Chem 120 Exam 5
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:58 PM on 4/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
1
New cards
glycerides (type of lipid)
glycerol-containing lipids
2
New cards
nonglyceride lipids (type of lipid)
sphingolipids, steroids, and waxes
3
New cards
complex lipids (type of lipid)
lipoproteins
4
New cards
the 7 lipid functions
1) energy source
2) energy storage
3) cell membrane structural components
4) hormones
5) vitamins and vitamin absorption
6) protection
7) insulation
2) energy storage
3) cell membrane structural components
4) hormones
5) vitamins and vitamin absorption
6) protection
7) insulation
5
New cards
energy currency for lipid function
ATP (Adenosine triphosphate)
6
New cards
Energy storage of lipids
in the form of triglycerides and stored in adipocyte cell
7
New cards
lipid function: energy source
good energy source
(more than 2x the energy is produced than the same amount of carbohydrates)
(more than 2x the energy is produced than the same amount of carbohydrates)
8
New cards
lipid function: cell membrane structural components
phosphoglycerides, sphingolipids, and steroids are basic structural components of all cell membranes.
9
New cards
lipid function: hormones
critical chemical messengers that allow body tissue to communicate with each other
10
New cards
lipid function: vitamins and vitamin absorption
lipid-soluble vitamine A,D,E, and K
Vitamin carrier transport to small intestines
Vitamin carrier transport to small intestines
11
New cards
lipid function: protection
fat serves as a shock absorber for vital organs
4% of total body fat is reserved for this critical function
4% of total body fat is reserved for this critical function
12
New cards
lipid function insulation
fat stored under skin for cold temperatures
13
New cards
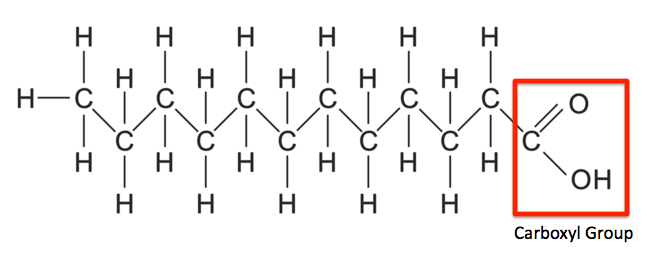
saturated fatty acids
has no double bonds
higher MP and BP because of packing
solid at room temperature
higher MP and BP because of packing
solid at room temperature
14
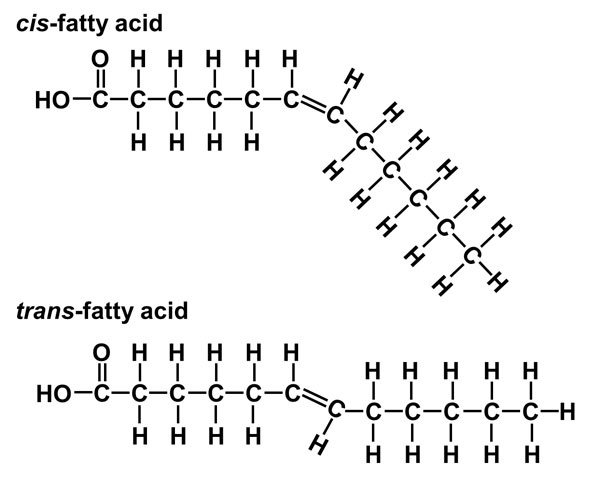
New cards
unsaturated fatty acids
do have a double bond
the double bond is normally in a cis configuration
double bonds lower the melting temperature
(the cis configuration doesn’t allow fatty acids to pack as close together)
liquid at room temperature
the double bond is normally in a cis configuration
double bonds lower the melting temperature
(the cis configuration doesn’t allow fatty acids to pack as close together)
liquid at room temperature
15
New cards
eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docsahexenoic acid (DHA) where are they found?
Omega-3 Fatty acid
found in salmon, albacore tuna, sardines, lake trout and mackerel
found in salmon, albacore tuna, sardines, lake trout and mackerel
16
New cards
a-linolenic acid where is this found?
