BIOL 110 - Exam 1
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
Element
substances that can’t be broken down into simpler substances by ordinary chemical reactions
Which of the following is an example of an element?
Oxygen
Atom
smallest unit of an element that retains that element’s chemical properties
Neutrons
Neutral
Protons
Positive
Electrons
Negative
Each atom is identified by its number of what within its atomic nucleus. It is written as a subscript to the left of the chemical symbol.
Protons
The periodic table is a chart of the elements arranged in order by what?
Atomic number
Atomic Number
Number of protons (electrons) in atomic nucleus.
Atomic Mass
protons + neutrons, expressed in atomic mass units or Daltons
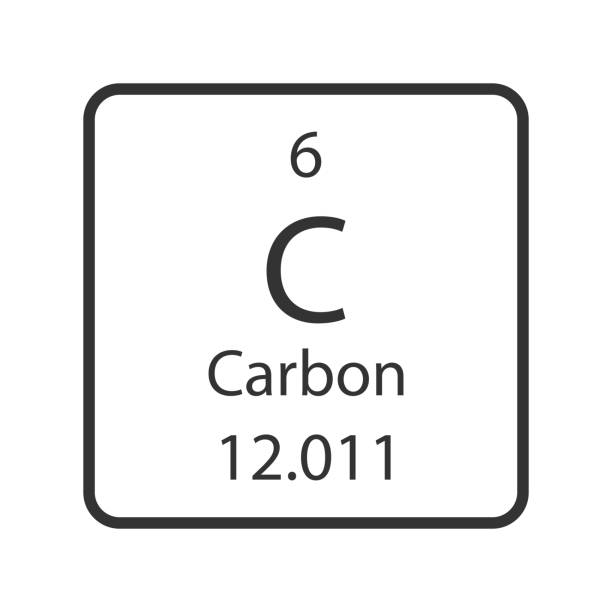
What is the Atomic Number?
6
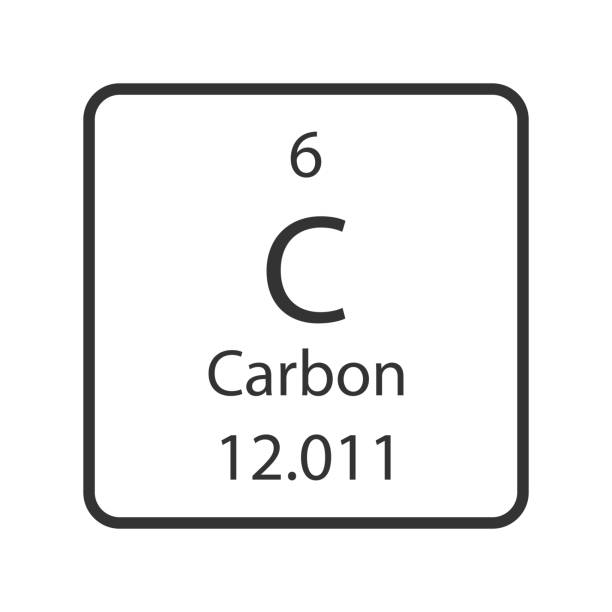
What is the symbol?
C
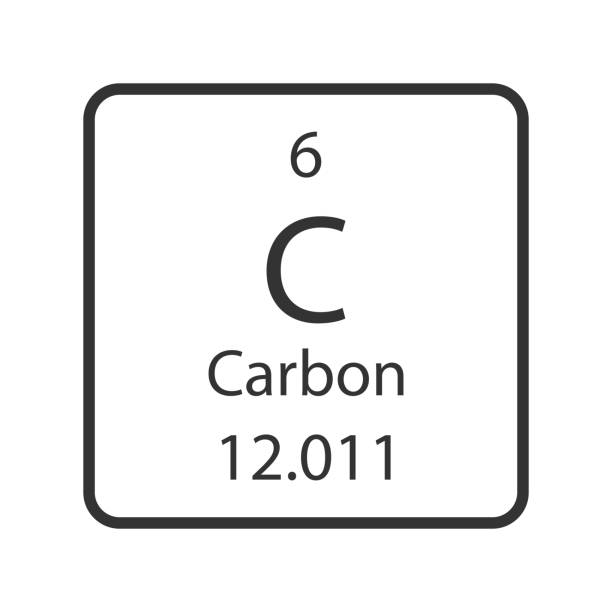
What is the Atomic Mass?
12
How do you get the neutrons from an elements atomic mass and atomic number?
Take the mass subtracted by protons
Isotopes
exist because most elements consist of a mixture of atoms with different numbers of neutrons and therefore different masses
Radioisotopes
unstable isotopes that are unstable and decay to a more stable isotope usually becoming a different element that emit radiation when they decay
Radioisotopes can be substituted for their nonradioactive counterparts, making them a valuable research tool
True
Electrons move through regions of three dimensional space or what?
orbitals (“electron clouds”)
The energy of an electron depends on the orbital it occupies, called the what?
electron shell
Why do electrons in a shell with a greater average distance from the nucleus have a greater energy?
