Lighting Systems Final
5.0(2)Studied by 9 people
Card Sorting
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:36 AM on 5/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
Richard Kelly’s Layers of Light
* Focal Glow
* Ambient Luminescence
* Play of Brilliants
* Ambient Luminescence
* Play of Brilliants
2
New cards
Contemporary/ Modern Layers of Light
* Focal
* Task
* Daylight
* Ambient (General)
* Decorative
* Task
* Daylight
* Ambient (General)
* Decorative
3
New cards
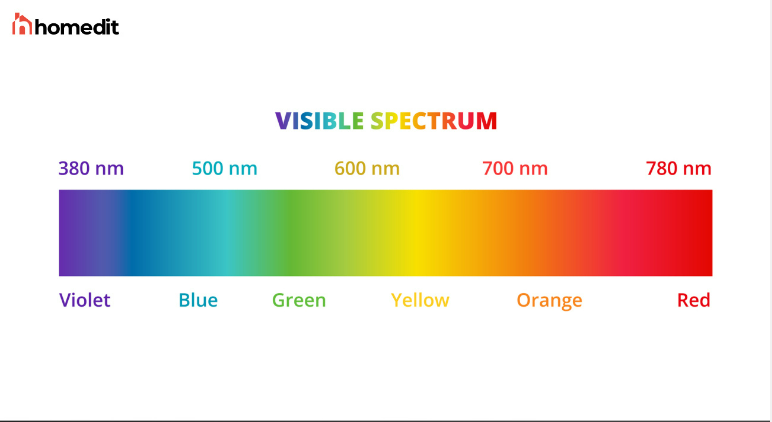
(Color) Spectrum
ROYGBIV
Spectral color is light of a specific wavelength, with a deep chromatic saturation.
Spectral color is light of a specific wavelength, with a deep chromatic saturation.
4
New cards
(Color) Is color emitted from a lamp an additive or subtractive system?
Additive- by adjusting and mixing intensity, any color can be created
5
New cards
(Color) Kelvin- Color Temperature (CCT)
* cool temperatures are higher in number and are energizing with daytime alertness
* warm temperatures are lower in number and are inviting, relaxing, and represent sunset and nighttime lighting
* warm temperatures are lower in number and are inviting, relaxing, and represent sunset and nighttime lighting
6
New cards
(Color) Ultraviolet and Infrared Wavelengths
Ultraviolet
* High frequency, shorter wavelengths on the right side of visible light on the spectrum
* Black lights, tanning lights, laser
* 380 nm
Infrared
* Longer wavelengths on the left side of visible light on the spectrum
* Makes up a bigger portion of sunlight than visible and UV
* Night vision lights 4. 900-700 nm, 3D spatial sensing
* High frequency, shorter wavelengths on the right side of visible light on the spectrum
* Black lights, tanning lights, laser
* 380 nm
Infrared
* Longer wavelengths on the left side of visible light on the spectrum
* Makes up a bigger portion of sunlight than visible and UV
* Night vision lights 4. 900-700 nm, 3D spatial sensing
7
New cards
(Physics & Basic Photometrics) Light Source
Device that emits light; it can also refer to the technology that produces light (ex. LED)
8
New cards
(Physics & Basic Photometrics) Bulb
Outer glass of a lamp
9
New cards
(Physics & Basic Photometrics) Lamp
Replaceable light source that connects to a holder (or socket) and a source of electricity
10
New cards
(Physics & Basic Photometrics) Luminaire
Complete the lighting device, including the source, mechanical and electrical connections, optics, and any auxiliary devices required
11
New cards
(Physics & Basic Photometrics) Light
Energy, typically described as part of electromagnetic radiation between 380 and 780 nm, that can excite the retina and produce a visual sensation
12
New cards
(Physics & Basic Photometrics) Luminous Flux
Light emitted in all directions by a source; measured in Lumens (lm)
13
New cards
(Physics & Basic Photometrics) Luminous Intensity
Light emitted in a specific direction by a source; measured in Candelas (cd)
14
New cards
(Physics & Basic Photometrics) Luminous Efficacy
Measure of how well a light source produces visible light; measured in Lumens per Watt (lm/W)
15
New cards
(Physics & Basic Photometrics) Illuminance
Density of light at any given point on a surface; measures in Footcandles (fc) or Lux
16
New cards
Density of light at any given point on a surface; measures in Footcandles (fc) or Lux
Light that is reflected from a surface in a given direction (towards the eyes); measured in Candelas per Square Meter (cd/m^2)
17
New cards
(Physics & Basic Photometrics) Exitance
Total quantity of light emitted, reflected, or transmitted in all directions from a surface; measured in Lumens per Square Foot (lm/sf)
18
New cards
(Physics & Basic Photometrics) Color Rendering Index (CRI)
Accounts for the difference of white lights - 80 is good - 90 is great - 100 is perfect
19
New cards
(Reflectivity & Light) Specular vs. Diffuse
Specular
* reflection of light off a smooth surface (ex. mirror)
Diffuse
* scattered and comes from all directions
* reflection of light off a smooth surface (ex. mirror)
Diffuse
* scattered and comes from all directions
20
New cards
(Psychology of Lighting Effects) Approaches to Describing the Psychology of Lighting- Stimulus
* response
* Determine your program for the space
* How much stimulation appropriate for space
* Determine your program for the space
* How much stimulation appropriate for space
21
New cards
(Psychology of Lighting Effects) Approaches to Describing the Psychology of Lighting- Emotional
* response
* James Russel
* How we feel effects how we behave in a space
* James Russel
* How we feel effects how we behave in a space
22
New cards
(Psychology of Lighting Effects) Approaches to Describing the Psychology of Lighting- Environmental Cognition
* Kaplan and Kaplan
* Factors that drive human preference for environments
* Coherence and complexity
* Factors that drive human preference for environments
* Coherence and complexity
23
New cards
(Psychology of Lighting Effects) Approaches to Describing the Psychology of Lighting- Subjective Impressions
* John Flynn
* Nature of human response to lighting
* spacious/confinement, visual clarity/haziness, relaxation/activation, public/private
* Nature of human response to lighting
* spacious/confinement, visual clarity/haziness, relaxation/activation, public/private
24
New cards
(Psychology of Lighting Basics) Which lighting approaches are best for a type of space or creating a specific feeling for a space?
1. Impressions of Spaciousness
1. increases intensity and uniformity of lighting
2. high illuminance values on horizontal surfaces
2. Impressions of Perceptual Clarity
1. increasing the general illumination levels makes spaces feel more public
2. low illuminance values correlate to private space, where people are veiled in shadow and silhouette
3. Impressions of Relaxation
1. non-uniform downlighting
2. wall-lighting
3. lower light levels
4. warmer tones
4. Impressions of Privacy
1. non-uniform
2. lower brightness in zone of user
3. higher brightness in zone of user
4. high brightness in zones surrounding the user
5. wall lighting
25
New cards
(Daylighting) Sunlight vs Skylight
* Sunlight - direct beam of light from the sun
* Skylight - diffuse reflection (indirect) of sunlight in the atmosphere
* Skylight - diffuse reflection (indirect) of sunlight in the atmosphere
26
New cards
(Daylighting) Summer and Winter Solstices
* Summer - moment of the earth's tilt toward the sun is at a maximum
* Winter - moment when the earth's axis tilts is furthest away from the sun
* Winter - moment when the earth's axis tilts is furthest away from the sun
27
New cards
(Daylighting) Taking Advantage of Daylight
1\. Skylights
2\. Sawtooth Monitors - strategically angles away from the southern direct sunlight, but still allows for natural light to be let into the space
3\. Monitors - bring a lot of diffuse daylight in the space and minimize direct sunlight
4\. Clerestories - part of an interior wall rising above the adjacent roof with windows admitting light
5\. Tubular Skylight - spherical dome located on the roof connected to an adjustable cylindrical reflector to bounce light down the tube to a terminal diffuser
6\. Light Well - an open area or vertical shaft in the center of the building, bringing light into the lower floors or basement