Omega-3 Fatty Acid
* found in flax seed, soybean, canola
* is essential fatty acid- must be acquired through diet
* found in flax seed, soybean, canola
* is essential fatty acid- must be acquired through diet
17
New cards
Omega-3 structure
draw it out
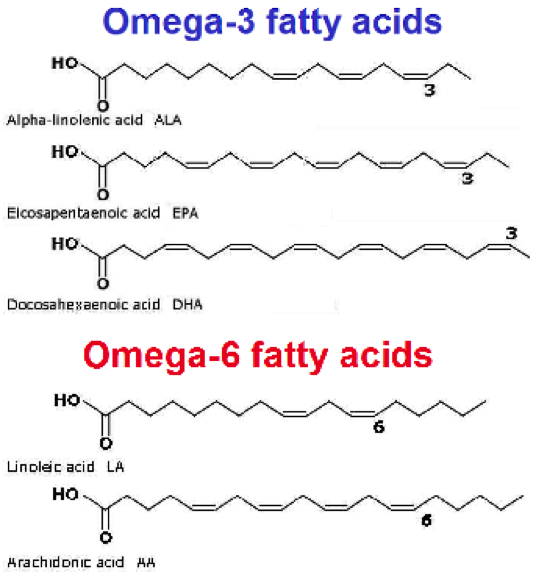
18
New cards
prostaglandins (describe and draw) (Eicosanoids)
Eicosanoids: Omega-3 Fatty acid
* act like hormones in controlling the body’s processes
* made in most tissues
* exert their effects on cells that produce them and cells in the immediate vicinity
* act like hormones in controlling the body’s processes
* made in most tissues
* exert their effects on cells that produce them and cells in the immediate vicinity
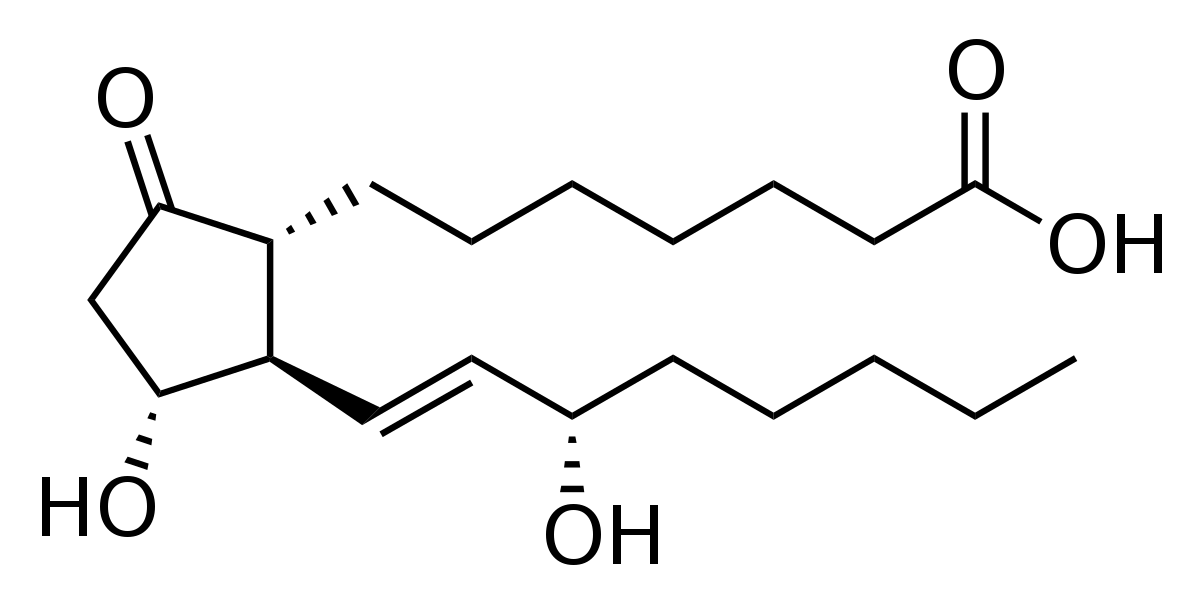
19
New cards
6 Biological Processes Regulated by Eicosanoids (and structure)
blood clotting
inflammatory response
reproductive system
gastrointestinal tract
kidneys
respiratory tract
inflammatory response
reproductive system
gastrointestinal tract
kidneys
respiratory tract
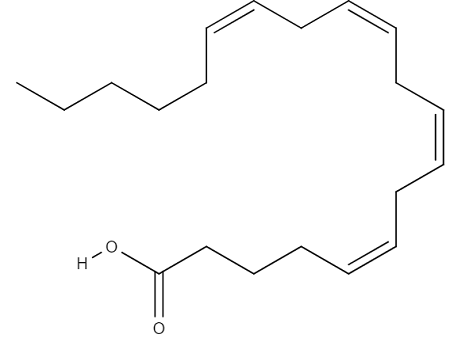
20
New cards
thromboxane
lipid
draw it out roughly
draw it out roughly
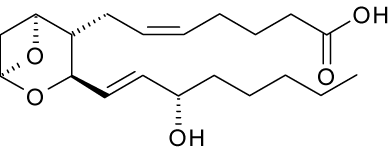
21
New cards
Leukotriene
lipid
draw it out roughly
draw it out roughly
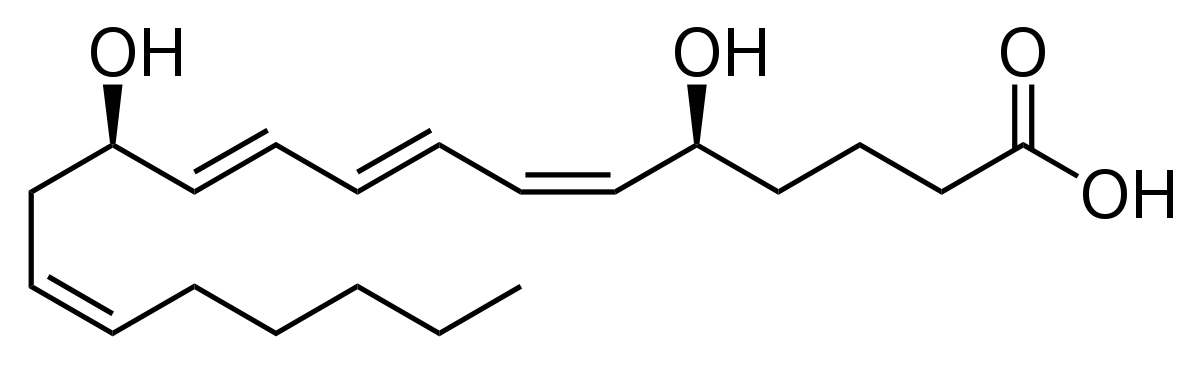
22
New cards
aspirin
lipid
inhibits prostaglandin (stimulates inflammation response) synthesis and helps alleviate the pain
inhibits prostaglandin (stimulates inflammation response) synthesis and helps alleviate the pain
23
New cards
glycerides and what you can make out of it.
