PD E2- Abdominal Exam
1/82
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
What is the 3rd MCC of cancer related death in men and women (2nd MCC when combined)?
Colon cancer
What should you think of with unexplained weight loss + stool changes + blood in stool + advanced age?
Colon cancer
What should ALWAYS be included if abdominal pain is below umbilicus?
GU exam
When do you examine the sites of discomfort?
Last
What should always be included in abdominal exam?
Digital rectal exam
What should you think of with early satiety with burning, postprandial fullness, and epigastric pain?
Dyspepsia
What is a rare autosomal recessive disorder that lacks a protease in serosal fluids that inactivate interleukin 8 and factor V?
Familial Mediterranean fever
How does familial mediterranean fever present?
Before age 20 with severe abd pain, guarding, & rebound and episodic bouts of pleuritis pain, joint pain, & acute peritonitis
What organs are in the RUQ?
Gallbladder, liver, kidney
What organs are in the epigastric region?
Stomach, pancreas, esophagus
What organs are in the LUQ?
Spleen & kidney
What organs are in the umbilical region?
Small intestine
What is the first site of appendicitis?
Umbilical region
The following potential diagnoses are associated with which region/quadrant?
cholecystitis
hepatomegaly
hepatitis
pyelonephritis
RUQ
The following potential diagnoses are associated with which region/quadrant?
gastritis/PUD
pancreatitis
esophagitis
Epigastric
The following potential diagnoses are associated with which region/quadrant?
splenic rupture
splenomegaly
pyelonephritis
LUQ
The following potential diagnoses are associated with which region/quadrant?
2nd site of appendicitis
diverticulitis
nephrolithiasis, pyelonephritis
PID, ectopic pregnancy
RLQ
The following potential diagnoses are associated with which region/quadrant?
cystitis
bladder distention
pregnancy, PID
Suprapubic
The following potential diagnoses are associated with which region/quadrant?
diverticulitis
nephrolithiasis
pyelonephritis
PID, ectopic pregnancy
LLQ
What organs are in the RLQ?
Appendix, ascending colon, ureter, fallopian tube
What organs are in the suprapubic region?
Urinary bladder, uterus
What organs are in the LLQ?
Descending colon, ureter, fallopian tube
At what serum bilirubin level is jaundice apparent?
≥ 2.5 mg/dL
What symptom might hyperbilirubinemia produce?
Generalized pruritus
What is a bluish periumbilical discoloration (usually accompanied by grey turner sign) from peritoneal hemorrhage?
Cullen’s sign
What are causes of Cullen’s sign?
Acute necrotizing pancreatitis, AAA rupture, ruptured ectopic pregnancy, splenic rupture, trauma, liver abscess, mets
What is flank ecchymosis from retroperitoneal hemorrhage?
Grey turner’s sign
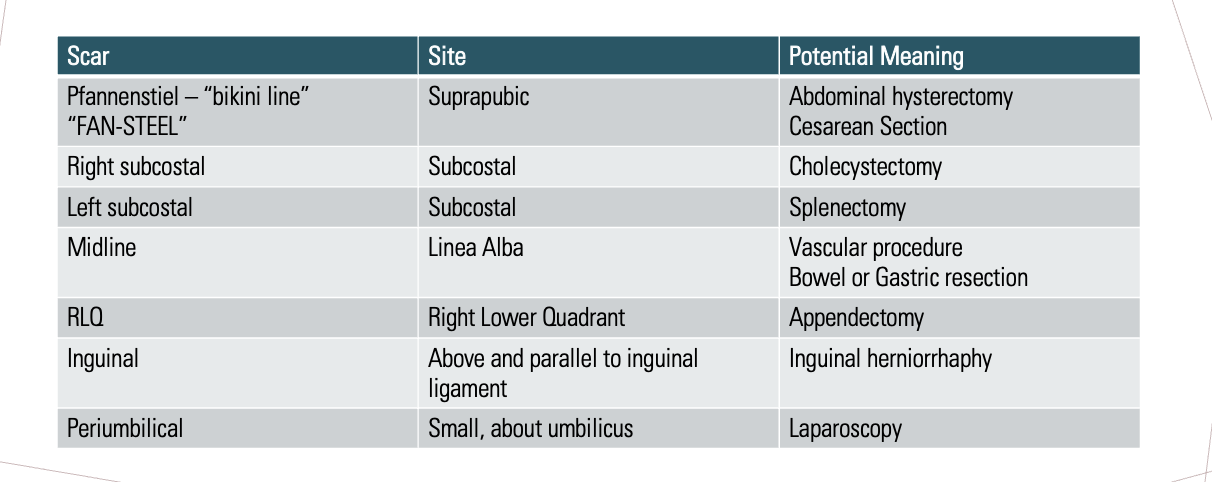
Scar locations and their potential cause
What is the SAD pucker mnemonic for abdominal retroperitoneal viscera?
