APC 11- homeostasis 1
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
define homeostasis , why is it vital for normal body function , explain the concepts of the homeostatic range, principles of negative and positive feedback , key examples of homeostatic processes , and understand how disruption of homeostasis leads to disease
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is homeostasis ?
The maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment despite a changing external environment and varying internal activity, using negative feedback mechanisms.
keeping the body’s precise internal conditions within a set range, despite internal or external environmental fluctuations
each system/ cells has a range - they can still work within that range higher or lower , when outside the range - no longer function
What are some examples of physiological ranges ?
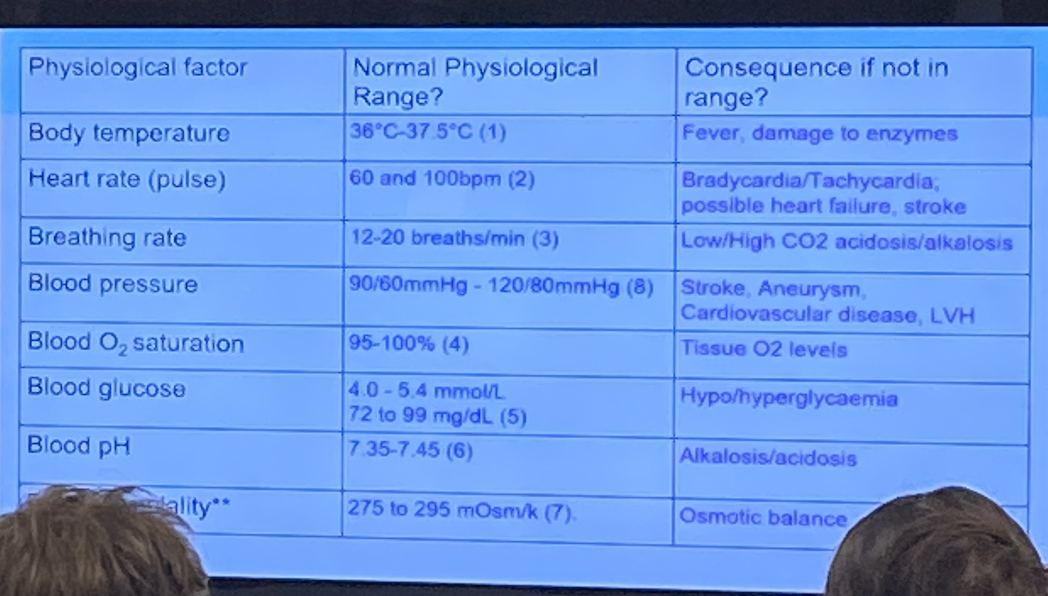
What are vital signs?
‘Vital signs’ provide valuable insight into a patient's condition, including how they are responding to medical treatment and, importantly, whether the patient is deteriorating
Early changes in vital signs often signal deterioration before symptoms become clinically obvious
How does the body maintain homeostasis ?
the nervous system ( brain ) - neural control
the endocrine system - endocrine control
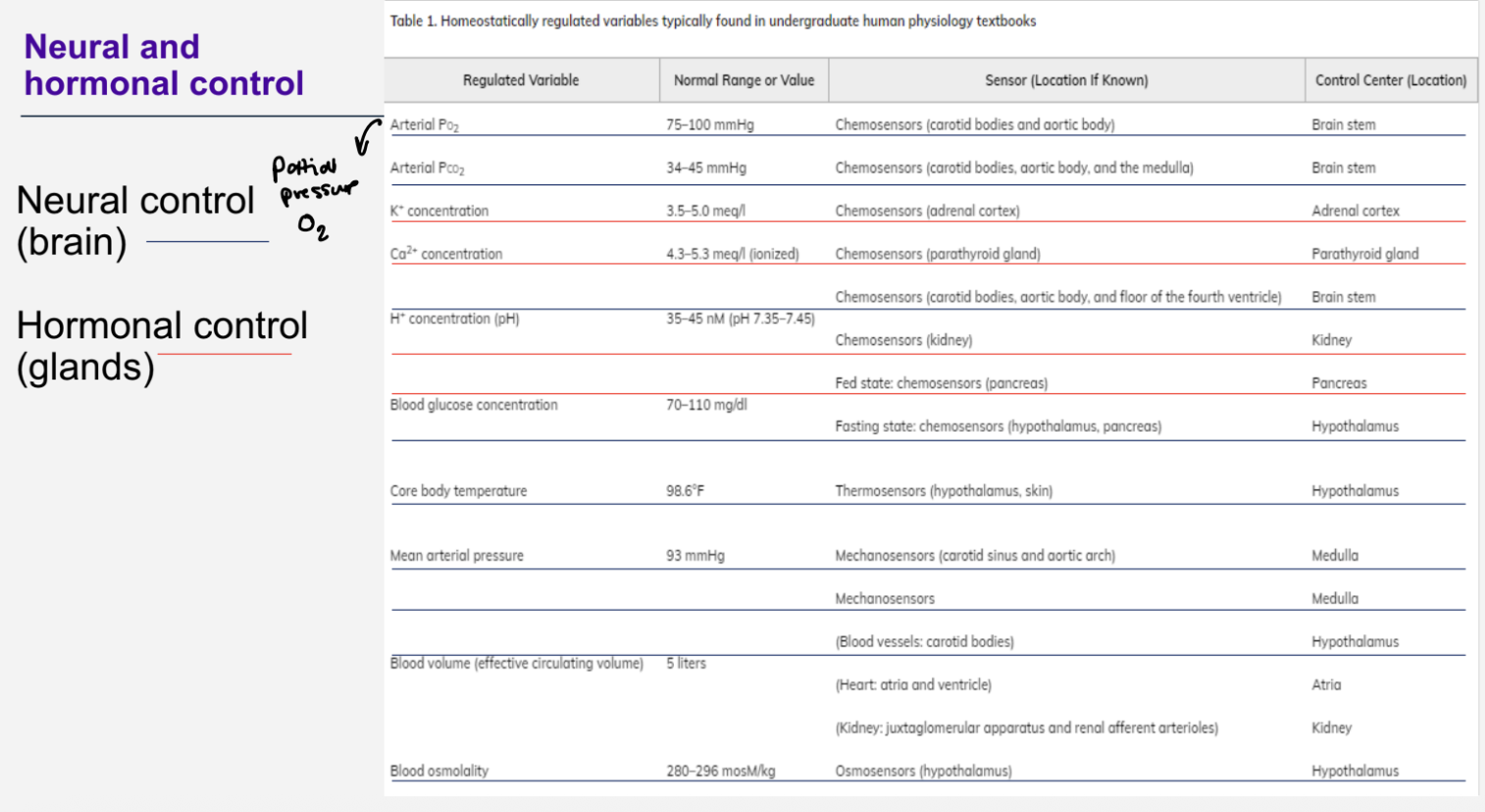
What are the structures involved in the neural control ?
Hypothalamus
Temperature control