lipid esters
esterification may occur at one, two, or all three alcohol positions producing
* monoglyceride
* diglycerides
* triglyceride
esterification may occur at one, two, or all three alcohol positions producing
* monoglyceride
* diglycerides
* triglyceride
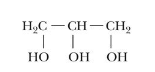
24
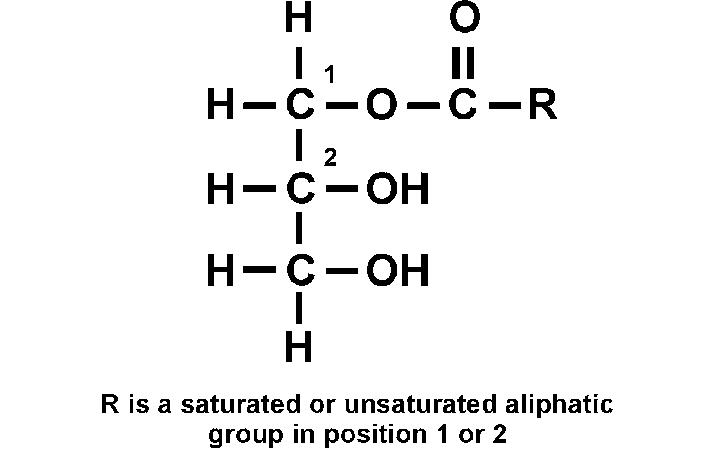
New cards
monoglyceride
lipid ester
has a fatty acid chain at one alcohol group of the glycerol
has a fatty acid chain at one alcohol group of the glycerol
25
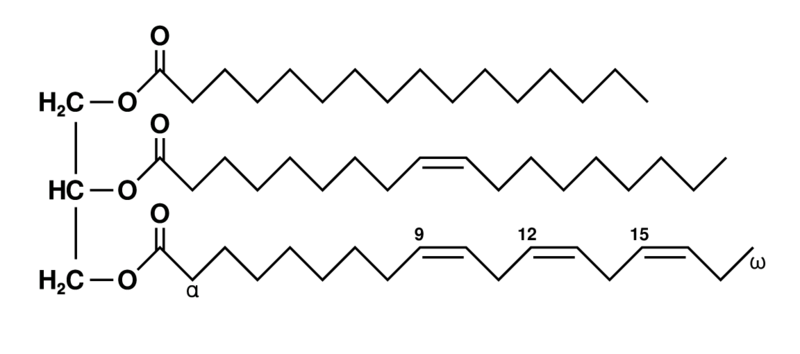
New cards
triglycerides
fatty acid chain at each alcohol group of the glycerol
26
New cards
Fats
come from animals, unless from fish, and are solid (higher MP) at room temp
have saturated fatty acid tails- pack closely together
have saturated fatty acid tails- pack closely together
27
New cards
oils
come from plants, and are liquid (lower MP) at room temp
contain unsaturated fatty acid tails that are kinked- can’t pack as closely together
