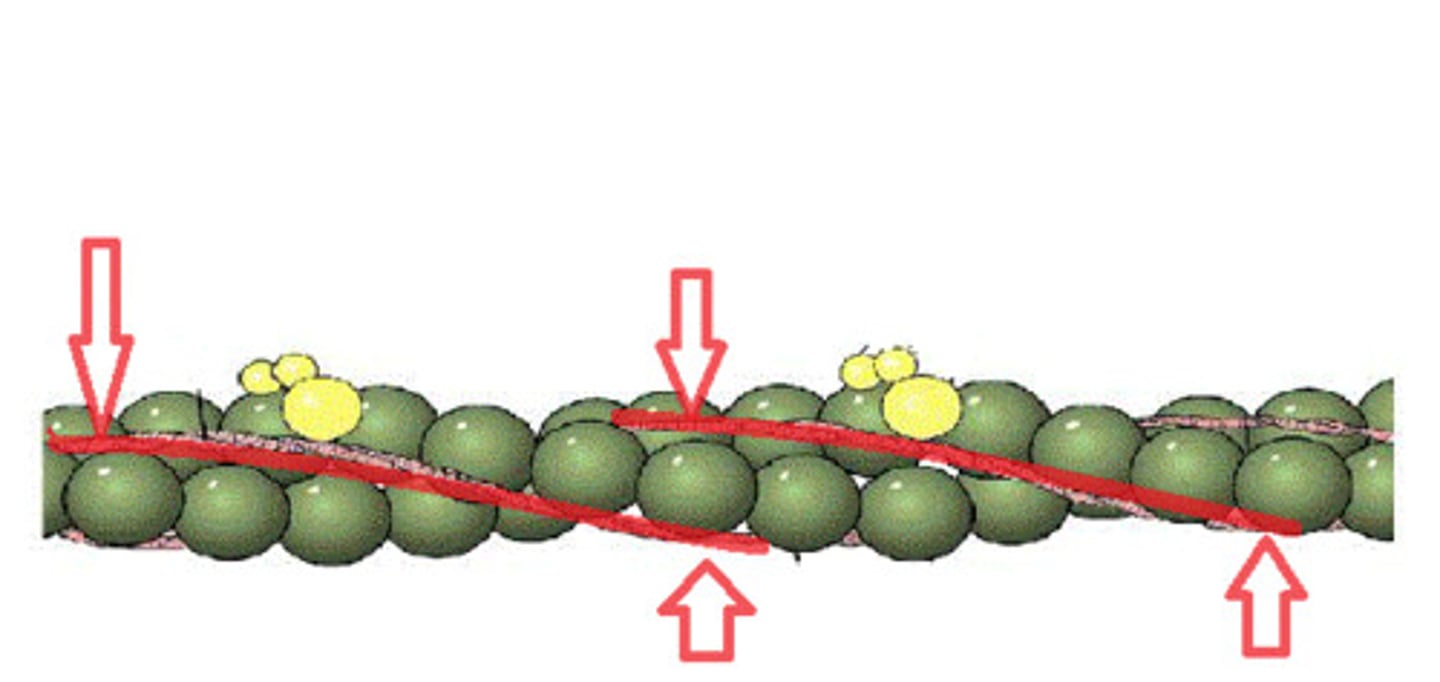
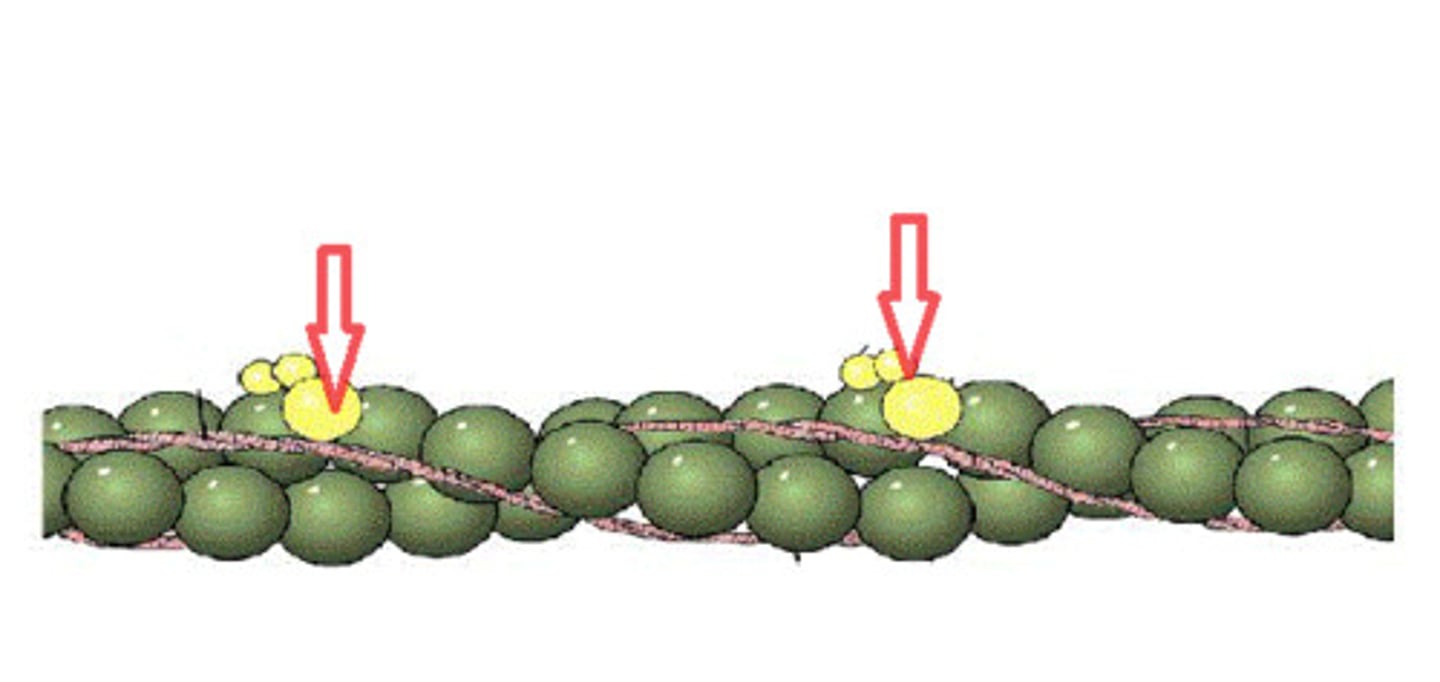
Troponin
Attached to tropomyosin, moves tropomyosin to allow myosin heads to attach to actin, creating cross-bridges when action potential is signalled.
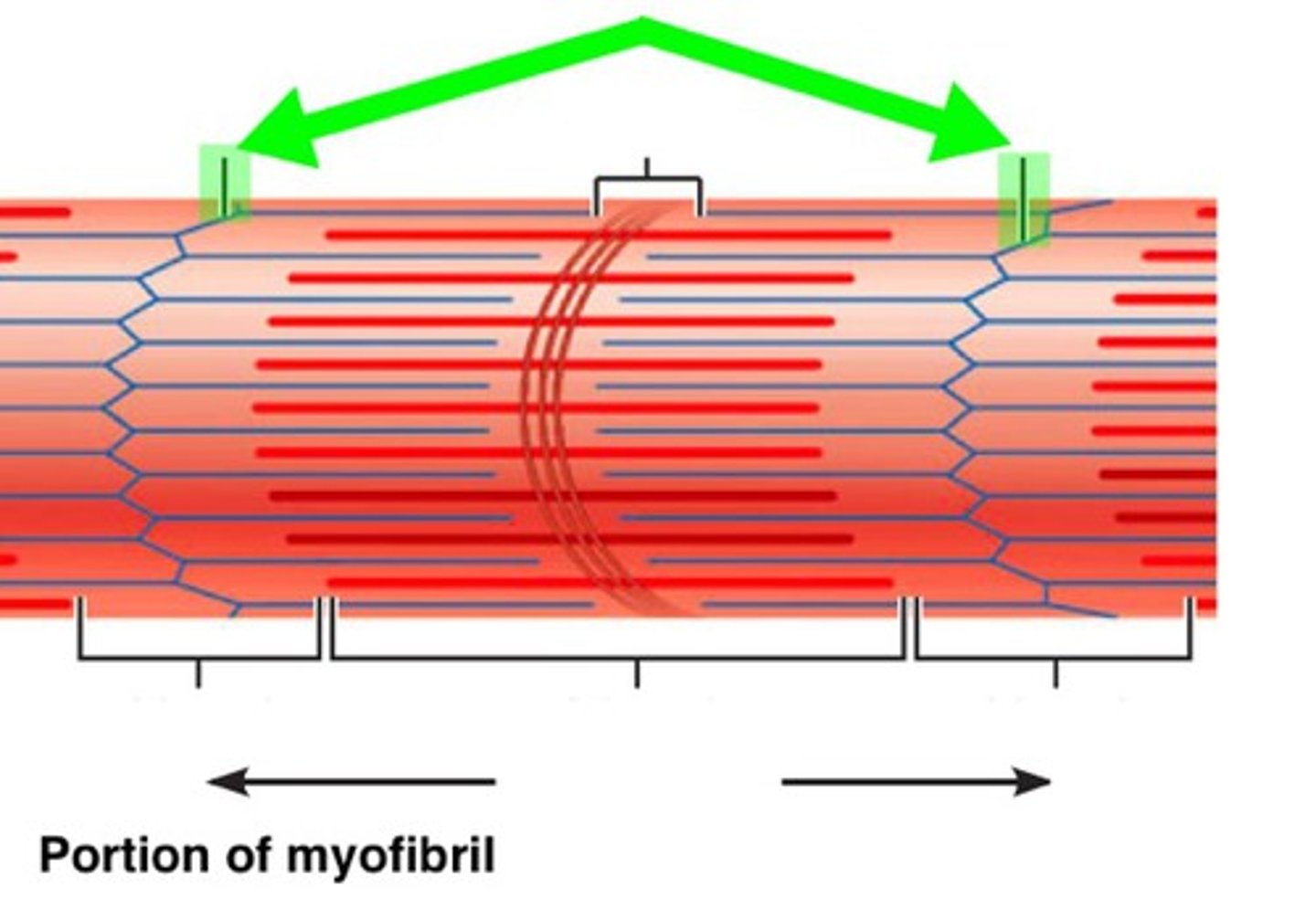
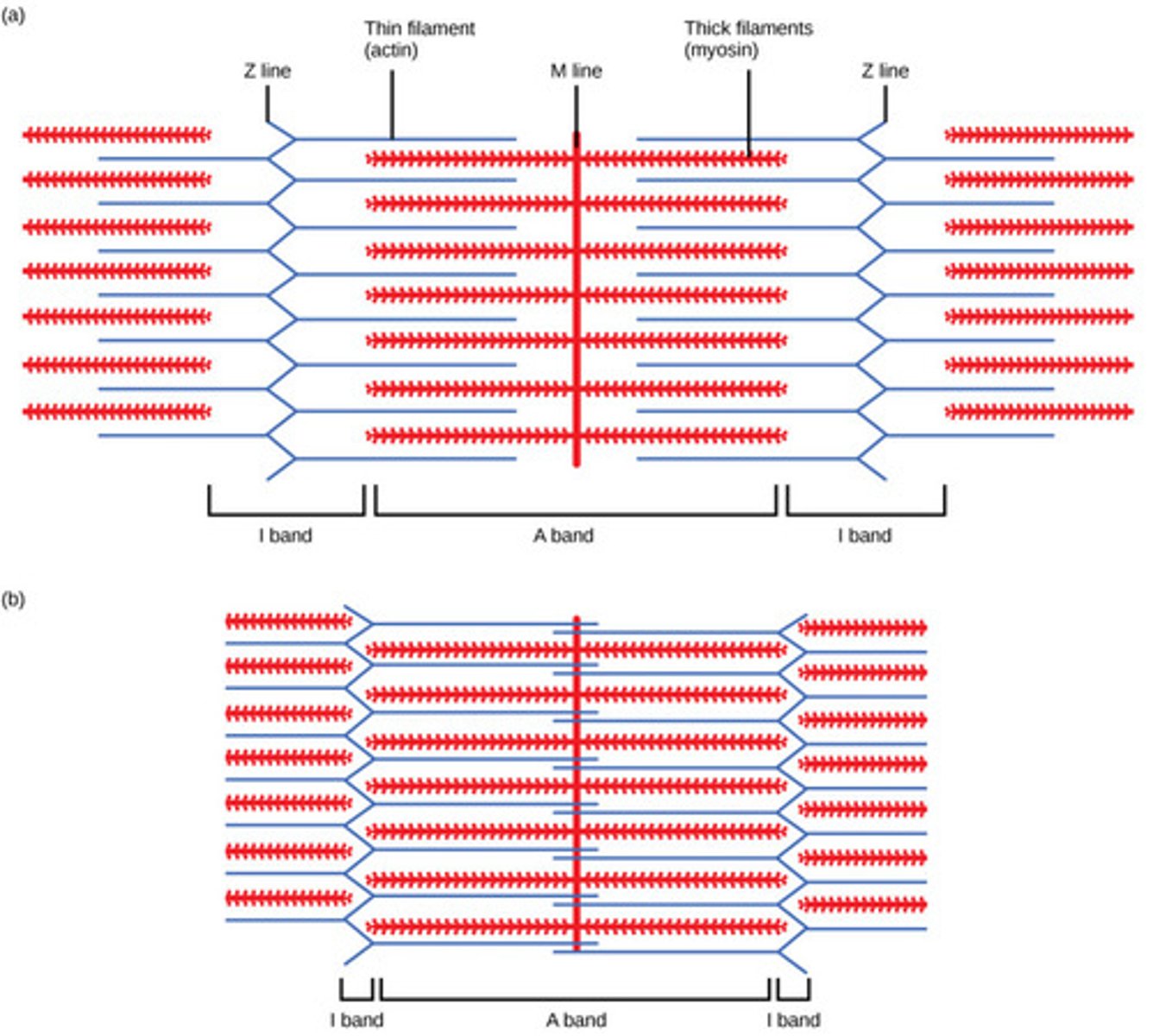
Sarcomere