7\. Side Lighting - as a window moves higher on a wall, the light can penetrate deeper into the interior - visual stimulation
2\. Sawtooth Monitors - strategically angles away from the southern direct sunlight, but still allows for natural light to be let into the space
3\. Monitors - bring a lot of diffuse daylight in the space and minimize direct sunlight
4\. Clerestories - part of an interior wall rising above the adjacent roof with windows admitting light
5\. Tubular Skylight - spherical dome located on the roof connected to an adjustable cylindrical reflector to bounce light down the tube to a terminal diffuser
6\. Light Well - an open area or vertical shaft in the center of the building, bringing light into the lower floors or basement
7\. Side Lighting - as a window moves higher on a wall, the light can penetrate deeper into the interior - visual stimulation
28
New cards
(Daylighting) Ways of Filtering Daylight
Drapery, shades, screens, blinds, louvers, awnings, overhangs, and season vegetation
29
New cards
(Distribution of Light) Glare vs. Sparkle
* Glare- not desirable; caused by light coming from the wrong direction - solutions: diffuser, physical barrier, reflector/refractor lens
* Sparkle - desirable; direct lighting in our field of view, providing variety and intrigue into your visual settings - direct sparkle, reflected sparkle, and transmitted sparkle
* Sparkle - desirable; direct lighting in our field of view, providing variety and intrigue into your visual settings - direct sparkle, reflected sparkle, and transmitted sparkle
30
New cards
(Distribution of Light) Primary Distribution Directions
1\. Direct - downward (concentrated and diffused)
2\. Indirect - upward (concentrated and diffused)
3\. Indirect/Direct - upward/downward (concentrated and diffused)
4\. Multidirectional - everywhere
2\. Indirect - upward (concentrated and diffused)
3\. Indirect/Direct - upward/downward (concentrated and diffused)
4\. Multidirectional - everywhere
31
New cards
(Distribution of Light) Wall Washing vs Wall Grazing
* Wall Grazing - accentuates texture and is a narrow spread Wall
* Washing - diffuse, wider spread, and hides texture and wall imperfections
* Washing - diffuse, wider spread, and hides texture and wall imperfections
32
New cards
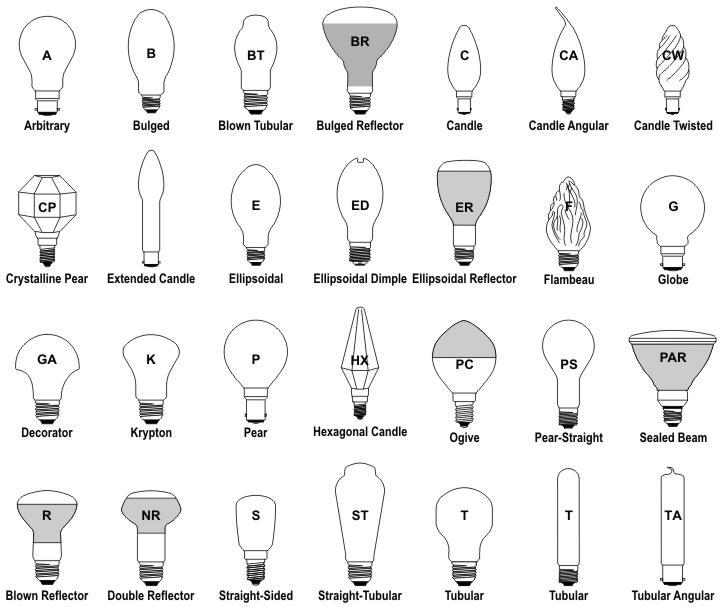
(Lamps) Types of Bulb Shapes
1. incandescent
2. fluorescent
3. compact fluorescent
4. HID
5. LED
33
New cards
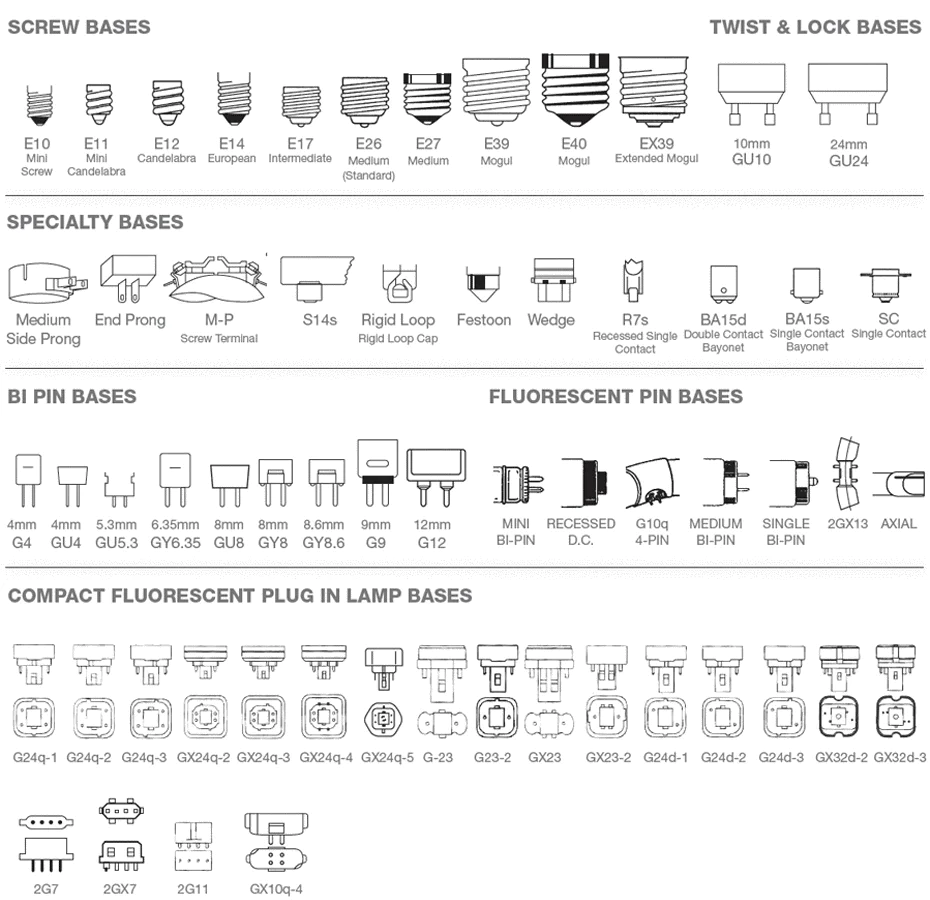
(Lamps) Types of Bases
1\. Typical American screw-in base (E26 or ES26)
- Edison-Style base - 26 represents that base thread outside diameter in mm
2\. Other common bases
- Candelabra (E12) - Intermediated based (E17) - Mogul base (E39)
- Edison-Style base - 26 represents that base thread outside diameter in mm
2\. Other common bases
- Candelabra (E12) - Intermediated based (E17) - Mogul base (E39)
34
New cards
(Light Control) Types of Contours, Reflectors, Lenses, Louvers, and Baffles
* Baffles and Louvers - shield glare from normal viewing angles
* Baffles: provide shielding in one direction
* Louvers: series of baffles used in multiple directions or in polar arrangements to shield from many directions
* Louvers and Reflectors - act as a barrier and redirect natural light so it isn't as harsh
* Baffles: provide shielding in one direction
* Louvers: series of baffles used in multiple directions or in polar arrangements to shield from many directions
* Louvers and Reflectors - act as a barrier and redirect natural light so it isn't as harsh
35
New cards
(Luminaires) What is a luminaire?