contain unsaturated fatty acid tails that are kinked- can’t pack as closely together
28
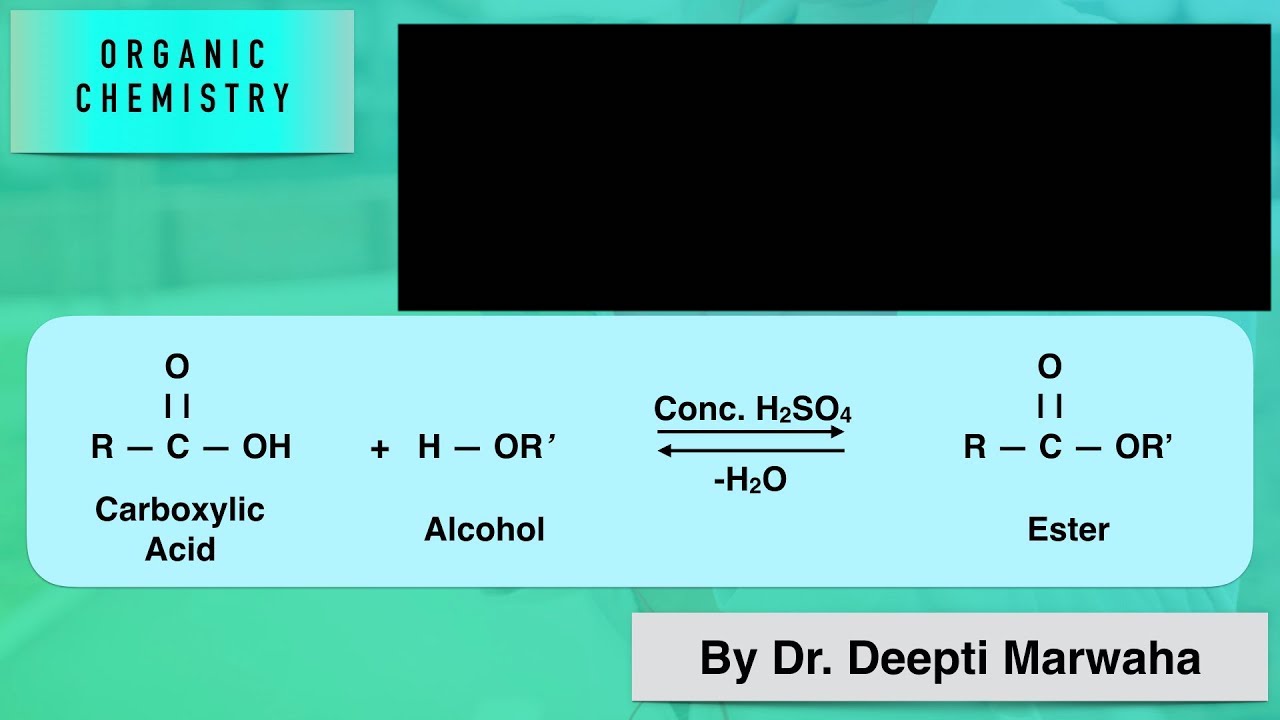
New cards
esterification
reaction between the carboxyl of the fatty acid and the hydroxyl of an alcohol
29
New cards
hydogenation
addition reaction of H2 converts unsaturated to saturated fat, food industry
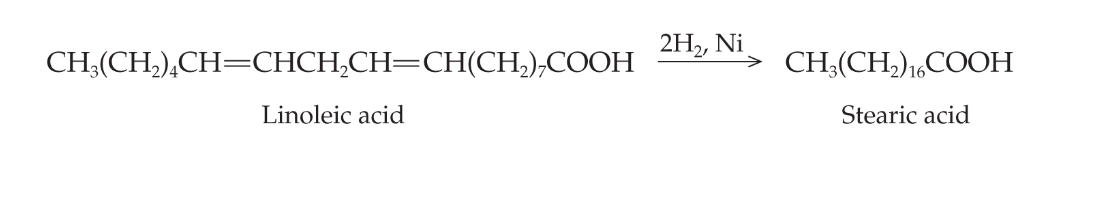
30
New cards
acid hydrolysis
produces the fatty acids and glycerol, a reverse of esterification
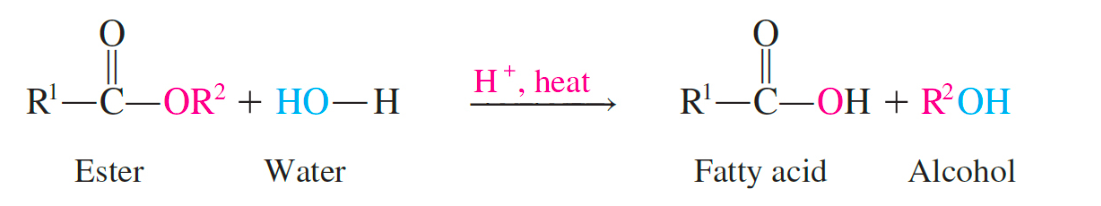
31
New cards
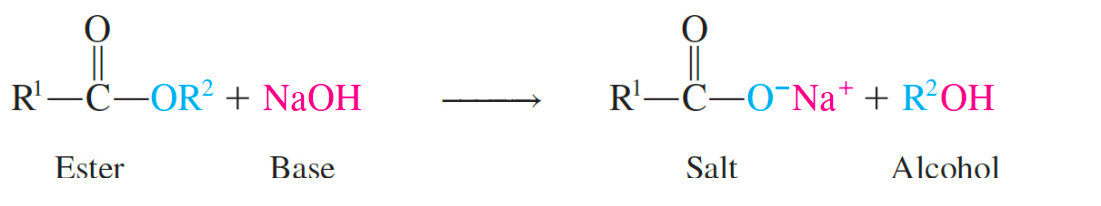
saponification
produces the fatty acid salts and glycerol; makes soap
32
New cards
what is phospholipid
any lipid containing phosphorus
33
New cards
what do phospholipids contain
* glycerol
* fatty acid
* phosphoric acid with an amino alcohol
* fatty acid
* phosphoric acid with an amino alcohol
34
New cards
what is amphipathic
are phospholipids amphipathic?
are phospholipids amphipathic?
