PHR 937 Block 1 kaitlyn
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
common joints affected by RA
hands, feet
also: shoulders, elbows, hips, knees
- symmetrical
proximal interphalangeal (PIP)
metacarpophalangeal (MCP)
metatarsalphalangeal (MTP)
common joints affected by OA
hands, weight bearing joints
also: neck, back
what tissue does RA target?
synovial
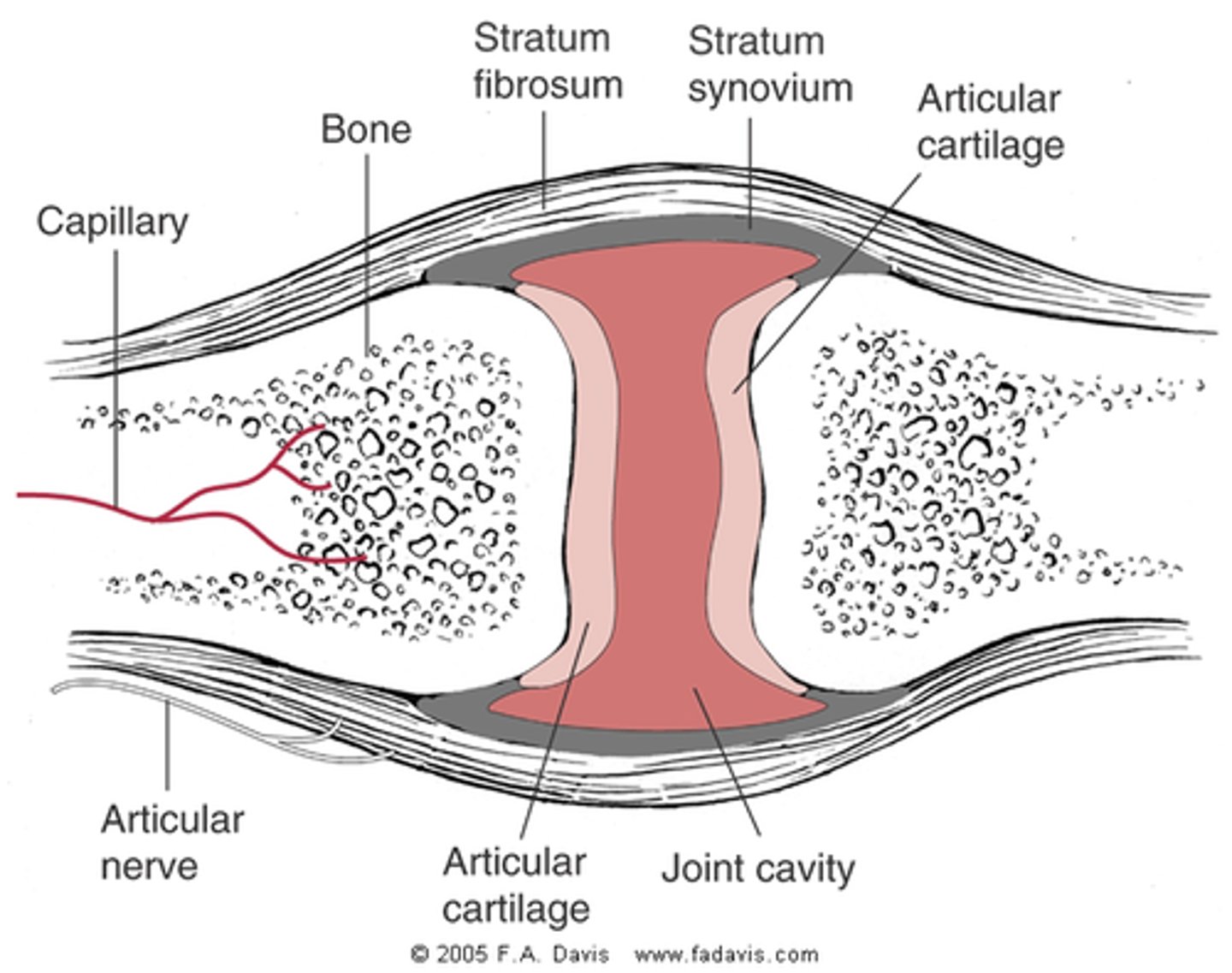
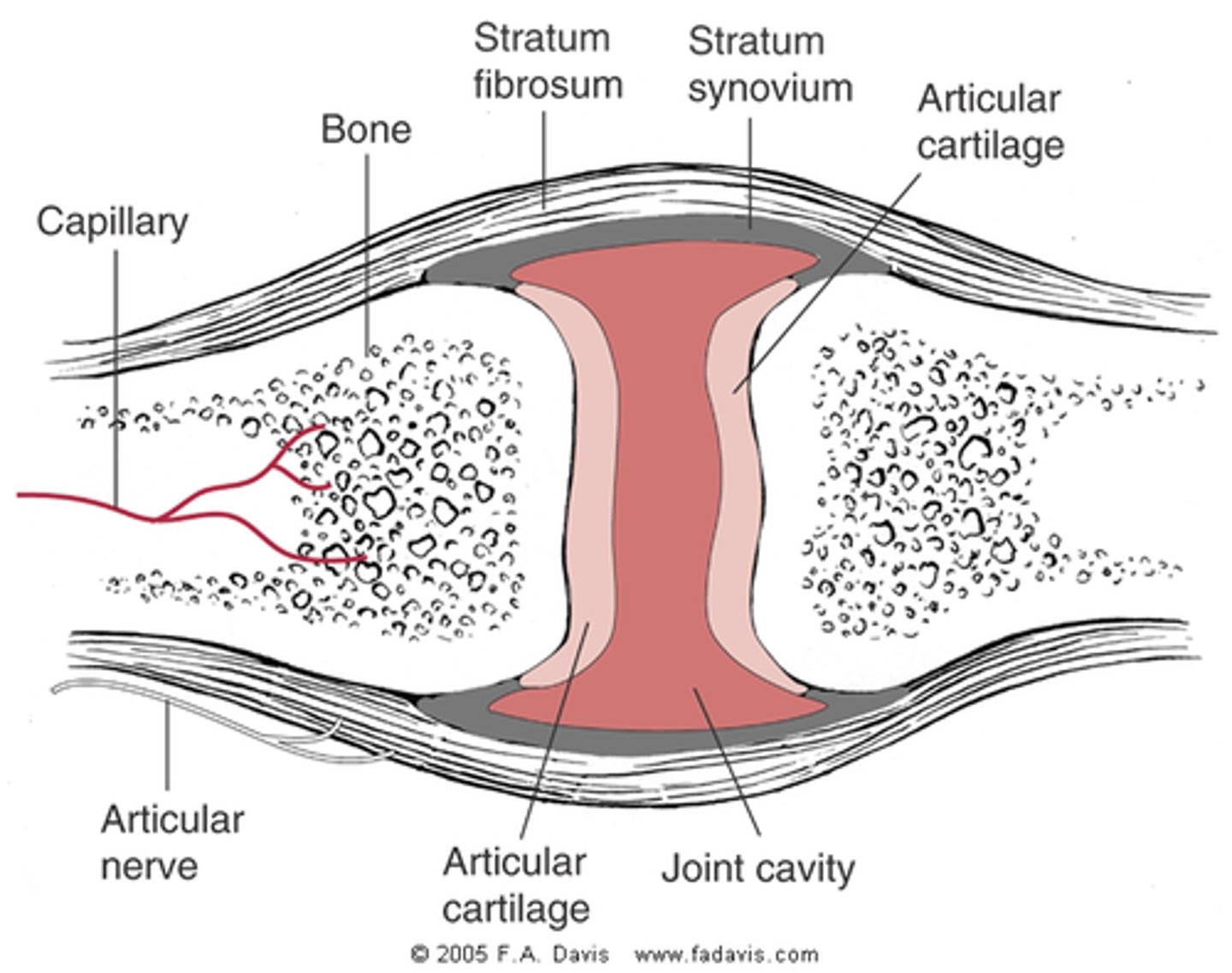
synovium
tissue that lines joints, tendons, and bursae
- contains macrophages and fibroblasts
- target of RA
lymph nodes
filter lymph - site of immune activation
rheumatology
focused on diseases of the joints and the surrounding soft tissue and connective tissue
rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by joint swelling, joint tenderness, and destruction of synovial joints - leading to severe disability and premature mortality
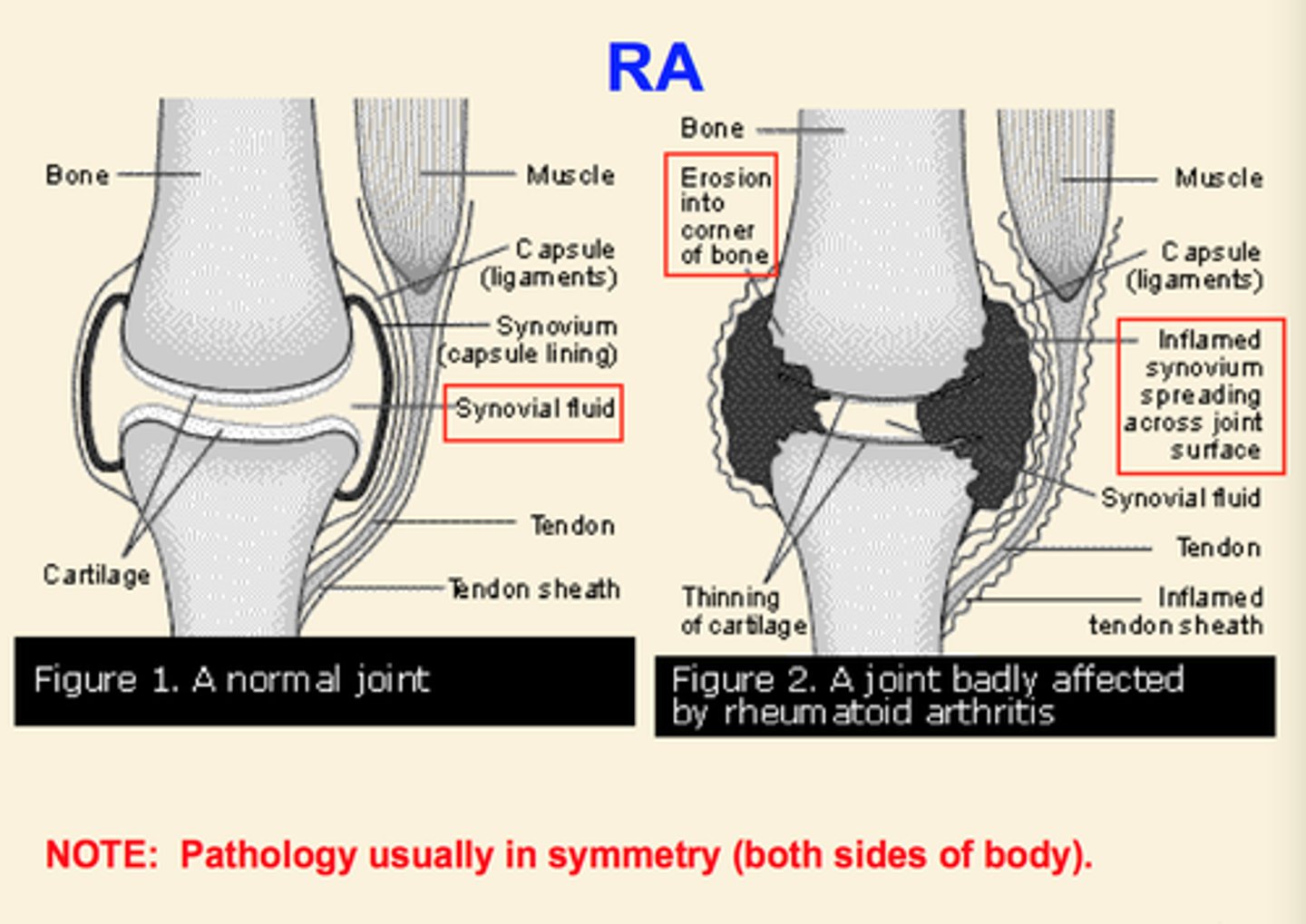
RA overview
- a chronic autoimmune disorder
- symmetrical erosive synovitis
- chronic fluctuating disease