Functional unit of myofibril; smallest unit of muscle contraction
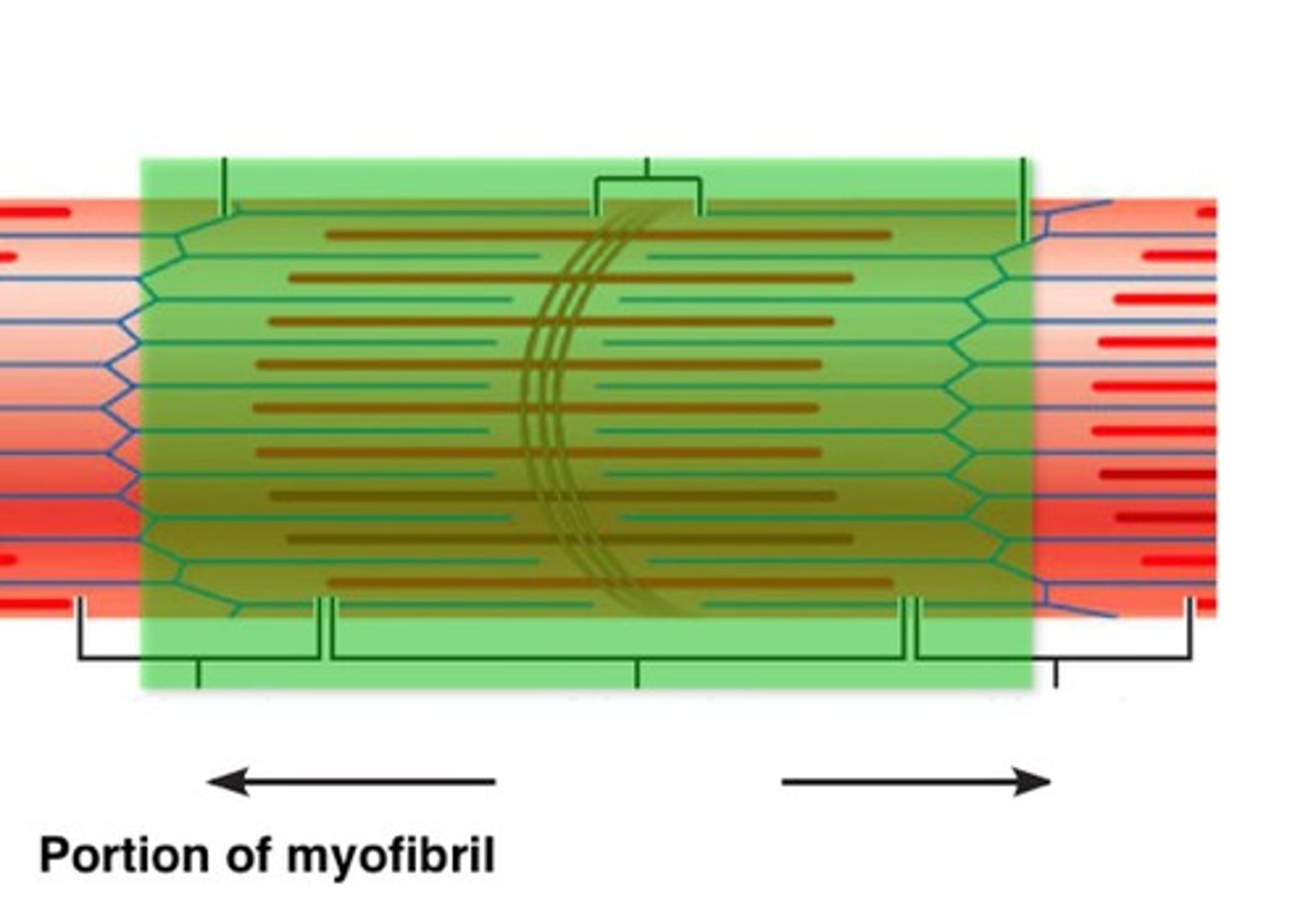
H zone
Center of sarcomere, contains only myosin filaments
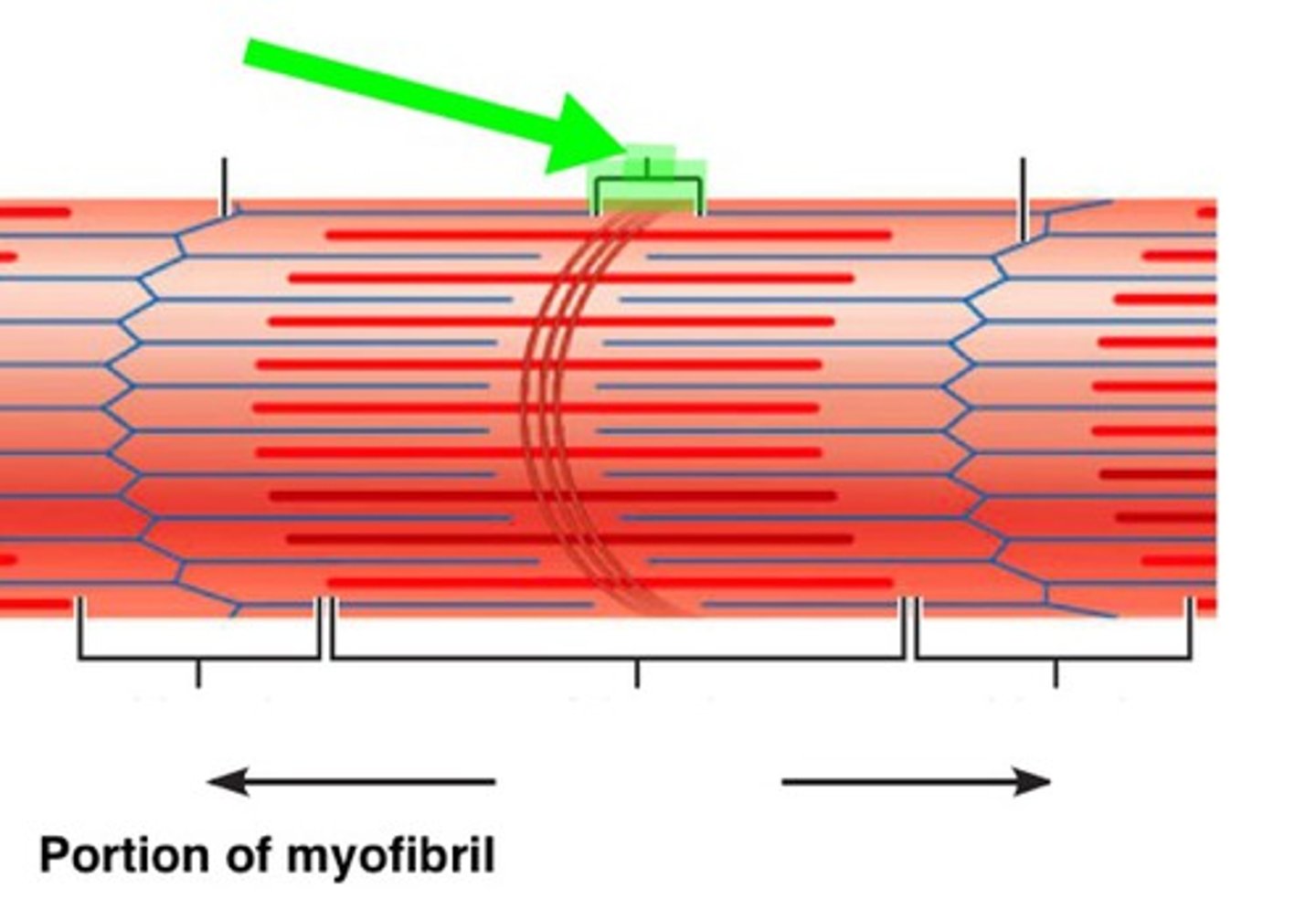
A band
Length of myosin, contains actin & myosin, stays same length during contraction
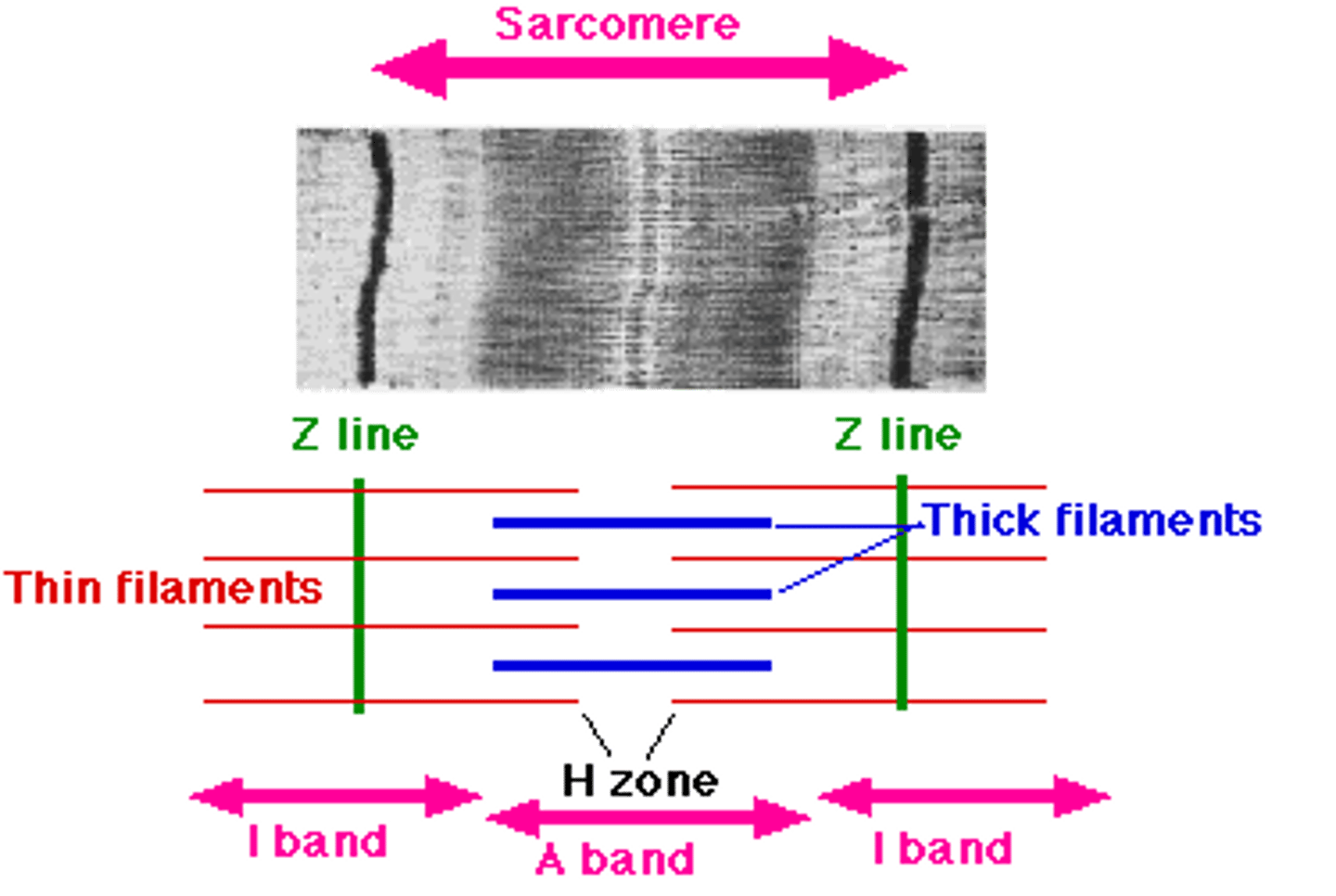
Z line
