Cell biology
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What are the features of eukaryotic cells?
Contain their genetic material enclosed in a nuclues
Have a:
cell membrane
cytoplasm
nuclues
What are the features of prokaryotic cells?
The genetic material is not enclosed in the nuclues (DNA strands or plasmids)
Much smaller
Have a:
cell membrane
cell wall
cytoplasm
What are the animal cells sub-cellular structures?
Nucleus - contains genetic material that controls the activities of the cell
Cytoplasm - gel like substance where most the chemical reactions take place and contains enzymes that control reactions
Cell membrane - holds the cell together and controls what goes in and out
Mitochondria - where most the aerobic reactions take place which transfers energy to cells
Ribosomes - where protiens are made
What are the plant cells sub-cellular structures?
Cell wall - made of cellulose, supports and strengthens cell
Permanent vacuole - contains cell sap (mixture of sugars and salts)
Chloroplast - allows photosynthesis to occur and contains chlorophyll for capturing light energy
Required pratical 1: microscopes
Place slide onto the stage and clip it into place
Select the lowest power objective lens (4x)
Position the objective lense by the coarse focusing dial to be almost touching the slide
Look through the eye piece and slowly turn the coarse focusing dial to increase the distance between the objective lens and slide to make the cell come into focus
Use the fine focusing dial to bring the cell into clear focus
What are the parts of a optical microscope?
Stage - the platform where slides are placed for observation and have clips to hold the slides into place
Lamp - passes up light into the slide (some may have a mirror to reflect light instead)
Objective lenses - magnify the image of the specimen by 4x, 10x and 40x
Eyepiece - where the viewer looks through to see the magnified image and contains a eye lense which magnifys by 10x
Coarse focussing dial and fine focussing dial
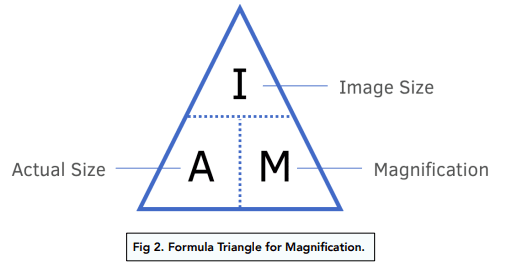
Calculate the total magnification
Magnification of the eyepiece lens x magnifiaction of the objective lens
What are the advantages of the electron microscope over the light microscope?
Light microscopes
limited magnification
limited resolution (blurry)
Electron microscopes
greater magnification
greater resolution
Calculation of magnifiaction of a microscope
Magnifiaction = size of image/size of real object
What is cell specialisation?
Adaptions which help them to carry out a particular function
Cells that have been specialised are called differentation
Most animal cells differentiate at an early stage
Most plant cells retain the ability to differentiate through out life
Sperm cell specialisation
Fertilizes the ovum
Long tail and streamlined head to swim easier
Contain mitochondria for energy to swim
Contain enzymes to digest through the ovum
Nerve cells specialisation
Sends electrical impulses around the body
Long axon that carries electrical impulese
Axon is covered in myelin which insuates the axon and speeds up transmission of nerve impulses
End of the axon has synapses which are junctions at the end that pass impulses to one nerve cell to another
Has dendrites which increase the surface area so nerve cells can connect easily
Muscle cells specialisation
Contract
Contain protien fibres to change their length eg get shorter to contract
Have mitochondria to provide energy for contraction
Root hair cells specialisation
Absorb water and minerals
Increases the surface area of the root for more absorbtion
Do not contain chloroplasts
Xylem cells sepcialisation
Carrywater and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves
Thick walls containing lignin which provide support to the plant
End walls between the cells are broken down to form a long tube for water and minerals to flow up easily
No nuclues, vavuole or chloroplast (no internal structure) for water and minerals to flow easier
Phloem cells specialisation
Carry disolved sugars up and down the plant
Phloem vessle cells
No nucleus and limited cytoplasm allow dissolved sugars to move through the cell
Pores called sieve plates allow dissolved sugars to move through the cell
Each have a companion cell connected by pores which provide mitochondria
What are chromosomes?
