23-ddx of sudden falls + digoxin and aspirin toxicity + thiazide-like diuretics
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pg 130- 174
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
vasovagal attack is usually due to ____________ or _____________ or ____________ e.g. _________. patient usually feels ______ and gets _________ before the attack
overwarm environment…prolonged standing…visual stimuli…seeing blood.
dizzy…tunnel visions
a condition in which you faint because of an abnormal heart rhythm
Stokes-Adams syndrome
ddx of sudden falls
drop attack →
stokes adam →
hypoglycemia →
vasovagal attack →
epilepsy →
digoxin toxicity : _______, _______, _______, ________
GIT, neurological, visual, arrythmias
digoxin toxicity
GIT : ________, ________, ________
Neurological : __________, __________
Visual : ________, ________, ________
arrythmias : ________, ________, ________
nausea, vomit, anorexia
confusion, hallucination
yellow haloes, blurred vision
bradycardia, V tach, premature contractions
management of digoxin toxicity
order digoxin level
digibind (digoxin immune FAB)
correct arrythmia
monitor potassium
aspirin toxicity earliest symptom is _______________ and __________. others may include ________, ________, ________, ________, ________, ________
ringing in the ears (tinnitus)… impaired hearing
rapid breathing, vomiting, dehydration, fever, double vision, feeling faint
thiazide like diuretics work by _____________ at the ____ of the ________ part of the ___________ by blocking the ___________________.
loop diuretics such as _________ and ________ inhibits the _____________ in the _______________
inhibiting Na reabsorption… beginning… proximal…distal convoluted tubule (DCT)…thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl symporter
furosemide…bumetanide…Na-K-Cl cotransporter…thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle
the main use of bendroflumethiazide was in the management of _____________ but NICE now recommend other thiazide-like diuretics such as ___________ and ____________.
hypertension
indapamide…chlortalidone
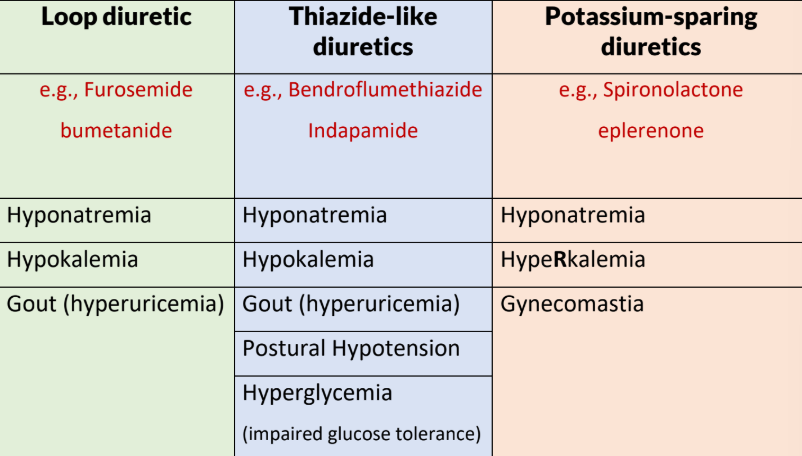
common adverse effects of thiazide like diuretics
postural hypotension
hypercalcemia and hypocalciuria
hypokalemia and hyponatremia
hyperuricemia
dehydration
impaired glucose tolerance
impotence
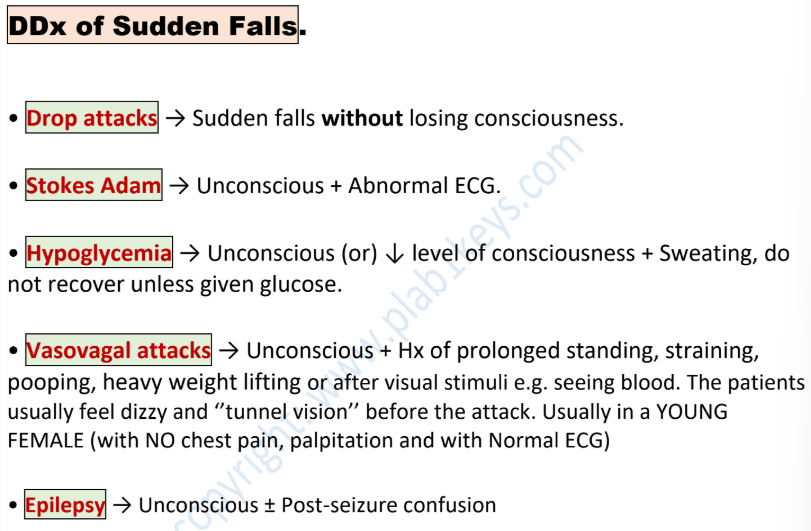
a patient with hypertension on treatment + recurrent falls when trying to get up, explain.