have hydrophobic and hydrophilic domains
yes they are…
* head is hydrophilic, tail is hydrophobic
yes they are…
* head is hydrophilic, tail is hydrophobic
35
New cards
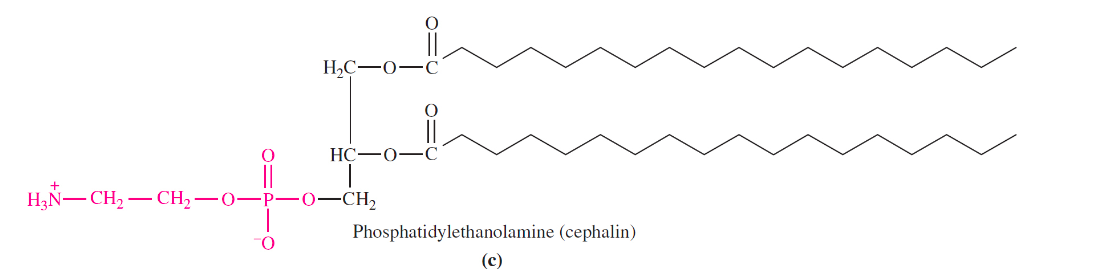
structure of phospholipids
replace an end fatty acid of a triglyceride with a phosphoric acid linked to an amino alcohol
36
New cards
phosphoglycerides in cells
structural component of cell membranes
suspended in water, they spontaneously rearrange into ordered structures
* hydrophobic group to center
* hydrophilic groups to water
* basis of membrane structure
suspended in water, they spontaneously rearrange into ordered structures
* hydrophobic group to center
* hydrophilic groups to water
* basis of membrane structure
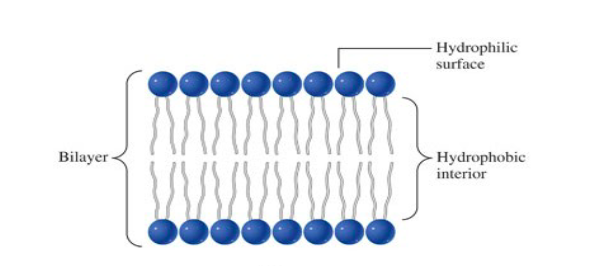
37
New cards
sphingosine (sphingolipids) and it’s categories
* nitrogen-containing
* amphipathic, like phospholipids
* polar head group
* two nonpolar fatty acid tails (1 being sphingosine)
* structural component of cellular membranes
* two major categories
* sphingomyelins
* glycosphingolipids
* amphipathic, like phospholipids
* polar head group
* two nonpolar fatty acid tails (1 being sphingosine)
* structural component of cellular membranes
* two major categories
* sphingomyelins
* glycosphingolipids
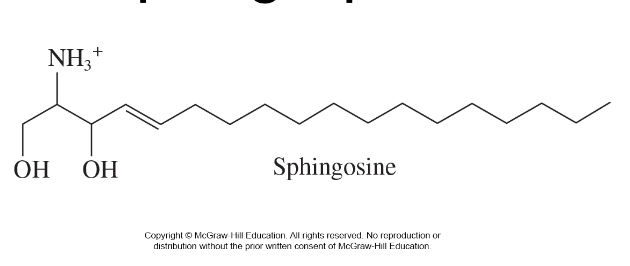
38
New cards
sphingomyelins
phospholipids
* structural lipid of nerve cell membranes
* myelin sheath feature
* structural lipid of nerve cell membranes
* myelin sheath feature
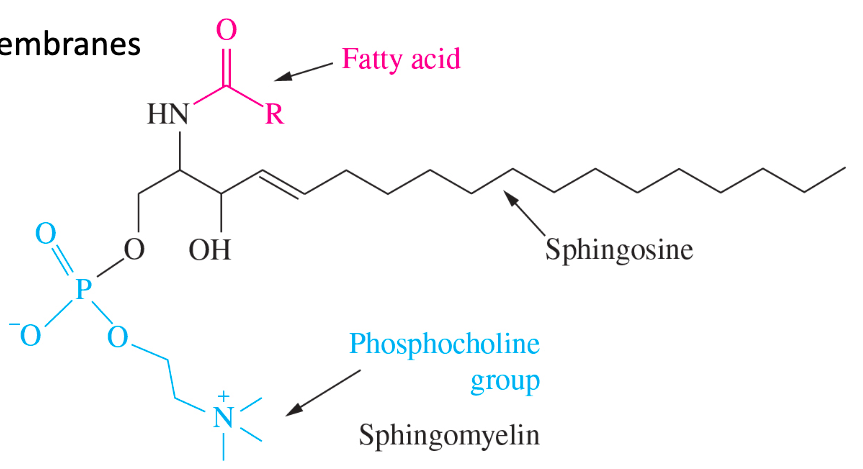
39
New cards
glycosphingolipids
phospholipid
* built on a ceramide
* cerebrosides have a single monosaccharide head group
* built on a ceramide
* cerebrosides have a single monosaccharide head group
40
New cards
2 Examples of glycosphingolipids and structures
glucocerebroside
galactocerebroside
glucocerebroside
galactocerebroside
glucocerebroside- in membranes of macrophages
galactocerebroside- in membranes of brain cells
galactocerebroside- in membranes of brain cells
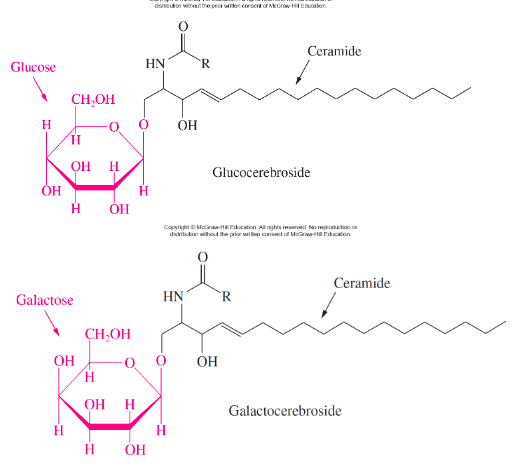
41
New cards
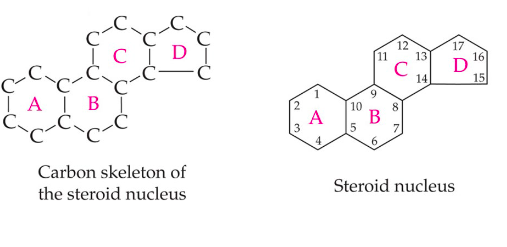
steroid
are synthesized from the five-carbon isoprene unit
part of a diverse collection of lipids called isoprenoids
* terpenes
contain the steroid carbon skeleton
* a collection of 4 fused carbon rings
part of a diverse collection of lipids called isoprenoids
* terpenes
contain the steroid carbon skeleton
