Unit 2A: Biological Psychology
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
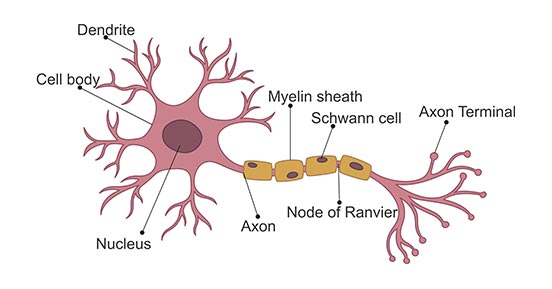
Neuron
specialized cell in the nervous system that receives and sends messages with electrochemical signals
Dendrite
receives messages from other cells
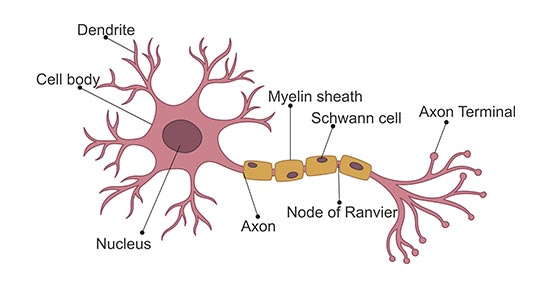
Soma
cell body that contains the nucleus
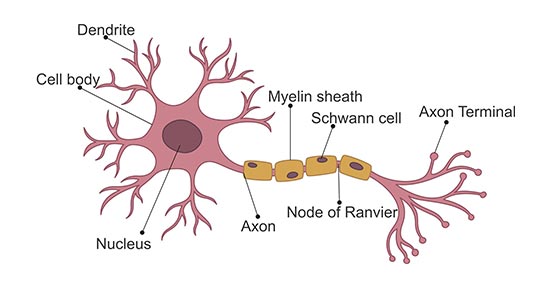
Axon
passes messages away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands
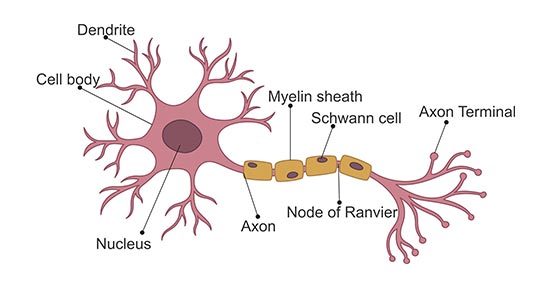
Myelin Sheath
fatty tissue that insulates axon, speeding up transmission of the message
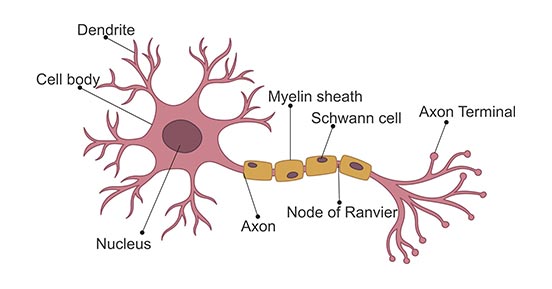
Terminal Button
the end point of a neuron that releases neurotransmitters into the synapse, hence sending the message on to the next neuron
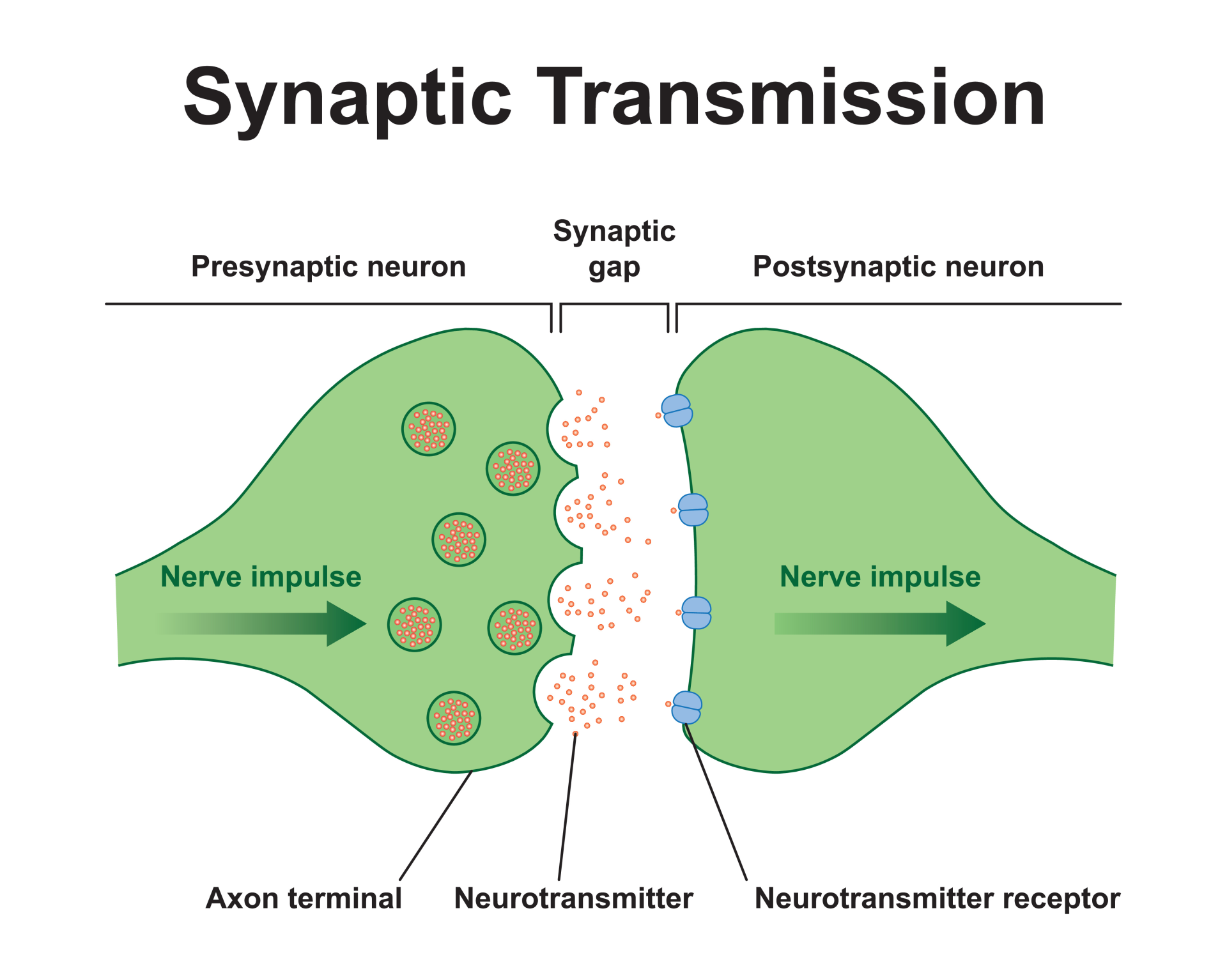
Synapse
the space between neurons
“All or Nothing” Response
when the nucleus decides to fire, it fires down the axon completely (all the way) or not at all; there must be enough energy to cross the threshold
Action Potential
(“nerve impulse”) the electrical charge that moves through the neuron
Depolarization
a change within a cell, during which the cell undergoes a shift in electric charge distribution, resulting in less negative charge inside the cell compared to the outside
Refractory Period
the period of time after firing that the neuron is focused on resetting, and therefore is unable to fire again
Reuptake
after the neurotransmitters stimulate the receptors on the receiving neuron, the chemicals are taken back up into the sending neuron to be used again
Neurotransmitters
chemical messenger that carries, boosts, and balances signals between neurons, or nerve cells, and other cells in the body
Endorphins
neurotransmitters that influence the perception of pain or pleasure (ex. oversupply with opiate drugs can suppress the body’s natural endorphin supply)
Acetylcholine
enables muscle action, learning, and memory (ex. ACh deteriorates in Alzheimer’s patients)
Norepinephrine
helps control alertness and arousel (ex. undersupply can depress mood)
Dopamine
influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion (ex. excess results in schizophrenia and undersupply results in decreased mobility of Parkinson’s disease)
Glutamate
a major excitatory neurotransmitter involved in memory (ex. oversupply can overstimulate the brain, producing migraines or seizures)
GABA
a major inhibitory neurotransmitter (ex. undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia)
Serotonin
affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousel (ex. undersupply linked to depression, antidepressants can be used as treatment)
Agonists
mimics neurotransmitter activity by fitting in the receptor site like a master key (ex. Morphine and Heroin)
Antagonists
block neurotransmitter activity by fitting in the receptor site like a fake key (ex. botox blocks acetylcholine)
Central NS (CNS)
coordinates the actions and interactions of the brain & spinal cord, body’s main control center
Peripheral NS (PNS)
includes the sensory nerves outside the brain and spinal cord that connect the CNS to the rest of the body
