Cell Biology Test 2
1/99
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What part of the phospholipid molecule carries a negative charge?
phosphate
What does the enzyme scramblase do?
adds phospholipids to the ER membrane
The name of the enzyme responsible for rearranging phospholipids on newly created membranes is?
flippase
The name for the sugar coating on the outside of the cell is?
glycocalyx
Proteoglycans contain ...
one or more long polysaccharide chains
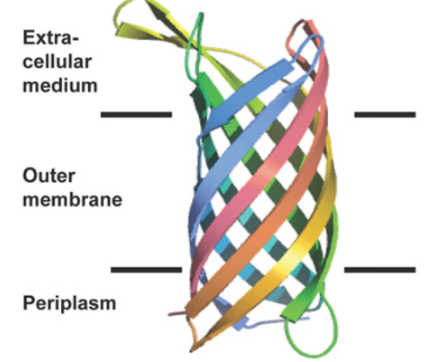
The type of transmembrane protein shown in this figure is a ....
beta barrel
Porins are a type of transmembrane protein structure found in the very most outer membrane of which cells?
bacteria
Cell membranes are transported by a process called?
vesicle budding and fusing
A membrane's orientation is always maintained?
True
A plasma membrane will be more fluid if it is made up of phospholipids with ...
shorter, unsaturated tails
Which molecules can successfully passively diffuse through the plasma membrane (select all which can pass through)?
small uncharged polar molecules (<50 Da)
small nonpolar molecules
Which substances can move via osmosis (select all)?
water
Channels transport molecules into cells after binding to the transmembrane protein?
False
A symport moves ...
more than one molecule type in one direction
Ca2+ and Na+ pumps are both ATPases, this is because they ...
hydrolyse ATP to ADP
Neurotransmitters are chemical signals, they are converted to electrical signals in the nerve cell but the signal needs to be converted back to a chemical signal to cross synaptic clefts because ...
electrical signals cannot cross the gap
The glucose-Na+ symport uses energy from ATP to move glucose into the cell
False
Hairs in the ear are responsible for hearing sounds?
True
In a concentration gradient substances move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration?
True
Which statements are correct (pick all the correct ones)?
Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cl- and H+ are the most important inorganic ions in cells.
Gradient proton pumps link the transport of one substance into the cell, with another exiting the cell
Na+ is the most common cation (positive charged ion) outside the mammalian cell; K+ is the most abundant inside.
Na+ outside the cell is balanced by extracellular Cl-; K+ is balanced by a number of different anions
Catabolism is a process of how many steps?
three
Glycolysis is the conversion of glucose to?
2 ATP, 2 NADH, and 2 pyruvate molecules
How many steps are involved in glycolysis?
10
Which enzyme converts glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 1,3-diphosphoglycerate, NADH and H+?
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Which enzyme catalyzes the 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate transfer of a phosphate to ADP, forming one molecule of ATP and a molecule of 3-phosphoglycerate?
Phosphoglycerate kinase
What process does pyruvate undergo to form acetyl Co-A?
oxidation
Select all the names by which the citric acid cycle is also known by (select all the correct answers)
TCA cycle
Krebs cycle
Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle
The products of the citric acid cycle are?
3 molecules of NADH, 1 of GTP, one of FADH2 and 2 molecules of CO2 are produced per turn
Which statement describes the role of citrate synthase?
Coverts acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate to form citrate
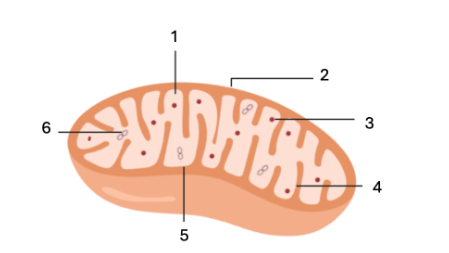
What feature does label 1 indicate?
matrix
What is the name of the process made up by the two components, the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis?
Oxidative phosphorylation
Which of the following complexes are transmembrane proteins? (select all the correct answers)
Complex III
Complex I
Complex IV
Ubiquinone oxidoreductase is also known as ...