Energy in required to move an electron further away from the nucleus
The most energetic electrons occupy the what?
valence shell
First shell holds a maximum of how many electrons?
2
Second shell holds a maximum of how many electrons?
8
changes in electron energy
energetic conversion
The chemical behavior of an atom is determined by the number and arrangement of its what electrons?
valence
Atoms with a full valence shell are stable
2 for hydrogen or helium, 8 for any other atom
Diatomics
H2 N2 F2 O2 I2 Cl2 B2
Compund
chemical combinations of atoms of different elements in a fixed ratio
Molecule
chemical combination of two or more of a similar atom
Chemical bonds
force of attraction atoms are held together by
Number of valence electrons equals?
number of bonds an atom can form
Bond Energy
energy needed to break a chemical bond
Covalent Bond
sharing of electrons between atoms in which each has filled a valence shell
Electronegativity
measure of an atoms attraction for shared electrons in chemical bonds
Non-polar covalent bonds
electrons are shared equally
Polar covalent bonds
differ in electronegativity and creates bonds with dissimilar ends (poles) that vary in charge
Cation
positively charged ion, tends to lose electrons
Anion
negatively charged ion, tends to gain electrons
Ionic Bonds
form as a consequence of the attraction between the positive charge of a cation and the negative charge of an anion
Ionic compound
is a substance consisting of anions and cations bonded by opposite charges
Ionic compounds tend to what into individual ions when placed in water
dissociate
Hydrogen bonds
form between an atom with a partial negative charge and a hydrogen atom that is covalently bonded to O or N
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of which type of bond?
Polar covalent
LEO says GER
Loss electrons oxidation, Gain electrons reduction
Transfer of energy equals
transfer of electron
Compare the physical properties (mass and charge) and locations of electrons, protons, and neutrons
Protons and neutrons are located together in the atom's central nucleus, while electrons are found in orbitals or shells that surround the nucleus
Define and describe an atom’s electron shell and relate electron shells to energy levels
distinct energy level, or region around an atom's nucleus, where electrons are found
Explain how the number of valence electrons of an atom is related to its
chemical properties.
because these are the electrons involved in chemical bonding and reactions
Describe the properties of carbon that make it the central component of organic compounds.
its four valence electrons allow it to form up to four stable, covalent bonds with other atoms, including itself, enabling it to form diverse chains and rings. C-C bonds have freedom of rotation.
Define functional group and identify the role of functional groups in molecular diversity
a specific cluster of atoms within a larger molecule that determines the molecule's unique chemical properties and reactivity
Carbohydrates
composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, with a ratio of hydrate of carbon 2:1, monosaccharides (single sugars like glucose, fructose, and galactose), disaccharides (two sugars linked together like sucrose), and polysaccharides (starches) quick energy for cells
Lipids
carbon and hydrogen, with a high proportion of carbon and hydrogen, making them hydrophobic. Lipids include triglycerides (fats and oils), phospholipids (components of cell membranes) Lipids serve as long-term energy storage
Proteins
composed of amino acids, which are linked together by peptide bonds. There are 20 different types of amino acids, each with a unique side chain that determines the protein's structure and function. primary (amino acid sequence), secondary (local folding like alpha helices and beta sheets), tertiary (overall folding of a polypeptide chain), and quaternary (interaction between multiple polypeptide chains) enzymes, structural components (e.g., collagen), transporters, hormones, and antibodies.
Isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures
Functional group
a group of atoms that help determine the types of chemical reactions and association in which the compound participates
Macromolecules
polymers (many) which are produced by linking small organic compounds monomers (1)
Humans lack the ability to break down cellulose what is that ability
enzymes
Chitin
is a modified carbohydrate that forms the external skeletons of insects, crayfish and anthropods
Phospholipid
consist of a glycerol molecule attached to two fatty acids (hydrocarbon
chain with carboxyl group, -COOH) at one end and a phosphate group at the other end. Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tail.
Phospholipids are critical components of the what?
cell membrane
Saturated fatty acids tend to be __________ at room temp. These include animal fat and vegetable shortening
solid
Unsaturated fatty acids tend to be ________ at room temperature because double bonds inhibit aligning with other chains
liquid
Proteins are composed of amino acids that contain what?
Amino Groups and a Carboxyl Group bonded to a carbon
Primary Structure very important
linear sequence of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
4 Levels of organization for proteins?
primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary
The biological activity of a protein can be disrupted by a change in
amino acid sequence (primary structure)?
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic disease caused by a mutation that causes the substitution of the amino acid valine for glutamic acid at position 6. This makes hemoglobin more likely to form crystal structures, causing a “sickle” shaped RBC.
Nucleic Acids
Transmit hereditary information, determine instructions for protein formation, act in cell signaling and metabolism
The basic unit of nucleic acids are what?
sugar + phosphate group + nitrogenous base
Molecules of nucleic acids are made of nucleotides joined by what?
phosphodiester linkages
Describe the cell theory
all organisms are composed of one or more cells
The cell is the basic unit of organization and function in all living things
All cells are produced by the division of preexisting cells
Explain the functional significance of cell size and shape
A cell's size, limited by its surface-area-to-volume ratio, dictates how effectively it can transport nutrients in and waste out. Variations in cell shape are a strategy for increasing ratio of surface area to volume.