postural hypotension due to thiazide used for hypertension
defib = asynchronized cardioversion
in 2 conditions 😀
vFib and pulseless ventricular tachycardia
cause of stable angina could be ________ and _________.
it is relieved by _________ and ___________.
exercise and emotional stress
rest and GTN(glyceryl trinitrates)
unstable angina occurs mostly at ________, ________ , _________.
rest, unpredictable, random
ecg shows - tall tented waves → hyperkalemia
(likely cause : use of ACEi)
causes of hyperkalemia : ACEi, ARB, spironolactone, NSAIDS
treatment : protect cardiac membrane with calcium gluconate then reduce potassium by giving insulin with dextrose
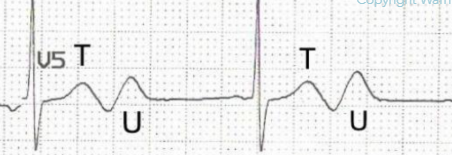
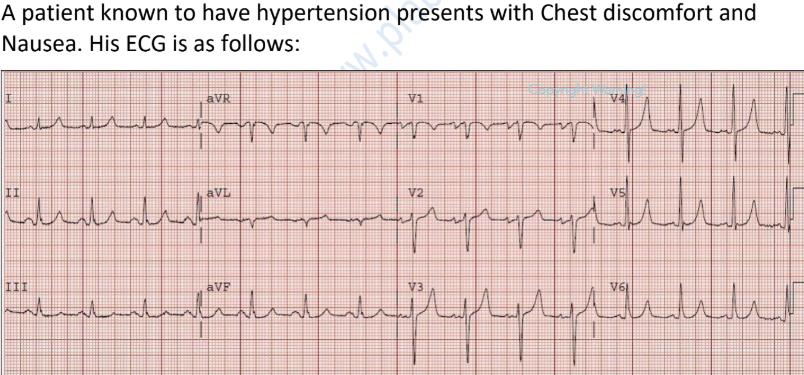
U wave in hypokalemia
(additional wave after T wave)
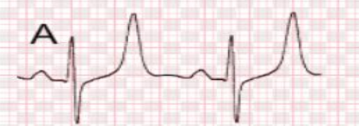
Tall tented T wave in hyperkalemia
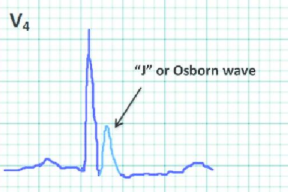
hypothermia
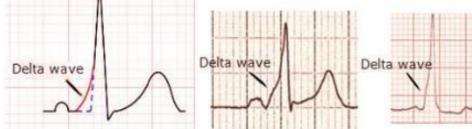
delta wave in WPW syndrome
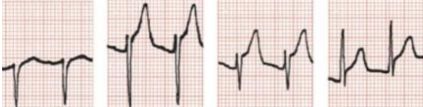
widespread saddled shape ST elevation with upward concavity + PR depression in pericarditis
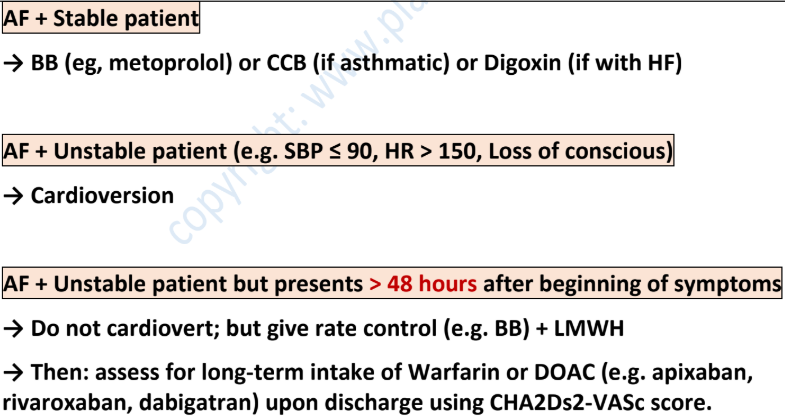
antiplatelets guide for :
ACS-MI and PCI → __________ and ____________
TIA & ischaemic stroke → __________ then ____________
ischemic stroke + AF → __________ then start ____________
peripheral arterial disease → _________
aspirin (lifelong) + clopidogrel/ticagrelor 12months
aspirin 300mg (2w) + clopidogrel 75mg (lifelong)
aspirin 300mg (2w) + DOAC/warfarin
clopidogrel (lifelong)
when is the best time to take statins? why?