Suprarenal glands
Aorta/IVC
Duodenum (2-3rd segments, some of 4th)
Pancreas (tail is intraperitoneal) & paraspinal muscle
Ureters
Colon (ascending & descending branches)
Kidneys
Esophagus
Rectum
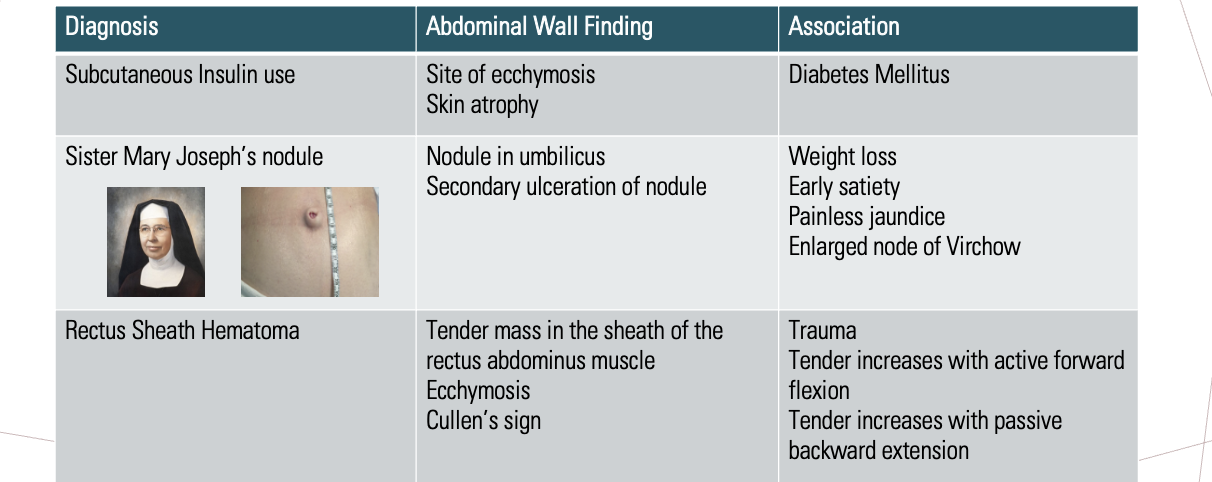
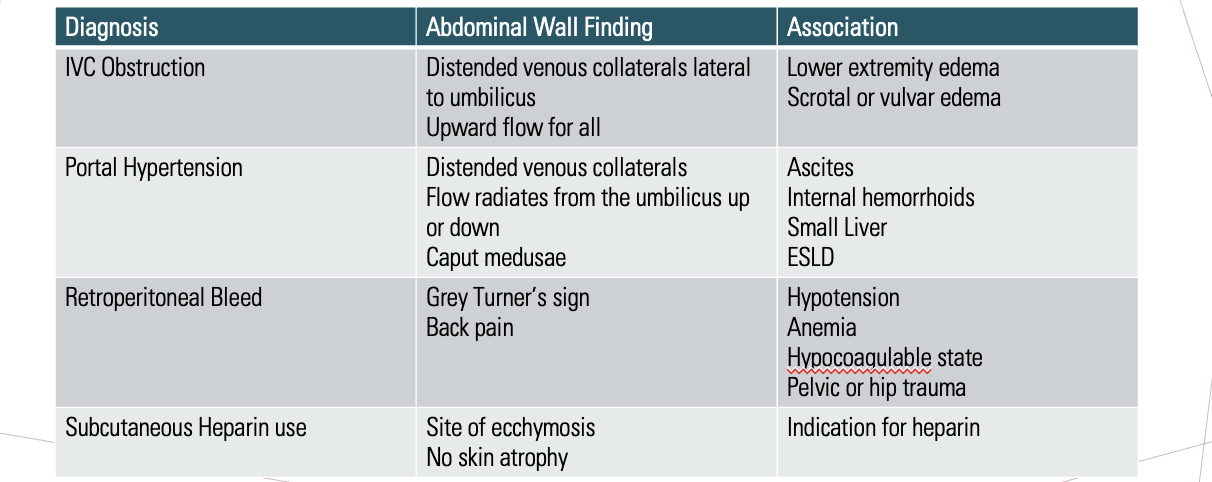
Abdominal wall diagnoses
What part of the stethoscope do you use to auscultate bowel sounds?
