CH 17 - Non-Coding RNAs
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
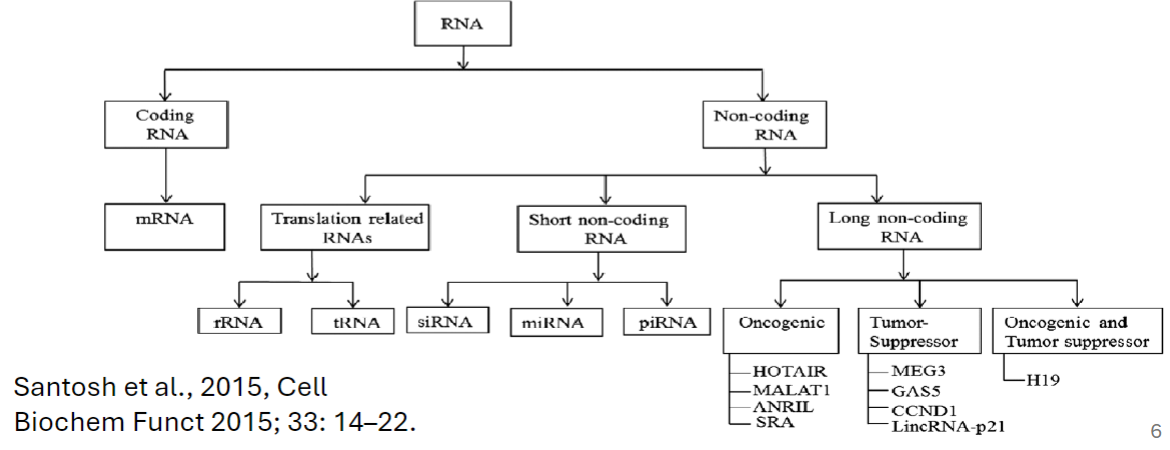
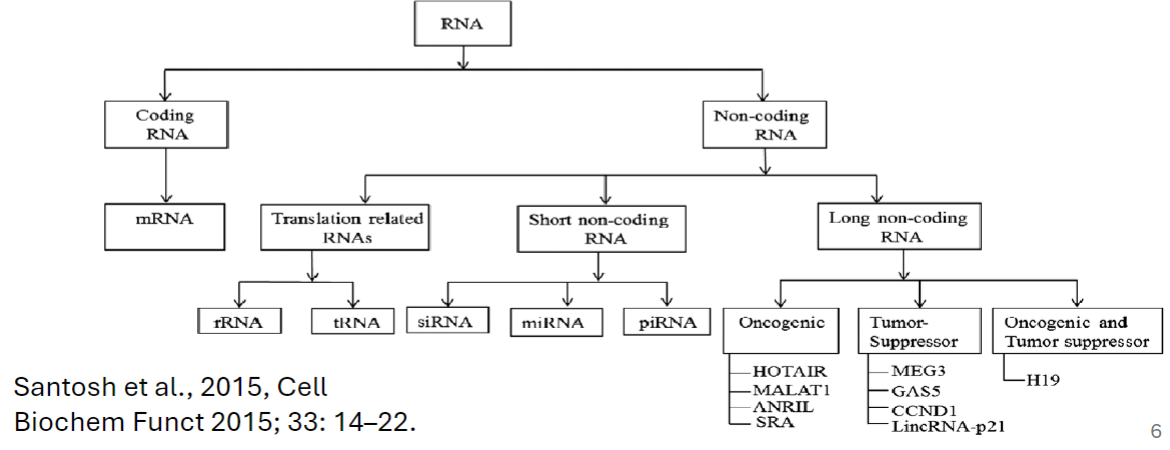
Coding RNAs
generally refers to mRNA that encodes protein
Noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs)
act as cellular regulators w/o encoding proteins
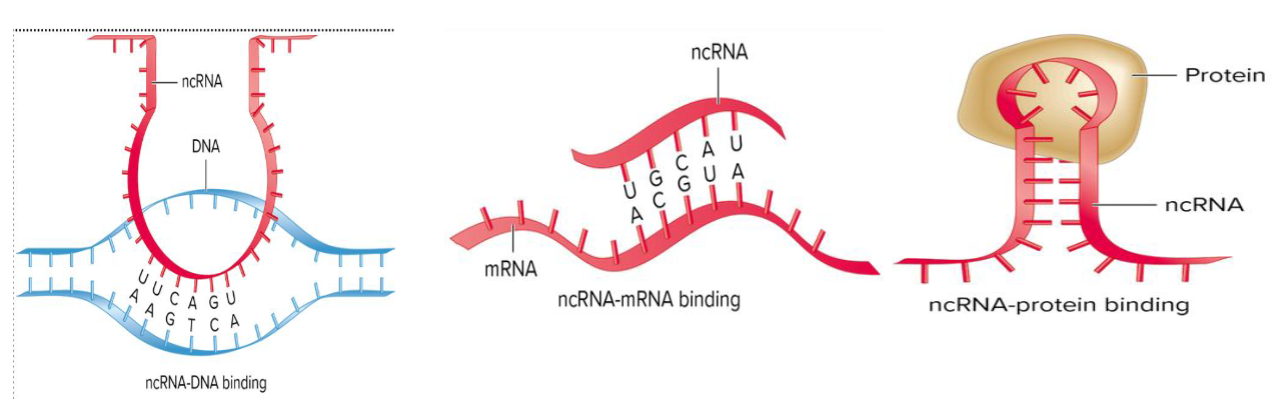
carry out many functions because they can bind to different types of molec
DNA: via complementary base pairing
Other RNAs: via complementary base pairing
Proteins
ncRNA molec can form stem-loop structures, which may bind to pockets on the surface of proteins
ncRNAs functions
scaffold: ncRNA binds to group of proteins
guide: binds to a protein and guides it to a specific cite in cell
alt of protein function/stability: binds to a protein and alters that protein’s structure
ribozyme: RNA molec w/ catalytic function
blocker: physically prevents/blocks a cellular process from happening
decoy: recognizes another ncRNA and isolates it
Long Non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs)
longer than 200 nucleotides
microRNA (miRNA)
small nuclear RNA (snRNA)
small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs)
short interfering RNAs (siRNA)
PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs)
Small non-coding/reg RNAs (aka ncRNAs)
shorter than 200 nucleotides
ncRNA effects on chromatin structure and transcription
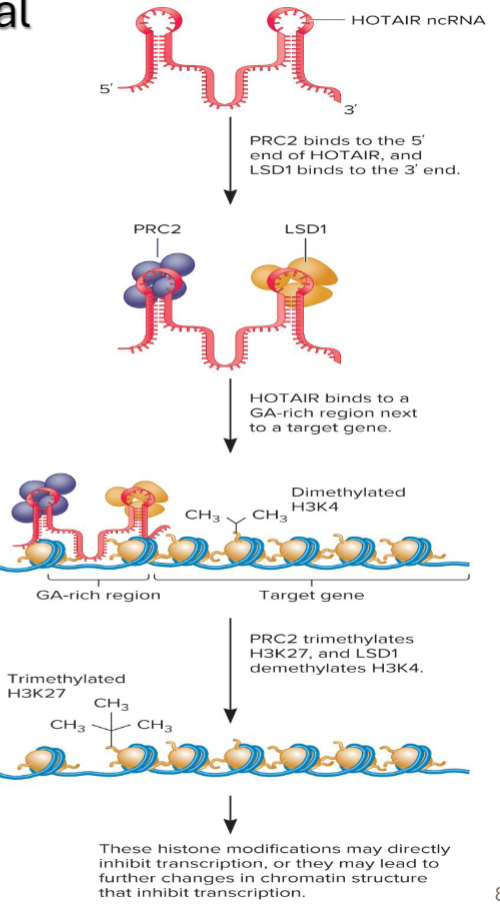
