BIOL 213 Chapters 5, 6, 7, 4
1/184
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
185 Terms
Federick Grifffith
Who showed that heat-killed infectious bacteria can transform harmless live bacteria into pathogens in the 1920s. The S strain (smooth) killed the mice, while the R strain lived on. The heat-killed S strain and injected it, mouse then lives. When mouse is injected with living R strain & heat-killed S strain, the mouse died. Hypothesized that mouse would live. However, transformation occurred and the mice died from the S strain infection.
In vivo
in a living model or aka:
S strain
What strain killed the mice?
DNA
Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty demonstrated that ____ was the transforming principle and the genetic material. (Mid 1940s)
Avery, MacLeod, McCarty; DNase; DNA
Who used enzymes to break down certain classes of molecules from S strain cells? Which enzyme resulted in an R strain cell or live mouse? When enzymes weren’t used to break down the molecules, which molecule, when put into the solution of R strain cells, caused a S strain cell or killed the mouse?
Chargaff’s Rule
What rule is A = T, G = C?
Hershey and Chase
Who took DNA labeled with 32p and Protein labeled with 35s into a solution of bacteria and then sheared off the viral heads from the bacteria, and then centrifuged, resulting in 32p infected bacteria but not 35s? The more dense was found in the bottom and was radioactive phosphor was in the bacteria and the radioactive sulfur was above in the liquid.
Antibiotic resistance
What can viruses help reverse with by attaching to a bacteria cell’s pump?
Watson and Crick; Rosalind Franklin
Used molecular models based on x-ray diffraction data from _______ _______ and Maurice Wilkins to propose a double helix structure for DNA where the bases were A-T and G-C pairs.
right-handed turn; Z
Most of the time DNA is _____. A-form is more condensed while B-form is less condensed and is most common. A left-handed turn is considered a __-form.
Hydrogen bonds
What exists between bases that contributes to helical stability?
the base pairs have identical widths
Why is the helix diameter uniform in widths?
Major and Minor grooves
What are important sites for DNA/protein interactions?
complementary
nucleotides on one chain are _______ to nucleotides on the other strand.
G and C; 3 hydrogen bonds
Which base pairing is harder to break? Why?
Phosphodiester bond
how are nucleotide subunits within a DNA strand are held together?
T, C
(Name the nucleoside closest to it) Which end is the 5’ and which end is the 3’?
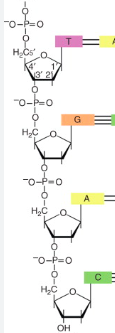
3’; 5’
The OH end is the ___. The Phosphate end is the ___.
32P; in the cells at the bottom
What was used to label the DNA in Hershey and Chase’s experiment? Where was this found in the container?
3’
What end of a DNA strand do new nucleotides add to?
2
How many hydrogen bonds do an A & T pairing make?
nucleotides
What are subunits of nucleic acids?
nucleotide
A _______ consist of a nitrogen-containing base, a five-carbon sugar, and one or more phosphate groups.
Double Helix
Implications of DNA being a ____ _____. linear arrangement of nucleotides could store genetic information and complementarity provided mechanisms for replication of it.
protein
The only genes that get transcribed into mRNA make _____.
A, B, D; noncoding RNA
Which of these genes produce mRNA? What would RNA C be called?
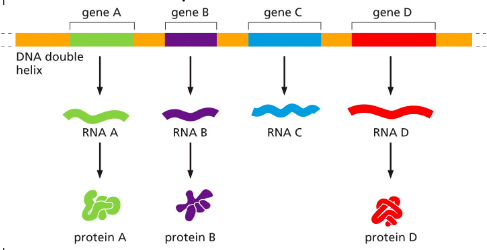
noncoding RNA
What is RNA that doesn’t produce a protein called?
3.4 billion base pairs
How big is the human genome?
polyploid
Carry multiple copies of the same genome
diploid
carry 2 copies of the same genome. (chromosomes in pairs)
haploid
carry 1 copy of the same genome
false
True or False: the more chromosomes, the bigger the genome.
Eukaryotes
________ have chromosomes that are very long, single DNA molecules associated with proteins that fold and pack it.
chromatin
The complex of DNA and associated proteins is called….
chromatid
A _____ is the structure of the part of the chromosome during cell division.
homologous
______ chromosomes in a pair that are very similar but not necessarily identical.
FISH
provides researchers with a way to visualize and map the genetic material in an individual’s cells, including specific genes or portions of genes.
GISH
a technique that allows distinguishing the genomes in a cell.
end of them
Where are the telemores located on the chromosome?
middle
Where is the centromere located?
duplicate
During interphase, the chromosomes ______.
During M-phase the chromosomes____.
metaphase
Which has more condensed chromosomes, metaphase or interphase?
A, E, D, B, C
Order these from least dense to most dense:
A) DNA strand
B) looped domains
C) chromatid
D) 30nm fiber
E) Nucleosome
nucleosomes
What are the basic units of eukaryotic chromatin structure?
cohesin
what makes the physical loops, all interphase?
condensin
What makes loops on loops before cell division?
false
True or false: Bacteria have nucleosomes
clamp protein interactions
What stops further looping?
euchromatin
loosely packed transcriptionally active DNA
heterochromatin
densely packed inactive DNA (shows up dark under a microscope)
replication origin
nucleotide sequence where DNA replication begins.
heterochromatin
chemical modification is required for what to be produced?
remodeling complex B
causes the dissociation (removal) of DNA-binding protein resulting in restoration of standard nucleosomes
remodeling complex A
allows for the addition of DNA-binding proteins
euchromatin
chromatin remodeling complexes alter chromatin structure in __________.
H1
which histone provides additional packaging of nucleosomes in the chromatin fiber?
SMC Ring complex
uses the energy of ATP hydrolysis to motor along the DNA, pushing out a loop of DNA in its wake
during mitosis
When are chromosomes in their most compact form?
positively, negatively
Histone proteins have a high proportion of __________ charged amino acids, which bind tightly to the ________ charged DNA backbone.
methylation
powerful gene silencer/repressor (can form heterochromatin) causes tightening of packing.
acetylation
gene promoter causing loosening of the packing trumps all when it is found at lysine 9
long, short
trimethyl groups are usually ____ term while single methyls are usually ______ term.
phosphorylation
neutralizes the positive charge on histones which loosens the packing (other than acetylation)
lysine 9
which is the most important (and commonly) protein on a histone tail to be modified to alter gene expression?
trimethyl
most common form of modification for long term heterochromatin
phosphorylation and acetylation
What is found together on a commonly used gene?
Histone 3
which histone can be modified?
methylation
DNA can also be modified by _________.
x inactivation
one or other of the two X chromosomes in each nucleus becomes highly condensed into heterochromatin early in embryonic development. Thereafter, the condensed and inactive state of that X chromosome is inherited in all of the many descendants of those cells. responsible for calico (tortoise shell) cats.
bar body
the x chromosome that is inactive and condensed
The co-color genes for cats are on the X chromosome. The cell that is chosen will have a designated x activation pattern which is why the clone has one color vs two. The bar body is maintained as heterochromatin structure.
Why are calico cats an unusual choice for a cloning experiment? How does chromatin alteration fit in?
somatic
Cloning involves an _______ cell.
imprinting
a gene is turned off in the father and also turned off in the offspring
DNA replication
Process of producing two identical replicas from one original DNA molecule
false
True or false: only one strand of the double stranded DNA can be used as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand.
semi-conservative
Original parent strand is separated, each new strand is half original, half synthesized
dispersive
initially chopped the DNA which led to each strand containing new and original strands.
conservative
the parent strands stay together while the newly synthesized DNA is together.
Meselson-Stahl
Whose experiment is this describing?
Parent production using 15N and 14N with 15N created a band at the bottom of the tube due to its high density and 14N created a band at the top due to its low density. After this, they put the solution of the parent 15N in a solution of 14N to create strands that were half N14 and half N15 an intermediate band was created from this. After this, they did the replication once more which led to a strands that were completely N14 or half N14 and half N15.
N15
Which is heavier N15 or N14?
DNA is semi-conservative
What was the conclusion of the Meselson-Stahl experiment?
100% N14
What would be shown at the end of the Meselson-Stahl experiment if DNA was dispersive?
Initiator proteins, replication origins
What protein begins the DNA synthesis and what are the DNA sequences they are bind to called?
initiator proteins
the ______ _____ pry the two DNA strands apart, (denature) breaking the hydrogen bonds between the bases. they can readily unzip short regions of the double helix at normal temperatures. They keep DNA strands separated.
one; 1 for every 3000bp
How many origins of replications do bacterias have? How about humans?
replication forks
DNA molecules in the process of being replicated contain Y-shaped junctions. What are these called?