Automatic NS
regulates involuntary and unconscious actions like breathing, digestion, heartbeat, work of other internal organs, and etc. (made up of sympathetic and parasympathetic)
Somatic NS (Voluntary)
includes the nerves that transmit signals from your brain to the skeletal muscles to allow voluntary movement; responsible for carrying sensory and motor information to and from the central nervous system
Sympathetic NS
emergency response system, If something alarms, enrages, or challenges you “Fight or Flight”
Parasympathetic NS
functions to calm the person “Rest & Digest”
Sensory (Afferent) Nerves
carry information from the nerves to the CNS
Motor (Efferent) Nerves
carry information from the CNS to muscle fibers throughout the body
Interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
measurement of the electrical activity of the brain by recording from electrodes placed on the scalp
CAT or CT scan
two-dimensional x-ray photographs from different angels and using to create three-dimensional representation of organ
PET scan
uses trace amounts of short-lived radioactive material to map functional processes in the brain (glucose)
MRI
brain-imaging method using radio waves and magnetic fields of the body to produce three dimensional detailed images of the brain
fMRI
measuring brain activity, detects the changes in blood oxygenation and flow that occur in response to neural activity (more oxygen=increases to active area)
Brainstem
lower brain; connects brain to spinal cord and sends messages to the rest of your body to regulate balance, breathing, heart rate, and more
Medulla Oblongata
lower brain; controls many vital autonomic functions such as heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure
Pons
lower brain; relays sensory information to cerebellum and handles sleep cycle and breathing
Reticular Formation
lower brain; network of nerves that carry messages between parts of the brain stem, helps control alertness or drowsiness, and provides useful sensory input while filtering out unnecessary stimuli
Cerebellum
lower brain; helps control posture, balance, and the coordination of voluntary movements
Thalamus
middle brain or limbic system; processes and transmits movement and sensory information, and considered the sensory “relay station” of the brain, passing information on to the cerebral cortex (receives information from all senses except smell)
Hypothalamus
middle brain or limbic system; connects with many other regions of the brain and is responsible for controlling hunger, thirst, emotions, body temperature regulation, and circadian rhythms (controls pituitary gland)
Amygdala
middle brain or limbic system; primarily involved in processing emotion and survival responses (coordinates fight-or-flight response that influences aggression and fear)
Hippocampus
middle brain or limbic system; the hippocampus plays a critical role in the formation, organization, and storage of new memories
Cerebral Cortex
higher brain; responsible for the higher-level processes of the human brain, including language, memory, reasoning, thought, learning, decision-making, emotion, intelligence and personality