* a collection of 4 fused carbon rings
42
New cards
LDL
“bad cholesterol”
carry cholesterol from liver to peripheral tissue
helps regulate cholesterol levels in those tissues
frequently 40% of the plasma cholesterol
carry cholesterol from liver to peripheral tissue
helps regulate cholesterol levels in those tissues
frequently 40% of the plasma cholesterol
43
New cards
HDL
“Good cholesterol”
picks up cholesterol for removal for recycling
made in liver
picks up cholesterol for removal for recycling
made in liver
44
New cards
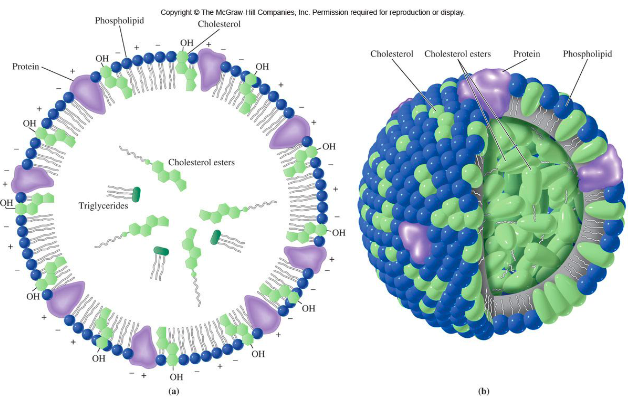
lipoprotein structure
contain:
neutral lipid core (cholesterol ester or triacylglycerol)
surrounded by a layer of
* phospholipid
* cholesterol
* protein
structure of a soap micelle and a lipoprotein are very similar
neutral lipid core (cholesterol ester or triacylglycerol)
surrounded by a layer of
* phospholipid
* cholesterol
* protein
structure of a soap micelle and a lipoprotein are very similar
45
New cards
chylomieron
transport triglycerides from intestines to other tissue
46
New cards
VLDL
bind triglycerides synthesized in liver and carry to adipose tissue and other tissue for storage
47
New cards
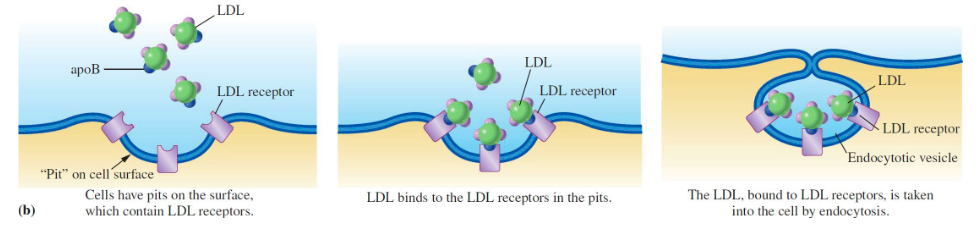
Familial hypercholesterolemia
LDL receptor was discovered during an investigation of this genetic disease
* when a cell needs cholesterol, it synthesizes the receptor, which migrates to a coated region of the membrane
* the “captured” cholesterol is absorbed by endocytosis
* failure to make the receptor or a defective receptor is the most common problem encountered for familial hypercholesterolemia.
* when a cell needs cholesterol, it synthesizes the receptor, which migrates to a coated region of the membrane
* the “captured” cholesterol is absorbed by endocytosis
* failure to make the receptor or a defective receptor is the most common problem encountered for familial hypercholesterolemia.
48
New cards
receptor-mediated Endocytosis drawn out
draw out
49
New cards
lipitor
synthesis of cholesterol by interfering with the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase
* blocks synthesis of Cholesterol inside cells
* stimulates synthesis of LDL-receptor proteins
* more LDL can then enter cells lowering cholesterol levels in plasma
* blocks synthesis of Cholesterol inside cells
* stimulates synthesis of LDL-receptor proteins
* more LDL can then enter cells lowering cholesterol levels in plasma
