Final Exam - Endocrine Disorders
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
endocrine system - closely linked with which 2 systems?
neurologic
immune
hypothalamus and pituitary gland relationship
hypothalamus monitors ALL hormones in the body, and if it detects a deficiency or excess of a specific hormone, it stimulates the pituitary to stimulate the specific gland to either stop production or increase production of the hormone
hypo/hyperthyroid - how is the TSH level affected?
HYPOthyroid - TSH is going to be INCREASED (as it is going to be continuously released to stimulate T3/T4 release, but failing)
HYPERthyroid - TSH is going to be DECREASED (already too much T3/T4, so releasing more TSH would worsen this)
thyroid - functions
cell development / growth
controls cellular metabolic activity
NECESSARY for normal reproduction
hypothyroidism - what is the autoimmune disease called?
Hashimoto’s disease
hypothyroidism - what is it? what is it characterized by?
a disease where a patient is unable to produce T3 or T4
characterized by “everything SLOWING DOWN, and is LOW”
hypothyroidism - manifestations
extreme fatigue
hair loss
brittle nails
dry skin
constipation
menstrual disturbances
low heart rate and BP
weight GAIN
cold intolerance
hypothyroidism - management
synthetic levothyroxine (T4) replacement therapy
T4 converts to T3 once in the body
need to follow up with blood tests to ensure proper dose (TSH levels)
hypothyroidism - EMERGENCY? what happens?
myxedema coma (RARE!!!!!!)
lethargy progresses to stupor, causes respiratory depression, and can be life threatening
hypothyroidism - how can myxedema coma be precipitated?
infection
UNTREATED hypothyroid
hyperthyroidism - another name?
Grave’s disease
hyperthyroidism - what is it? what is it characterized by?
TOO MUCH T3/T4, and enlarged thyroid becomes a goiter
“everything SPEEDS UP/RUNS you into the grave”
hyperthyroidism - manifestations
nervousness/tremors
high HR/systolic BP
HEAT intolerance
skin flushed, warm, soft, and moist
exophthalmos (eyes bulging out of head)
increased appetite, but weight LOSS
cardiac dysrhythmias (A-FIB!!!!)
hyperthyroidism - management (meds, surgery)
meds
methimazole (kills the thyroid!!)
will be put on levothyroxine for the rest of your life after this; same with thyroidectomy
dexamethasone (decreases inflammation)
beta-blockers
radioactive iodine therapy
surgery
thyroidectomy
hyperthyroidism - EMERGENCY? what precipitates it?
THYROID STORM (metabolic rate rises RAPIDLY!!)
precipitated by uncontrolled hyperthyroid and infection
hyperthyroidism - thyroid storm (4 main s/s)
HYPERTHERMIA (not a fever response)
HTN
delirium
a-fib
what is the treatment of choice for thyroid cancer?
THYROIDECTOMY!!
what procedures are done concurrently with the thyroidectomy?
modified/radical neck dissection
radioactive iodine therapy to minimize metastasis
thyroidectomy - PREOPERATIVE GOALS
reduction of stress and anxiety to avoid precipitation of a thyroid storm
thyroidectomy - preoperative education
dietary guidance to meet patient metabolic needs
avoidance of caffeinated beverages and other stimulants
explanation of tests and procedures
head and neck support used AFTER surgery
patient is admitted to the floor after the procedure to ensure that airway is secured!!
thyroidectomy - post-op care
monitor respirations (potential airway impairment)
monitor for potential bleeding/hematoma formation
assess pain and provide pain relief measures
semi-fowler’s position; support head and neck
assess voice, discourage talking
potential hypocalcemia related to injury or removal of parathyroid glands
parathyroid gland - location? function?
four glands located on the posterior thyroid gland
parathyroid hormone (PTH) regulates calcium and phosphorus balance
INCREASED PTH elevates blood calcium by INCREASING calcium absorption from kidney, intestine, and bone; simultaneously DECREASES phosphorus reabsorption
hyperparathyroidism - manifestations
HYPERCALCEMIA
bone decalcification
renal calculi
fatigue
muscle WEAKNESS
N/V
constipation
HTN
cardiac dysrhythmias
psychological manifestations
hyperparathyroidism - management
parathyroidectomy
hydration therapy
encouraging mobility
encourage fluids
restrict calcium intake
calcium plays a major role in what? what does this mean in HYPERPARATHYROIDISM?