In the nuclues we fine chromosomes which are made of the molecule DNA
Body cells contain two of each chromosome which are paired (23 paire)
Each chromosome carries a large number of genes which determine our features
What is the cell cycle?
Cells have to be able to divide which is the cell cycle
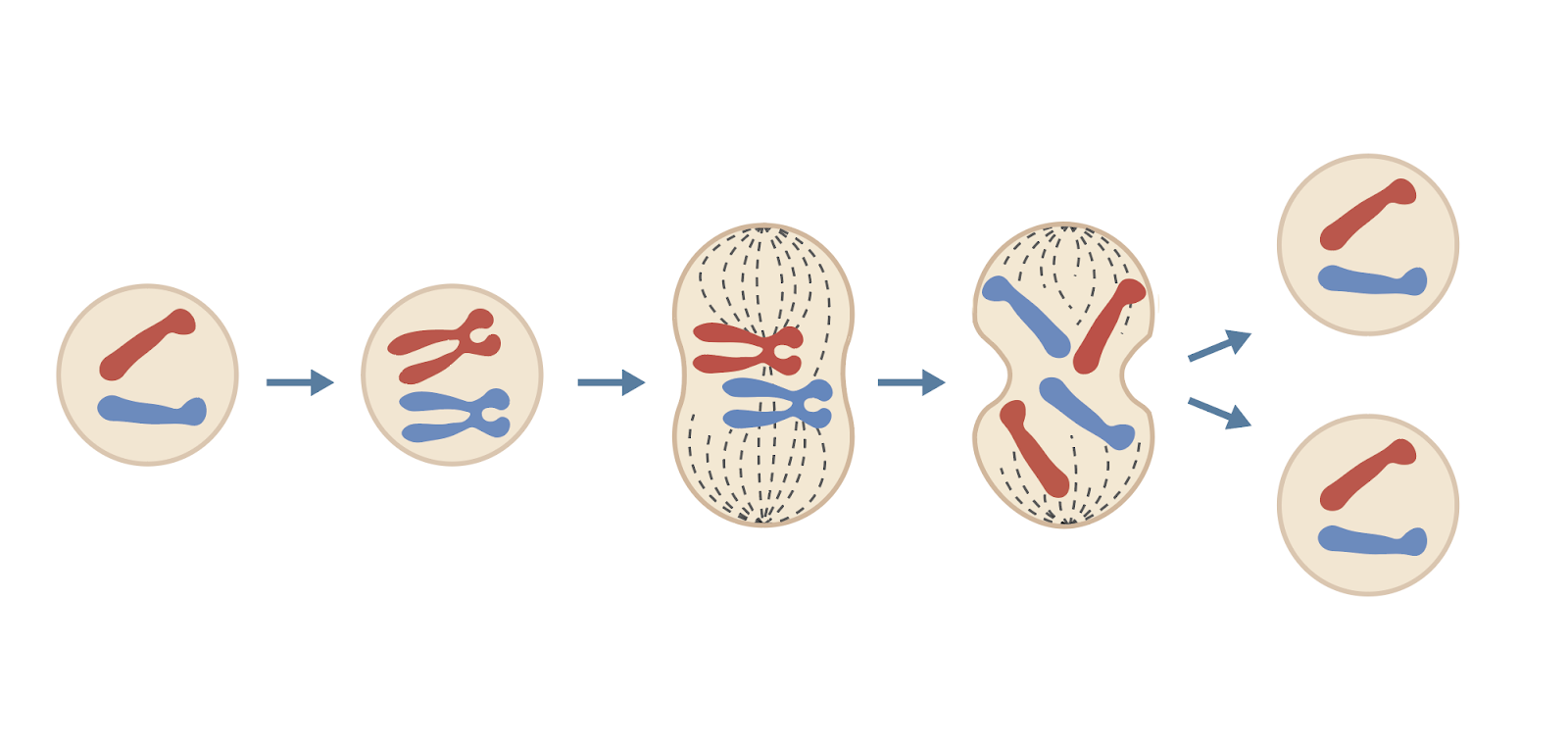
What is the mitosis cell cycle?