- may result in joint destruction and disability
RA etiology
overall, unknown cause
- infectious: mycoplasma, epstein-barr, rubella
- genetic predisposition: major histocompatability complex and antigen presenting cells
- autoimmune: trouble differentiating between self and non-self
RA pathophysiology
1. arthriogenic antigen exposed to a genetically susceptible host
2. antigen activates T and B cells
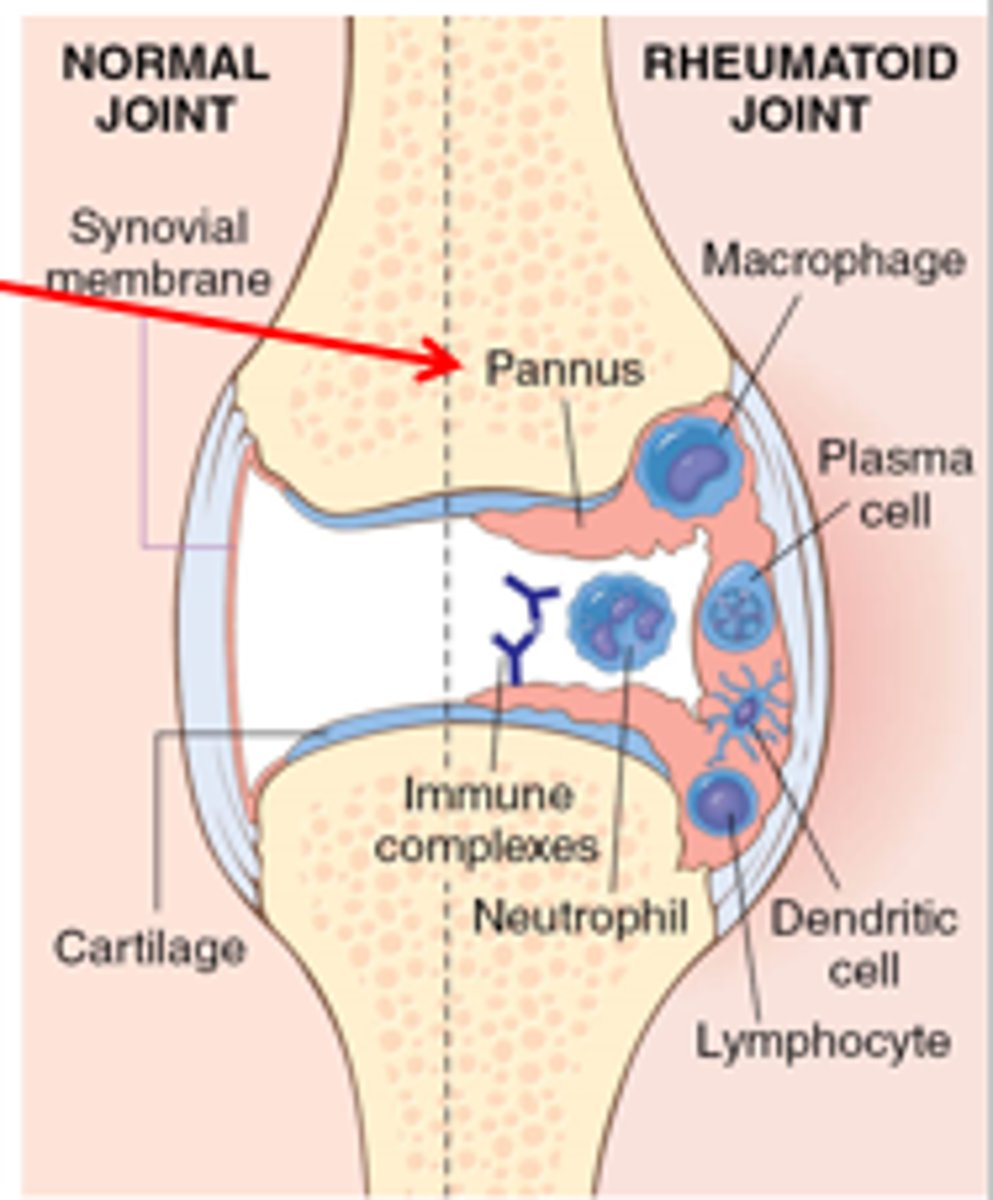
3. chronic inflammation of synovial tissue (lines the joints) - called a pannus
4. pannus invades cartilage
5. bone and cartilage erosion
pro-inflammatory cytokines
TNF-α
IL-1
IL-6
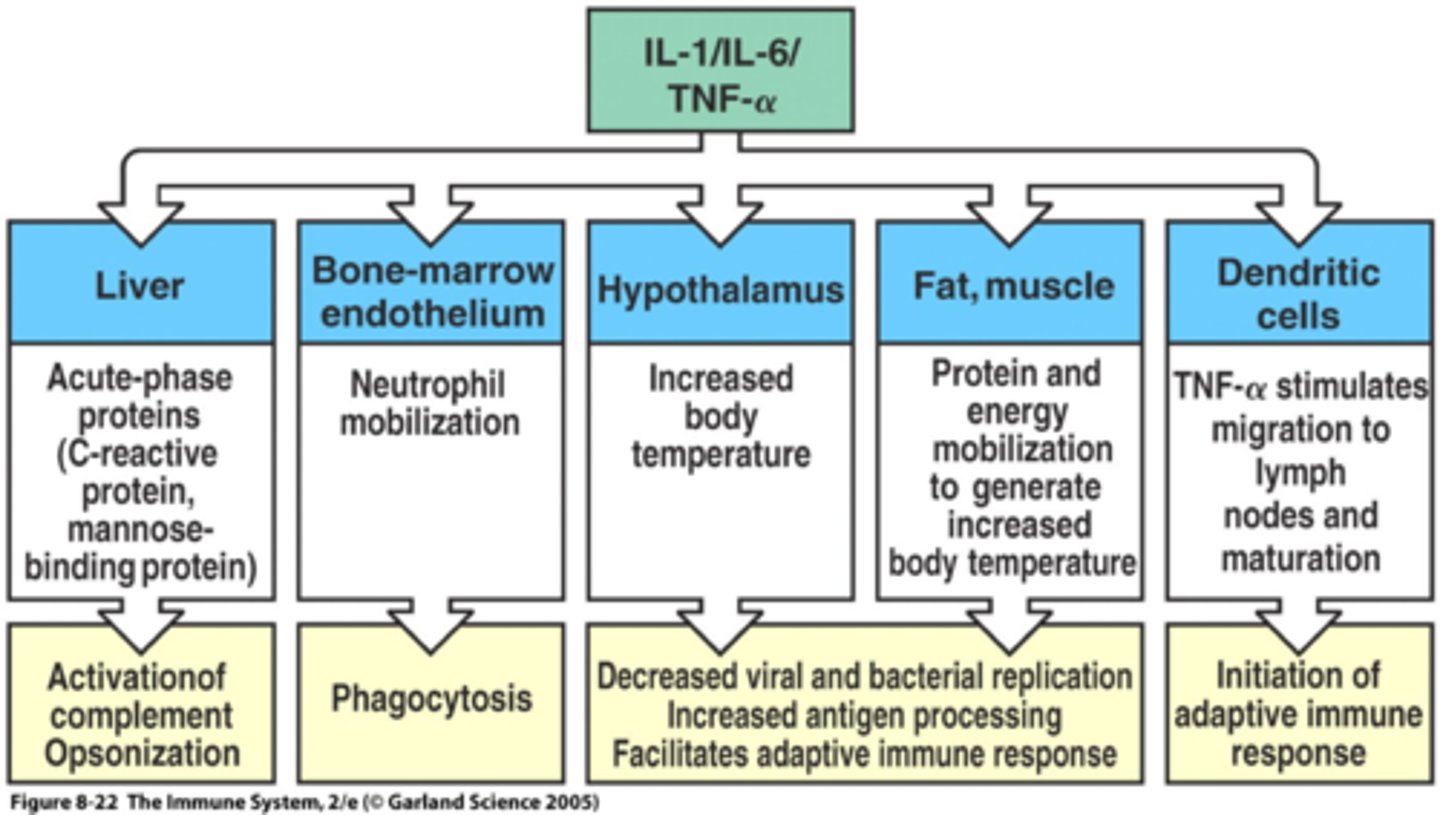
how do cytokines affect the joints in RA?