Diaphragm
What is a silent abdomen?
>2 minutes with NO bowel sounds
What part of the stethoscope do you use to auscultate vascular sounds?
Bell
What is the proper technique for abdominal auscultation?
Pt supine w/ hips at 45° and knees at 90° → auscultate minimum of 30s in atleast 2 of 4 quadrants
Which is done first, auscultation or palpation of abdomen?
Auscultation
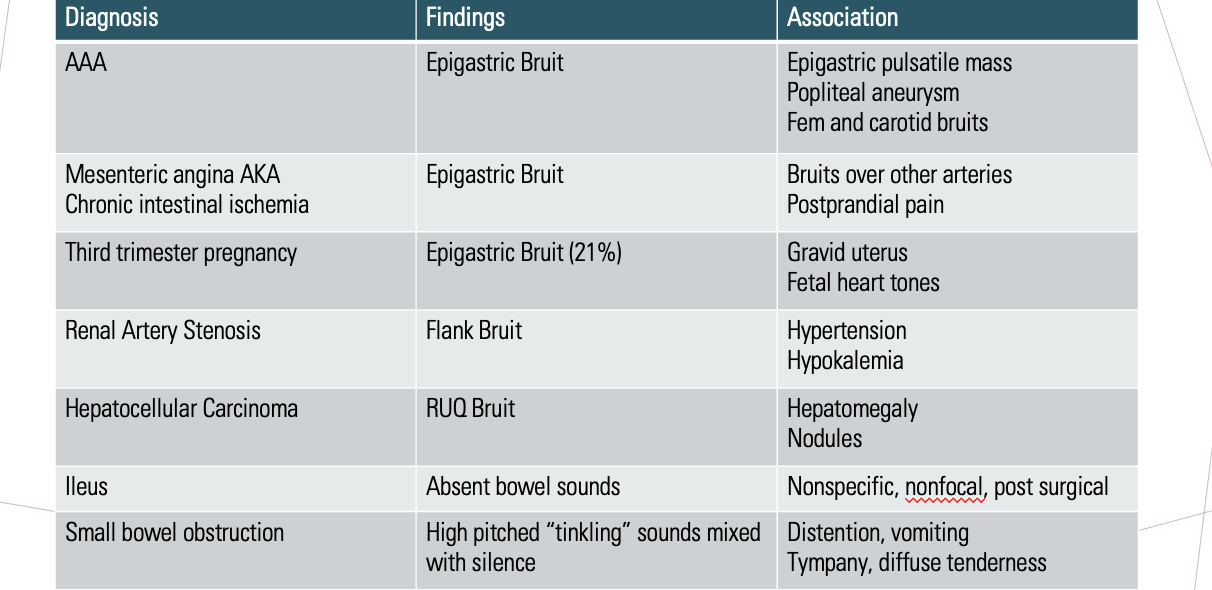
Bowel sounds & associations
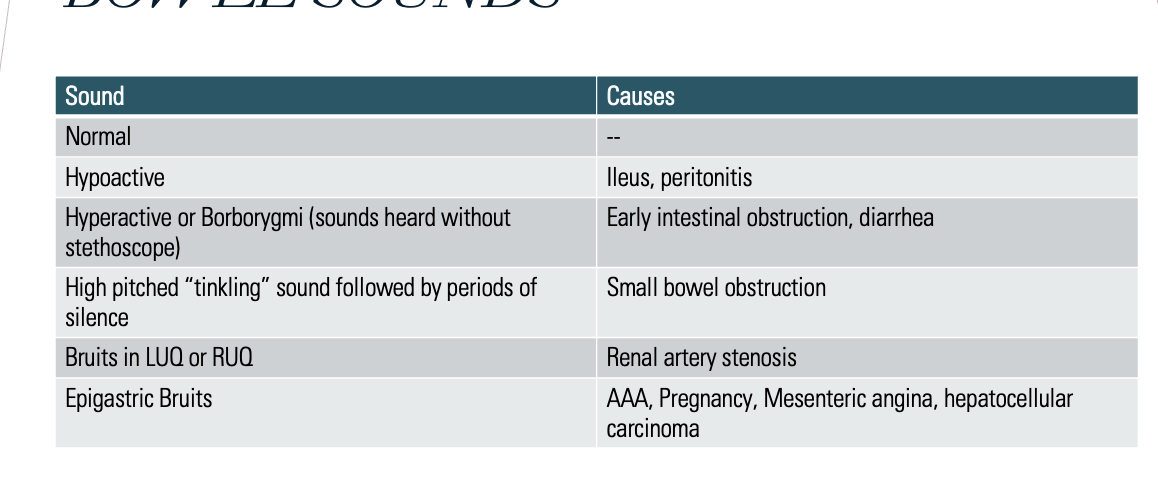
What is tympany?