Frontal Lobes
higher brain; areas of the cortex located in the front and top of the brain, associated with reasoning, motor skills, higher level cognition, planning, judgement and expressive language
Parietal Lobes
higher brain; sections of the brain located at the top and back of each cerebral hemisphere containing the centers for processing sensory signals such as touch, pressure, temperature, and pain
Temporal Lobes
higher brain; areas of the cortex located just behind the temples containing the neurons responsible for the sense of hearing and meaningful speech (most of the angular gyrus and Wernicke’s Area are here)
Occipital Lobes
higher brain; section of the brain located at the rear and bottom of each cerebral hemisphere containing the visual centers of the brain (visual cortex)
Motor Cortex
higher brain; this area of the brain receives information from various lobes of the brain and utilizes this information to carry out body movements
Prefrontal Cortex
higher brain; this brain region has been implicated in planning complex cognitive behavior, personality expression, decision making, and moderating social behavior
Somatosensory Cortex
higher brain; part of your brain that receives and processes sensory information from the entire body
Auditory Cortex
higher brain; the part of the temporal lobe that processes auditory information
Visual Cortex
higher brain; receives and processes visual information relayed from the retinas
Corpus Callosum
higher brain; bundle of nerve fibers that connects the two hemispheres, messages move from one side of the brain to the other
Glial Cells
higher brain; (glue) provide physical and chemical support to neurons and maintain their environment
Angular Gyrus
speech centers; it transforms visual representations (ex: the alphabet) into an auditory code
Wernicke’s Area
speech centers; it is located in the temporal lobe on the left side of the brain and is responsible for the comprehension of speech
Broca’s Area
speech centers; located in the lower portion of the left frontal lobe, controls motor functions involved with speech production and language comprehension
Aphasia
speech centers; inability to speak
Phineas Gage
split brain; rod went through his head and his personality changed from the damage
Right Hemisphere
(unconscious parallel processing) appears to specialize in more widespread processing involving perception, visualization, spatial perception, recognition of patterns, faces, emotions, melodies, and expression of emotion
Brain Plasticity
split brain; the ability to constantly change both the structure and function of many cells in the brain in response to experience and even trauma
Hormones
endocrine system; chemical messengers that travel to target organs where they bind to specific receptors
Pineal Gland
endocrine system; (melatonin) to receive information about the state of the light-dark cycle from the environment
Pituitary Gland
endocrine system; (HGH) pea-sized structure located in the core of the brain, where it is controlled by an adjacent brain area, the hypothalamus; regulates stress, growth and reproduction, including some parts of pregnancy and childbirth