Separates sarcomere, decreases in length during contraction
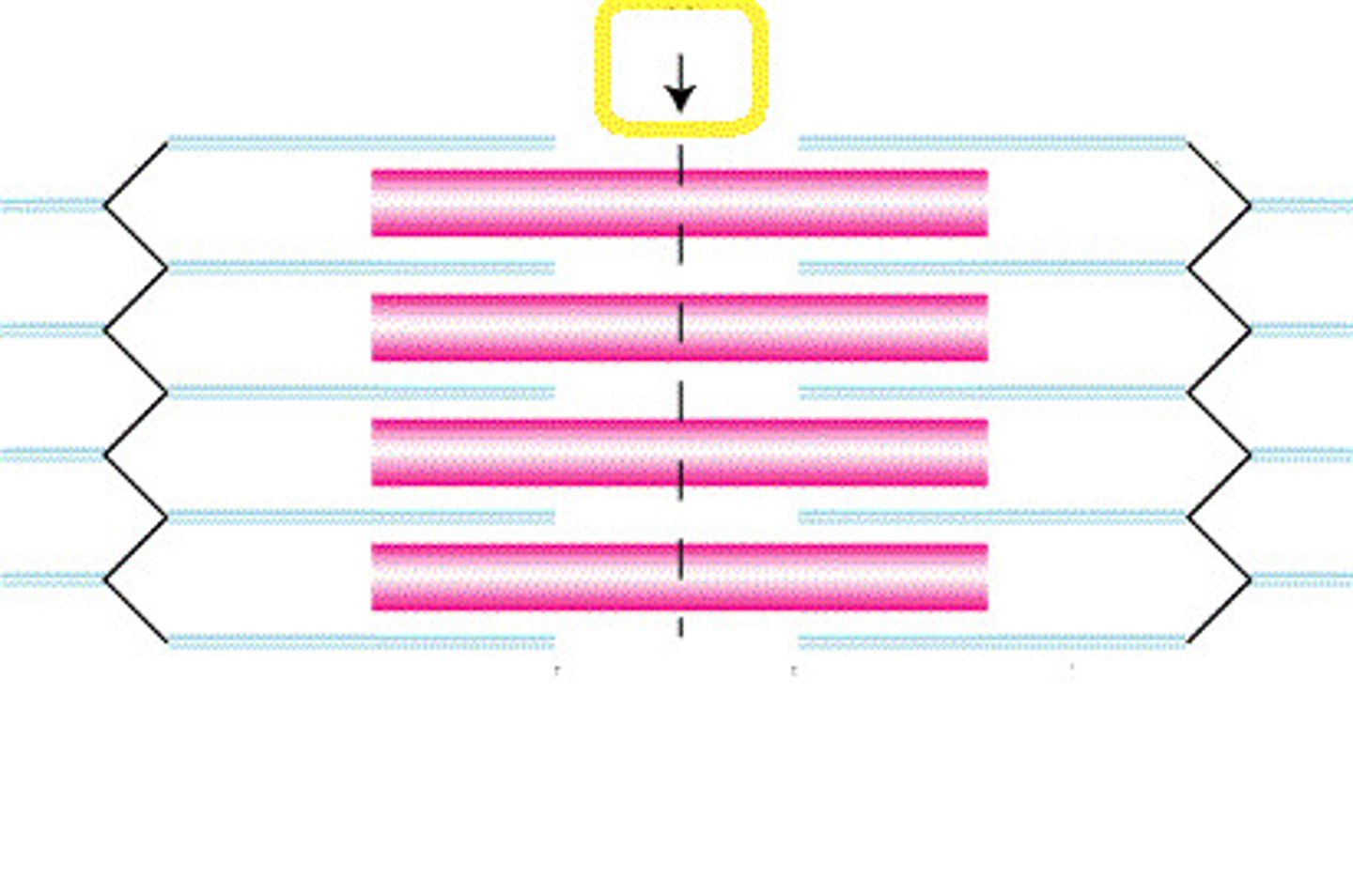
M line
Middle of sarcomere
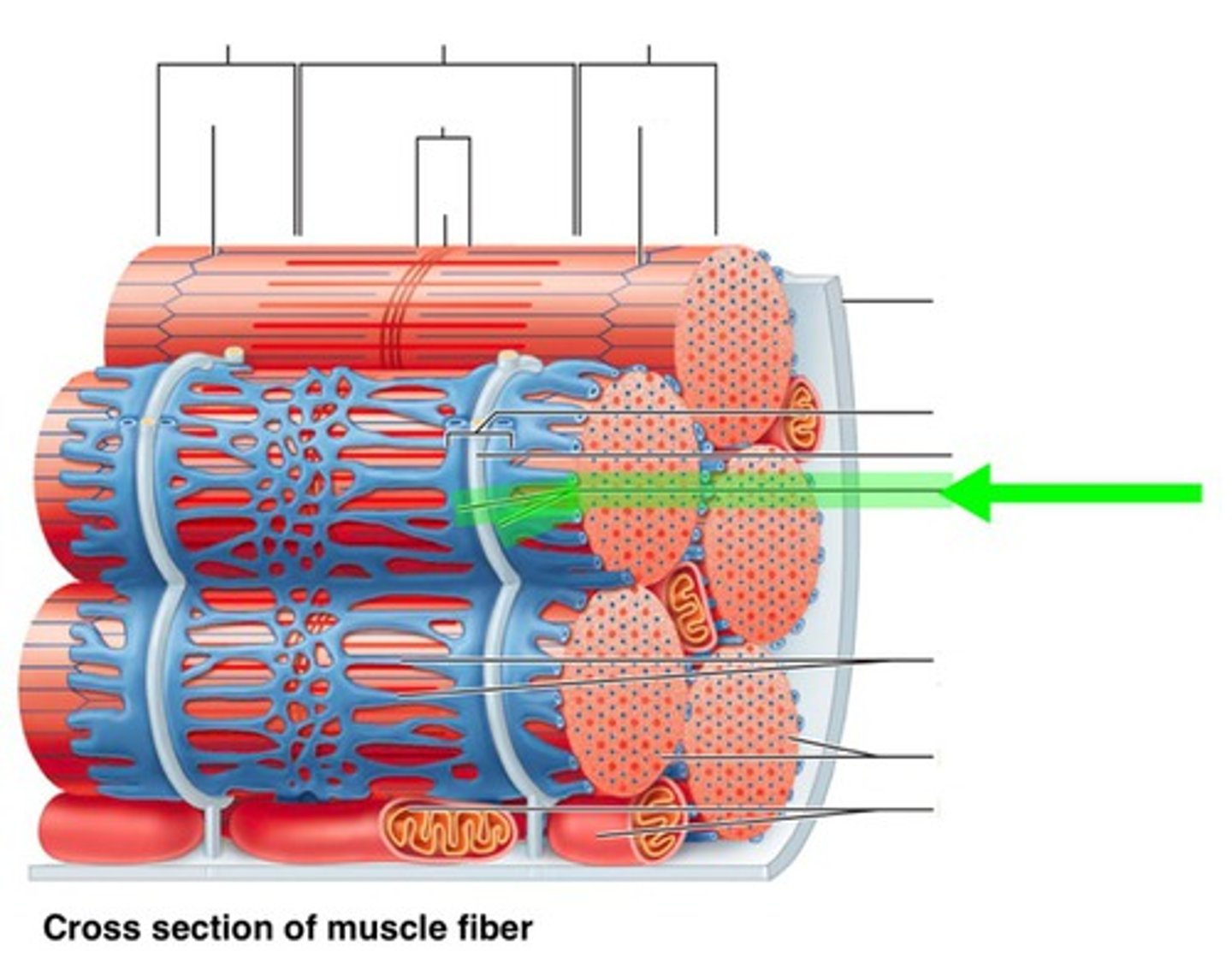
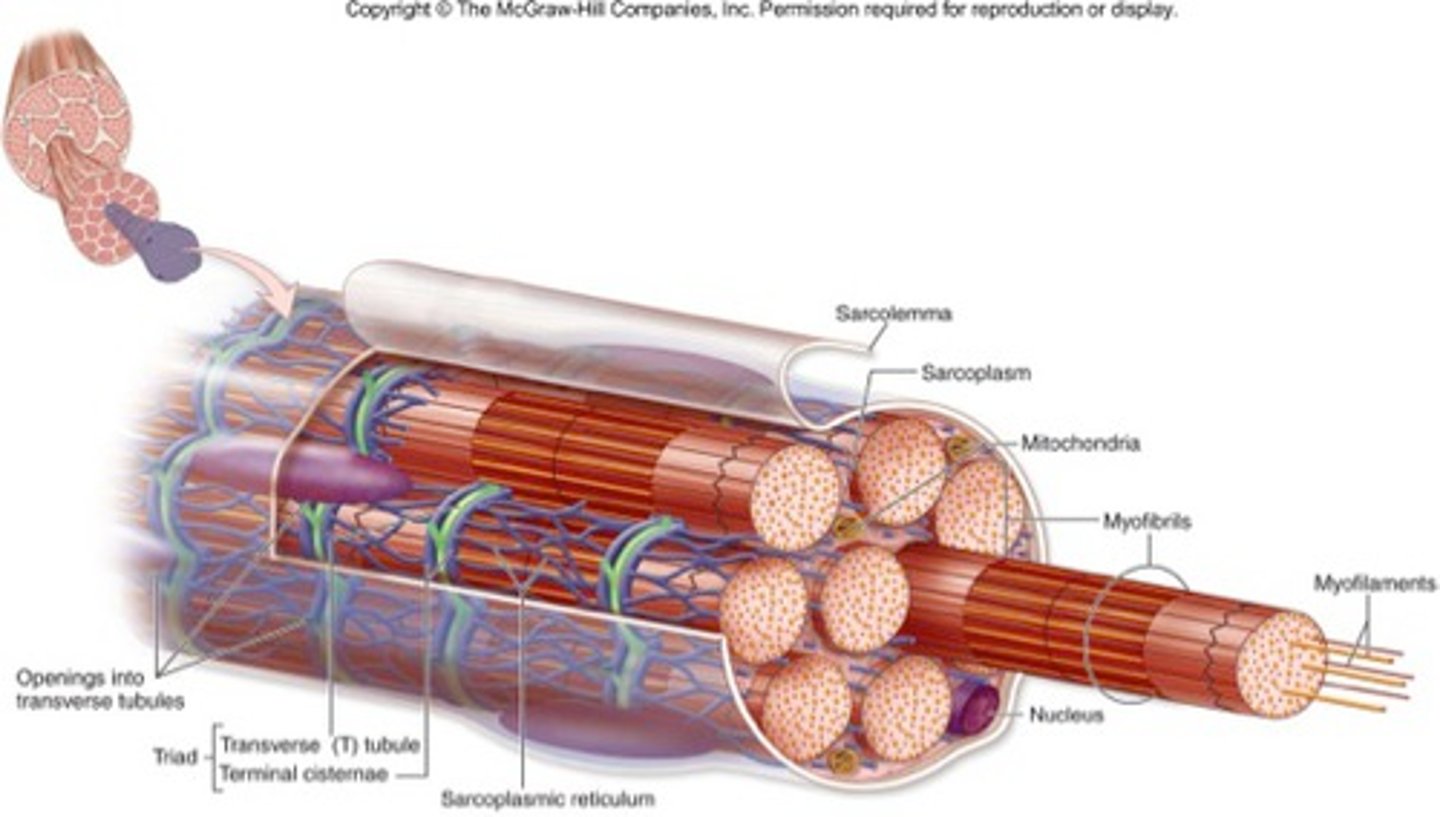
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Surrounds the myofibril. Stores & releases calcium in the muscle fibre
step 1 of the role of the nuerotransmitter stimulating the skeletal muscle.
The impulse is sent by the brain (CNS)
step 2 of of the role of the nuerotransmitter stimulating the skeletal muscle.
The impulse travels down the neuron (dendrites, cell body, axon, and motor end plate)
step 3 of the role of the neurotransmitter stimulating the skeletal muscle.