Air filled (gastric bubble, normal intestines)
What does a dull sound to percussion indicate?
Solid (liver/spleen, impacted colon)
When percussing the abdomen, what is indicated by dullness in the lower area and tympany in the upper/periumbilical area?
Fluid (ascites d/t liver failure, hepatitis, cirrhosis)
Where is the liver?
4-8cm midsternal line & 6-12cm midclavicular line
*determined by tympany below area of dullness & resonate above area of dullness
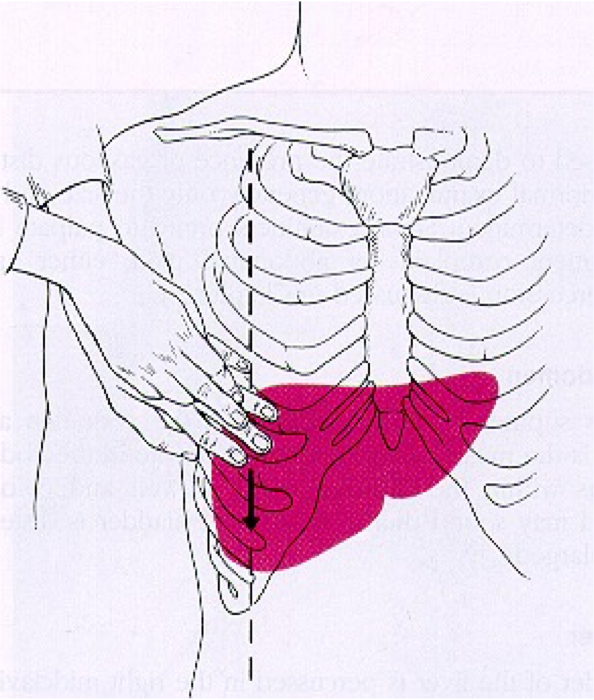
How do you perform liver fist percussion?
Place left palm on pts lower right ribs → make a fist & utilize lateral aspect of hand to deliver blow to left hand
*positive = pain → think inflammation, acute cholangitis
What is more sensitive than Murphy’s for detecting hepatobiliary infections?
Liver fist percussion
What does dullness to percussion in the RUQ over 12 cm indicate?
Enlarged liver → hepatitis, cirrhosis
Where is the spleen located?