Hox transcript antisense intergenic RNA (HOTAIR) - recently discovered ncRNA that alters chromatin structure
the HOTAIR gene is located on human chromosome 12 within a cluster of genes called the HoxC genes
2.2-kb-long ncRNA
transcribed from the opp (antisense) strand w/ respect to the HoxC genes
acts as scaffold that guides two histone-modifying complexes to target genes
Mechanism of HOTAIR Transcriptional Repression
acts as scaffold for the binding of 2 protein complexes (PRC2 & LSD1)
Polycomb Repressive Complex 2
Lysine specific Demethylase (LSD1)
Binds PRC2 to the 5’ end and LSD 1 to the 3’ end
Guides the 2 protein complexes to a GA-rich region
GA-rich region contains many purines
PRC2 functions as a histone transferase
Trimethylates lysine 27 on histone H3
LSD1 demthylates mono- and demethylated lysines
ncRNAs: effects on translation and mRNA degradation
ncRNAs can affect the ability of mRNAs to be translated or degraded
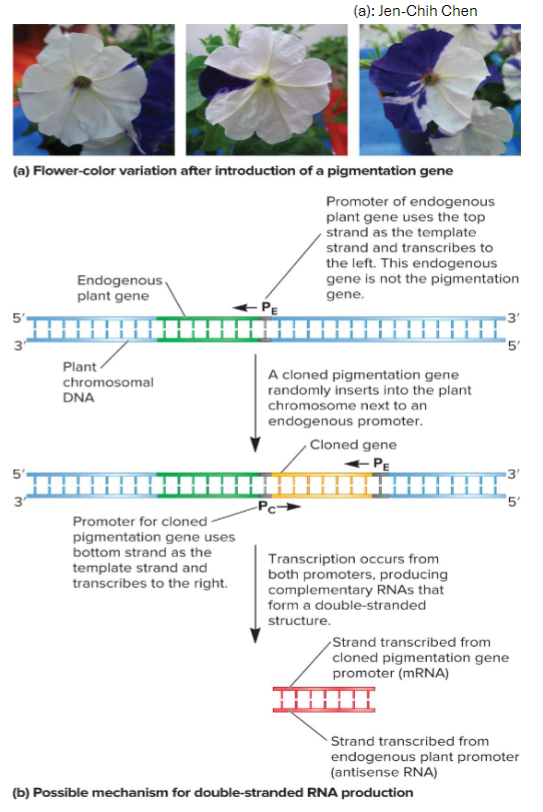
Example of RNA silencing in petunias
researchers Jorgensen and Stuitje attempted to produce strains of petunias w/ deeper flower colors
methodology: involved inserting into petunia genome copies of cloned genes that coded enzymes involved in the synthesis of flower pigment
findings: flower pigmentation in some cases did not deepen, but instead showed variegation
conclusions: additional copies of gene can sometimes suppress the expression of both itself and its endogenous counterpart