Complete unit that provides housing, lamp, control elements, peripheral equipment, and an electrical connection
36
New cards
(Luminaires) 5 Primary Types of Luminaires
1. Recessed
2. Semi-recessed
3. Surface Mounted (includes sconces)
4. Pendant Mounted
5. Track Mounted
37
New cards
What is Photometry?
The science of measuring light
38
New cards
What is the IES
Illuminating Engineering Society
39
New cards
What is LPD?
Lighting Power Density
40
New cards
Who would a designer consult with about lighting decisions?
Lighting Designer
41
New cards
Where would you find and read a luminaire cut/spec-sheet?
Through credible manufacturers
42
New cards
What is Ohm's Law?
I=V/R (current = voltage/resistance) measured in (Amperes = Volts/Ohms)
43
New cards
What is a circuit?
The pathway electricity follows
44
New cards
What is a conductor? What is used in most buildings?
An object or type of materials that allows the flow of charge (electric current) in one or more directions; copper is most commonly used in wiring applications
45
New cards
What is an insulator? What is used in buildings?
A material in which electric current does not flow freely; insulated wires
46
New cards
What is the difference between DC and AC current?
* Alternating Current (AC) flows in a single direction at a time, but that direction is reversed at regular intervals - AC is what our typical electrical supply and fixtures utilize
* Direct Current (DC) flows only in one direction
* Direct Current (DC) flows only in one direction
47
New cards
What are the different types of controls (electrical controls: like switches, dimmers, sensors, etc.)?
* Controls - devices that control the flow of electricity in a circuit
* manual switches, dimmers, programmable switches, timers, smart switches, occupancy sensors, photo/daylight sensors, central (building) controls
* manual switches, dimmers, programmable switches, timers, smart switches, occupancy sensors, photo/daylight sensors, central (building) controls
48
New cards
What is multi-way switching?
The interconnection of two or more electrical switches to control an electrical load (often, but not always, lighting) from more than one location
49
New cards
What are smart controls?
Controls that work in tandem with smart devices and apps networked to provide fine-tuned controlled lighting, dimming, and color
50
New cards
What are construction documents?
Construction documents are the primary means of communicating your design to your contractors and fabricators; define the quantities and qualities of, and relationships among, all materials required to construct a project
51
New cards
What are contract documents?
* Contract documents are general conditions of the contract for construction, drawing set, job book or project manual, owner-designer agreement, owner-contractor agreement, change orders, and certificate for substantial completion
* The set can range from a single sheet to potentially hundreds of sheets, and can include drawings that address the architecture, interiors, plumbing, mechanical systems, structural, and landscape designing for a project
* The set can range from a single sheet to potentially hundreds of sheets, and can include drawings that address the architecture, interiors, plumbing, mechanical systems, structural, and landscape designing for a project
52
New cards
Which type of drawing is most used to communicate a lighting plan?
RCP - reflected ceiling plan
53
New cards
What are lighting schedules used to communicate in a construction drawing?
Found in construction drawings - usually lists luminaire type, type code, manufacturer, any specific specs, quantity, and location
54
New cards
What does circuiting/switching indicate on a lighting plan?
Illustrates desired lighting control groupings and switch locations; if the lighting plan only included the luminaires, you will be relying on the electrician to determine the groupings, switching, and controls locations
55
New cards
What are specifications?
External documents assembled into a binder format that includes individual product cutsheets for luminaires, fixtures, and other relevant equipment
56
New cards
What is the purpose of a light map?
To introduce the exploration of lighting into a project; part of the schematic design phase and design proposal presentation