Bt ribs 9-11 lateral left abdomen, proximal to castell’s point to triangle of traube
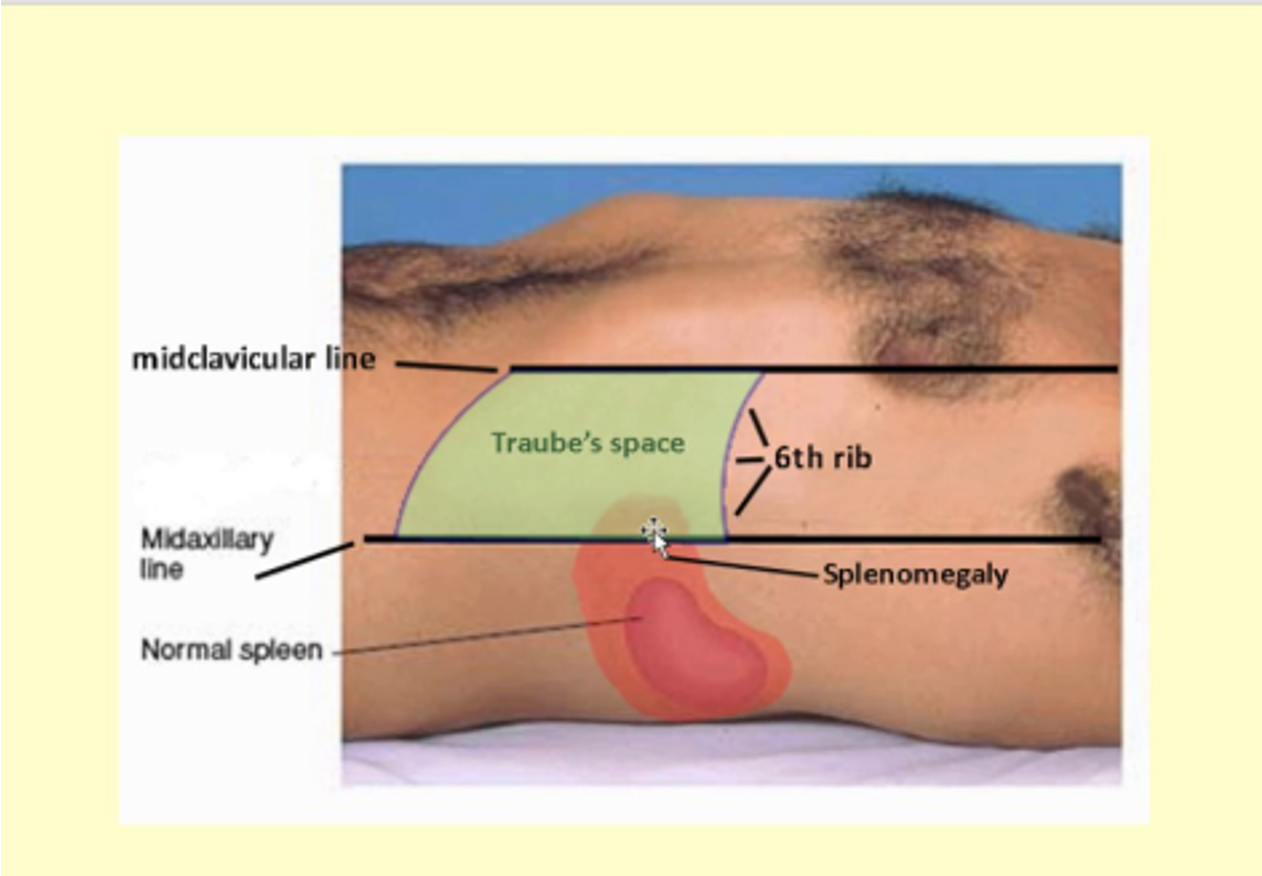
What is castell’s point?
Intersection of left subcostal margin & anterior axillary line
What is the triangle of traube?
Bordered laterally by anterior axillary line, superiorly by 6th rib & inferiorly by left costal margin
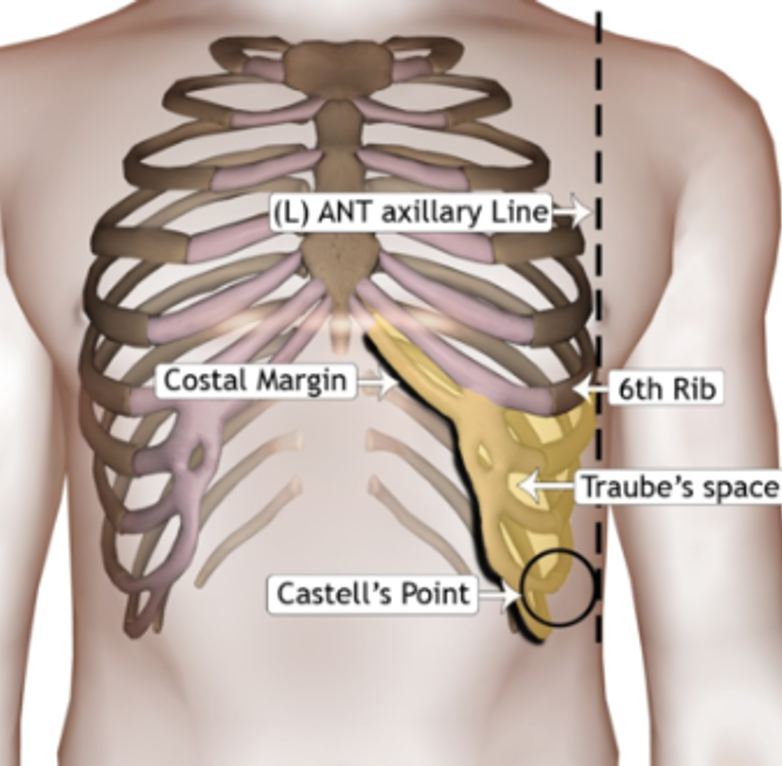
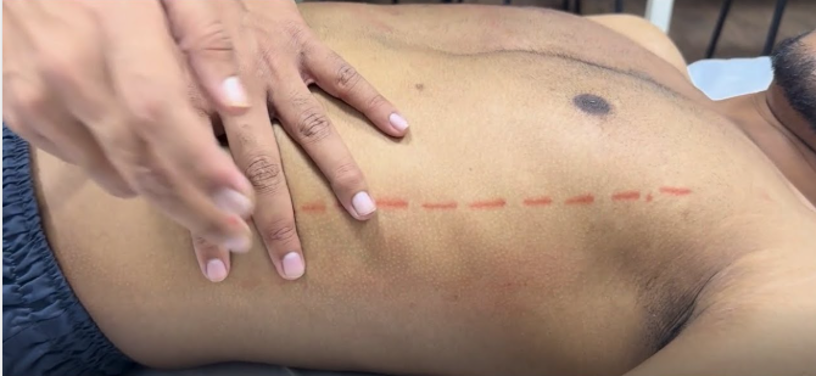
How do you percuss the spleen?
Have pt expire & percuss the lowest interspace in left AAL, usually tympanic → ask pt to take deep breath in & percuss, tympanic if spleen is normal (positive if dull with inspiration)
How does a gastric bubble sound to auscultation?
Tympany lower in pitch than tympany of the intestine
Where do gastric bubbles appear?
Left lower anterior rib cage & left epigastric region
What is in situs inversus?
Organs are reversed & gastric air bubble is on the right & liver dullness is on the left
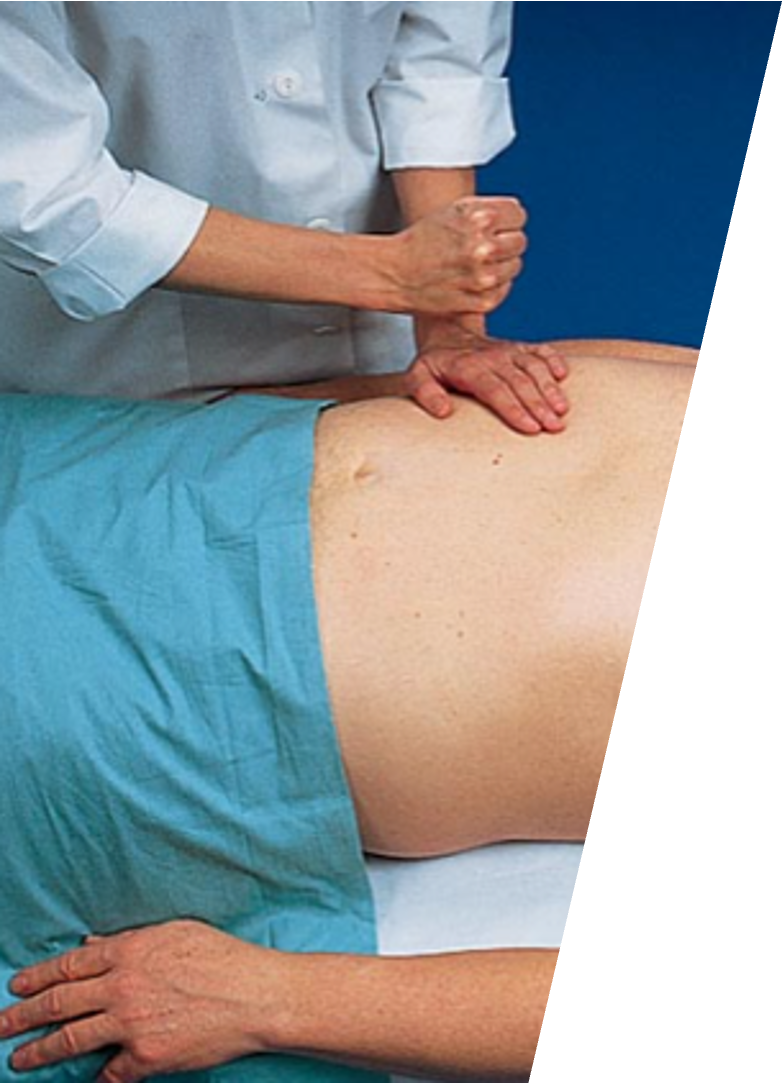
What is kidney percussion / CVA tenderness / Murphy’s punch?
With pt sitting on exam table, use heel of closed fist to strike firmly over costovertebral angles; tenderness often associated with renal disease
What is fluid wave?
Ask assistant to press edge of hand firmly down midline of abdomen → tap on one flank sharply w/ finger tips & feel opposite flank for an impulse transmitted through the fluid
*fluid wave (succession splash) suggests ascites
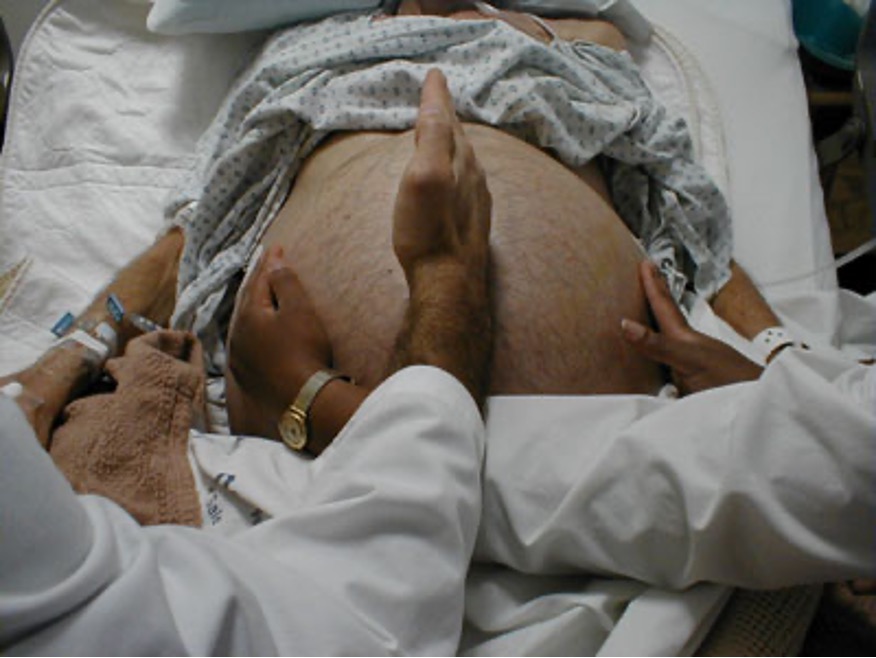
How do you perform shifting dullness?
Percuss abdomen to outline areas of dullness & tympany → have pt roll away from you & percuss again → if dullness has shifted to areas of prior tympany, there is excess peritoneal fluid
What does shifting dullness suggest?
Ascites d/t hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver disease
What does rebound tenderness indicate?
Peritoneal irritation, appendicitis
How does pain with appendicitis present?
Pain may start around periumbilical area, resolves for 6 hrs then returns with intensity in McBurney’s point for 24036 hrs then disseminates through abdomen
What does involuntary guarding / rigidity of abdominal wall suggest?
Advanced peritonitis → acute or surgical abdomen
What is icterus?
Yellow discoloration of sclera, assoc w/ liver disease
What is bilirubinuria?
Golden/brown discoloration of urine
What can increased systemic estrogen cause?
Gynecomastia, spider angioma (dilated arteriole MC on skin of upper chest), testicular atrophy
What causes varices?
Blood finds alternative pathways back to heart that do not pass through liver due to portal HTN; MC via splenic & short gastric vein through esophageal venous plexus enroute to SVC
What are the MC varices seen in portal HTN?
Esophageal varices
What causes caput medusae?
Blood utilizes recanalized umbilical vein to direct blood through dilated superficial veins in abd wall to get back to the heart, seen in portal HTN
What is a tremor of the had when the wrist is extended, seen in severe liver disease?
Asterixis
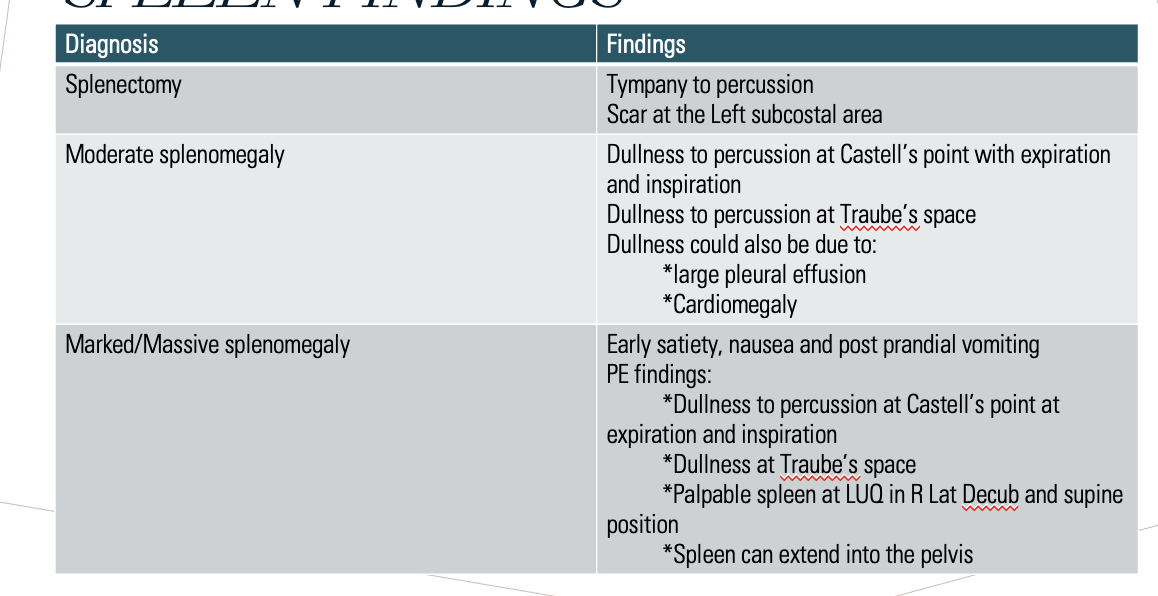
Spleen findings
What kind of hernia is a surgical URGENCY?
Incarcerated (tender/nontender & non reducible)
What kind of hernia is a surgical EMERGENCY?
Strangulated (very tender & non reducible)
How do abdominal hernias normally appear?
Nontender & reducible
What is a palpable or visible mass at the site of a surgical scar, more likely to happen in patients with uncontrolled DM or high dose steroid users?
Incisional hernia
How would an inguinal hernia appear?
Palpable/visible mass in lower medial abdomen
What is an umbilical hernia?
Palpable/visual nodule or mass replacing the umbilicus
What does an umbilical hernia that points upward indicate?
Pregnancy
What does an umbilical hernia that points downward indicate?
Ascites
What is a palpable pulsatile mass in midline, epigastric area with a bruit, usually associated with longstanding HTN & diminished pulses in extremities?
*PE often unsatisfactory, must order CT w/ contrast
AAA
What condition is associated with the following presentation?
palpable nontender mass RUQ (courvoiser’s sign) near murphy’s point
palpable gallbladder with jaundice
associated with: jaundice, clay colored stool, & darkened urine
Periampullary carcinoma
What are common, SC fleshy nodules that remain present with contraction of abdominal muscles, & can be accentuated when completing Carnett’s sign?
Lipoma
What is hepatomegaly?
Liver > 14 cm in right MCL
What is dullness to percussion at castle’s point & traube’s space?
Splenomegaly
What is Carnett’s sign?
Positive = abd pain gets worse when abd wall gets more tense → somatic type of pain
Negative = pain dec → intra abdominal cause of pain (visceral)
How would a distended urinary bladder appear?
Dullness to percussion & fullness in suprapubic area, enlarged prostate on DRE in men (d/t obstruction from BPH)
What is a mass?
> 3cm
What is a nodule?
< 3 cm
What should you think of with palpable gallbladder + pain + jaundice?
Periampullary carcinoma