A-T; 2 hydrogen bonds
Replication origins are more likely to be A-T or G-C rich? Why?
bidirectional
DNA replication in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes are considered _______ because the replication forks have two replication machines moving in opposite directions.
5, 3
DNA synthesis always proceeds from the ___’ to the ____’
DNA polymerase
what enzyme catalyzes the addition of nucleotides by forming phosphodiester bonds to the 3ʹ end of a growing DNA strand, using one of the original, parent DNA strands as a template?
pyrophosphate; 2 phosphates; irreversible
What molecule is released by the polymerization reaction? What does this molecule get hydrolyzed to? Why is this significant? (hint it makes this reaction _______>
helicase
the “unzipper”. Breaks the hydrogen bonds at each replication fork.
Leading strand
the new 5’ to 3’ strand formed
Okazaki fragments
the fragments of 3’ to 5’ strand
DNA polymerase
proof reads strand from 3’ to 5’ and makes new strand 5’ to 3’. Can only add nucleotides to the 3’ end.
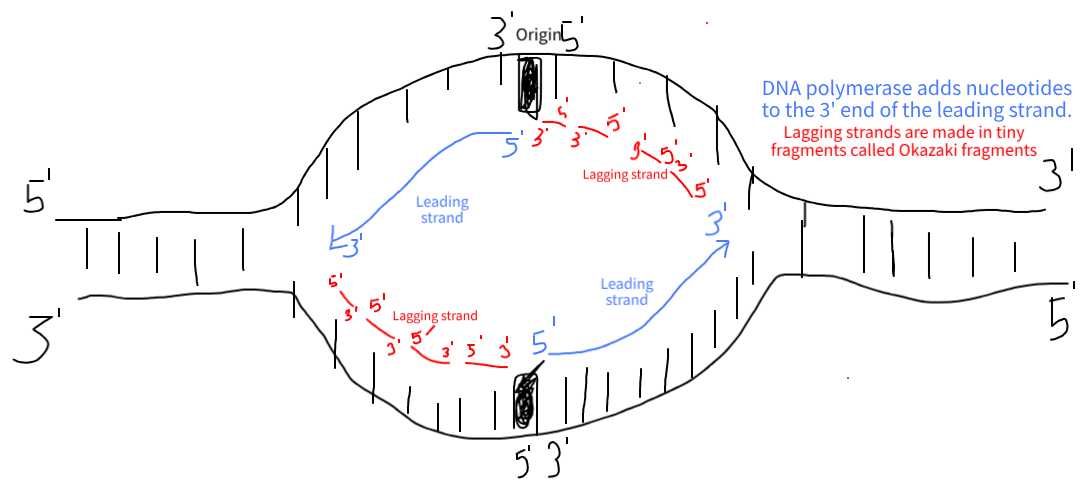
Draw the leading and lagging strands in a replication fork. Make sure the leading strand is showing where nucleotides are being added to.
RNA; primers; primase
short length of ____ serve as _____ for DNA synthesis used by DNA polymerize as a template. They are synthesized by the enzyme _______.
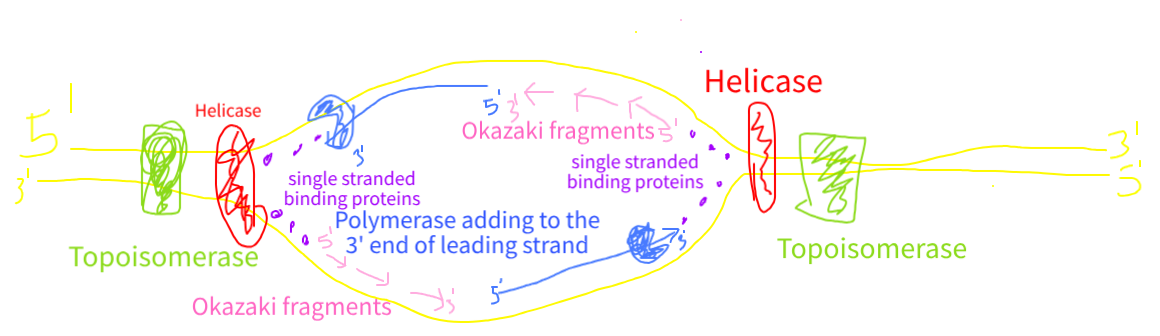
Draw out the DNA replication process with the enzymes and label everything of importance
topoisomerase
This enzyme creates a single stranded break in the double helix structure to relax the coiling of the Double stranded DNA