Complex I
The electrochemical gradient forms in the ...
Intermembrane space
The mitochondrial inner membrane is folded into ...
cristae
Porins are water filled channels found on the mitochondrial ...
outer membrane
Which ETC complex does not pump H+ ions through the membrane?
Complex II
In total how many ATP molecules are created from one molecule of NADH going through the ETC?
3
What is the missing component from the equation:
Glucose + Oxygen → XXX + Water + Energy
Carbon dioxide

What process is this statement true for?
Anaerobic respiration
What feature is present in chloroplasts but not mitochondria?
thylakoid membranes
Chlorophylls are very effective photoreceptors because ...
they contain networks of alternating single and double bonds
Bacteriorhodopsin is a pigment of which color?
purple
The first step of photosynthesis begins with light being captured - this takes place in ...
photosystem II
The primary electron acceptor in photosynthesis is called ...
plastoquinone
Electrons are transferred to cytochrome B6F to photosystem I via ...
plastocyanin
In photosynthesis ATP is synthesized by?
ATP synthase
How many molecules of carbon dioxide are required for carbon fixation?
6
Complete the equation which summarizes photosynthesis:
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
The light-dependent stage is known as the carbon fixation cycle or the Calvin cycle.
False
Which feature makes up more than half a cell's volume?
cytosol
What is the function of the smooth ER?
The production of lipids and steroids
How do proteins 'know' where to go in the cell?
N-terminal signal peptides
The rough ER is made up of folded membranes called ...
cisternae
Which type of glycosylation is involved in secretory proteins?
O
Signal peptide peptidases are used to ...
cleave N-terminal signal peptides
The molecular switch Ran uses energy from ...
GTP
Where in the cell are TOM and TIM found?
mitochondria
Which is NOT a fate for receptor proteins?
phagocytosis
The process by which substances in membrane-bound vesicles are removed from the cell, into the extra-cellular space, is called?
exocytosis
Only eukaryotic cells use cell signaling?
False
Which is NOT a step in cell signaling?
transformation
Which are classes of membrane receptors - select all that are correct.
enzyme-coupled
ion-channel-coupled
G-protein-coupled
Which type of membrane receptor does the following describe?
'Hydrolysis of GTP to GDP inactivates the receptor.'
G-proteins-coupled
Phosphorylation of RTKs occurs ____ a signal molecule is bound [what is the missing word?]
after
Intracellular receptors bind to signals that are ...
small
Which of the following are examples of second messengers? [select all the correct answers]
cyclic AMP
calcium ion
Which of the following can occur during transduction?
phosphorylation cascade
What cell receptors does the poison strychnine bind to?
glycine
What is the name of the enzyme that naturally occurs in chili peppers, giving them their characteristic 'heat'?
capsaicin
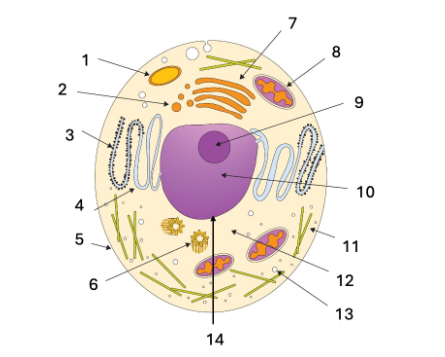
What is the name of structure #6?
centriole
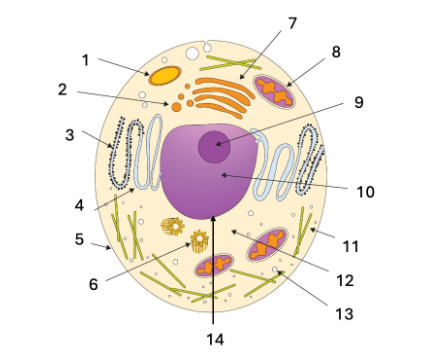
What is the name of the structures show in #11?
microtubules
Which cytoskeleton structure has a diameter of 10nm?
intermediate filaments
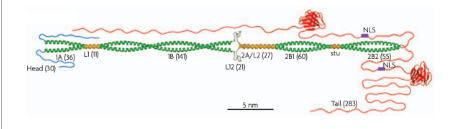
Where is the intermediate filament below located in the cell & how did you determine this?