The impulse depolarises the motor end plate causing an influx of calcium ions, which in turn, allows acetylcholine to be released into the synapse
step 4 of the role of the neurotransmitter stimulating the skeletal muscle.
Acetylcholine changes the electrical impulse into a chemical stimulus which binds to the receptors on the muscle fibres, allowing the action potential to travel from the synapse into the muscle cells
step 5 of the role of the neurotransmitter stimulating the skeletal muscle.
Cholinesterase is an enzyme (ase) that breaks down Acetylcholine, immediately repolarising the membrane (resetting it), allowing the muscle to relax.
step 1 of sliding filament theory
The action potential travels through the muscle fibre, down the myofibrils and to the sarcomere via the t-tubules, where the impulse finally arrives at the sarcoplasmic reticulum
step 2 of sliding filament theory
Calcium ions are released by the sarcoplasmic reticulum
step 3 of sliding filament theory
The calcium ions binds with troponin
step 4 of sliding filament theory
Troponin and tropomyosin are then moved as they change shape, exposing the active sites of the actin.
step 5 of sliding filament theory
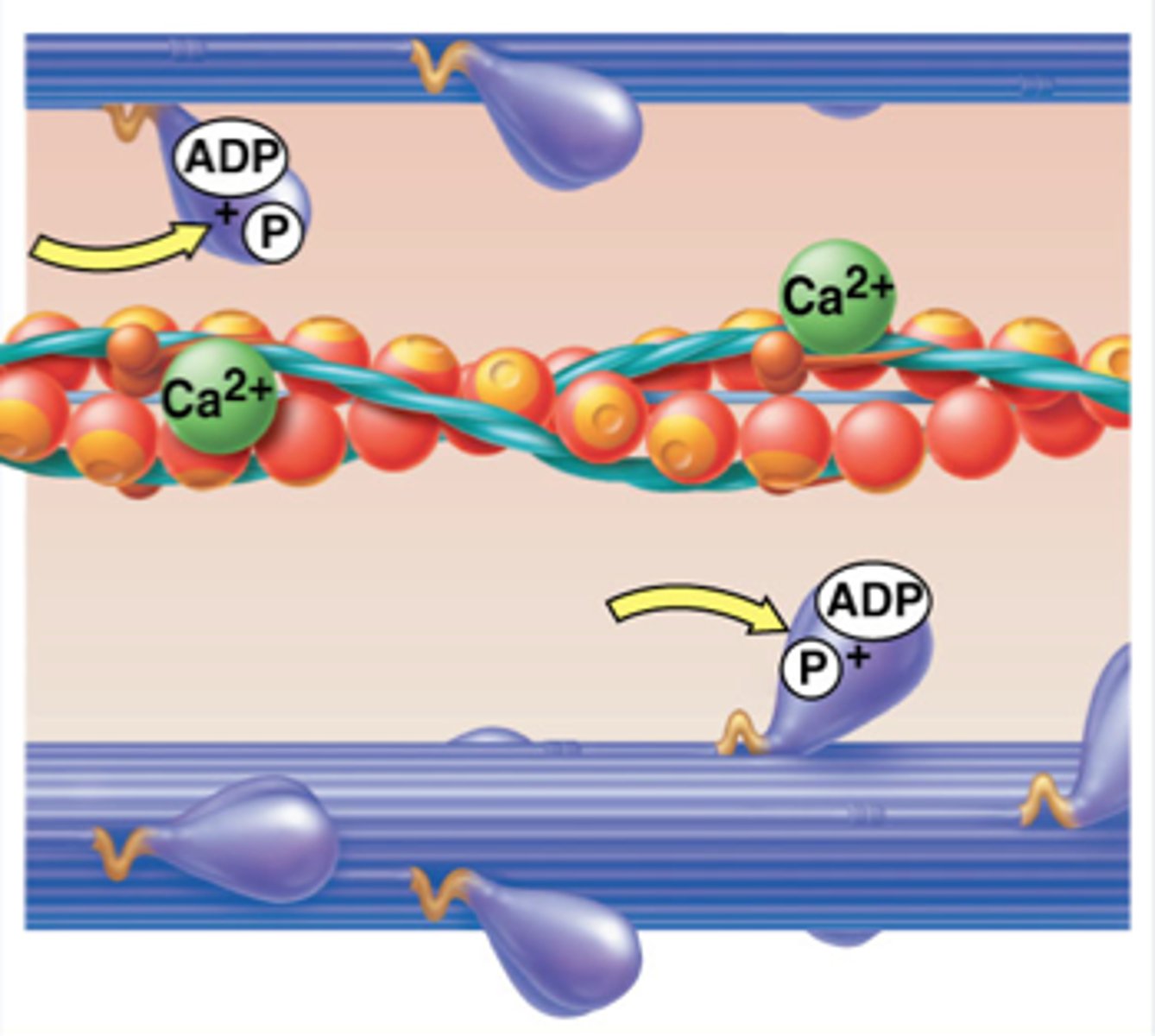
Actin and myosin (with stored ATP) bind together causing a cross bridge
step 6 of sliding filament theory
ATP is broken down to release energy, which allows myosin heads to drag actin causing the H zone and the Z line to shorten. This happens in every sarcomere in each myofibril within the muscle fibre.
step 7 of sliding filament theory
Immediately after the power stroke has taken place, and movement has occurred the actin and myosin release and return to resting position for ready for a new cross bridge. As long as there is ATP and calcium ions present this sliding filament model will continue until myosin filaments reach the Z discs resulting in the H Zone disappearing, thus causing muscle contraction.
step 8 of sliding filament theory
Cholinesterase is released into the synapse, breaking down the acetylcholine, therefore the action potential can not reach the receptors and no muscle contraction can occur and the muscle relaxes
Type 1 Muscle Fibre (slow twitch)
Fairly slow nerve transmission speeds & small muscle forces maintain contractions for long time, fatigue resistant
Type 1 Muscle Fibre example
Walking/jogging
Type 2a Muscle Fibre (fast twitch)
Fast neural transmission times & strong contraction forces, fatigue resistant
Type 2a Muscle Fibre example
Swimming/cycling
Type 2b Muscle Fibre (fast twitch)
High fatigue rate/doesn't maintain contractions for prolonged period of time
Type 2b Muscle Fibre example
Sprinting, jumping, throwing, weightlifting
Dentrite
Receives communications
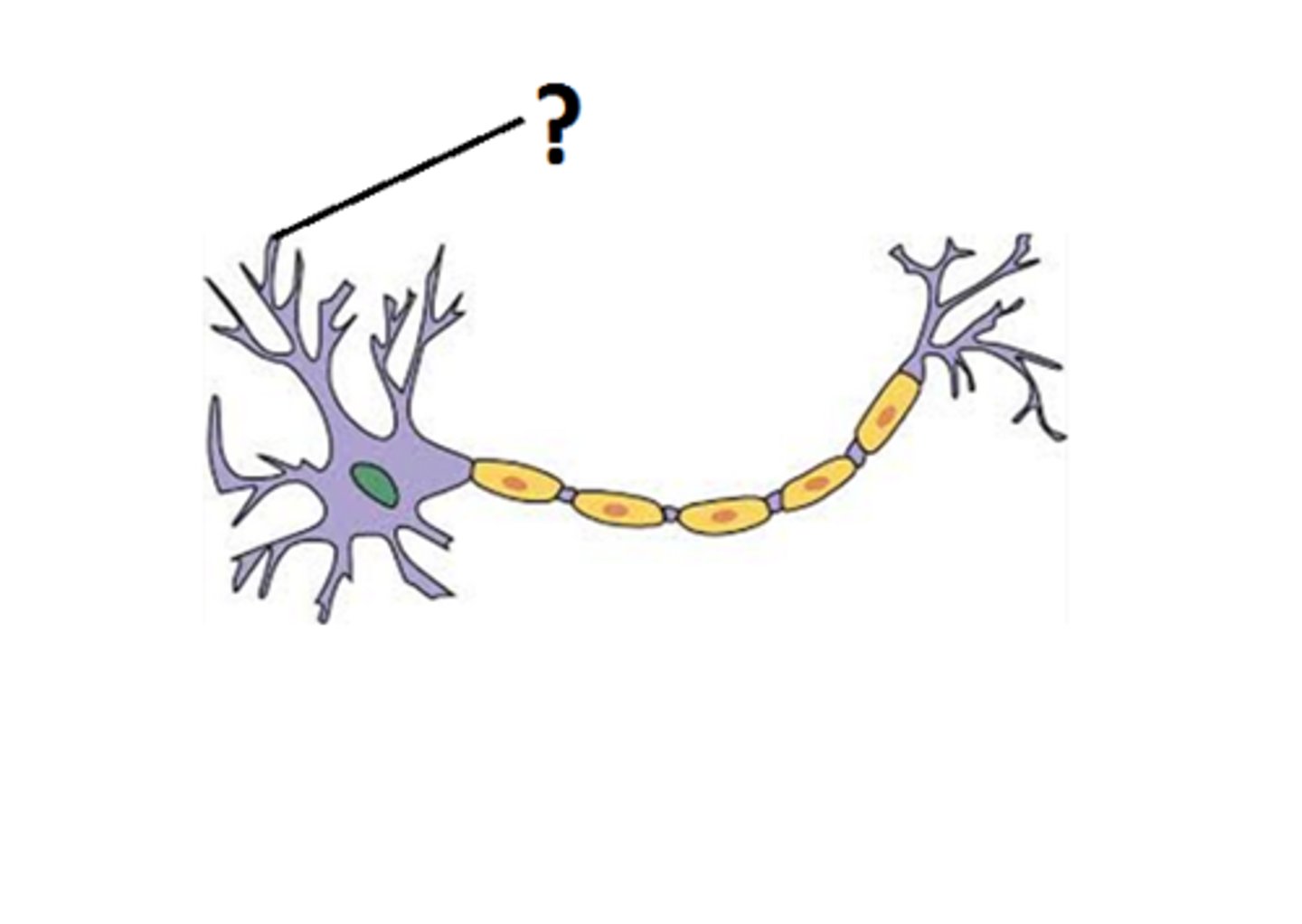
Cell body
Maintains the neuron's structure, and provides energy to drive activities.