- they produce metalloproteinases/ other cytotoxic substances leading to the erosion of bone and cartilage
- they also attract other inflammatory mediators to the joint, perpetuating the destructive process
- ultimately are responsible foe the destruction of the joint
RA presentation
small joints affected 1st
joint swelling
rheumatoid nodules
fatigue (usually later in the day)
weakness
low grade fever
musculoskeletal pain
joint stiffness (usually 30+ mins in the morning)
RA lab results
- antinuclear antibody (ANA) + (autoimmune disease marker)
- rheumatoid factor (RF) +
- anti-CCP +
- ↑ ESR and ↑ CRP (inflammatory markers, non-specific)
- joint fluid aspiration + for neurtophils, high protein content (non-specific inflammatory arthritis)
- mild to moderate normocytic anemia
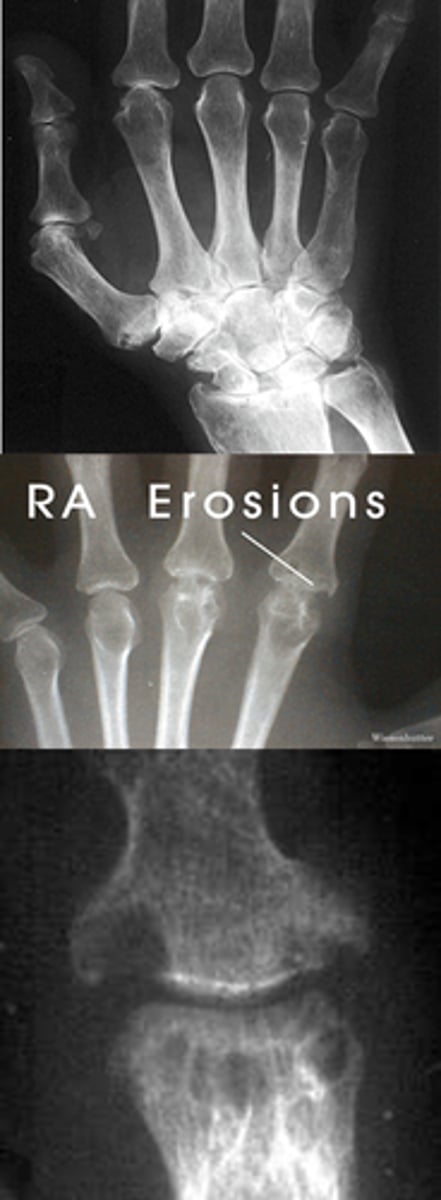
RA imaging