This intermediate filament is found in the nucleus forming the nuclear lamina. This was determined by the nuclear localizing signals in the tails of this filament.
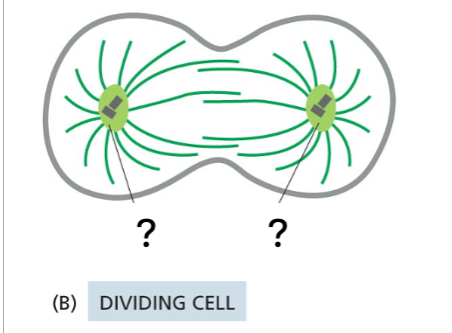
What is the name for the structures holding microtubules indicated by '?' in the figure below?
centrisomes
Which cell protrusions contain a loose bundle of 10-20 actin filaments?
filopodia
Actin filaments are two stranded helices, with a twist every how many nm?
37
In actin formation, if the numbers of ATP-bound monomers bind faster than the rate of ATP to ADP hydrolyses then the actin filament will grow, if the rate is the same it is called?
treadmilling
What is the name of the actin-binding proteins which uses ATP to move their cargo along an actin filament via a process of binding, detachment, and rebinding?
myosins
The molecular basis of muscle contraction is called the ...
sliding filament theory
Which is not a phase of interphase?
M
What is the correct order for the subphases of mitosis?
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
During cytokinesis this cell type forms a cell plate - what type of cell is this?
plant
If cells do not enter another phase of G1 after mitosis, what phase do they go into?
G0
How many checkpoints are present during the cell cycle?
3
Proteins which regulate the cell cycle are called?
CDKs
Cyclin-dependent kinases require what in order to be activated?
cyclin
A growth factor receptor which continuously sends signals, even when there is no growth factor bound to it, is an example of a?
oncogene
p53 identifies damaged DNA in the cell, this type of regulator is termed as a ...
tumor suppression protein
Which cell cycle check point checks whether all sister chromatids are correctly attached to the spindle fibers?
M-checkpoint
What is the term given to a single cell which has the ability to divide and produce all the differentiated cells in an organism?
totipotency
Bacteria in biofilms communicate via ...
quorum sensing
Cells which are unable to divide to make new copies of themselves are termed?
terminally differentiated.
Adult stem cells can be engineered to become ...
induced pluripotent
Select all the examples of cell types which are replaced in the body by stem cells, not by dividing? [Select all the correct answers]
intestinal epithelial cells
red blood cells
epidermal cells
What type of tumors are associated with stem cells?
teratomas
Which cell types are naturally pluripotent? [Select all correct answers]
fetal stem cells
embryonic stem cells
How many basic tissue types are there?
4
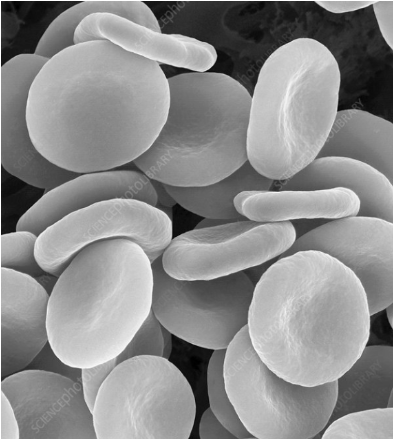
What cell type is in the picture below?
red blood cells
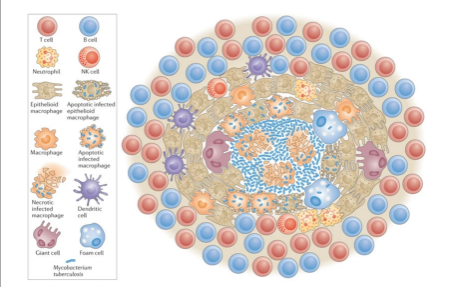
What is the name of the highly organized immune cell structure shown below?
granuloma