Water balance (through
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Medulla oblongata (part of brainstem)
Important vital signs:
• Breathing
• Heart rate
• Blood pressure •
Chemosensors for CO2
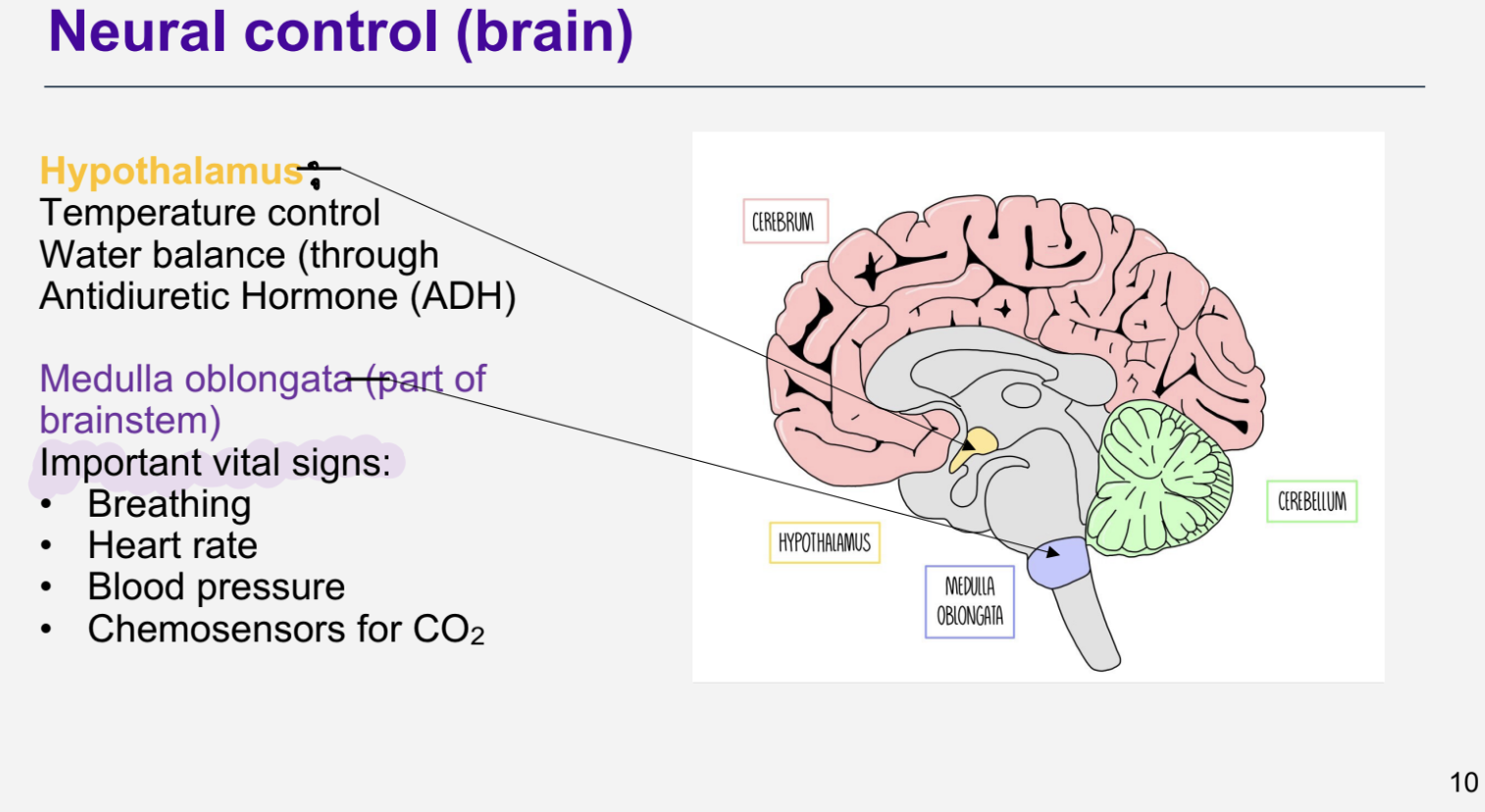
What structures are involved in endocrine control ?
Some examples:
Pituitary gland – several hormones (master regulator)
Pineal gland – melatonin (sleep/wake)
Adrenal gland (aldosterone)
Pancreas (insulin and glucagon)
Thyroid gland (thyroid hormone; calcitonin)
Parathyroid glands (parathyroid hormone)
What is the negative feedback loop ?
if the variable is disturbed , this system restores it towards it set point value
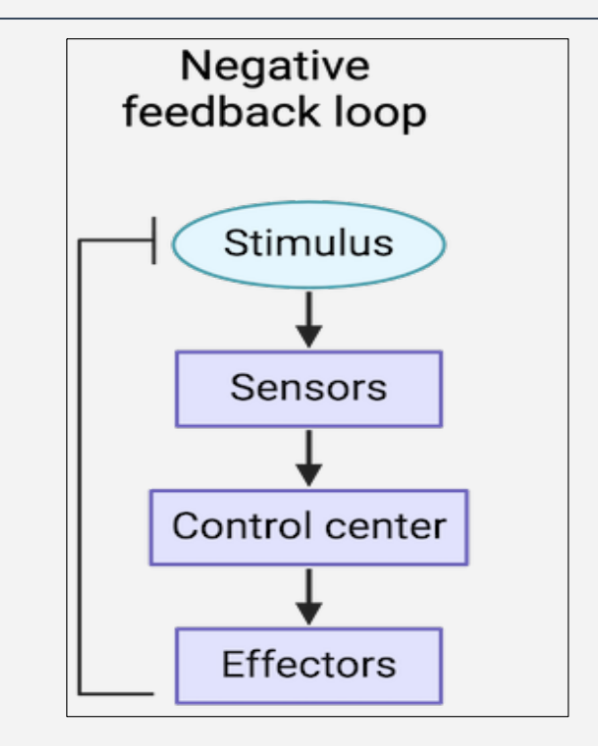
What Are some examples of negative feedback ?
