ap psych - unit 5
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:09 PM on 3/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
1
New cards
effortful processing
active processing of information that needs sustained conscious effort and requires attention
2
New cards
automatic processing
the unconscious processing of well-learned material (basically muscle memory)
3
New cards
deep processing
processing information with consideration to its meaning which leads to better recall
4
New cards
shallow processing
uses surface characteristics to process information
5
New cards
structural shallow processing
encoding information with the use of visual and physical characteristics
6
New cards
phonemic shallow processing
encoding information using auditory characteristics
7
New cards
selective attention
the ability to focus on one particular stimuli while blocking out others
8
New cards
divided attention
* the ability to focus on multiple stimuli at the same time
* requires more automatic processing than selective attention
* requires more automatic processing than selective attention
9
New cards
metacognition
the ability to be aware and control of your own thoughts and cognitive processes
10
New cards
short-term memory
* the type of memory that can only be stored for a brief period of time
* the capacity for short-term memory is seven plus/minus two
* the capacity for short-term memory is seven plus/minus two
11
New cards
long-term memory
an unlimited capacity for memory that can store it for sustained periods of time
12
New cards
explicit memory
stored memory of facts that are made in the hippocampus
13
New cards
semantic explicit memories
memory of facts, ideas, and concepts
14
New cards
episodic explicit memories
memories of personal experiences
15
New cards
implicit memories
type of long-term memory that is remembered unconsciously
16
New cards
sensory implicit memories
the ability to retain sensory information even after the stimulus has ended
17
New cards
echoic sensory memories
memory of sound that lasts for about three to four seconds
18
New cards
iconic sensory memories
memory of visual stimuli that lasts for about 1/4th to 1/2th of a second
19
New cards
prospective sensory memories
remembering to perform an action at a certain time
20
New cards
flashbulb memories
a clear memory of an emotionally significant event
21
New cards
elizabeth loftus
associated with research on false memories
22
New cards
encoding
process of sensing, processing, and storing information
23
New cards
visual encoding
process of remembering visual images + forgotten easily
24
New cards
acoustic encoding
processing and encoding of sound + somewhat forgotten easily
25
New cards
semantic encoding
when a word, pictures, or phrase is encoded based on the basis of its meaning rather than its sound/vision
26
New cards
maintenance rehearsal
process of repeatedly thinking about or verbalizing a certain piece of information
27
New cards
elaborative rehearsal
process of using active thinking about the meaning of the term
28
New cards
self-reference effect
when someone applies a situation to themselves, they are more likely to remember what the situation is
29
New cards
storage
the process of maintaining or keeping information readily available
30
New cards
Atkinson-Shiffrin Model
model that shows information going from shallow to deep memory
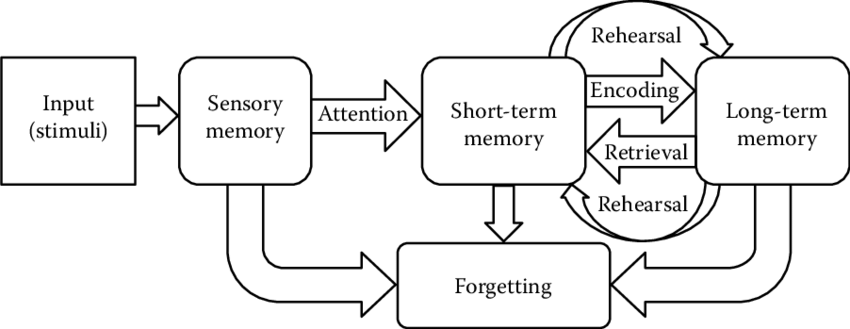
31
New cards
sensory memories
events coming from the environment that can become a part of short-term memory
32
New cards
chunking
process of grouping information to be stored or processed as single concepts
33
New cards
hierarchies
a method used to organize information by starting with broad information and then into specific classes
34
New cards
schemas
a concept of framework that helps an individual to make sense of information
35
New cards
concept
mental grouping of events, people, and similar things p
36
New cards
prototype
a mental image or the best representative of a certain category
37
New cards
anterograde amnesia
the inability to form new memories but remembers past memories
38
New cards
long-term potentiation
strengthening of neural connections which creates a longer-lasting memory
39
New cards
retrieval
process of recalling memories such as feelings, images, and events
40
New cards
recall
process of bringing information from stored memories into conscious awareness
41
New cards
recognition
when someone notices something that they have previously learned
42
New cards
relearning
how much faster someone can learn material has been previously learned and then forgotten
43
New cards
serial-position effect
people tend to remember information in a list that is mentioned first or last
44
New cards
primacy effect
remembering the first thing in a list that was said
45
New cards
recency effect
remembering the last thing in a list that was said
46
New cards
mnemonic devices
tools used to help remember an idea or phrase and can enhance memory and retention
47
New cards
method of loci
a mnemonic device in which a person memorizes information by placing each item in different locations
48
New cards
tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon
the temporary inability to remember information s
49
New cards
semantic network theory
states that a person’s brain likes to form new memories by connecting its meaning to other memories and their meanings
50
New cards
priming
activation of a memory by association
51
New cards
context-dependent memory
when someone remembers information in the same place that they encoded it
52
New cards