calcium plays a big role in CLOTTING
in hyperparathyroidism, LOTS of clotting can occur, increasing the mortality rate!!
hyperparathyroidism - what is it exclusively caused by?
tumor/cancer of parathyroid hormone
what is secondary hypothyroidism?
hypothyroidism that occurs after the patient had hyperthyroid, but either had it killed or taken out
hypoparathyroidism - causes?
thyroidectomy/parathyroidectomy
radical neck dissection
hypoparathyroidism - what happens to calcium and phosphorus levels?
hypocalcemia
hyperphosphatemia
hypoparathyroidism - manifestations
tetany (muscle spasms/cramps)
numbness
tingling in extremities
stiffness of hands and feet
bronchospasm
laryngeal spasm
carpopedal spasm
anxiety/irritability/depression
delirium
EKG changes
Positive Chvostek’s and Trousseau’s sign
hypoparathyroidism - management
calcium gluconate IV / calcium replacement
PTH administration
HIGH calcium/LOW phosphorous diet
long-term calcium supplementation
adrenals (medulla vs. cortex) - what’s the difference?
medulla - functions as part of autonomic nervous system (releases epi/norepi)
cortex - releases glucocorticoids (cortisol), mineralocorticoids (ALDOSTERONE!!), and androgens (male sex hormone)
what hormone causes the adrenal glands to release cortisol?
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) released by the pituitary to stimulate the adrenal glands
the human body naturally secretes cortisol, which is equal to how much prednisone each day?
5mg of prednisone / day
adrenal crisis (what is it?)
adrenal suppression caused by CHRONIC STEROID USE that is abruptly stopped (ACTH is not being released, causing no cortisol release/damage to adrenal gland); this is ACUTE!!!
addison’s disease (what is it?)
CHRONIC adrenal insufficiency (autoimmune-related, or from tumors)
adrenal crisis/addison’s disease - signs and symptoms
muscle WEAKNESS
anorexia
GI symptoms
fatigue
dark pigmentation of skin/mucosa
HYPOtension
HYPOnatremia and HYPERkalemia
emotional instability/apathy
confusion
adrenal crisis/addison’s disease - how are they treated?
prednisone (gives the patient the cortisol that is not being released naturally)
adrenal crisis/addison’s disease - nursing considerations
note ANY ILLNESS OR STRESSORS that may precipitate problems
F/E status!!
VS and orthostatic BP!!
note s/s related to adrenocortical insufficiency (weight loss, muscle weakness, fatigue, etc)
Cushing syndrome - what is it? cause?
excessive adrenocortical activity!!
caused by excessive corticosteroid use (TITRATE THE DOSE OF PREDNISONE TO AVOID GETTING THIS!!)
Cushing syndrome - manifestations
hyperglycemia
central-type obesity with “buffalo hump”
heavy trunk and thin extremities
fragile/thin skin; ecchymosis; striae
weakness; osteoporosis (pulls calcium out of bones)
muscle wasting
HTN
“moon face”
acne
infection/slow healing
increased androgens in women →hirsutism (facial hair growth)
HYPERnatremia
HYPOkalemia
ACTH - how does it affect sodium and potassium levels?
ACTH causes renal sodium RETENTION and potassium EXCRETION
Cushing syndrome - same signs and symptoms of what?
s/s are the same as the SIDE EFFECTS of taking prednisone
Cushing syndrome - nursing considerations
activity level and ability to carry out self-care
skin assessment!!
changes in physical appearance and patient responses to these changes
mental function
emotional status (especially due to body disturbances)
primary aldosteronism - what is it?
excess production of aldosterone by the adrenal glands, resulting in low renin levels
primary aldosteronism - (2 most common causes)
an aldosterone producing adrenal tumor
bilateral adrenal hyperplasia
primary aldosteronism - manifestations
HTN (especially in young)
low K+→ALKALOSIS!!