night, it is when the majority of the cholesterol synthesis takes place.
statin primary and secondary prevention
primary → atorvastatin 20mg OD
10 year cvs risk ≥ 10%
type 1 DM
CKD if eGFR<60
secondary → atorvastatin 80mg OD
IHD (MI)
cerebrovascular disease (stroke)
peripheral arterial disease


important side effects of diuretics (loop, thiazide like, K sparing)
Na, K, Uric


secondary prevention (long-term) of ischemic stroke/TIA
control bp. if with DM, add ACEi
statins
anti platelets
with AF → warfarin or DOAC
without AF → clopidogrel 75mg OD
ABCD2 score is used to identify the _____________ in the following ____ days in patients who have had a suspected ______ .
risk of future stoke..7…TIA
hypertensive patient on treatment + ankle swelling/edema.
the likely cause is
amlodipine (CCB)
CCB cause ankle swelling as it causes vasodilation
2 important side effects of CCB (verapamil, diltiazem, amlodipine, nifedipine)
ankle swelling/edema
gingival hyperplasia
2 most important test to be done before initiating lithium are
-thyroid fn test
-kidney fn test

atropine
symptomatic bradycardia (norm pulse 60-100 bpm)
excessive alcohol → _________ (__________ on xray) → ___________
acute alcohol intake can lead to _____ or ____ (___________ syndrome)
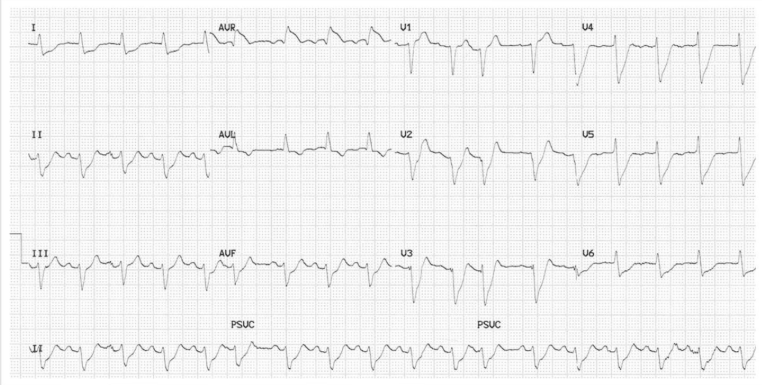
alcoholic cardiomyopathy…cardiac enlargement…aFib
aFib…flutter…holiday heart syndrome

Triple Vessel Disease is
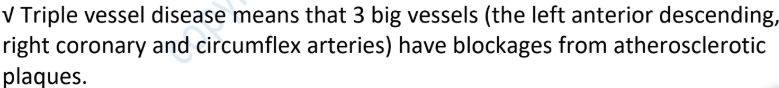
blood transfusion is indicated if
hb <80g/L + anemia symptoms or
hb <70 w or w/o symptoms
complications of MS
__________ → __________→ _________ → __________ →
left atrial enlargement
aFib
venous thromboembolism
cerebral infarction