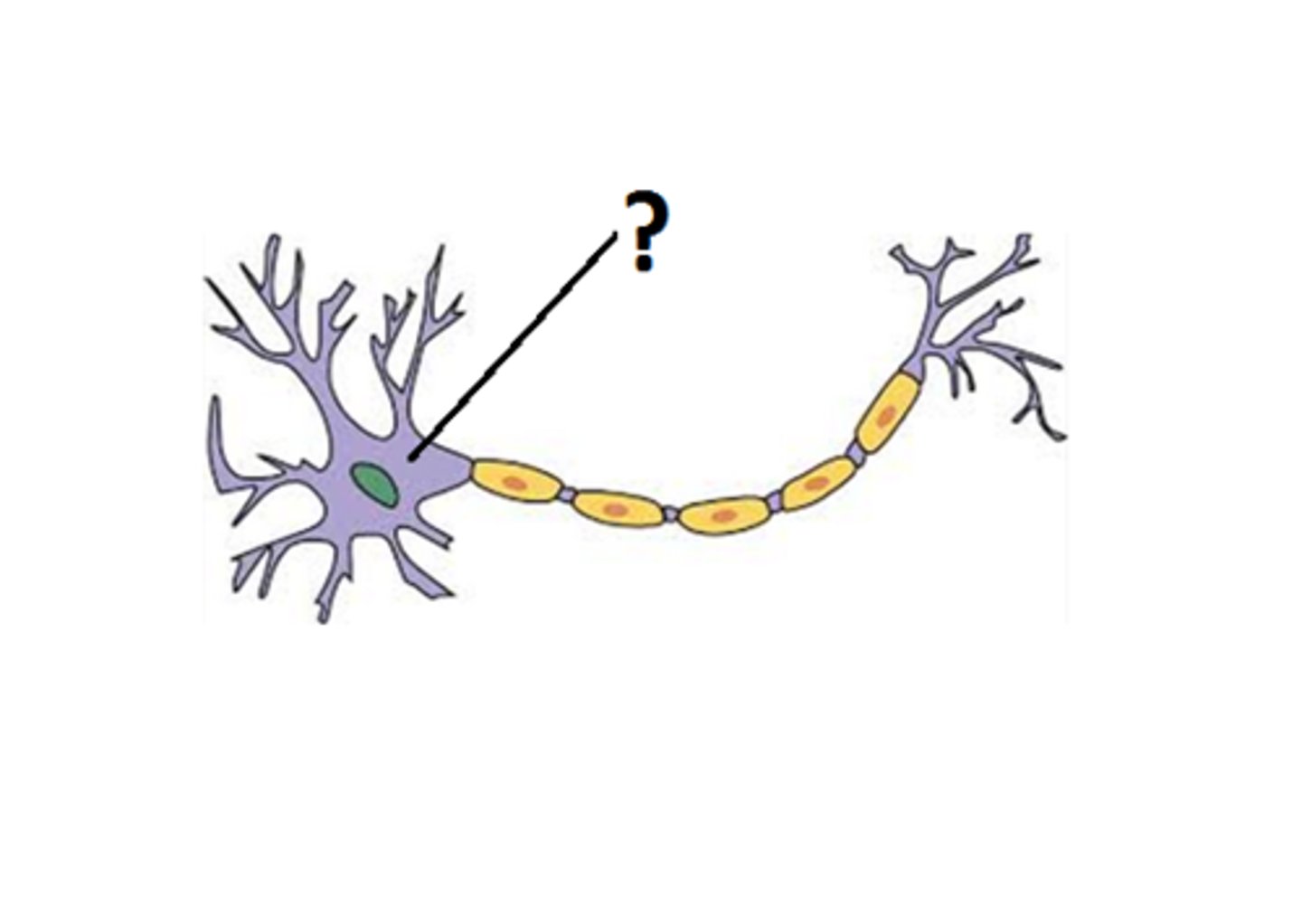
Nucleus
The intelligence that keeps the cell running and has all the programming that operates the neuron
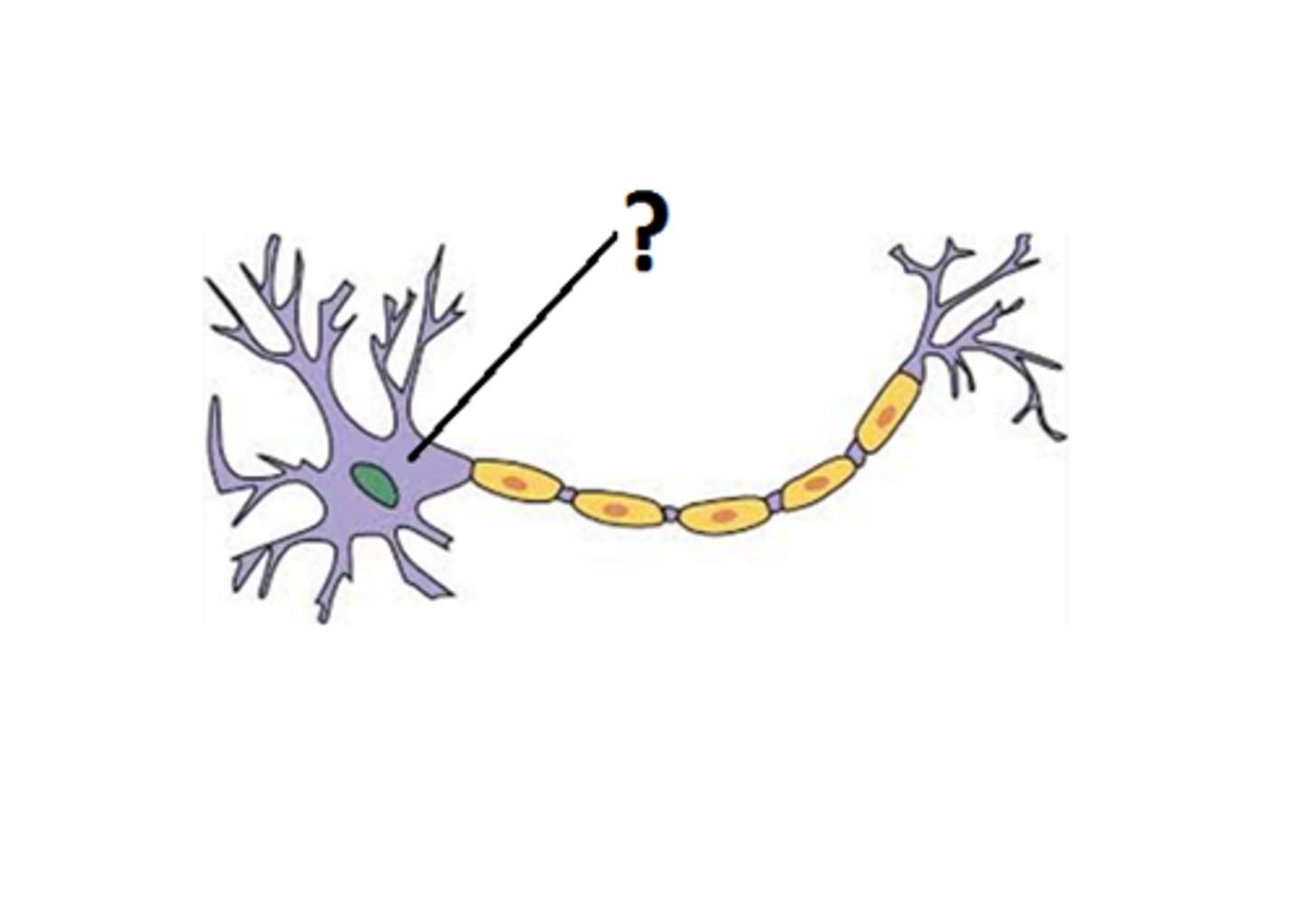
Axon
Carries nerve impulses (electrical action potential) away from the cell body.