later research found the production of double-stranded RNA to be involved in lowering mRNA levels
Injection of antisense and double-stranded RNAs into C. elegans to compare their effects on mRNA silencing
Involved in mRNA coded by a gene, mex-3 (Andrew Fire and Craig Mell)
abundant mRNA in early embryos of C. elegans
sense and antisense mex-3 RNA were made in vitro using cloned genes for mex-3 w/ promoters on either side of gene
RNA pol and nucleotides added to synthesize RNA
either mex-3 antisense RNA or a mix of mex-3 sense and antisense RNA injected into the gonads of C. elegans
RNA is taken up by the eggs and early embryos, control, not injected w/ any RNA
incubation and in situ hybrid of early embryo
a labeled probe is added that is complementary to mex-3 mRNA
if cells express mex-3, the mRNA in the cells will bind to the probe and become labeled
after incubation w/ a labeled probe, cells were washed to remove unbound probe
embryos were observed under the microscope
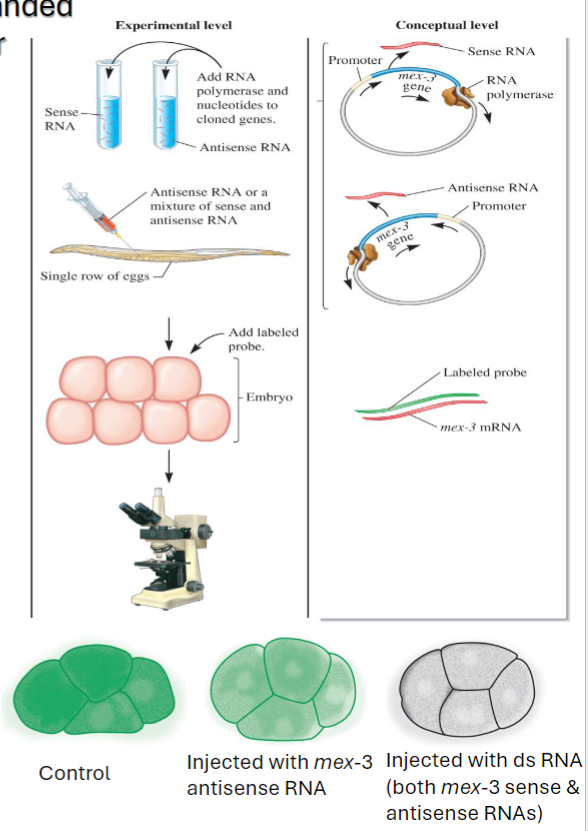
Andrew Fire and Craig Mello: Interpreting the Data
the data indicate that double-stranded RNA is more potent at silencing mRNA than is antisense RNA
mex-3 mRNA was completely degraded
RNA interference (RNAi): describes phenomenon of double-stranded RNA causes silencing of mRNA
RNA interference is mediated by microRNA/small-interfering RNAs
RNA interference is found in most euk species
mediated by 2 types of ncRNAs: microRNA (miRNA) & small-interfering RNAs (siRNA)