radiologic tests show:
- joint space narrowing
- soft tissue swelling
- bony erosions
extra-articular involvement
- rheumatoid nodules
- vasculitis
- pulmonary fibrosis
- cardiovascular involvement
- Fetty's syndrome
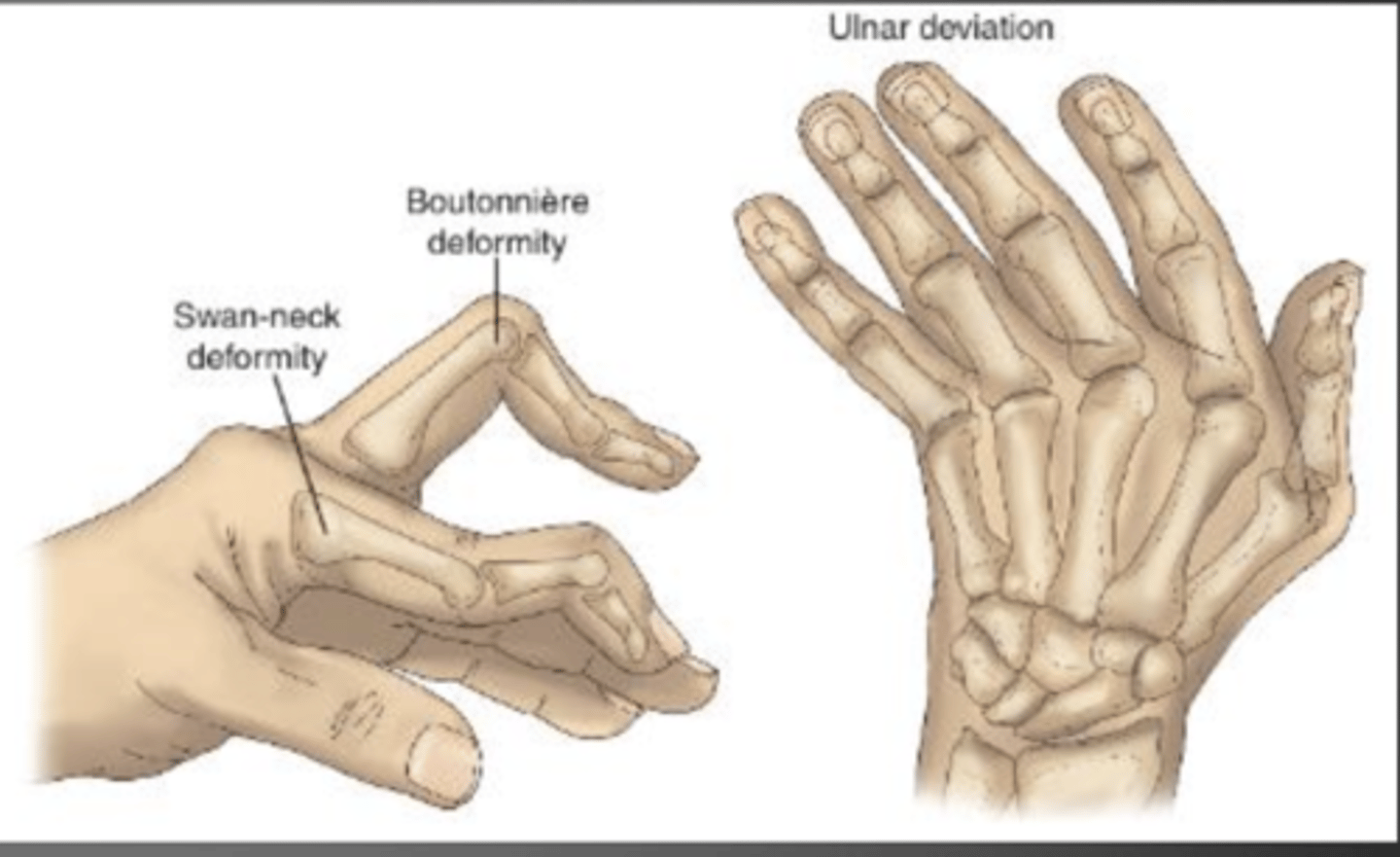
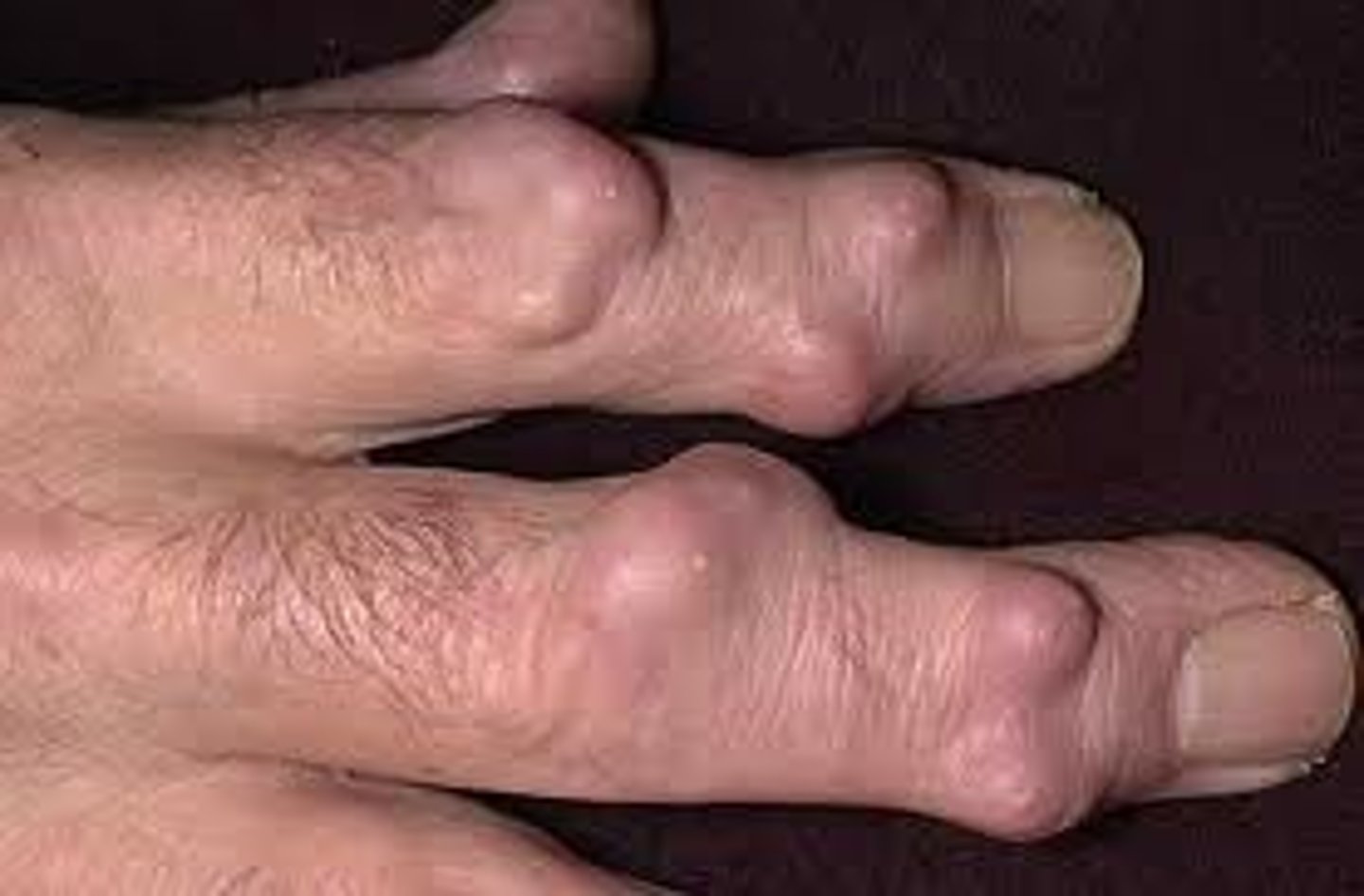
joint deformities
structural changes in joints due to RA
- swan neck
- boutonniere
- hammer toe
- hyperextension