50
New cards
each type of cell has a unique membrane composition with varying percentages of…
lipids, proteins, and some carbohydrates
51
New cards
fluid mosaic model
of a lipid bilayer- lipids are can move (are “fluid”) and are interspersed with proteins much like a mosaic
52
New cards
what does the degree of saturated vs. unsaturated fatty acids and amount of cholesterol effect
rigidity/fluidity of membrane
53
New cards
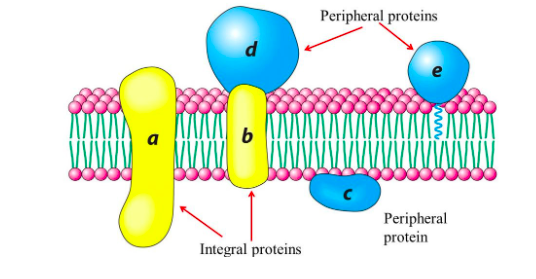
peripheral membrane proteins
are bound to membranes primarily through interactions with integral protiens
54
New cards
transmembrane proteins (integral membrane proteins)
embedded in and extend through the membrane
55
New cards
drawn out membrane layer with peripheral and integral proteins
drawn out
56
New cards
Fluid Mosaic Model of Membrane Structure drawn out
drawn out
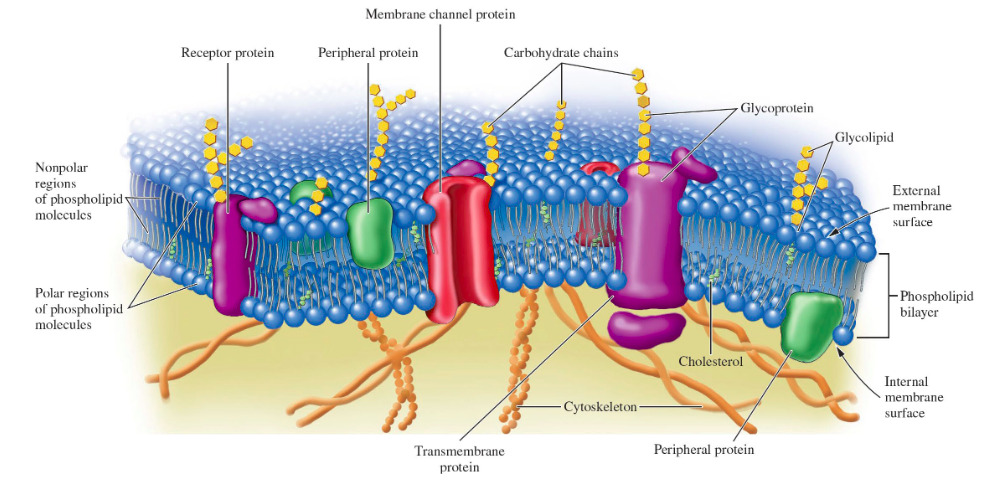
57
New cards
essential fatty acid
any fatty acid that cannot be synthesized by the body
58
New cards
Protein meaning
“of first importance”
most abundant macromolecule in the cell
most abundant macromolecule in the cell
59
New cards
polymers of proteins
amino acid → folded protein
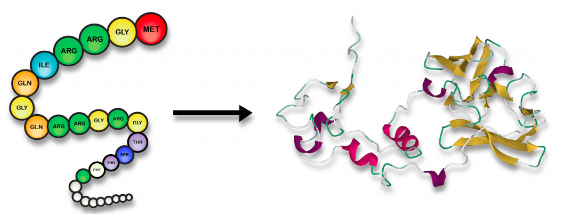
60
New cards
8 functions of Proteins and a brief description
structure
* coverings and structure (collagen)
catalyst
* enzymes (accelerate chemical reactions)
movement
* muscles, flagella
regulation
* regulate metabolism, gene expression
transport
* move material around in the body
hormones
* chemical messengers
protection
* antibodies, blood clotting
storage
* storage of materials
* coverings and structure (collagen)
catalyst
* enzymes (accelerate chemical reactions)
movement
* muscles, flagella
regulation
* regulate metabolism, gene expression
transport
* move material around in the body
hormones
* chemical messengers
protection
* antibodies, blood clotting
storage
* storage of materials
61
New cards
draw amino acid molecule
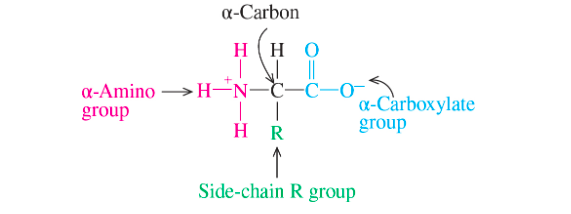
62
New cards
out of 20 how many amino acids are stereoisomers
19/20
63
New cards
Zwitterion
a molecule that contains positive and negative charges in equal amounts to have a net zero charge
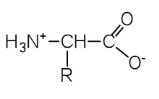
64
New cards
amino acid Zwitterion pH
At physiological pH (7.0)
65
New cards
are amino acids soluble
Amino acids are all soluble in water because of zwitterion formation.