The DNA replicates to form two copies of each chromosome and the cell grows and copies its internal structure
One set of chromosomes are pulled to each end of the cell and the nucleus divides
The cytoplasm and the cell membrane divide to form two identical cells
Function of mitosis
Essential for growth and development of multicellular organisms
Takes place when a organism repaires itself
Occurs during asexual reproduction
What are stem cells?
Any cell that is undifferentiated and is capable of differentiating into any types of body cell
What is the function of stem cells from embryos?
Early-stage embryos contain stem cells and is capable of differentiating into any type of body cell
What is the function of stem cells in adult bone marrow?
The stem cells in bone marrow differentiate to form cells found in our blood eg white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets
What is the function of stem cells in meristem plants?
The stem cells in meristem plants can be found in the root and can differentaite into any type of plant and carry this ability through out its life
Stem cell treatments - bone marrow transplant
Bone marrow transplant - treats leukaemia (bone marrow cancer)
Exisiting bone marrow destroyed with radation
Transplant of new bone marrow
Stem cells in new bone marrow divide to form new bone marrow
Problems:
Patient must be compatible with the donor otherwise whiteblood cells may attack the patients body
Viruses may be passed on
Stem cell treatements - therapeutic cloning
An embryo is produced with the patients genes
Stem cells from the embryo can be transpanted into the patient without being rejected
Once inside the patient the stem cells can differentiate to replace cells which have stopped working correctly
Can be useful for medical conditions such as diabetes and paralysis
Some people may have ethical objections to this procedure
Stem cell treatments - cloneing plants
Stem cells from meristems in plants can be used to produce clones of plants quickly and economically
-Rare species can be cloned to protect against extinction
-Crop plants with special features such as disease resistance can be cloned to produce large number of identical plants for farmers
What is diffusion?
The spreading out of particles resulting in a net movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration through the cell membrane
Describe the diffusion of oxygen
Cells are surrounded by a high concentration of oxygen
Oxygen cells move into the cells through diffusion (high concentration to low concentration)
Describe the diffusion of carbon dioxde
-the diffusion oxygen is used to generate energy for the cell in respiration and this then produces carbon dioxide
-this means there is a higher concentration of carbon inside the cell then outside
-so the carbon dioxide diffuses out of the cell (high concentraon to a low concentration)
Describe the diffusion of urea
-urea is a waste product produced in cells
-it diffuses out the cell (high concentraon to a low concentration) into the blood plasma to be excreted by the kidneys
What can effect the rate of diffusion?
The difference in concentration
The greater the concentration gradient(the amount of molecules), the faster the diffusion takes place (more molecules diffuse through)
The temperature
The higher the temperature, the greater the rate of diffusion
Particles have more kinetic energy and move faster
Surface area of the membrane
The larger the surface area the greater the rate of diffsion as more molecules can pass through
Surface area to volume ratio
What is osmosis
The diffusion of water from a dilute solution (contain a high concentration of water) to a concentrated solution (contain a low concentration of water) through a partially permeable membrane (allow some molecules to pass through but not all molecules)
Animal cell - increase of water in a cell - increase or burst
Plant cell - increase of water in a cell - cell wall prevents it from bursting and instead swells - this is called turgid
Animal and plant cell - decrease of water in a cell - shrink - this is called flaccid
Required pratical 3: effects of osmosis on plants
Peel a potato
Use a cork border to produce three cylinders of potato
Use a scalpel to trim the cylinders to the same length(3cm)
Measure the lengh with a ruler and weigh it to find the mass
Place each cylinder into a test tube and add 10cm of a 0.5 molar sugar to the first test tube, 0.25 to the second and distalled water (contains no dissolved substances) to the third
Leave overnight to allow osmosis to take place
Remove cylinders and roll onto a paper tell to remove Surface moisture
Measure the length and mass of the cylinder again
Percentage change calculation
% change = change in value/original value x 100