headache
vision problems
fatigue
muscle cramps/weakness
primary aldosteronism - 2 management techniques
surgical removal of gland (permanently resolving high BP and K deficiency, and brings aldosterone levels back to normal)
aldosterone-blocking drugs (SPIRONOLACTONE!!) and lifestyle changes (if medications are stopped, high BP and low K will return!!)
primary aldosteronism - surgical removal of gland (when will BP drop?)
drops gradually after a unilateral adrenalectomy and meds are adjusted
Diabetes - diagnostics
blood glucose levels!!
fasting blood sugar (over 125)
hgb A1C (above 6.5% (6-6.4% = PREDIABETES, and will be started on metformin)
glucose tolerance test (always done when moms are pregnant)
diabetes (treatment GOALS!!)
NORMAL blood sugar levels
prevention of systemic damage
hyperglycemia damages EVERY organ system in the body!!
diabetes - hyperglycemia damages EVERY body system/organ, meaning WHAT complications can occur?
CKD/ESRD
strokes
heart attacks
PAD
neuropathies
decreased immune system / healing
diabetes - lifestyle changes
meal planning (carb control) → DIABETIC DIET!!
exercise
medication adherence
insulin types (general)
rapid acting (sliding scale; given before meals, about 15 min)
short acting (ONLY on that go in IV!!; can reduce potassium)
intermediate acting
long acting
BOTH are given 1 time a day to reduce sugars for 24 hours
insulin - EDUCATION!
uses and action of insulin
signs and symptoms of hypo/hyperglycemia
REQUIRED ACTIONS THAT MUST BE TAKEN!!
blood glucose monitoring is KEY
teach patient how to self-inject their insulin
how to use to insulin pump (usually always for type 1)
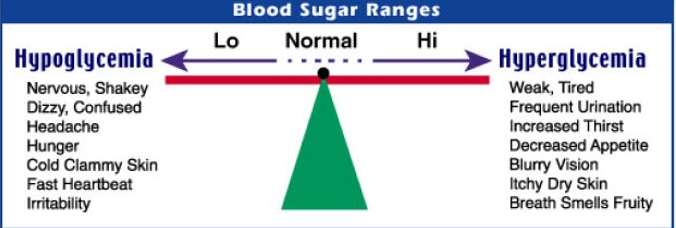
Hypoglycemia vs. Hyperglycemia (CHART)
why are oral agents for diabetes not used in TYPE 1 DM?
type 1 is AUTOIMMUNE, meaning that the pancreas is not working at ALL, meaning this medication would literally do ABSOLUTELY NOTHING!!!!!!
oral diabetic agents - major side effect? metformin?
MAJOR SIDE EFFECT: hypoglycemia
metformin: diarrhea (will eventually go away)
oral diabetic agents - nursing interventions
MONITOR BLOOD GLUCOSE for hypoglycemia and other potential side effects
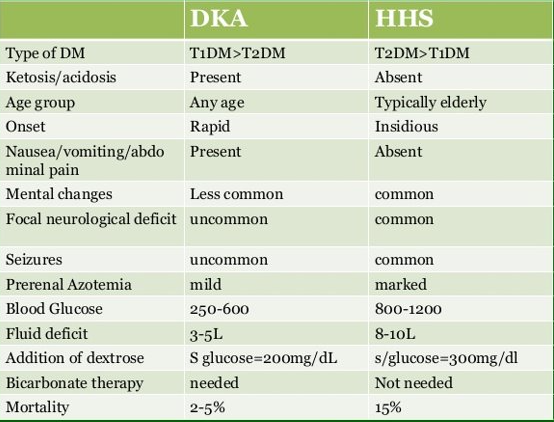
2 acute complications of DM? (which complication is associated with which DM type?)
DKA (Type 1)
HHS (Type 2 → hyperglycemia WITHOUT the acidosis)
DKA - 2 precipitating factors
patient does not know that they have diabetes
INFECTION !!
DKA - general definition
absence or inadequate amount of insulin, resulting in abnormal metabolism of carbs, proteins, and fats
DKA - 3 clinical features
hyperglycemia
dehydration
acidosis
DKA - diagnostics?