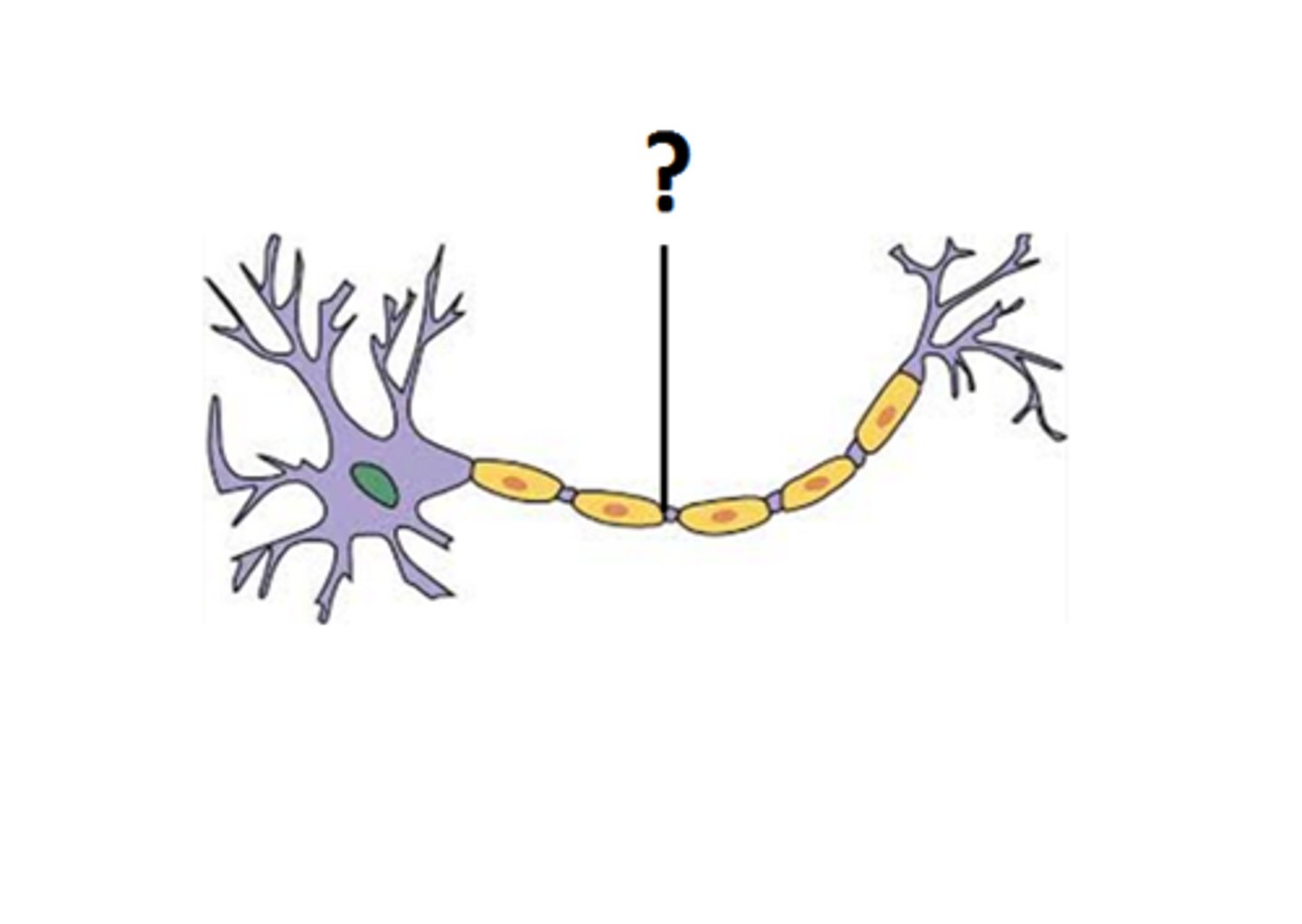
Motor end plate (neuromuscular junction)
When stimulated by a nerve impulse, depolarises and releases the chemical neurotransmitter.
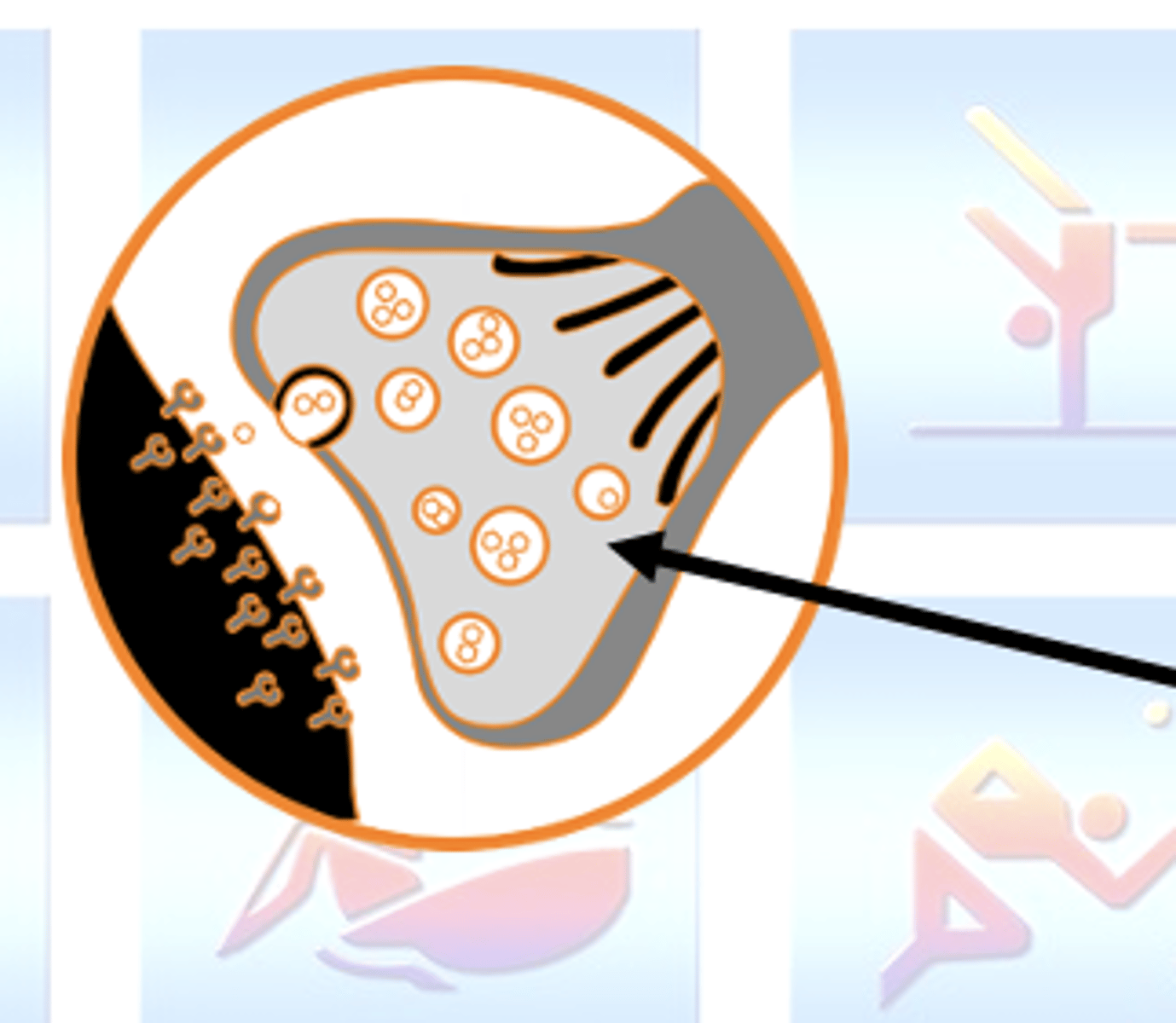
Synapse
Junction between the motor neuron and the muscle fibre
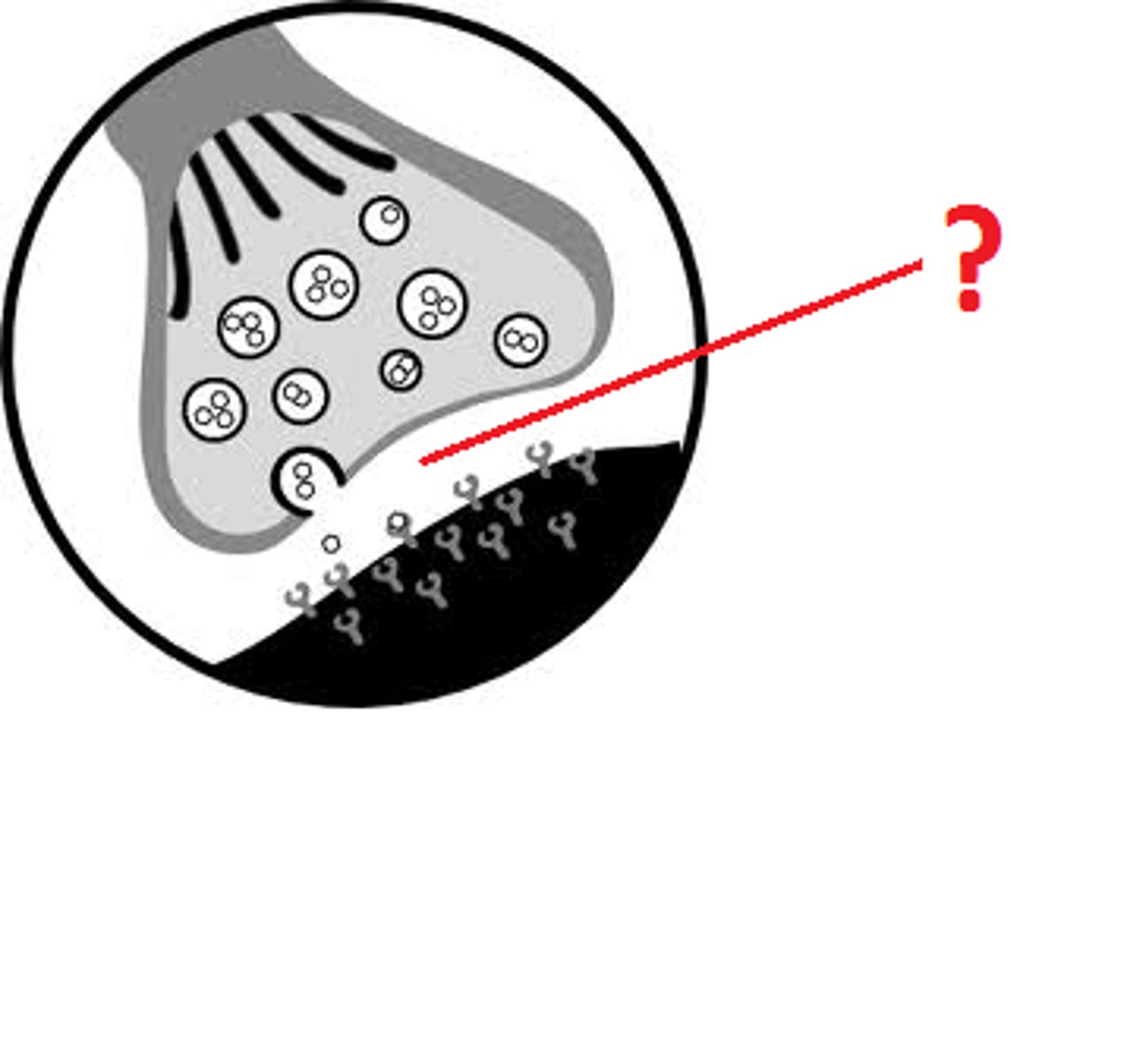
Muscle fibre
Where the receptors sit to allow action potential to then travel into the muscle cell
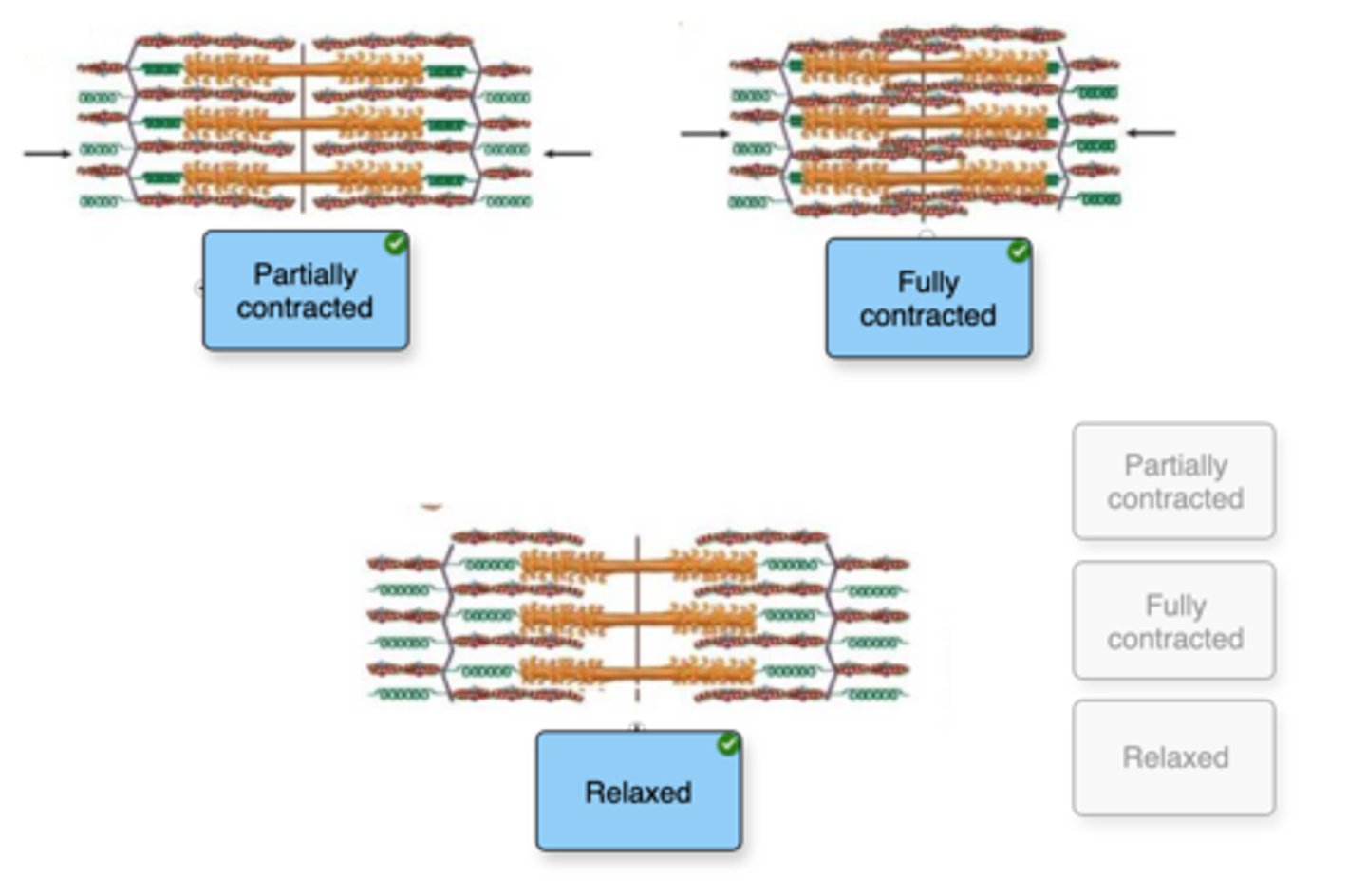
Relaxed muscle
Tropomyosin blocks the binding site
Partially contracted muscle