Thyroid Gland
endocrine system; (thyroxin) located inside the lower neck, secretes a hormone called thyroxin that regulates metabolism, growth, and appetite
Parathyroid Glands
endocrine system; located below the thyroid gland, this PTH regulates the amounts of calcium, phosphorus and magnesium in the bones and blood
Adrenal Glands
endocrine system; (adrenaline, epinephrine, & norepinephrine) two glands on top of each kidney involved in stress response
Pancreas
endocrine system; (insulin) helps control blood sugar levels and digestion of food
Ovaries
endocrine system; (estrogen) in females
Testes
endocrine system; (testosterone) in males
Chromosomes
x-shaped structures made largely of DNA molecules
Genes
segments of DNA that contain the code for a particular protein and determine our biological development
Gregor Mendel
father of genetics
Down’s Syndrome
extra chromosome, intellectual disability, and unique physical features
Turner’s Syndrome
abnormal sex chromosome, no ovaries, and girls have limited sexual development
Klinefelter’s Syndrome
abnormal sex chromosome, extra x chromosome, and minimal male sexual development
PKU
lacks enzyme to produce amino acid PKU
Tay-Sachs Syndrome
recessive gene defect, typically in European Jews, and causes degeneration of the CNS
Albinism
failure to synthesize or store pigment, very pale skin and hair
Huntington’s Disease
dominant gene defect, causes degeneration of nervous system and loss of motor movement
Natural Selection
an evolutionary process through which adaptive traits are passed on to ongoing generations because these traits help animals survive and reproduce
Artificial Selection
biologists like Belyaev and Trut (1999) were able to artificially rear and domesticate wild foxes, selecting them for friendly traits
Nature vs. Nurture
hereditary vs. environment
Gender Differences on Sexuality
casual sex- male
sex for affection- female
think about sex everyday- male
Functionalism
describes the mind as a functional tool that allows us to adapt to our environments, the purpose of our thoughts and feelings
Behaviorism
(REWARDS) focuses on the idea that all behaviors are learned through interaction with the environment
Cognitive
how we think, remember, and learn by trying to understand how we PERCEIVE PAST EVENTS and make decisions
Humanistic
(Freud & Skinner) Focuses on the idea of PERSONAL FULFILLMENT
Charles Darwin
created the theory of natural selection
Edward B. Titchener
(structuralist) founder of structuralism who used introspection
John B. Watson
(behavioralist) believed that behavior could be shaped through conditioning
William James
(functionalist) father of American psychology
Sigmund Freud
(psychoanalyst) founded and developed psychoanalysis
Operational Definitions
a description of something in terms of the operations (procedures, actions, or processes) by which it could be observed and measured
Random Sampling
the process of choosing the research participants from the population
Random Assignment
each participant has equal chances of being placed into any group
Descriptive Study
used to describe characteristics of a population or phenomenon being studied