66
New cards
what will happen to the charges of amino acids at extremely acidic and basic conditions
\+=acid
\-=basic
\-=basic
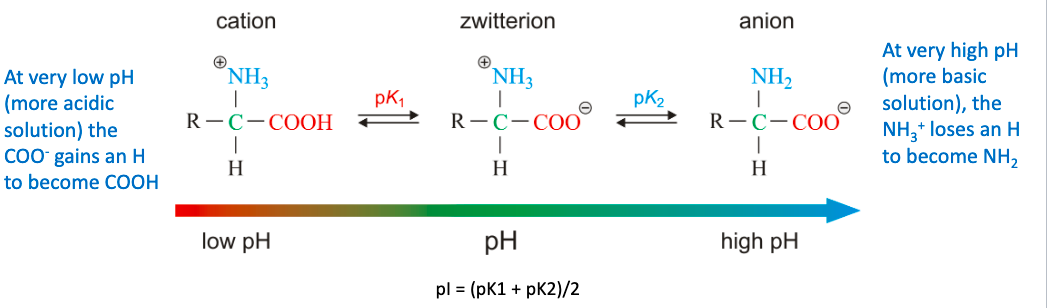
67
New cards
isoelectric point
pH at which a sample of amino acids or proteins has an equal number of positive and negative charges
68
New cards
D and L isomers drawn out
L is the naturally occurring one
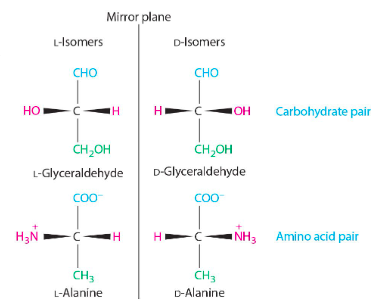
69
New cards
hydrophobic
water fearing
non-polar neutral-- no charge
non-polar neutral-- no charge
70
New cards
hydrophillic
water loving
polar
acidic → negatively charged side chains (-)
basic → positively charged side chain (+)
polar
acidic → negatively charged side chains (-)
basic → positively charged side chain (+)
71
New cards
peptide bond
an amide bond between the a-amino group of one amino acid and the carboxylic acid of another amino acid eliminating a molecule of water
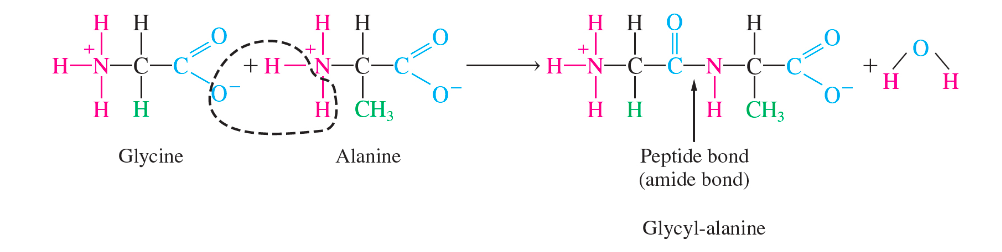
72
New cards
peptides
shorter chains of amino acids
73
New cards
dipeptide
when 2 amino acids are condensed or dehydrated
74
New cards
polypeptides
longer chains are of amino acids
75
New cards
N-terminus
the end containing the amino acid with a free -NH3+ group/amino group
76
New cards
C-terminus
the end containing the amino acid with a free -COO- group/carboxyl group
77
New cards
primary structure
amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain “beads on a string”
78
New cards
second structure
the primary sequence of the polypeptide folds into regularly repeating structures called the secondary structure
* a-helix (most common)
* B- pleated sheet
* a-helix (most common)
* B- pleated sheet
79
New cards
tertiary structure
three-dimensional folding pattern of a protein due to side chain interactions
* fibrous- insoluble
* globular- soluble
* fibrous- insoluble
* globular- soluble
80
New cards
in 3\* *and 4*\* conformations are stabilized in four ways
1. covalent bonds: disulfide bonds (S-S)
2. hydrogen bonds
3. salt bridges: the attraction between ions of opposite charge. + attracted to -
4. hydrophobic interactions: polar groups outward towards water; non-polar groups inward away from water-- London dispersion
81
New cards
quaternary protein structure
2 or more polypeptide chains held together
4 subunits
4 subunits
82
New cards
Fibrous proteins
proteins arranged in fibers or sheets, insoluble in water. Exp: hair, nails, horns, collagen
* mechanical strength
* structural components
* movement
* mechanical strength
* structural components
* movement
83
New cards
Globular proteins
protein with a generally spherical shape, soluble in water Exp: myoglobin, hemoglobin, immunoglobins
* transport
* regulatory
* enzymes
* transport
* regulatory
* enzymes
84
New cards
hemoglobin
is the oxygen-transport protein of higher animalsm
85
New cards
myoglobin
is the oxygen storage protein of skeletal muscle
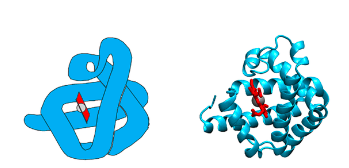
86
New cards
prosthetic group
a nonprotein molecule that binds to a protein
87
New cards
Heme
oxygen binds to it, it is a prosthetic group
it has iron (Fe2+) in it
it has iron (Fe2+) in it
88
New cards
protein denaturation
when the protein unfolds, i.e. the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure is disrupted, and the protein loses its 3-D shape
89
New cards
coaguation
proteins are unfolded and entangled
90
New cards
6 causes of protein denaturation
\-temp (coagulation)
\-pH (Acids and Bases)
\-organic solvents like alcohol
\-detergents
\-heavy metals
\-mechanical stress (stirring,whipping, and shaking)
\-pH (Acids and Bases)
\-organic solvents like alcohol
\-detergents
\-heavy metals
\-mechanical stress (stirring,whipping, and shaking)
91
New cards
catalyst
chemical that increases the rate of a chemical reaction
\-metals
\-polymers
\-proteins
\-metals
\-polymers
\-proteins
92
New cards
enzyme and naming of one
a biological catalyst, typically a protein
add -ase to end of name
add -ase to end of name
93
New cards
oxidoreductase definition
catalyzes an oxidation/reduction reaction(transfers electron)
94
New cards
transferase definition
transfers a functional group
95
New cards
hydrolase definition
causes hydrolysis reaction (addition of H2O to break a bond)
96
New cards
ligase definition
typically joins pieces together and often breaks/makes C-O, C-C, or C-N bonds(DNA ligase in DNA replication)
97
New cards
Isomerase definition
rearranges functional groups(change shape)
98
New cards
lyase definition
forms/breaks double bonds by removing/adding groups other than by hydrolysis(look for double bonds)
99
New cards
oxidoreductase reaction

100
New cards
transferase reaction