ABG (GOLD STANDARD) - shows acidosis (metabolic acidosis, with respiratory compensation (KUSSMAUL RESPIRATIONS!!!))
urinalysis (ketones in blood and urine)
basic metabolic panel (shows increase in creatinine/BUN, hematocrit, and K (SHOWS DEHYDRATION!!))
DKA - why are patients hyperkalemic? what is given to combat this?
insulin affects the amount of potassium in the blood (without it, there is nothing pushing potassium back into the cells)
that’s why patients are put on an insulin drip, pushing K back into the cells and out of the blood stream 🙂
DKA - ketoacidosis (how do you know?)
low serum bicarb
low pH
low PCO2 reflects respiratory compensation (Kussmaul respirations)
DKA - while on an insulin drip, why is the patient also on dextrose?
dextrose is given to prevent hypoglycemia while on the insulin drip
DKA - insulin vs. dextrose
insulin = more focused on helping with the acidosis
dextrose = more focused on reaching a normal blood glucose level
DKA - what other lab should you look at, indicating metabolic acidosis?
ANION GAP!! (elevated)
DKA - treatment
rehydration with IV fluid (leads to increased plasma volume and decreased K)
IV continuous infusion of regular insulin
reverses the acidosis/restores electrolyte balance (TREATING THE ANION GAP, NOT THE BLOOD GLUCOSE VALUE)
pushes K from bloodstream into the cells
DKA - when on insulin drip, how often is blood sugar checked?
EVERY HOUR!!
DKA - when getting treated, what should you monitor?
blood glucose (EVERY HOUR)
renal function (Cr/BUN) / urinary output
anion gap !!!
EKG (high K is dangerous!!)
other electrolyte levels due to dehydration
VS
lung assessments for signs of fluid overload (from IV fluids)
HHS - 2 clinical features
hyperglycemia
dehydration
REMEMBER THERE IS NO KETOACIDOSIS!!!
HHS - what does the hyperglycemia cause?
osmotic diuresis!!!
loss of water/electrolytes
HYPERnatremia
increased osmolality
HHS - manifestations
hypotension
profound dehydration
tachycardia
variable neurologic signs, caused by CEREBRAL DEHYDRATION!!
HHS - 2 precipitating factors
patient does not control their type 2 DM well
patient does not know they have type 2 DM
HHS - why do patients present sicker?
the patient’s blood sugar tends to slowly rise overtime, and the body is adjusting to this increase, and the damage is going to be continuously done until it is too late to do anything
HHS - treatment
rehydration!!
IV insulin (given to decrease blood sugar, as there is NO ACIDOSIS!!)
monitor fluid volume and electrolyte status !!!
HHS - prevention
diagnosis and management of diabetes!!
assess and promote self-care management skills
DKA vs. HHS (CHART)
hypoglycemia - blood glucose level? causes?
blood glucose LESS THAN 70
causes: too much insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents, excessive physical activity, not enough food
hypoglycemia - manifestations
sweating
tremors / nervousness
tachycardia / palpitations
hunger
inability to concentrate
headache
confusion
memory lapses
SLURRED SPEECH (can mimic stroke symptoms)
drowsiness
SEVERE hypoglycemia - manifestations
disorientation
seizures
loss of consciousness (usually at around 40 years old)
DEATH!!
hypoglycemia management (CONSCIOUS patient)
give 15 g of fast-acting, concentrated carbohydrates
3-4 glucose tablets
4-6 oz of juice or regular soda (NOT DIET)
retest blood glucose in 15 minutes (retreat if STILL below 70 or if symptoms persist more than 10-15 min/testing is not possible)
provide a snack with protein and carbs (unless patient plans to eat a MEAL within 30-60 min)
hypoglycemia - why is simply giving a patient juice/soda NOT enough for blood sugar fluctuation?
this is only going to TEMPORARILY raise their blood sugar back to a normal level, and it will not sustain it
this is why we give the patient a MEAL with complex carbs to sustain a normal blood sugar
hypoglycemia management (UNCONSCIOUS PATIENT)
subq or IM glucagon (1 mg)!!!
serves sort of like an “epipen” in DM type 1
25-50 mL of 50% dextrose solution IV