MicroRNAs (miRNAs)
transcribed from endogenous euk genes
reg gene expression
single type of miRNA inhibits the translation of several diff mRNAs thru partial complemntarity
60% of human genes may be reg by microRNAs
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs)
ncRNAs that usually originate from exogenous sources (not normally made by cells)
can be from viruses/experimentally injected by researchers
Mechanism of RNA interference
1st pri-miRNA is made
makes hairpin recog by 2 proteins, Drosha and DGCR8
Cleaved @ both ends into 70 nucleo pre-miRNA and exported from nucleus
cut by dicer to 50-25 bp
short souble-stranded RNA assoc w/ proteins to form RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC)
1 RNA strand degrades, the other is complementary to the mRNA that is silenced
siRNA don’t go thru processing events that occur in nucleus (they’re either derived from viral RNAs or introduced into cell by researchers)
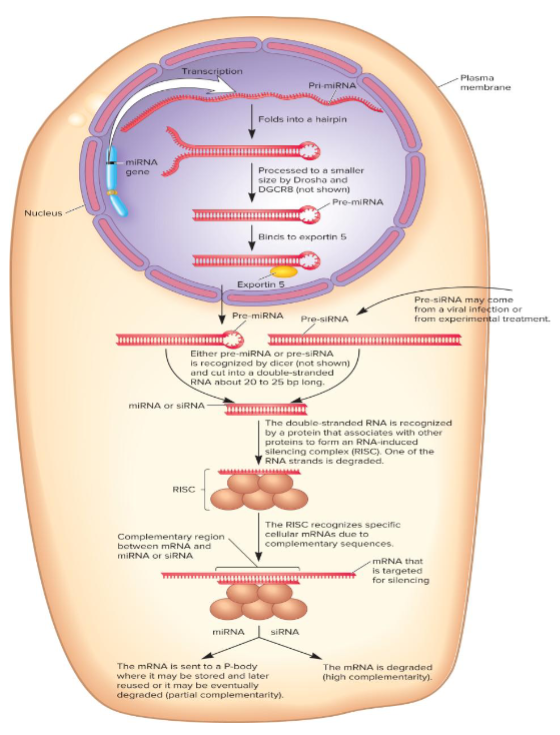
RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC)
after RISC binds to an mRNA, the effects may be:
RISC may inhibit translation w/o degrading the mRNA, often partially complementary to their mRNAs
processing body (p-body) stores RISC mRNA until it is used/degraded
RISC may direct degradation of MRNA thru cleavage by Argonaute (occurs w/ siRNAs)
Functions and benefits of RNA interference
RNAi is vital for gene reg in plants and animals