state-dependent memory
what someone learns in one state will be easier to recall when in that same state
53
New cards
mood-congruent memory
when humans store memories about an event, they also store the emotion felt in that memory
54
New cards
constructive memory
memories can be false details of real events or a completely made up event
55
New cards
recovered memory phenomenon
individuals can suddenly remember repressed memories (usually via therapy)
56
New cards
spacing effect
people learn material more easily and effectively when it is studied many times over a long period of time
57
New cards
testing effect
when someone has enhanced memory after retrieving information rather than rereading it
58
New cards
herman ebbinghaus
a psychologist that studied human memory and made the forgetting curve
59
New cards
forgetting curve
people forget 75% of the information that they learn within one day (without relearning/rehearsing)
60
New cards
retroactive interference
when it is hard to recall old information because of new information
61
New cards
proactive interference
when it is hard to recall new information because of old information
62
New cards
retrograde amnesia
when someone is unable to recall recent memories/memories of their general past
63
New cards
source amnesia/misattribution error
an individual’s inability to remember how they learned previously acquired information
64
New cards
deja vu
a person’s false sense that they have experienced a situation before
65
New cards
misinformation effect
a person’s recollection of an event is negatively impacted and becomes less accurate because of information after the event
66
New cards
motivated forgetting
can be conscious or unconscious in order to shy away from unacceptable behaviors or painful memories
67
New cards
hippocampus
responsible for the formation of memory and processes explicit memories for storage
68
New cards
what happens when there is damage to the left side of the hippocampus?
an individual will have trouble remembering verbal information
69
New cards
what happens when there is damage to the right side of the hippocampus?
an individual will have trouble remembering visual information
70
New cards
frontal lobes
processes incoming auditory and visual information + makes sense of new information
71
New cards
thalamus
helps encoding sensory memory into short-term memory
72
New cards
cerebellum
stores implicit memories that are formed by classical conditioning and conditioned reflex
73
New cards
basal ganglia
helps form procedural memories
74
New cards
amygdala
the emotions produced by the amygdala can fuel the brain which can cause memories to last longer
75
New cards
algorithm
step by step method that guarantees to solve a particular problem
76
New cards
heuristic
methods used to quickly solve a problem and are less effective than algorithms
77
New cards
mental set
individuals try to solve a problem the same way all the time because it has worked in the pastfi
78
New cards
fixation
the inability to look at a problem with a different perspective
79
New cards
intuition
sensing something without a direct reason and basically an automatic thought
80
New cards
insight (discovered by Wolfgang Kohler)
when an individual suddenly understands something
81
New cards
inductive reasoning
reasoning from something specific to something general
82
New cards
deductive reasoning
reasoning from something general to something specific
83
New cards
convergent thinking
logical way of thinking; used in IQ and intelligence tests
84
New cards
divergent thinking
creative way of thinking
85
New cards
functional fixedness
the tendency to only think of the familiar functions of an object
86
New cards
availability heuristic
the ability to easily recall immediate examples about something
87
New cards
representativeness heuristic
when someone judges someone based on how much they match their prototype
88
New cards
confirmation bias
tendency of individuals to support or search for information that aligns with their opinions and ignore information that doesn't
89
New cards
belief perseverance
the tendency to hold onto a belief even if it has lost its credibility
90
New cards
belief bias
the tendency for our preexisting beliefs to distort logical thinking
91
New cards
self-serving bias
a person attributes positive outcomes to their own doing and negative outcomes to external factor
92
New cards
attentional bias
when people’s perceptions are influenced by recurring thoughts
93
New cards
actor-observer bias
a person might attribute their own actions to external factors and the actions of others to internal factor
94
New cards
anchoring bias
an individual relies heavily on the first piece of information given when making a decision
95
New cards
hindsight bias
when you think you knew something all along after the outcome has occurred
96
New cards
framing
a cognitive bias in which people decide on an option based on whether or not a positive or negative connotation is given
97
New cards
g factor (charles spearman)
underlines specific mental abilities that can be measured on an intelligence test
98
New cards
factor analysis
a statistical procedure identifying *clusters* of items that could measure your intelligence
99
New cards
charles spearman
found that if you have a high intelligence in one of the subjects, you have an overall high general intelligence
100
New cards
L.L. Thurstone
thought that intelligence could be broken up into different clusters: world fluency, verbal comprehension, spatial ability, perceptual speed, numeric ability, inductive reasoning, and memory