Prokaryotic
single cell, has no nucleus, don’t contain membrane bonded organelles
Eukaryotic
multi-ceulluar more often, has a nucleus, organelles are smaller
Plant cells
have a rigid cell wall for structural support, a large central vacuole for water regulation, and chloroplasts for photosynthesis
animal cells
lack these features but possess lysosomes for digestion and centrosomes for cell division
Ribosomes
protein production
function of cell membranes
Why are cells small?
If the cell is too big it’ll take too long to move across, leave and enter the cell, inefficient if the cell was larger
cell membranes
control what enters and exits
nucleus
contains genetic form of DNA and controls protein synthesis by transcribing information from DNA into mRNA. Surrounded by nuclear envelope that separates nuclear contents from cytoplasm. Studded by nuclear pores that regulate passage of large materials across nuclear membrane. Contain nucleoli (singular = nucleolus) for production of rRNA.
ribosomes
Responsible for protein manufacturing within the cytoplasm, Contain enzymes needed to form peptide bonds, which join amino acids to form proteins. Found free in the cytosol or attached to cytoplasmic membranes. Consist of a large subunit and small subunit Number of ribosomes within a cell can be adjusted to meet metabolic need.
endomembrane system
a network of organelles that exchange materials through small membrane-enclosed transport vesicles. Vesicles act to route contents to its destination. Fusion of transport vesicle with target
causes release of contents. ER, Golgi Complex, Lysosomes, mitochondria, chloroplasts, plasma membrane
lysosomes
compartments for digestion. without them waste can’t leave properly
vacuoles
“empty”, Membrane-enclosed, fluid-filled sacs that lack internal structure, Particularly important in plants for: Structural support [take in water, pushing outward on cell wall] Storage [pigments, compounds, waste products
mitochondria
facilitate energy conversion, powerhouse of the cell, Grow and reproduce independently, produce ATP through aerobic respiration
chloroplasts
facilitate energy conversion, convert light energy into chemical energy via photosynthesis, Present in algae and plant cells, Contain chlorophyll, a pigment that traps light energy for photosynthesis
cytoskeleton
Dense network of protein fibers that support cell shape and ability to move, Important in cell division and transport of materials within the cell
Consist of 3 major types of protein filaments: microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments
Plant color is a result of
chloroplast number
SA:V
the concept of the surface area to volume ratio; As an object's size decreases, its SA:V ratio increases. This is because as volume grows, surface area does not increase as rapidly
fluid mosaic model
a cell membrane consists of a phospholipid bilayer of phospholipid molecules in which proteins are embedded or otherwise associated.
Relate properties of the lipid bilayer to properties and functions of cell membranes
Biological membranes are composed of phospholipid molecules that form a bilayered structure. Lipid bilayers resist forming free ends and are self-sealing (form closed vesicles) and also flexible (change shape without breaking). These properties allow lipid bilayers to facilitate transfer of material through membranes
Describe the ways that membrane proteins associate with the lipid bilayer.
There are major groups of membrane proteins based on how tightly they are associated with the lipid bilayer:
Integral membrane proteins are bound to the membrane and are amphipathic. They can be transmembrane, extending completely through the membrane. Some span the membrane multiple times in the form of an alpha helix. Some form beta-pleated sheets.
Peripheral membrane proteins are not embedded in the lipid bilayer but are located on the inner or outer surface of the plasma membrane. They are usually bound to exposed regions of integral proteins via noncovalent interactions – easily removed
Describe the importance of selectively permeable membranes.
The fluid mosaic structure of biological membranes allows them to be selectively permeable, allowing only some substances to pass through. A cell can regulate chemical traffic across its plasma membrane, allowing control over molecular composition
Contrast simple and facilitated diffusion with active transport
In simple diffusion, small non-polar (uncharged) solutes move through the membrane, down their concentration gradient.
In facilitated diffusion, a transport protein makes the membrane permeable to a specific solute (ion, polar molecule). Net movement is still from an area of high solute concentration to an area of low solute concentration.
In active transport, the cell must expend metabolic energy to move materials from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration, against the concentration gradient, with energy provided by ATP
Isotonic solutions
equal solute concentration to the fluid within a cell → no net movement of water; the cell will not shrink or swell.
Hypotonic solutions
lower concentration of dissolved materials than the cell → water will enter the cell and cause it to swell (burst).
Hypertonic solutions
higher concentration of dissolved materials than the cell → water will leave the cell and cause it to dehydrate and shrink
Form = Function
The lipid bilayer is self-sealing (form closed vesicles) and flexible (change shape without breaking).
Because of this form, the function is that it can facilitate transfer of material through membranes and also compartmentalize the cell without leaking
What is energy used to move in passive transport
concentration gradient
tonicity
relative solute concentration of a solute