Thick and thin filaments start to slide past one another. The sarcomere, I band, and H zone are narrower and shorter
Fully-contracted muscle
The H zone and I band disappear, and the sarcomere is at its shortest length.
Myofibril
Tightly packed filament bundles found within skeletal muscle fibres.
Myofilaments
The contractile proteins, actin and myosin, of muscle cells
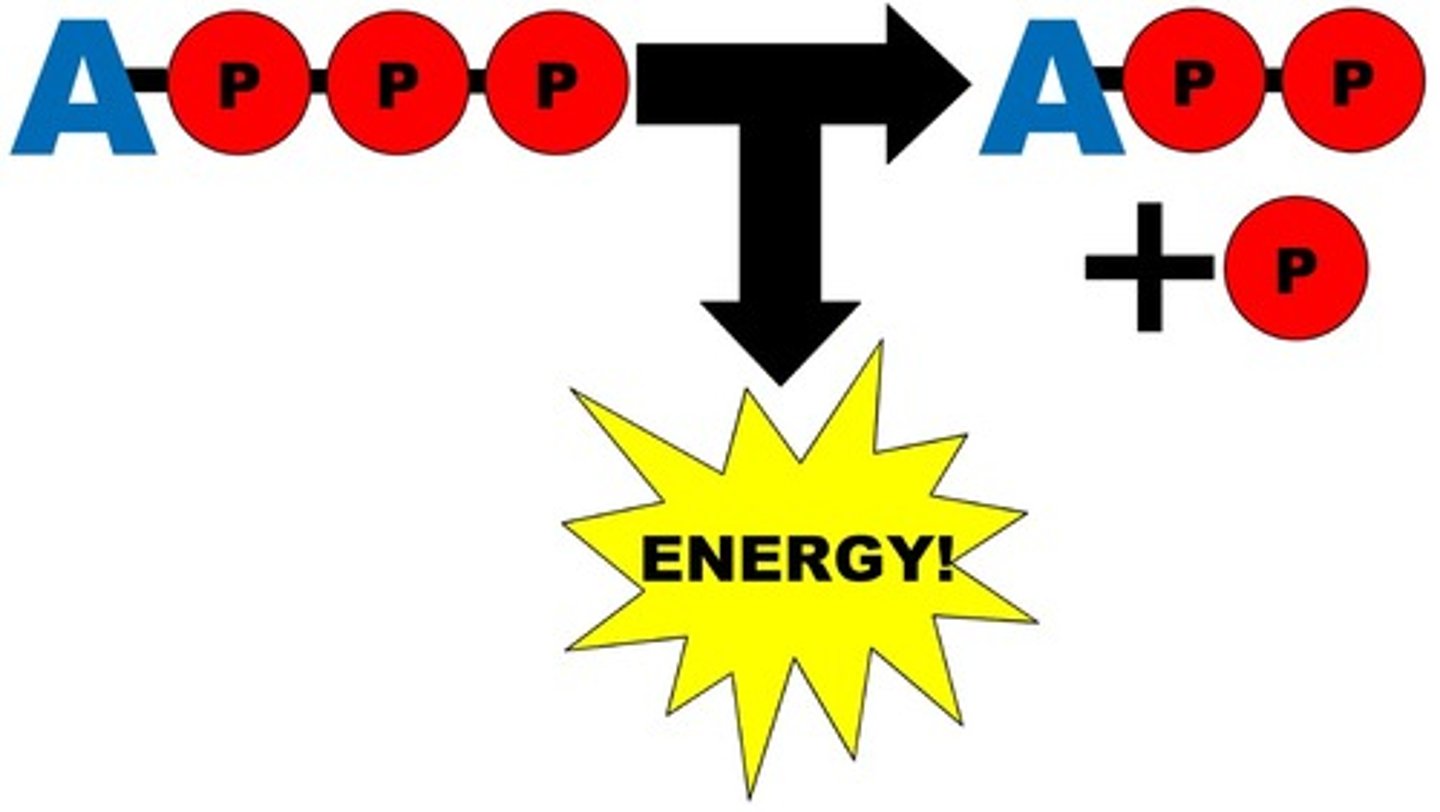
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate, main energy source that cells use for most of their work. Broken down to ADP + P