Body temperature (thermoregulation)
Blood osmolality (osmoregulation)
Blood glucose (glucoregulation)
and many more
What is thermoregulation ?
the homeostatic process by which organisms maintain a stable internal core body temperature within a narrow, optimal range for enzymatic function, typically around 37°C (98.6°F) in humans
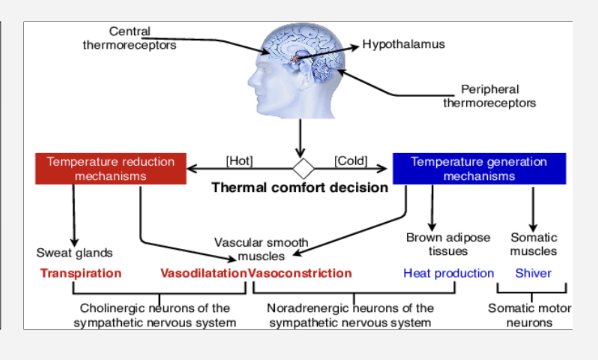
What is osmoregulation ?
the process of maintaining the balance of water and mineral salts in the body's fluids, a key part of homeostasis. It is vital for cells to function properly, as cells can burst or shrivel if they lose or gain too much water through osmosis
Osmolarity here means the amount of solutes dissolved in the blood
An increase in blood osmolarity means the concentration of solutes gets higher
This is due to a decrease in the amount of water in the blood, usually due to dehydration
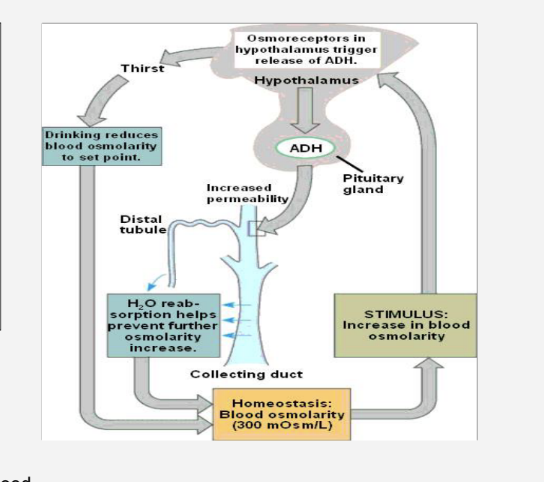
What is glucoregulation ?
the physiological process that maintains stable blood glucose (sugar) levels through the coordinated action of hormones, primarily insulin and glucagon, released by the pancreas
too high - beta receptors
too low - alpha receptors
Glycolysis: The breakdown of glucose into pyruvate to produce energy (ATP).
Glycogenesis: The synthesis of glycogen from excess glucose for storage, primarily in the liver and muscle cells, stimulated by insulin.
Glycogenolysis: The breakdown of stored glycogen into glucose, which is then released into the bloodstream to raise blood sugar levels, stimulated by glucagon during fasting or exercise.
Gluconeogenesis: The production of new glucose from non-carbohydrate sources (such as amino acids and glycerol from fats), mainly in the liver and kidneys, a process stimulated by glucagon and cortisol during prolonged fasting.
`Why do we need to keep blood glucose concentration constant ?
Hyperglycaemia:
Damages microvasculature:
Eyes: retinopathy
Kidneys: nephropathy
Nerves: neuropathy
Damages macrovasculature (lining of arteries)
Hypoglycaemia
Damages brain – reduced cognition, coma, death
What is positive feedback loop ?
It has the opposite action to a negative feedback loop
A positive feedback loop MAGNIFIES the original response instead of correcting it
examples -
During blood clotting, the stimulus
(wound) activates a cascade which
rapidly accelerates blood clotting
During childbirth, stretching of the
cervix leads to more stretching, not less
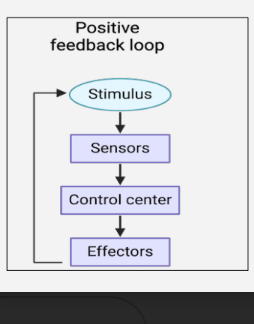
summary
Homeostasis is defined as ‘The maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment despite a changing external environment and varying internal activity, using negative feedback mechanisms’.
Homeostasis is involved in thermoregulation, osmoregulation, and glucoregulation
The nervous and endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis