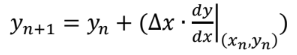AP CALC BC COLD QUIZ
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Definition of absolute value
√x^2
Definition of the derivative:
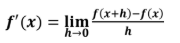
Alternate form of definition of derivative
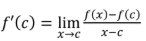
Point slope form of a line
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
Definition of contiunity
1) f(c) is defined
2) limx→c f(x) exists;
3) limx→c f(x) = f(c).
Average Rate of Chage
f(x) AROC = f(b)-f(a)/b-a
Intermediate Value Theorem Conditions
continuous on a closed interval
MVT Conditions & Equation
continuous on [a,b] and differentiable (a,b)
f'(c)=f(b)-f(a)/b-a
Rolles Theorem
f(a)=f(b) -> f'(c)=0
d/dx [c]
0
d/dx [x^n]
nx^n-1
d/dx [f(x)g(x)]
f(x)g′(x) + g(x)f′(x)
d/dx [f(x)/g(x)]
g(x)f'(x)-f(x)g'(x)/g(x)^2
d/dx [f(g(x))]
f'(g(x)) * g'(x)
d/dx sinu
cosu (du/dx)
d/dx cosu
-sinu (du/dx)
d/dx tanu
secu^2(du/dx)
d/dx secu
secutanu(du/dx)
d/dx cotu
-cscu^2(du/dx)
d/dx cscu
-cscucotu(du/dx)
EVT conditions
continuous on [a,b]
Definiton of a Critical Number
f'(c)=0 or undefined
Finding Absolute Max/Min
Candidates Test
f is ___ if x1
increasing
f is ___ if x1
decreasing
If f'(x)>0 then f is
increasing
If f'(x)<0 then f is
decreasing
If f'(x)=0 then f is
constant
if f'(x) changes from negative to positive then its a ____ of f
relative minimum
if f'(x) changes from positive to negative then its a ____ of f
relative maximum
f is ___ if f'(x) is increasing
concave up
f is ___ if f'(x) is decreasing
concave down
if f''(x)>0 then f is ___
concave up
if f''(x)<0 then f is ___
concave down
Definition of Inflection Point
f''(c)=0 or DNE
f'' changes between positive and negative
f' changes between increasing and decreasing
if f'(c)=0 and f''(c)>0 then f is ___
relative minimum
if f'(c)=0 and f''(c)<0 then f is ___
relative maximum
(f^-1)'(a)
1/f'(f^-1(a))
if f(g(x))=x then g'(x)
1/f'(g(x))
velocity
s'(t)
speed
|v(t)|
acceleration
v'(t) = s''(t)
displacement
b
∫v(t)dt
a
total distance
b
∫|v(t)dt|
a
speed is increasing when
velocity and acceleration have the same sign
speed is decreasing when
velocity and acceleration have the opposite sign
Left Riemann Sum underapproximates when f(x)
increasing
Left Riemann Sum overapproximates when f(x)
decreasing
Right Riemann Sum underapproximates when f(x)
decreasing
Right Riemann Sum overapproximates when f(x)
increasing
Trapezoidal Riemann Sum underapproximates when f(x)
concave down
Trapezoidal Riemann Sum overapproximates when f(x)
concave up
∫ x^ndx
x^(n+1)/(n+1) + C
∫ sinudu
-cosu + C
∫ cosudu
sinu + C
∫ sec^2(u)du
tanu + C
∫ csc^2(u)du
-cotu + C
∫ sec(u)tan(u)du
secu + C
∫ csc(u)cot(u)du
-cscu + C
b
∫f(x)dx
a
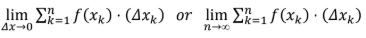
b
∫f'(x)dx
a
f(b)-f(a)
1st FTC
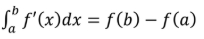
x
d/dx∫f(t)dt
a
f(x)
2nd FTC
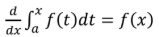
2nd FTC chain rule
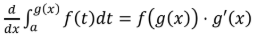
Average Value
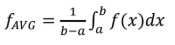
∫1/u du or ∫du/u
ln|u| + C
∫tanu du
-ln|cosu| + c
∫cotu du
ln|sinu| + c
∫secu du
ln|secu + tanu| + C
∫cscu du
-ln|cscu + cotu| + c
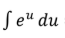
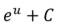
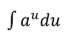
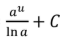
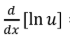
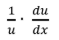
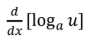
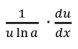
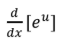
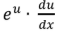
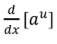
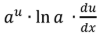
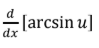
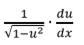
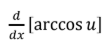
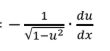
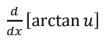
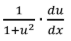
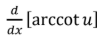
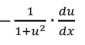
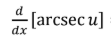
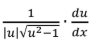
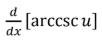
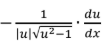
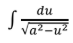
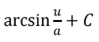
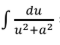
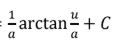
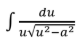
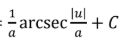
L’Hopital’s Rule

Volume by cross sections
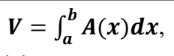
A semi-cricle
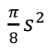
A isosceles w/ leg as base
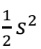
A equilateral triangle
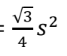
A isosceles w/ hypotenuse as base
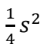
Volume around a horizontal axis by discs
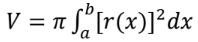
Volume around a horizontal axis by washers
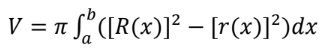
Length of arc for functions
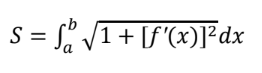
Integration by parts
Euler’s Method