production of miRNAs silences the expression of specific mRNAs
RNAi provides defense against viruses
siRNA can inhibit transc by causing chromatin modifications
effect shared w/ piRNAs
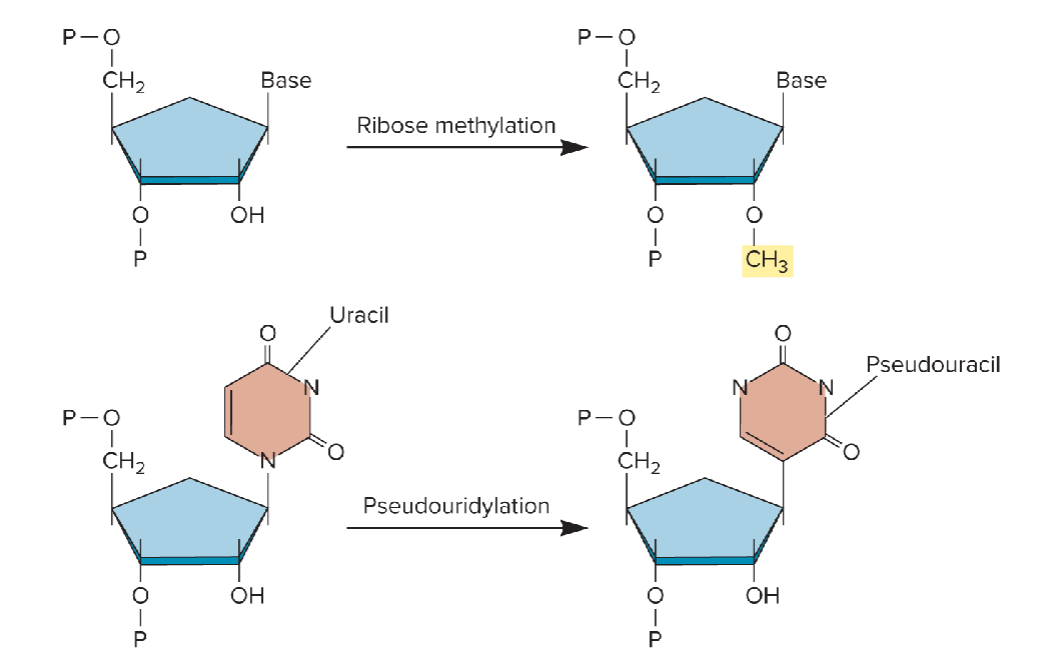
Non-coding RNAs: Effects of RNA modifications
small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are found in high amounts in nucleolus
synthesis of ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) and assembly of ribo subunits occurs in nucleolus
snoRNAs covalently modify RNAs
methylation of ribose on the 2’ hydroxyl group
conversion of uracil to pseudouracil
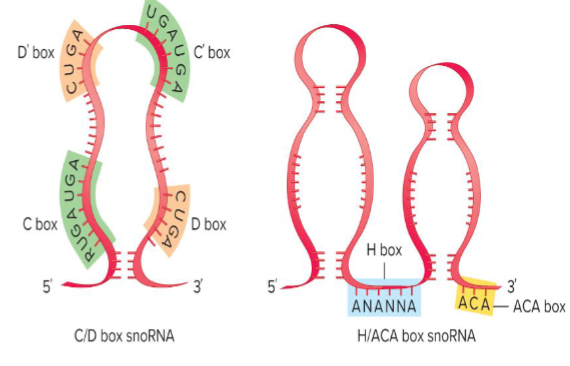
C/D box snoRNAs
70-120 nucleotides and guide methylation of target RNAs
form snoRNP w/ 2 copies of a protein that catalyzes the methylation of ribose
H/ACA box snoRNAs
~100-200 nt and guide pseudouridylation
forms a snoRNP w/ two copies of a protein that catalyzes the conversion of uracil to pseudouracil
small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein: ea type provides a scaffold to form ““
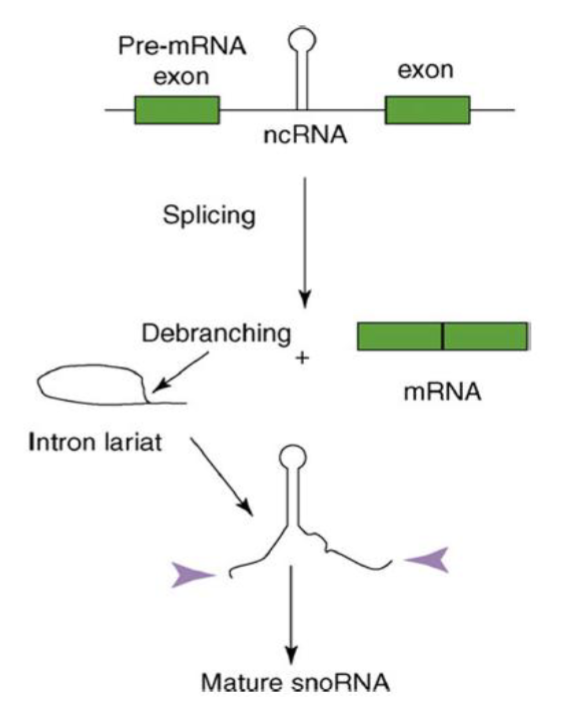
snoRNAs also act as guides
snoRNAs have antisense seq that are complementary to sites in RNAs
guide the proteins in the snoRNP complex to theirtarget rRNAs for chemical modification
methylation of ribose
conversion of uracil to pseudouracil

Effects if ncRNAs are expressed abnormally
disease conditions occur
cancer
multiple sclerosis
alzheimer’s disease
heart arrhythmias/heart fail